b1BANK Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
b1BANK Bundle
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for b1BANK reveals a dynamic competitive landscape, highlighting moderate buyer power and a significant threat from emerging fintech disruptors. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating b1BANK's market.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore b1BANK’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Depositors hold significant bargaining power over b1BANK as they are the primary source of its funding. Their collective ability to shift funds to higher-yielding alternatives directly impacts b1BANK's cost of capital. In 2024, the average savings account interest rate offered by major banks hovered around 0.35%, while high-yield savings accounts from online banks and credit unions could offer rates exceeding 4.5%, demonstrating the sensitivity of depositors to rate differentials.
The ease with which depositors can move their money, especially with the proliferation of digital banking platforms and a wide array of financial institutions, further amplifies their influence. This accessibility means that if b1BANK fails to offer competitive deposit rates or superior digital services, customers can readily switch, forcing the bank to adjust its offerings to retain these crucial funds.
Technology and software providers hold significant bargaining power over banks like b1BANK. Core banking systems, essential for daily operations, and crucial cybersecurity solutions are often proprietary, meaning banks have limited options if they need to switch. In 2024, the global FinTech market was valued at over $1.1 trillion, highlighting the immense scale and specialized nature of these technology providers.
The reliance on a few key vendors for these critical services can give suppliers leverage, potentially leading to increased costs or reduced flexibility for b1BANK. For instance, a cybersecurity breach can have catastrophic consequences, making banks hesitant to compromise on the quality or reliability of their security software providers, further solidifying supplier power.
The availability and demand for experienced banking professionals significantly impact b1BANK's operational costs and service quality. In 2024, the banking sector continued to face a competitive job market, with specialized roles like commercial lenders, treasury management specialists, and IT experts in high demand. This scarcity allows skilled employees to negotiate higher salaries and more attractive benefits, directly increasing b1BANK's labor expenses.
A shortage of qualified talent can also pose a direct threat to b1BANK's growth trajectory and its ability to maintain high service standards. For instance, a lack of experienced IT professionals could delay crucial digital transformation initiatives, while a deficit in commercial lenders might limit the bank's ability to expand its loan portfolio and serve new clients effectively.
Financial Market Infrastructure Providers
Financial market infrastructure providers, like payment networks and credit reporting agencies, wield substantial bargaining power over banks such as b1BANK. These entities offer essential services that banks cannot operate without, meaning their pricing and terms directly influence a bank's cost of doing business and overall efficiency.
For instance, transaction fees from payment networks represent a significant operational cost for banks. In 2023, global payment processing fees were estimated to be in the hundreds of billions of dollars, a figure that continues to grow. Any increase in these fees directly impacts b1BANK's profitability.
The reliance on these critical suppliers means that disruptions or escalating costs from them can have a material effect on b1BANK's business operations and financial performance.
- Interdependence: Banks like b1BANK are fundamentally reliant on financial market infrastructure providers to facilitate transactions and access crucial data.
- Cost Impact: Fees charged by these providers, such as for payment processing or credit information, directly add to a bank's operational expenses.
- Operational Risk: Any interruption in services from these suppliers poses a significant operational risk, potentially halting key banking functions.
- Limited Substitutes: For many core functions, the number of viable alternative suppliers is limited, concentrating power in the hands of existing providers.
Regulatory and Compliance Service Providers
Regulatory and compliance service providers, while not traditional suppliers, wield significant influence over banks like b1BANK. The intricate and constantly shifting regulatory environment means banks must rely on specialized expertise for software, legal advice, and auditing. This reliance, coupled with the high demand for these essential services, grants them considerable bargaining power.
The necessity of adhering to regulations, with penalties for non-compliance being severe, makes these services indispensable for banks. For instance, in 2024, the global regulatory compliance market was valued at approximately $117.5 billion, highlighting the substantial economic importance and inherent power of these specialized firms.
- High Demand: The constant need for up-to-date compliance solutions drives demand for these services.
- Specialized Knowledge: Their unique expertise in navigating complex regulations is difficult for banks to replicate internally.
- Risk Mitigation: Banks pay a premium for services that prevent costly fines and reputational damage from non-compliance.
- Market Value: The significant market size of compliance services underscores the financial leverage these providers possess.
Suppliers of specialized banking technology and software, particularly core banking systems and cybersecurity solutions, hold considerable bargaining power over b1BANK. These providers often offer proprietary systems, limiting a bank's ability to switch vendors easily. The global FinTech market's valuation exceeding $1.1 trillion in 2024 underscores the specialized and concentrated nature of these technology suppliers, allowing them to command higher prices or dictate terms due to banks' critical reliance on these essential services for operational integrity and security.
What is included in the product
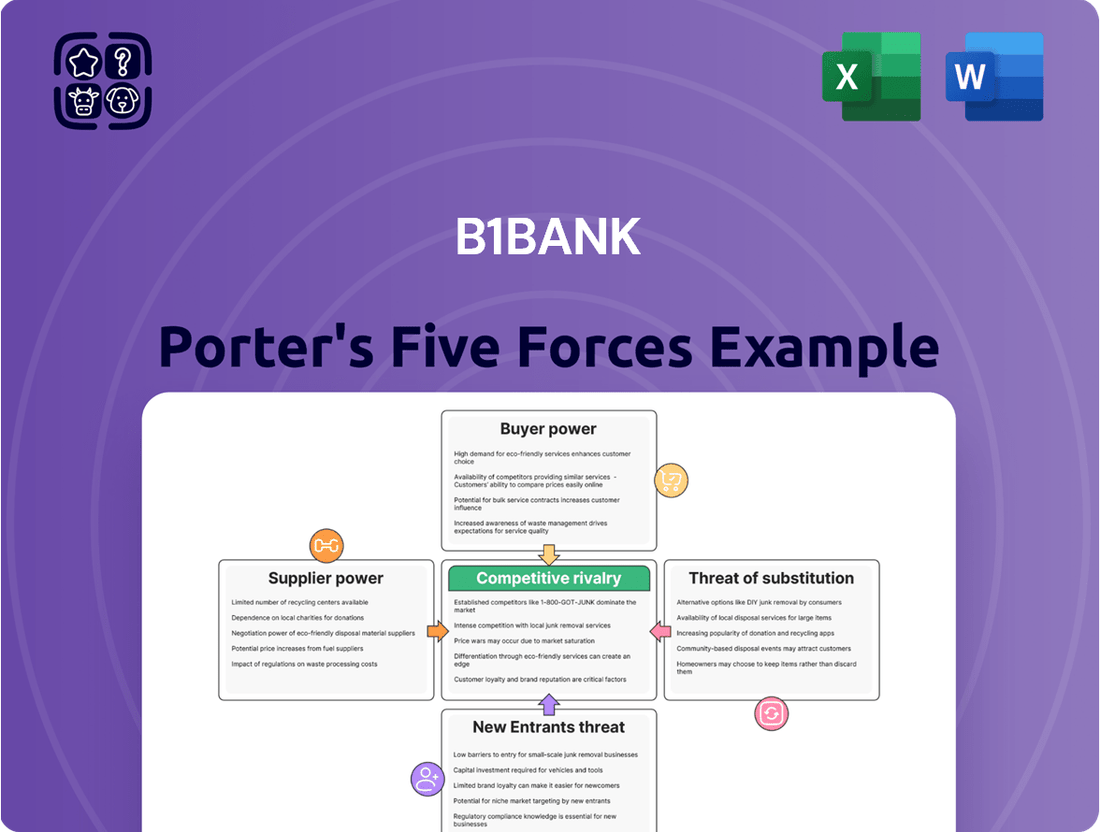
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting b1BANK, revealing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of all five forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
b1BANK's target customers, primarily small and medium-sized businesses and professionals, face a banking landscape brimming with options. They can readily access services from large national institutions, community-focused regional banks, member-owned credit unions, and increasingly, agile online lenders. This abundance of choice significantly amplifies their bargaining power.
The ability to easily compare banking products and switch providers, particularly for straightforward offerings like deposit accounts and standard business loans, further empowers these customers. In 2024, the digital transformation in banking has made this comparison and switching process even more seamless. For instance, many fintech platforms allow for quick account opening and fund transfers, reducing the friction typically associated with changing banks.
This broad accessibility and ease of switching means b1BANK must remain highly competitive. They are compelled to consistently offer attractive products, competitive pricing, and exceptional customer service to retain their client base. Failure to do so risks losing customers to rivals who can offer a better value proposition, especially in the commoditized segments of the banking market.
While some commercial banking relationships can be sticky due to integrated services like treasury management, many basic deposit accounts and standard loans have relatively low switching costs. Customers can often transfer funds or refinance loans with minimal friction, making it easier to shop around for better deals.
This low barrier to exit significantly increases customers' bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer switches their primary checking account every 5-7 years, indicating a willingness to move for better interest rates or lower fees. This ease of movement forces banks to compete more aggressively on pricing and service to retain their customer base.
Today's business clients are remarkably savvy, armed with extensive knowledge of market rates, fees, and the diverse product suites offered by various financial institutions. The ease of online research and comparison significantly amplifies their negotiating power.
This increased transparency compels b1BANK to meticulously define and communicate its unique value proposition, moving beyond mere price competitiveness. For instance, in 2024, the average business customer surveyed indicated they spent over 5 hours researching financial products before making a decision, highlighting the importance of clear, accessible information.
Volume of Business for Larger Clients
While b1BANK primarily serves small and medium-sized enterprises, larger commercial clients within this segment can exert considerable influence. Their substantial transaction volumes or significant credit needs mean they can negotiate better terms, such as lower interest rates or reduced service fees.
For instance, a large business client might represent a significant portion of a branch’s loan portfolio. In 2024, the average loan size for commercial clients in the SME sector varied, but for those clients representing 10% or more of a bank's total commercial lending, the bargaining power is amplified. These clients can leverage their financial footprint to secure more competitive pricing, potentially impacting the bank's profitability on those specific relationships.
- Significant Transaction Volumes: Clients with high transaction frequency and value can demand concessions.
- Substantial Credit Facilities: Larger credit lines allow clients to negotiate interest rates and terms more aggressively.
- Retention Value: Banks may offer preferential terms to retain key clients whose business is crucial to their revenue.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of alternative lenders or financial products can empower large clients to seek better deals elsewhere if their demands are not met.
Ability to Bundle Services
Customers looking for a complete package of banking services, such as business loans, checking and savings accounts, and cash management, often gain more negotiating leverage. This is because they can use the prospect of consolidating their business to secure more favorable pricing or tailored offerings. In 2024, banks that can effectively bundle these services are better positioned to retain these valuable clients.
For instance, a large corporation requiring extensive treasury management alongside significant commercial credit lines might be able to negotiate a lower overall cost of capital by committing to multiple product lines. This bundling capability is a key factor in customer retention and can influence a bank's profitability.
- Bundling Advantage: Customers seeking integrated financial solutions, like commercial lending, deposit accounts, and treasury management, possess enhanced bargaining power.
- Negotiation Leverage: The ability to offer bundled services allows customers to negotiate better pricing or customized terms across their entire banking relationship.
- B1BANK's Strategy: B1BANK's strength in providing integrated solutions is a critical differentiator, but it also creates customer expectations for value across all services.
- Market Trend: In 2024, the demand for comprehensive banking packages continues to grow, emphasizing the importance of a bank's ability to deliver seamless, bundled offerings.
The bargaining power of b1BANK's customers is substantial due to the highly competitive banking sector and the ease with which clients can switch providers. This is particularly true for standard services where differentiation is limited, forcing b1BANK to offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain its clientele.
In 2024, the digital landscape has significantly lowered switching costs for businesses, allowing them to easily compare rates and services across numerous institutions. This transparency empowers customers to demand better terms, especially larger clients with significant transaction volumes or credit needs.
| Customer Segment | Key Bargaining Factors | Impact on b1BANK |
|---|---|---|
| SMEs & Professionals | Abundance of choice, ease of switching, digital comparison tools | Pressure on pricing and service levels for commoditized products |
| Larger Commercial Clients | High transaction volumes, substantial credit facilities, bundled service needs | Ability to negotiate preferential rates and terms, requiring tailored relationship management |
| All Customers | Increased market transparency, readily available information on rates and fees | Need for clear value proposition beyond price, focus on integrated solutions |
What You See Is What You Get
b1BANK Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for b1BANK details the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these forces is crucial for b1BANK to develop effective strategies for sustained competitive advantage and profitability in the dynamic banking sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The banking markets in Louisiana and Texas are incredibly crowded, with numerous national banks, large regional players, and a significant number of community banks and credit unions all vying for business. This maturity means b1BANK operates in a highly competitive arena, facing pressure across all customer segments.
This intense competition, with many financial institutions seeking market share, naturally compresses profit margins and necessitates a constant drive for innovation to stand out. For instance, as of Q1 2024, the FDIC reported over 4,200 FDIC-insured institutions operating nationwide, with a substantial portion concentrated in these mature Southern markets, highlighting the sheer density b1BANK contends with.
Many core banking products, like basic checking and savings accounts, are highly commoditized. This means it's tough for banks to stand out on features alone, pushing competition towards price. For instance, the average interest rate on savings accounts in the US hovered around 0.46% in early 2024, highlighting the price sensitivity of these products.
B1BANK needs to differentiate itself beyond just these standard offerings. Focusing on superior customer service, specialized industry knowledge for commercial loans, or cultivating strong, personal relationships with clients can help avoid a race to the bottom on pricing.
The traditional banking sector is experiencing sluggish growth, particularly in developed markets. For instance, in 2023, the global banking industry saw a modest revenue growth of around 3-4%, a figure expected to remain similar for 2024, indicating a mature and saturated market.
This slow market expansion forces financial institutions like b1BANK to intensely compete for a finite customer base. When the pie isn't getting bigger, every bank is fighting harder for a larger slice of the existing market share.
Consequently, competitive rivalry escalates as banks deploy aggressive pricing strategies, enhanced product offerings, and innovative digital solutions to attract and retain customers, making it a challenging landscape for all players.
High Exit Barriers for Banks
Banks face substantial exit barriers, including massive investments in physical branches and sophisticated technology infrastructure, making it costly to divest. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to maintain a bank branch remains significant, deterring closure. These high costs, coupled with deeply entrenched, long-term customer relationships built over decades, create a sticky environment.
Furthermore, the intricate web of regulatory compliance, such as Basel III and IV requirements, adds another layer of complexity and expense to exiting the market. These obligations are not easily shed, forcing even struggling banks to remain operational. This persistence means that even banks with weaker performance continue to compete, intensifying overall rivalry.
- High Fixed Asset Costs: Banks have significant investments in property, plant, and equipment, estimated in the billions for major institutions globally.
- Long-Term Customer Relationships: Customer loyalty in banking can span generations, making it difficult for new entrants or exiting banks to shift market share easily.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with stringent banking regulations requires ongoing investment and expertise, creating a barrier to a clean exit.
- Brand Reputation: A bank's reputation is a critical asset, and exiting a market can damage brand value for any affiliated entities.
Aggressive Marketing and Relationship Banking
Competitors in the banking sector are heavily invested in aggressive marketing and relationship banking strategies to capture and keep commercial clients. This often involves offering attractive promotional rates, unique service packages, and assigning dedicated relationship managers to foster loyalty and attract new business. For instance, in 2024, many regional banks increased their marketing spend by an average of 8% year-over-year to highlight competitive loan offerings and digital banking solutions.
To counter this, b1BANK needs to significantly bolster its own sales and marketing initiatives. Cultivating deep, personalized client relationships is paramount. This means not only matching competitive pricing but also providing superior service and tailored advice that larger, more resource-rich rivals might overlook. The ability to build trust and demonstrate value beyond mere transactional banking is a key differentiator.
- Aggressive Marketing: Competitors are leveraging extensive advertising campaigns and promotional offers to gain market share.
- Relationship Banking: Emphasis is placed on personal connections and dedicated client management to retain business.
- Client Acquisition Tactics: Banks are using promotional rates and specialized services as key tools to attract commercial clients.
- b1BANK's Strategy: Investment in sales, marketing, and relationship management is crucial for b1BANK to effectively compete.
The competitive rivalry within the banking sector, particularly in markets like Louisiana and Texas where b1BANK operates, is exceptionally fierce. This intensity stems from a mature industry with slow growth, forcing institutions to battle aggressively for existing customers. As of early 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts remained low, around 0.46%, underscoring the commoditized nature of basic banking products and the pressure on pricing.
Banks are compelled to differentiate through superior customer service, specialized expertise, and strong relationship management to avoid a price-driven competition. Many institutions are increasing marketing spend, with regional banks boosting it by approximately 8% in 2024, to highlight competitive loan offerings and digital solutions. This environment demands b1BANK invest heavily in its sales and marketing efforts to build trust and provide value beyond standard transactions.
Exit barriers, such as substantial investments in technology and physical infrastructure, along with regulatory compliance and entrenched customer relationships, keep even underperforming banks in the market. This persistence fuels ongoing competition, as banks deploy aggressive pricing, enhanced products, and innovative digital strategies to capture market share in a landscape where the overall market pie is not expanding significantly, with global banking revenue growth projected to be around 3-4% for 2024.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech lending platforms present a substantial threat to b1BANK's commercial lending business. These online platforms, like Kabbage (now American Express) or OnDeck, offer businesses faster, more streamlined loan applications and approvals compared to traditional banking. In 2024, fintech lenders continued to capture market share, particularly among SMBs seeking quick capital infusions, often bypassing the more rigorous due diligence of established institutions.
The convenience and speed offered by fintech alternatives directly challenge b1BANK's traditional model, which often involves more extensive paperwork and longer waiting periods. This digital-first approach allows fintechs to operate with lower overhead, translating into potentially more competitive rates or faster funding cycles, thereby eroding b1BANK's customer base for certain loan products.
Credit unions and Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs) present a notable threat of substitutes for traditional banks like b1BANK. These member-owned or community-focused entities often provide competitive interest rates and a more personalized, local banking experience, which can be particularly appealing to small businesses and individuals. For instance, as of early 2024, credit unions collectively held over $2.3 trillion in assets, demonstrating their significant market presence and ability to attract customers away from conventional banks by offering lower fees and specialized services.
The rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services, including those offered by b1BANK. These platforms provide alternative avenues for businesses, especially startups and SMEs, to secure capital, thereby diminishing their reliance on conventional bank loans. For instance, by mid-2024, the global P2P lending market was projected to reach over $300 billion, showcasing a substantial shift in capital accessibility.
Crowdfunding platforms, in particular, have democratized fundraising, allowing a broad base of individual investors to directly support businesses. This disintermediation means b1BANK faces increased competition from a more accessible and often faster funding source. In 2023 alone, crowdfunding campaigns raised billions globally, demonstrating the growing impact of these substitute channels on traditional financial institutions.
Internal Financing and Corporate Bonds
Established or larger businesses within b1BANK's market might bypass traditional lending by using internal financing, such as retained earnings, or by issuing corporate bonds. This allows them to raise capital directly from financial markets, lessening their reliance on bank credit. Companies with robust credit histories find these direct financing methods particularly attractive.
In 2024, corporate bond issuance remained a significant capital-raising tool. For instance, the US corporate bond market saw substantial activity, with investment-grade issuance reaching hundreds of billions of dollars throughout the year, demonstrating a strong appetite for direct market funding among creditworthy corporations.
- Internal Financing: Businesses can utilize retained earnings, reinvesting profits to fund operations and growth, thereby avoiding external debt.
- Corporate Bonds: Companies with strong credit ratings can issue bonds to investors, securing long-term capital directly from the market.
- Reduced Bank Dependence: These alternative methods decrease a company's reliance on traditional bank loans and credit facilities.
- Market Competitiveness: The availability and attractiveness of these substitutes can exert downward pressure on the pricing and terms of bank loans offered by institutions like b1BANK.
Non-Bank Payment Processors and Cash Management Solutions
Companies such as Square and PayPal are increasingly offering robust payment processing and cash management solutions. These platforms can directly substitute some of b1BANK's treasury management services by providing integrated tools for sales, invoicing, and financial reporting. This reduces a business's need for traditional banking services for managing operational liquidity and processing transactions.
These specialized processors often provide greater convenience and features tailored to specific business needs, directly competing with b1BANK's established offerings. For instance, in 2023, PayPal reported facilitating $1.36 trillion in total payment volume, showcasing the significant market share these alternatives command.
- Square's Cash App processed over $200 billion in payments in 2023, highlighting its significant role as a substitute for traditional banking transaction services.
- PayPal's continued expansion into business services, including working capital loans and advanced payment gateways, directly challenges bank-provided treasury solutions.
- The growing adoption of these platforms by small and medium-sized businesses indicates a clear shift in how companies manage their day-to-day financial operations, bypassing traditional banking channels for many functions.
The threat of substitutes for b1BANK is significant, encompassing fintech lenders, credit unions, P2P platforms, and even internal corporate financing. These alternatives offer speed, convenience, and often lower costs, directly challenging b1BANK's traditional lending and treasury services.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | 2024 Impact/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech Lenders | Fast approvals, streamlined applications | Continued market share gains among SMBs |
| Credit Unions/CDFIs | Competitive rates, personalized service | Over $2.3 trillion in assets held by credit unions (early 2024) |
| P2P/Crowdfunding | Alternative capital access for startups/SMEs | Global P2P lending market projected over $300 billion (mid-2024) |
| Internal Financing/Bonds | Direct capital from retained earnings or markets | US corporate bond issuance in hundreds of billions (2024) |
| Payment Processors (Square, PayPal) | Integrated financial tools, payment processing | PayPal's $1.36 trillion total payment volume (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like b1BANK, faces a significant threat from new entrants due to exceptionally high regulatory and compliance barriers. Obtaining a bank charter is a complex, time-consuming, and costly endeavor, requiring extensive documentation and adherence to strict operational standards. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain a national bank charter in the US could extend over a year, involving multiple federal and state agencies.
New players must meticulously navigate a labyrinth of compliance frameworks. These include stringent capital adequacy ratios, robust anti-money laundering (AML) protocols, and comprehensive consumer protection laws. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, deterring many potential entrants. The sheer cost and complexity of meeting these requirements, such as implementing advanced cybersecurity measures to protect customer data, effectively act as a formidable barrier.
Establishing a new bank, like b1BANK, demands substantial capital, often in the billions, to satisfy stringent regulatory requirements and build essential infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, new challenger banks often need to demonstrate robust capital adequacy ratios well above the Basel III minimums to gain regulatory approval, a significant barrier to entry. This high initial investment, coupled with the inherent risks in the financial sector, deters many potential competitors, thereby protecting incumbent institutions. b1BANK’s strong existing capital base provides a significant advantage in this regard.
Brand loyalty and trust are significant barriers for new entrants looking to challenge established banks like b1BANK. For instance, in 2024, customer retention rates in the banking sector remained robust, with many consumers preferring to stick with institutions they know and trust, often citing security and reliability as primary concerns. Newcomers face the daunting task of not only offering competitive products but also convincing a risk-averse public to switch, a process that historically takes years and substantial marketing investment.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established banks leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in technology infrastructure and marketing reach. For instance, major global banks in 2024 often operate with billions in annual IT spending, allowing them to spread these costs over a vast customer base. This scale translates into lower per-transaction costs, a barrier for new entrants who must invest heavily to achieve comparable efficiency.
The experience curve further solidifies the advantage of incumbent banks. Years of operational refinement have led to optimized processes in areas like loan origination, risk management, and customer service. A new bank entering the market in 2024 would face a steep learning curve, potentially leading to higher initial operating costs and slower service delivery compared to established players who have already navigated these challenges.
- Economies of Scale: Large banks can spread fixed costs like technology investments over millions of customers, reducing the average cost of service delivery.
- Experience Curve: Incumbents have developed process efficiencies over decades, leading to lower operational costs and faster service times.
- Cost Competitiveness: New entrants struggle to match the cost structures of established banks, making it difficult to compete on price for core banking products.
- Investment Requirements: Achieving operational parity requires substantial upfront investment in technology and talent, a significant hurdle for startups.
Access to Distribution Channels and Talent
New banks face significant hurdles in establishing distribution channels and securing skilled personnel. Building an extensive network of physical branches or sophisticated digital platforms demands considerable capital and a lengthy development period. For instance, a new entrant might need to invest tens of millions of dollars to establish a meaningful physical footprint.
Attracting and retaining experienced banking professionals, particularly in high-demand areas like commercial lending or treasury management, presents another substantial challenge. The competition for top talent is fierce, and established institutions often have more attractive compensation and career progression opportunities. In 2024, the average salary for a senior commercial banker in a major metropolitan area could easily exceed $150,000 annually, plus bonuses.
- Distribution Network Costs: New entrants must budget for significant capital expenditure to build or acquire physical branches and develop robust digital banking infrastructure.
- Talent Acquisition Expenses: Competitive salaries and benefits packages are necessary to attract and retain experienced banking professionals, increasing operational costs for newcomers.
- B1BANK's Advantage: B1BANK's established presence in Louisiana and Texas offers a distinct advantage in terms of existing customer relationships, brand recognition, and operational infrastructure, mitigating these entry barriers.
The threat of new entrants for b1BANK is generally moderate due to substantial barriers, though fintech innovation presents a persistent challenge. Regulatory hurdles, significant capital requirements, and the need for established trust are formidable deterrents. However, agile fintech firms can bypass some traditional brick-and-mortar costs, focusing on niche digital services and potentially eroding market share in specific segments.
In 2024, the landscape continues to be shaped by digital-first challengers and the ongoing need for robust compliance. For instance, neobanks, while still needing to navigate regulations, can launch with significantly lower overhead than traditional banks, often focusing on user experience and specialized services. This agility allows them to attract specific customer demographics, posing a competitive threat that incumbents like b1BANK must actively address through innovation and customer-centric strategies.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict licensing, capital adequacy, AML, KYC rules | High Cost & Time Intensive | Continually evolving, increasing complexity |
| Capital Requirements | Billions needed for charter, operations, tech | Significant Financial Barrier | Minimum capital for new charters often exceeds $10M-$20M |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Customer preference for established, secure institutions | Difficult to Acquire Customers | High customer retention rates persist, especially for security-conscious segments |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large customer base | Disadvantage in Cost Structure | Major banks invest billions in IT, creating significant cost advantages |
| Distribution Channels | Need for physical branches and/or advanced digital platforms | High Infrastructure Investment | Digital platform development can cost tens of millions |
| Talent Acquisition | Competition for experienced banking professionals | Increased Operational Costs | Senior roles can command salaries exceeding $150k-$200k annually |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our b1BANK Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including industry-specific market research reports, financial filings from banking institutions, and regulatory disclosures from financial authorities. This comprehensive approach ensures an accurate assessment of competitive intensity and strategic positioning within the banking sector.
