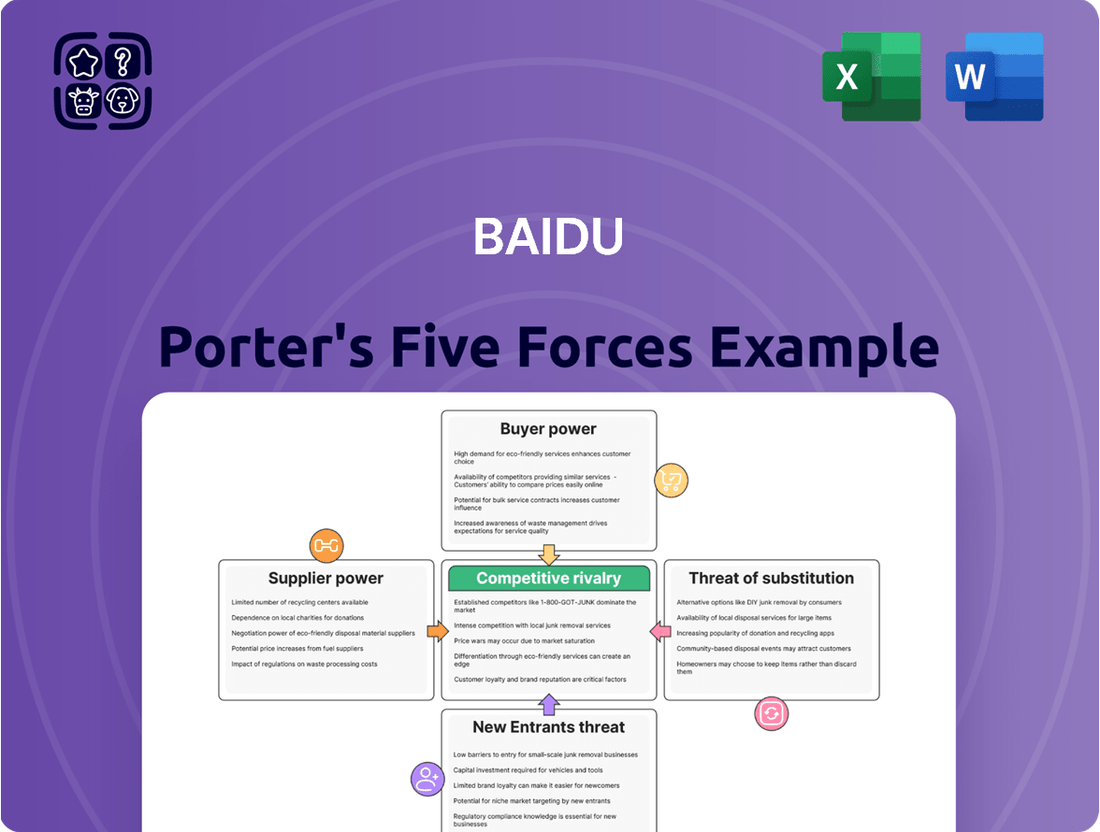
Baidu Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Baidu Bundle
Baidu navigates a dynamic digital landscape, facing intense rivalry from established tech giants and agile startups alike. Understanding the bargaining power of its suppliers and the constant threat of new entrants is crucial for its sustained growth.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Baidu’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Baidu's reliance on a limited number of high-end semiconductor and cloud infrastructure suppliers, such as NVIDIA and Intel for AI chips, grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. NVIDIA, for instance, held a substantial share of the AI chip market in 2023, making it a critical, yet powerful, partner.
To counter this, Baidu is investing heavily in its own technologies. By 2026, the company aims to achieve 35% self-sufficiency in key areas, particularly through advancements in its AI technology and the development of proprietary chips, reducing its dependence on external providers.
Baidu's significant dependence on key technology providers for critical components like NVIDIA A100 GPUs and Intel Xeon processors directly impacts its bargaining power. These essential hardware and software dependencies grant suppliers considerable leverage, as evidenced by Baidu's substantial annual expenditures on cloud infrastructure hardware.
The current geopolitical climate, particularly U.S. export controls on advanced chips, further amplifies this supplier power. This situation compels Chinese tech giants like Baidu to actively explore and integrate domestic alternatives, such as Huawei's Ascend chips, to mitigate risks and ensure supply chain stability.
Baidu's significant R&D investments in proprietary technologies, particularly in AI and chip development, are a direct strategy to mitigate supplier bargaining power. By building internal capabilities, Baidu aims to lessen its dependence on external vendors for crucial components, thereby strengthening its negotiating position.
A prime example of this is Baidu's launch of its third-generation Kunlun AI chip cluster. This advancement in domestically developed large-scale AI computing infrastructure showcases Baidu's commitment to self-sufficiency and reduces reliance on foreign chip manufacturers, a key area where suppliers often hold considerable sway.
Potential for Vertical Integration Strategies
Baidu is actively pursuing vertical integration, particularly in its AI development. By investing in custom AI chips and building internal semiconductor research capabilities, Baidu seeks to control more of its technology pipeline. This move directly challenges the bargaining power of external chip suppliers.
This strategy is evident in Baidu's proactive engagement with key players in the semiconductor industry. For example, Baidu was an early adopter of Huawei's Ascend 910B AI chips, indicating a strategic effort to secure critical components and foster closer supplier relationships. Such collaborations are designed to align supplier capabilities with Baidu's specific AI modeling infrastructure needs.
- Baidu's AI chip development: Baidu is investing in creating its own AI chips to reduce reliance on external suppliers.
- Internal semiconductor research: The company is building in-house teams dedicated to semiconductor research and development.
- Strategic supplier relationships: Baidu is collaborating with companies like Huawei to advance its AI infrastructure, exemplified by its early orders of Ascend 910B chips.
- Reducing supplier leverage: By bringing more of the supply chain in-house, Baidu aims to diminish the bargaining power of its external suppliers.
Government Policies Promoting Domestic Supply Chains
Government policies in China, like the ambitious Made in China 2025 initiative and the Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan, are actively pushing for domestic self-sufficiency in critical technology sectors, particularly AI chips. This strategic focus by the Chinese government directly influences the bargaining power of suppliers by fostering the growth and consolidation of local chipmakers and AI enterprises.
These policies encourage domestic players to forge alliances and establish robust local supply chains. Such a development could significantly diminish the long-term leverage that foreign suppliers might otherwise hold over companies like Baidu, as domestic alternatives become more viable and competitive.
- China's 'Made in China 2025' initiative aims to upgrade manufacturing capabilities and reduce reliance on foreign technology.
- The 'Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan' targets China becoming a global leader in AI by 2030, emphasizing domestic innovation and supply chains.
- Government incentives and funding are directed towards nurturing domestic semiconductor and AI companies, strengthening their position against international competitors.
Baidu's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly influenced by its reliance on critical components, particularly advanced AI chips. Companies like NVIDIA, a dominant player in the AI chip market, hold considerable leverage due to Baidu's dependence on their high-performance GPUs, such as the A100 series, for its AI development and cloud services. This dependence was highlighted by Baidu's substantial investments in cloud infrastructure hardware in recent years.
To mitigate this, Baidu is strategically investing in developing its own AI chips, like the Kunlun series, and fostering domestic supply chain relationships. For instance, Baidu's early adoption of Huawei's Ascend 910B chips demonstrates a proactive approach to diversifying its supplier base and reducing reliance on foreign technology. This aligns with China's national strategy to boost domestic technological self-sufficiency.
| Supplier Dependency | Baidu's Mitigation Strategy | Supplier Leverage Factor |
|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA GPUs (e.g., A100) | In-house AI chip development (Kunlun) | Market dominance of NVIDIA in AI chips |
| Intel Processors | Exploring domestic alternatives | Criticality of processors for cloud infrastructure |
| Cloud Infrastructure Hardware | Vertical integration in AI | High capital expenditure on hardware |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity within China's internet sector, Baidu's bargaining power with suppliers and customers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Baidu's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a streamlined framework to quickly identify and address competitive threats, alleviating the pain of strategic uncertainty.
Customers Bargaining Power
Baidu's broad reach across individual users, with 214.9 million monthly active users in its mobile ecosystem as of Q4 2023, and enterprise clients for services like online marketing and cloud computing, generally dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer group. This wide customer base means no one segment can dictate terms easily.
However, the online marketing sector, a significant revenue driver, experienced a year-over-year revenue decrease in Q4 2024. This softness in a key segment could potentially increase the bargaining power of larger advertising clients within that specific area.
Users deeply embedded in Baidu's expansive ecosystem, encompassing services like the Baidu App, Baidu Maps, Baidu Wenku, and Apollo Go, face substantial hurdles when considering a shift to competing platforms. The inconvenience of migrating personalized data, losing accumulated benefits, and re-learning new interfaces significantly diminishes their inclination to switch. This inherent lock-in effect effectively curbs their bargaining power for these integrated services.
Baidu's online marketing and cloud services customers exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is particularly evident as China's digital advertising market, where Baidu primarily operates, faces increasing competition. For instance, in 2023, China's digital ad spending was projected to reach over $100 billion, with a substantial portion allocated to search and social media platforms, creating a buyer's market.
Larger enterprise clients, especially those with substantial advertising budgets or significant cloud infrastructure needs, can leverage their scale to negotiate more favorable pricing. This bargaining power is amplified by the presence of formidable competitors such as Alibaba and Tencent, both of whom offer integrated digital marketing and cloud solutions, forcing Baidu to remain competitive on price to retain and attract these key accounts.
Increasing User Expectations for AI-Native Experiences
As artificial intelligence becomes more integrated into daily life, customers are naturally expecting more advanced and personalized interactions with digital platforms. This rising tide of user expectations directly impacts companies like Baidu, as they must adapt their offerings to remain competitive.
Baidu's strategic push to make its search engine more 'AI-native' is a direct response to this trend. By infusing AI capabilities into core products, such as the document-sharing platform Baidu Wenku, the company aims to deliver richer, more intelligent user experiences. For instance, Baidu Wenku's AI features can help users find relevant information more efficiently, understand complex documents, and even generate summaries, directly addressing the demand for sophisticated AI-powered tools.
- User expectation for AI-driven personalization is growing significantly.
- Baidu's investment in AI-native search aims to meet these heightened user demands.
- Features in products like Baidu Wenku showcase the company's commitment to AI integration.
- Meeting these expectations is key for Baidu to retain its user base and market position.
Impact of Alternative Content and Information Platforms
The proliferation of alternative content and information platforms, such as Douyin and Xiaohongshu, directly impacts Baidu's customer bargaining power. These platforms offer integrated search and curated content, diminishing user dependence on traditional search engines. For instance, Douyin's massive user base, exceeding 700 million daily active users in 2024, provides a significant alternative avenue for information discovery, thereby strengthening user leverage.
This shift empowers consumers by presenting them with a wider array of choices for accessing information and entertainment. Users can now find product reviews, tutorials, and lifestyle content directly within these social platforms, bypassing the need to navigate to Baidu for many queries. This fragmentation of information sources increases the switching costs for users to remain solely with Baidu, giving them more power to demand better services or seek out competitors.
- Increased User Options: Platforms like Douyin and Xiaohongshu offer native search and content discovery, reducing reliance on Baidu.
- Fragmented Information Landscape: Users can access information and product insights directly on social media, bypassing traditional search.
- Enhanced Consumer Leverage: The availability of alternatives strengthens users' ability to switch platforms, increasing their bargaining power.
- Competitive Pressure: Baidu faces pressure to innovate and improve its offerings to retain users in this evolving digital ecosystem.
Baidu's extensive user base, with 214.9 million monthly active users in its mobile ecosystem as of Q4 2023, generally dilutes individual customer bargaining power. However, a year-over-year revenue decrease in its online marketing sector in Q4 2024 suggests larger advertising clients in this segment may gain leverage due to market softness.
Users are increasingly embedded in Baidu's ecosystem, making switching difficult and reducing their bargaining power for integrated services. Conversely, price sensitivity among online marketing and cloud customers is high, especially given China's competitive digital advertising market, projected to exceed $100 billion in 2023.
Large enterprise clients can negotiate better terms due to their scale and the presence of competitors like Alibaba and Tencent. Growing user expectations for AI-driven personalization also empower customers, pushing Baidu to enhance its AI-native search and integrated product experiences, such as those in Baidu Wenku.
The rise of platforms like Douyin, with over 700 million daily active users in 2024, offers alternative information discovery, strengthening user leverage. This fragmentation of information sources increases switching costs for users to remain solely with Baidu, giving them more power to demand better services.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Baidu |
|---|---|---|
| General Users (Baidu App, Maps) | High switching costs due to data integration and ecosystem lock-in. | Low individual bargaining power. |
| Large Online Advertisers | Price sensitivity and market softness in the digital ad sector (>$100B in China, 2023). | Potentially increasing bargaining power, especially with competitors like Alibaba. |
| Enterprise Cloud Clients | Scale and comparison with offerings from Tencent and Alibaba. | Significant bargaining power for pricing and service terms. |
| Users Seeking AI Features | Growing expectation for advanced AI personalization. | Empowers users to demand better AI integration; Baidu investing in AI-native search. |
| Users of Alternative Platforms (Douyin) | Availability of integrated search and curated content on competing platforms. | Increased user leverage and potential for platform switching. |
What You See Is What You Get
Baidu Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Baidu Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive instantly after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for immediate use, providing valuable strategic insights into Baidu's market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Baidu commands a substantial portion of China's search engine landscape, holding an estimated 50% to 55% market share in 2023. This dominance creates significant barriers to entry for rivals, leveraging network effects and ingrained user habits. However, a noticeable decline in its desktop search market share, partly attributed to the rise of competitors like Bing, highlights the dynamic nature of this rivalry.
The AI and cloud computing landscape in China is fiercely contested, with giants like Alibaba, Tencent, and Huawei heavily investing in and advancing their own AI and cloud offerings.
Despite Baidu's AI Cloud revenue experiencing robust growth in Q1 2025, it contends with formidable competitors in this rapidly expanding market, making market share gains a constant challenge.
The generative AI landscape in China is exploding, with new competitors like DeepSeek, MiniMax, and Tencent Yuanbao rapidly gaining user traction. These emerging players are directly challenging Baidu's established AI services, including its ERNIE Bot, by offering innovative and increasingly sophisticated AI models.
Competition from Content and Short Video Platforms
Baidu contends with intense rivalry from content and short video platforms like Douyin and Xiaohongshu. These platforms are rapidly evolving into primary destinations for information discovery and entertainment, siphoning user attention and advertising spend that might otherwise go to search engines. For instance, Douyin's user base in China surpassed 700 million daily active users by late 2023, showcasing its immense reach and influence in capturing user engagement.
This shift directly impacts Baidu's market position by fragmenting the digital landscape where users seek answers and content. As users increasingly rely on these immersive, algorithm-driven experiences, the traditional search paradigm faces pressure. This competitive dynamic means Baidu must innovate beyond its core search function to retain users and advertising revenue in a rapidly evolving digital ecosystem.
- Intensifying Rivalry: Douyin and Xiaohongshu are emerging as major competitors for user attention and ad revenue.
- User Behavior Shift: Users are increasingly turning to short video and content platforms for information and entertainment.
- Market Share Erosion: This trend diverts traffic and advertising dollars away from traditional search engines like Baidu.
- Douyin's Dominance: Douyin reported over 700 million daily active users in China by late 2023, highlighting its significant user engagement.
Global Competitors with Limited China Presence
While Google remains a global search giant, its direct impact on China's search landscape has been minimal since 2010. This limited presence, stemming from censorship and regulatory issues, has historically provided a significant advantage to Baidu.
However, the competitive environment is evolving. Microsoft's Bing, for instance, actively operates within China and has been steadily gaining market share. This growth is particularly notable as Bing integrates advanced AI search functionalities, offering a more sophisticated user experience that could challenge Baidu's dominance.
- Google's global search market share remains dominant, exceeding 80% in many regions.
- Baidu has historically benefited from Google's limited direct presence in China since 2010.
- Microsoft's Bing operates in China and has seen market share gains, particularly with AI integration.
Baidu faces intense competition in its core search business from both established players like Microsoft's Bing, which is integrating AI, and emerging content platforms such as Douyin. Douyin, with over 700 million daily active users in China by late 2023, is increasingly becoming a primary destination for information discovery, diverting user attention and advertising revenue. This dynamic is further complicated by the rapid growth of generative AI startups like DeepSeek and MiniMax, which are directly challenging Baidu's AI offerings, including ERNIE Bot.
| Competitor | Market Segment | Key Competitive Factor | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bing | Search Engine | AI Integration, Market Share Growth | Actively operating and gaining share in China |
| Douyin | Short Video/Content Platform | User Engagement, Information Discovery | 700M+ Daily Active Users (Late 2023) |
| DeepSeek, MiniMax | Generative AI | Innovative AI Models | Rapidly gaining user traction |
| Alibaba, Tencent, Huawei | AI & Cloud Computing | Heavy Investment, Advanced Offerings | Significant presence in China's AI/Cloud market |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While Baidu holds a commanding presence in China's search market, users have alternatives. Competitors such as Bing, Sogou, and 360 Search offer different interfaces and features, catering to varied user preferences. These platforms represent direct substitutes for accessing information within China.
Globally, search engines like Google, despite its limited accessibility in mainland China, and newer entrants like Perplexity.ai, present a different kind of substitution threat. Perplexity.ai, for instance, provides direct, cited answers, which can bypass the need for traditional search engine result pages, offering a distinct user experience and a substitute for how users find information.
Social media and content platforms represent a significant threat of substitutes for Baidu. Platforms like Douyin (TikTok), WeChat, and Xiaohongshu have become primary sources for information, reviews, and content discovery for many Chinese users. This direct engagement with content bypasses traditional search engine queries, directly impacting Baidu's user base and market share.
The rise of AI chatbots and generative AI presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional search engines like Baidu. These advanced AI models, including Baidu's ERNIE Bot and competitors such as DeepSeek and Tencent Yuanbao, can directly answer user queries and generate content, bypassing the need to navigate multiple search results. For instance, in 2024, the adoption rate of generative AI tools for information retrieval saw a substantial increase among internet users globally, directly impacting the time spent on conventional search platforms.
Vertical-Specific Applications and Super Apps
Users increasingly turn to specialized applications, often called 'super apps,' that are designed for specific tasks. For instance, dedicated e-commerce platforms for shopping, advanced mapping services for navigation, or curated news applications for staying informed can diminish reliance on general search engines for those particular functions. This trend means users might bypass a broad search engine when they have a very specific need that a specialized app can fulfill more efficiently.
Baidu itself operates several such specialized services, including Baidu Maps and Baidu Health. These platforms can act as direct substitutes for general web search when users are looking for specific information or services within those domains. For example, a user needing directions would likely go directly to Baidu Maps rather than initiating a general search query.
- Specialized Apps as Substitutes: Dedicated platforms for e-commerce, navigation, and news reduce the need for general search engines for specific tasks.
- Baidu's Own Substitutes: Baidu Maps and Baidu Health offer specialized functionalities that can replace general search queries for relevant needs.
- User Behavior Shift: The rise of super apps and niche applications reflects a user preference for streamlined, task-specific solutions.
Offline Information Sources and Traditional Media
While the digital realm dominates, traditional offline information sources like newspapers and television remain viable substitutes for online search, albeit with diminishing reach. These channels still cater to specific demographics and offer a different user experience for information gathering.
Although their direct threat to Baidu's core search business is minimal, these offline channels represent a foundational alternative for accessing information for certain segments of the population. For instance, in 2024, television advertising spending in China was projected to reach approximately $20 billion, indicating continued investment in traditional media, even as digital channels grow faster.
- Newspapers and Print Media: While circulation has declined, niche publications and regional newspapers still hold sway with dedicated readerships.
- Television and Radio: These broadcast mediums continue to reach a broad audience, particularly for news and entertainment, offering an alternative to digital content consumption.
- Word-of-Mouth and Community Networks: Personal recommendations and local community information sharing persist as a powerful, albeit informal, substitute for online research.
The threat of substitutes for Baidu is significant, driven by evolving user behaviors and technological advancements. AI-powered conversational interfaces and specialized applications are increasingly bypassing traditional search, directly addressing user needs. Even offline media, though less impactful, still serves as a substitute for certain demographics.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on Baidu | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Chatbots & Generative AI | Baidu ERNIE Bot, DeepSeek, Tencent Yuanbao, Perplexity.ai | Directly answers queries, bypassing search results. | Increased user adoption for information retrieval. |
| Social Media & Content Platforms | Douyin, WeChat, Xiaohongshu | Primary source for content discovery, reducing search queries. | Dominant platforms for information and reviews. |
| Specialized Apps (Super Apps) | E-commerce apps, Baidu Maps, Baidu Health | Fulfills specific needs more efficiently than general search. | Growing user preference for task-specific solutions. |
| Traditional Media | Television, Newspapers | Serves specific demographics, offering alternative information access. | Continued investment in traditional media advertising. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering China's competitive tech landscape, particularly in fields like search, AI, and autonomous driving, demands immense capital. Companies need significant funding for building robust infrastructure, advancing cutting-edge technology, and attracting top-tier talent.
Baidu's commitment to research and development underscores this challenge. In 2024, the company invested a considerable $3.56 billion in R&D, establishing a formidable barrier that deters new players from easily entering these technologically intensive sectors.
Baidu enjoys formidable brand recognition and a deeply entrenched user base within China, particularly for its core search engine and expanding mobile ecosystem. This established loyalty presents a substantial barrier for any newcomers aiming to capture market share.
For instance, as of early 2024, Baidu's search engine consistently holds a dominant position in China's search market, often exceeding 70% share. This level of user habituation and trust makes it incredibly difficult for new platforms to attract and retain users, as they must overcome significant switching costs and established preferences.
The threat of new entrants in Baidu's market is significantly mitigated by the sheer technological complexity and data requirements involved. Developing and maintaining cutting-edge search algorithms, sophisticated AI models like those powering its Ernie Bot, and autonomous driving systems demands substantial, specialized expertise and continuous investment in research and development. For instance, Baidu invested over RMB 20 billion (approximately $2.8 billion USD) in AI research and development in 2023, a figure that highlights the capital intensity new players must overcome.
Baidu's established position, built on decades of operating its dominant search engine and a wide array of other internet services, grants it access to an unparalleled volume of user data. This vast data reservoir is crucial for training and refining its AI models, a process that is incredibly difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate. By early 2024, Baidu reported over 600 million daily active users across its core platforms, providing a continuous stream of valuable information that fuels its competitive edge.
Regulatory Hurdles and Government Oversight
The Chinese market presents a formidable barrier to entry due to its intricate regulatory landscape. Newcomers, especially international firms, must contend with strict censorship laws and stringent data compliance mandates. Navigating these complex requirements and securing the necessary operating licenses can be a significant hurdle, demanding substantial investment and time.
For instance, in 2024, China's Cyberspace Administration (CAC) continued to enforce its Cybersecurity Review Measures, impacting foreign tech companies seeking to operate within the country. This often necessitates local data storage and adherence to specific content moderation policies, adding considerable operational complexity and cost for new entrants.
- Censorship Compliance: Adhering to China's strict content regulations requires ongoing investment in moderation systems and personnel, a significant cost for new platforms.
- Data Localization: Requirements for storing user data within China add infrastructure and operational expenses for foreign companies.
- Licensing and Approvals: Obtaining necessary permits and licenses from various government bodies can be a lengthy and unpredictable process, delaying market entry.
Intense Competition from Existing Tech Giants
Baidu faces significant threats from established Chinese tech titans such as Alibaba, Tencent, and Huawei. These giants are also channeling substantial resources into AI, cloud infrastructure, and a broad range of internet services, intensifying the competitive landscape.
Any new player entering this arena must contend not only with Baidu but also with these formidable, well-entrenched incumbents, making market penetration exceptionally challenging.
- Alibaba's Cloud Computing (Aliyun) Revenue: For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Alibaba Cloud reported revenue of RMB 91.3 billion (approximately $12.6 billion USD), showcasing its significant scale in cloud services.
- Tencent's AI Investments: Tencent has been a major investor in AI research and development, with its AI lab contributing to various product enhancements and new ventures.
- Huawei's AI Strategy: Huawei's Ascend AI chips and cloud services position it as a direct competitor to Baidu in the AI hardware and infrastructure space.
The threat of new entrants for Baidu is considerably low due to the immense capital requirements in China's tech sector, particularly in AI and autonomous driving. Baidu's substantial R&D investments, like the $3.56 billion in 2024, create a high financial barrier.
Furthermore, Baidu's established brand loyalty and dominant market share, with over 70% in search as of early 2024, make it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. The technological complexity and vast data needs for AI development also deter new players.
Regulatory hurdles, including censorship compliance and data localization mandates, add significant operational complexity and cost for any new entrant, particularly foreign firms navigating China's stringent cybersecurity laws.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Baidu's Position |
| Capital Requirements | High (Infrastructure, R&D, Talent) | Significant R&D Investment ($3.56B in 2024) |
| Brand Loyalty & User Base | Low (Difficult to attract users) | Dominant Search Share (>70% early 2024), 600M+ Daily Active Users |
| Technological Complexity | High (AI, Autonomous Driving) | Extensive AI Expertise, Large Data Reservoir |
| Regulatory Environment | High (Censorship, Data Localization) | Established Compliance Framework |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Baidu Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Baidu's official financial statements, investor relations disclosures, and comprehensive industry reports from reputable market research firms. We also incorporate insights from regulatory filings and macroeconomic data to provide a holistic view of the competitive landscape.
