Avianca Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Avianca Holdings Bundle
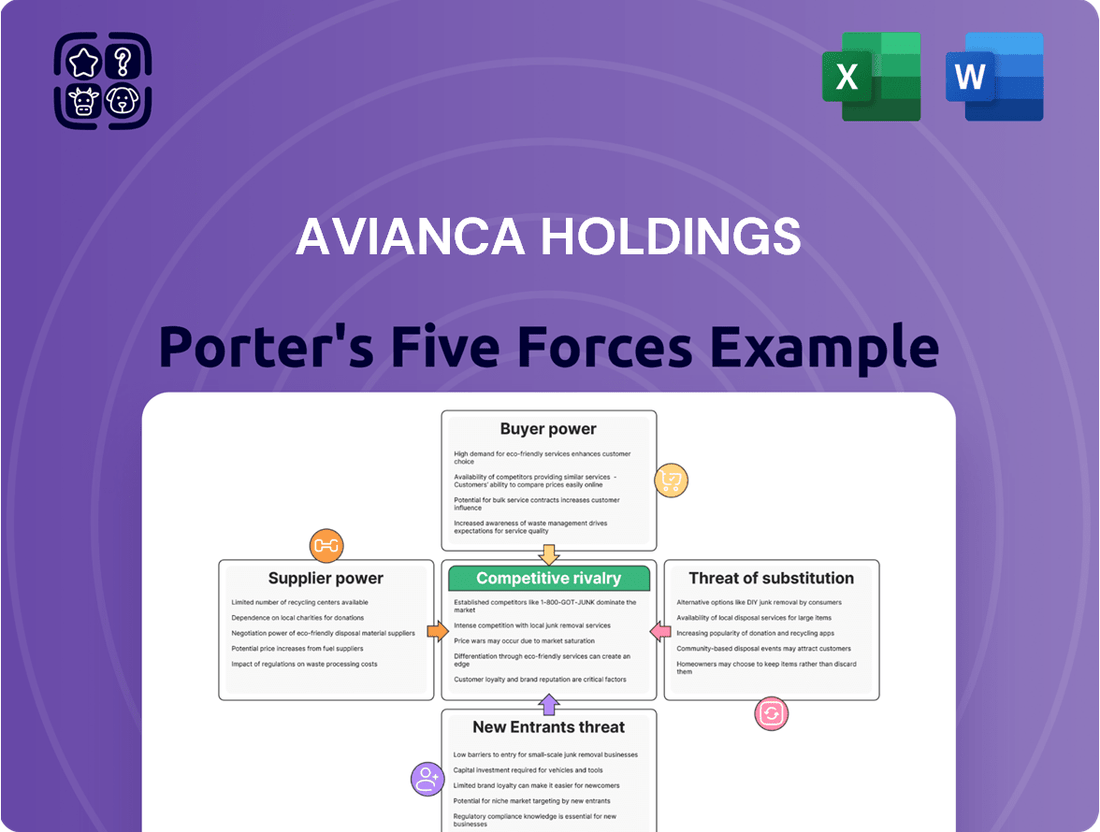
Avianca Holdings navigates a complex competitive landscape, with intense rivalry and the significant bargaining power of buyers posing considerable challenges.
The threat of new entrants and the availability of substitutes also exert pressure, demanding strategic agility from Avianca.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Avianca Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Aircraft manufacturers like Boeing and Airbus hold substantial bargaining power over airlines. In 2024, the continued reliance on these two major players for new aircraft and spare parts means Avianca, like other carriers, faces limited options. This duopoly allows manufacturers to dictate terms on pricing, delivery slots, and even the technological specifications of new planes, directly impacting Avianca's capital expenditures and long-term fleet strategy.
Fuel suppliers wield considerable power over airlines like Avianca Holdings because jet fuel represents a substantial operating cost. The fluctuating prices of oil directly impact Avianca's bottom line, making them vulnerable to supplier decisions.
In 2024, jet fuel prices experienced significant volatility, with benchmarks like West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil trading within a range that directly influenced airline operating expenses. For instance, if crude oil prices surged by 10% in a quarter, Avianca's fuel costs could increase proportionally, impacting its profitability.
To counter this, Avianca employs strategies such as fuel hedging, a financial tool used to lock in fuel prices for future purchases. This helps to stabilize costs and reduce the impact of sudden price spikes, though it also carries its own set of risks and costs.
Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) providers hold significant bargaining power over airlines like Avianca. The highly specialized nature of aircraft MRO, requiring certified technicians and specific tooling, creates a concentrated market with fewer qualified suppliers. This limited competition means airlines often face less favorable pricing and terms from these essential service providers, directly impacting operational costs and potentially delaying crucial maintenance schedules.
Airport Operators and Air Traffic Control
Airport operators and air traffic control services hold significant bargaining power due to their nature as essential, often monopolistic, infrastructure. These entities dictate crucial operational parameters for airlines like Avianca.
Their influence is felt through various channels:
- Airport Fees and Charges: Airlines incur substantial costs related to landing fees, gate usage, passenger service charges, and other airport-related expenses. For instance, in 2024, airport operating costs represent a considerable portion of an airline's total expenditure, directly impacting profitability.
- Slot Allocation: The availability and allocation of landing and take-off slots at congested airports are critical for route planning and maximizing aircraft utilization. Limited slots can restrict an airline's ability to operate desired routes or expand its network.
- Operational Regulations: Airport operators and air traffic control set and enforce operational rules, including noise restrictions, turnaround times, and security protocols, which can affect an airline's efficiency and on-time performance.
Labor Unions
Labor unions, particularly those representing highly skilled personnel like pilots, flight attendants, and mechanics, exert considerable bargaining power over airlines such as Avianca Holdings. These skilled workers are essential for safe and efficient operations, giving their unions leverage in negotiations. In 2023, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) reported that labor costs represent a significant portion of an airline's operating expenses, often ranging from 25% to 40%.
The ability of these unions to negotiate favorable contracts regarding wages, benefits, and working conditions directly impacts Avianca's cost structure. Furthermore, the potential for industrial actions, such as strikes or work slowdowns, can lead to significant operational disruptions, flight cancellations, and substantial financial losses, thereby amplifying the bargaining power of these labor groups.
- Skilled Workforce: Pilots, mechanics, and flight attendants are critical for airline safety and service delivery.
- Negotiating Leverage: Unions can demand higher wages and better benefits due to the specialized skills and essential nature of their members.
- Operational Impact: Labor disputes can halt operations, causing severe financial and reputational damage.
- Cost Component: Labor costs are a substantial part of an airline's overall expenses, making union agreements financially impactful.
Aircraft manufacturers and specialized MRO providers hold significant sway due to the concentrated nature of these industries and the high barriers to entry. For Avianca, this translates into less flexibility on pricing and delivery schedules for new aircraft and essential maintenance services.
Fuel suppliers, particularly in the volatile energy markets of 2024, exert considerable power as jet fuel constitutes a major operating expense. Avianca's reliance on these suppliers, coupled with the inherent price fluctuations of oil, makes the airline susceptible to cost increases, even with hedging strategies.
Airport operators and air traffic control services act as near-monopolies, dictating crucial fees and slot allocations. These charges, along with operational regulations, directly impact Avianca's cost structure and network efficiency.
Labor unions, representing pilots, mechanics, and flight attendants, wield substantial bargaining power. Given that labor costs can represent 25-40% of an airline's expenses, as noted by IATA, union negotiations significantly influence Avianca's financial health and operational stability.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Avianca |
|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Manufacturers (Boeing, Airbus) | Duopoly, high R&D costs, long lead times | High capital expenditure, limited fleet options |
| Fuel Suppliers | Commodity price volatility, limited global suppliers | Significant operating cost fluctuations, need for hedging |
| MRO Providers | Specialized skills, certifications, limited qualified providers | Higher maintenance costs, potential for service delays |
| Airport Operators/ATC | Essential infrastructure, often monopolistic | High fees, restricted slot availability, operational constraints |
| Labor Unions (Pilots, Mechanics) | Essential skilled workforce, potential for strikes | Significant labor cost component, operational disruption risk |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Avianca Holdings dissects the competitive intensity within the Latin American airline industry, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Instantly visualize Avianca's competitive landscape with a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Effortlessly adapt to changing market dynamics by customizing pressure levels based on new data or evolving industry trends.
Customers Bargaining Power
Leisure travelers, a significant segment for airlines like Avianca, exhibit strong price sensitivity. This means they are quite responsive to changes in ticket prices, often choosing the cheapest available option. For instance, in 2024, the average airfare for domestic flights in many regions saw fluctuations, directly impacting booking decisions.
The proliferation of online travel agencies (OTAs) and sophisticated price comparison websites has dramatically amplified customer power. These platforms allow travelers to effortlessly compare fares across numerous airlines, including Avianca, in real-time. This transparency compels airlines to maintain competitive pricing strategies and offer a variety of fare classes to attract price-conscious consumers.
The airline industry, including Avianca Holdings, faces significant customer bargaining power due to a plethora of choices. In 2024, the global airline market saw hundreds of carriers operating, with low-cost carriers (LCCs) like Ryanair and Spirit Airlines significantly increasing competitive pressure by offering highly competitive pricing. This abundance of options means passengers can readily compare fares and services across numerous airlines.
Furthermore, switching costs for airline customers are remarkably low. Passengers can effortlessly shift between airlines for their next flight with minimal effort or financial penalty. For instance, booking a flight typically takes minutes online, and loyalty programs, while encouraging retention, do not create insurmountable barriers for a customer seeking a better deal elsewhere, especially for leisure travelers. This ease of switching empowers customers to demand better value from airlines like Avianca.
While customers hold significant bargaining power in the airline industry, Avianca's LifeMiles loyalty program seeks to counter this by fostering customer retention through tiered rewards and elite status benefits. However, the effectiveness of such programs is directly tied to the overall customer experience; a single negative interaction can easily lead a customer to switch to a competitor, especially given the readily available alternatives.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Travel Demand
The bargaining power of Avianca's customers significantly increases when economic conditions worsen. During periods of economic downturn, consumers tend to cut back on non-essential spending, including air travel. This reduced demand forces airlines like Avianca to compete more aggressively on price.
In 2024, with ongoing global economic uncertainties, travelers have become more price-sensitive. This heightened sensitivity translates directly into greater customer bargaining power, as individuals and businesses seek the most economical travel options. Avianca, like its competitors, may find itself compelled to offer lower fares to attract passengers, potentially squeezing profit margins and impacting revenue per available seat mile (RASM).
- Economic Downturns Increase Customer Price Sensitivity: As discretionary spending tightens, customers prioritize cost savings in travel.
- Pressure on Fares: Airlines face pressure to reduce ticket prices to stimulate demand during economic slowdowns.
- Impact on Revenue: Lower fares can negatively affect Avianca's revenue per passenger and overall profitability.
- Competitive Landscape: In a weak economy, the airline industry often sees intensified price competition among carriers.
Direct Booking and Ancillary Services
The increasing prevalence of direct booking channels, such as airline websites and mobile applications, significantly enhances customer bargaining power. These platforms enable passengers to meticulously tailor their travel itineraries and opt for specific ancillary services, directly impacting Avianca's revenue streams.
This direct engagement empowers customers to meticulously select and pay for only the services they deem valuable, such as preferred seating or extra baggage. This can lead to a more price-sensitive approach to bundled offerings, forcing airlines to be more competitive. For instance, by 2024, a substantial portion of airline revenue is derived from these ancillary services, making customer choice in this area a critical factor.
- Direct Booking Growth: Airlines are increasingly investing in their own digital platforms to capture more direct bookings, bypassing online travel agencies.
- Ancillary Revenue Focus: Ancillary services, including baggage fees, seat selection, and in-flight meals, represent a growing and vital revenue component for airlines.
- Customer Customization: Passengers can now easily compare and choose individual services, shifting the focus from package deals to à la carte options.
- Price Sensitivity: Direct access to service pricing allows customers to more readily compare costs and negotiate value, increasing their bargaining power.
Avianca's customers wield considerable bargaining power due to the sheer volume of airline choices available. In 2024, the global market featured hundreds of carriers, with low-cost airlines intensifying price competition. This abundance of options allows passengers to easily compare fares and services, pushing airlines to offer competitive pricing and flexible fare structures to attract and retain them.
Switching costs for airline passengers are minimal, empowering them to easily move between carriers for better deals. While loyalty programs exist, they often don't prevent customers from seeking more economical options elsewhere, particularly leisure travelers. This ease of switching compels airlines like Avianca to continuously provide value and competitive pricing to maintain customer loyalty.
The rise of online travel agencies and price comparison sites has significantly amplified customer power by offering real-time fare comparisons across numerous airlines. This transparency forces airlines to maintain competitive pricing and diverse fare classes to appeal to cost-conscious travelers.
Economic downturns further bolster customer bargaining power as travelers become more price-sensitive, leading airlines to compete more aggressively on fares. In 2024, this heightened sensitivity means Avianca may need to offer lower prices, potentially impacting revenue per available seat mile (RASM).
| Factor | Impact on Avianca | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | High bargaining power for customers | Hundreds of global carriers, including LCCs |
| Switching Costs | Low, empowering customer choice | Minimal financial or effort barriers to change airlines |
| Information Availability | Increased price transparency | Widespread use of OTAs and comparison websites |
| Economic Conditions | Heightened price sensitivity | Ongoing global economic uncertainties impacting travel budgets |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Avianca Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Avianca Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape within the airline industry. You're looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you’ll receive instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Avianca faces formidable competition within Latin America, notably from giants like LATAM Airlines Group and Copa Holdings. These established carriers are locked in a constant battle for routes, passengers, and overall market share, intensifying rivalry.
In 2023, LATAM Airlines Group reported operating revenue of approximately $11.5 billion, showcasing its significant scale and market presence. Copa Holdings, another major player, generated around $3.1 billion in revenue during the same period, highlighting the substantial resources and reach of Avianca's competitors.
The rise of low-cost carriers (LCCs) like JetSmart in Latin America has dramatically increased competitive pressure on Avianca. These LCCs, known for their aggressive pricing and streamlined offerings, force legacy carriers to constantly re-evaluate their fare structures to remain competitive in the market.
For instance, in 2024, LCCs captured a significant share of the regional market, with some reporting passenger growth exceeding 20% year-over-year. This expansion directly challenges Avianca's ability to balance competitive ticket prices with the costs associated with its full-service model, such as onboard amenities and broader network connectivity.
Airlines are locked in a fierce battle, constantly broadening their flight paths and boosting the number of seats available to snag a bigger piece of the market. This aggressive expansion directly fuels the competitive rivalry.
Avianca, for instance, has been busy. In 2024, they added a significant number of new routes and destinations, and they're not stopping there, with further network growth planned for 2025. This ongoing expansion by Avianca and its peers intensifies the competition.
Price Wars and Promotional Activities
The airline industry, including Avianca's operating regions, is characterized by intense rivalry, frequently triggering price wars and extensive promotional campaigns. This competitive pressure forces airlines to lower fares to capture market share, directly impacting profitability.
For instance, during 2024, major Latin American carriers, alongside Avianca, engaged in significant fare adjustments, particularly on high-demand routes. This strategy, while aiming to boost passenger volume, often leads to reduced revenue per passenger. Airlines are constantly offering deals and loyalty program incentives to stand out.
- Intense Competition: Airlines like Avianca face constant pressure from other carriers, leading to aggressive pricing strategies.
- Eroding Profit Margins: Price wars and promotions can significantly decrease the profitability of all airlines involved.
- Customer Sensitivity: Passengers are highly responsive to price changes, making it a critical factor in route selection.
- Promotional Tactics: Airlines utilize discounts, bundled offers, and loyalty programs to attract and retain customers in a competitive landscape.
Service Differentiation and Customer Experience
Airlines differentiate themselves through service quality, loyalty programs, and overall customer experience, making this a key battleground. Avianca's efforts to enhance its premium offerings, such as improved cabin amenities and personalized service, are vital for standing out. In 2023, Avianca reported a significant improvement in its on-time performance, reaching 87.5% for its domestic operations, a critical factor for customer satisfaction and loyalty in a market where reliability is highly valued.
The airline's focus on operational efficiency, including baggage handling, directly impacts the customer journey. By minimizing lost or delayed baggage, Avianca aims to build trust and encourage repeat business. This commitment is reflected in their operational metrics, where they’ve seen a reduction in mishandled baggage rates, contributing to a more seamless travel experience for passengers.
- Service Quality: Avianca is investing in cabin upgrades and crew training to elevate its premium offerings.
- Loyalty Programs: The LifeMiles loyalty program continues to be a cornerstone for customer retention, offering enhanced benefits and personalized rewards.
- Customer Experience: Improvements in on-time performance and baggage handling are central to Avianca's strategy for differentiating itself.
- Operational Metrics: In 2023, Avianca's domestic on-time performance reached 87.5%, demonstrating a commitment to reliability.
Competitive rivalry within the Latin American airline industry is intense, with Avianca facing strong headwinds from established players like LATAM Airlines Group and Copa Holdings, as well as a growing number of low-cost carriers. These competitors are actively expanding their networks and aggressively adjusting fares, creating a dynamic market where price and service differentiation are crucial for survival and growth.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| LATAM Airlines Group | $11.5 billion | Scale and Market Presence |
| Copa Holdings | $3.1 billion | Network Reach |
| JetSmart (LCC) | N/A (Significant Market Share Growth) | Aggressive Pricing, Streamlined Offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For shorter domestic and regional routes, road transportation, particularly intercity buses and private cars, poses a significant threat of substitution to Avianca's services. In 2024, the demand for intercity bus travel in Latin America, a key market for Avianca, remained robust, with many passengers opting for more economical or convenient ground transport for distances under 500 kilometers. This trend is exacerbated by ongoing investments in road infrastructure across several South American nations, making car and bus journeys faster and more comfortable, thereby directly competing with short-haul flights.
While rail transportation is not a dominant substitute for air travel in most of Latin America currently, future investments in high-speed rail could alter this landscape. For instance, if significant upgrades occur, routes like the proposed Mexico City-Querétaro high-speed rail, which was discussed for development, could offer a competitive alternative for medium-distance business and leisure travel, potentially impacting Avianca's domestic and regional passenger volume.
The rise of virtual communication and remote work, a trend significantly amplified by events in recent years, directly impacts the demand for business travel. This shift presents a substantial substitute threat to airlines like Avianca, particularly within their corporate client base.
For instance, a 2023 report indicated that 59% of U.S. workers were in jobs that could be done remotely, a stark increase from pre-pandemic levels, suggesting a persistent reduction in the need for physical business meetings and, consequently, air travel.
Sea Travel (Cruises and Ferries)
For leisure travelers, particularly those heading to island or coastal destinations, sea travel like cruises and ferries can act as substitutes for air travel. These alternatives offer a different experience and can sometimes present a more budget-friendly option. For instance, in 2024, the global cruise industry saw a significant rebound, with passenger numbers projected to reach pre-pandemic levels, indicating a strong appeal of sea-based vacations.
The threat of substitutes for Avianca Holdings, specifically from sea travel, is moderate. While air travel is generally faster and more convenient for longer distances, cruises and ferries cater to a specific segment of the travel market. Many travelers opt for cruises not just for transportation but for the all-inclusive experience, which air travel alone does not provide.
- Substitution Potential: Cruises and ferries offer a distinct travel experience, appealing to leisure travelers seeking different vacation styles, especially for shorter, scenic routes or to island destinations.
- Price Sensitivity: For price-sensitive leisure travelers, especially those not constrained by time, sea travel can be a viable alternative, potentially offering lower overall costs for the vacation package.
- Industry Trends: The cruise industry experienced robust growth in 2024, with major lines reporting strong booking trends, underscoring the persistent demand for sea-based leisure travel as a substitute for other vacation types.
Other Forms of Tourism and Leisure
The threat of substitutes for Avianca Holdings, particularly from other forms of tourism and leisure, is significant. Consumers have a wide array of choices for how they spend their discretionary income on recreation and travel. A notable trend observed in 2024 and continuing into 2025 is the increasing popularity of staycations and local tourism, driven by factors such as cost-consciousness and a desire for more accessible experiences. This can directly impact demand for air travel, as individuals opt for destinations reachable by car or train, or even choose non-travel related leisure activities altogether.
These alternative leisure pursuits can range from home-based entertainment and digital experiences to local cultural events and outdoor activities. For instance, the growth in the experience economy, where consumers prioritize spending on memorable activities over material goods, means that money spent on concerts, theme parks, or culinary experiences might otherwise have been allocated to airfare. In 2023, global tourism spending saw a robust recovery, but the composition of that spending is shifting, with a greater emphasis on unique, localized experiences potentially diverting funds from traditional long-haul or even short-haul air travel.
The ease and affordability of these substitutes play a crucial role. For example, the expansion of high-speed rail networks in various regions offers a competitive alternative for shorter to medium-haul travel, often providing a comparable or even superior travel time when factoring in airport procedures. Furthermore, the digital transformation of entertainment, from streaming services to virtual reality experiences, offers compelling alternatives for leisure time that do not require physical travel, posing an indirect but persistent substitute threat.
- Shift to Localized Leisure: A growing preference for domestic travel and staycations, observed in 2024, reduces reliance on air travel for vacations.
- Experience Economy Diversion: Spending on local events, dining, and activities competes directly with travel budgets.
- High-Speed Rail Competition: Improved rail infrastructure offers a viable substitute for short to medium-haul air routes.
- Digital Entertainment Alternatives: Streaming services and virtual experiences provide leisure options that bypass the need for travel.
For Avianca, the threat of substitutes is multifaceted, encompassing ground transportation, evolving travel preferences, and alternative leisure activities. Road travel, particularly buses and private cars, remains a strong substitute for shorter domestic and regional routes, especially where road infrastructure is improving. For instance, in 2024, intercity bus travel in Latin America continued to be a popular choice for cost-conscious travelers on journeys under 500 kilometers.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Avianca | 2024/2023 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Intercity Buses/Private Cars | High for short to medium-haul domestic/regional routes | Robust demand in Latin America; infrastructure improvements enhance competitiveness. |
| High-Speed Rail | Potential future threat for medium-haul routes | Ongoing discussions and potential investments in select corridors could create alternatives. |
| Virtual Communication/Remote Work | Significant threat to business travel | Reported 59% of US jobs could be done remotely in 2023, indicating a persistent reduction in business travel needs. |
| Sea Travel (Cruises/Ferries) | Moderate for leisure, especially island/coastal destinations | Cruise industry saw strong rebound in 2024, with passenger numbers nearing pre-pandemic levels. |
| Staycations/Local Tourism | Growing threat to leisure travel | Increasing popularity in 2024 due to cost-consciousness and accessibility. |
| Digital Entertainment/Experiences | Indirect threat to leisure spending | Growth in experience economy diverts discretionary spending from travel. |
Entrants Threaten
The sheer scale of investment needed to launch an airline is a formidable barrier. Acquiring a fleet of modern aircraft, building extensive maintenance and operational infrastructure, and securing necessary regulatory approvals can easily run into billions of dollars. For instance, a new wide-body aircraft can cost upwards of $300 million, and an airline needs many to operate effectively.
This substantial capital requirement directly limits the pool of potential new entrants capable of challenging established carriers like Avianca. The financial risk is immense, as new airlines must not only cover these upfront costs but also compete on price and service from day one against companies with decades of operational experience and economies of scale.
The aviation sector is characterized by an exceptionally strict regulatory environment, including rigorous safety standards and extensive licensing requirements. These complex and costly compliance procedures act as a significant barrier, deterring potential new entrants from easily entering the market.
Avianca Holdings benefits from significant brand loyalty and established networks, a major barrier for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, Avianca continued to leverage its extensive routes across Latin America, serving over 100 destinations. Replicating such a well-developed network and the associated customer trust would require substantial time and investment for any newcomer, hindering their ability to quickly gain market share.
Access to Airport Slots and Partnerships
New airlines face significant hurdles in securing prime airport slots at major hubs, a critical factor for operational efficiency and customer accessibility. Avianca's long-standing relationships and established operational footprint give it a distinct advantage in this area, making it harder for newcomers to gain comparable access. For instance, in 2024, major airports like London Heathrow (LHR) and New York JFK continued to operate at near-full capacity, with slot availability being a major bottleneck for new carriers.
Furthermore, forging strategic partnerships with other airlines, travel agencies, and even ground handling services is essential for new entrants to build a competitive network and offer seamless travel experiences. Avianca's existing network of codeshare agreements and alliances, cultivated over years, provides it with a broader reach and customer base that is difficult for new players to replicate quickly. These partnerships are vital for market penetration and revenue generation in the highly competitive airline industry.
- Airport Slot Scarcity: Major international airports often have limited available takeoff and landing slots, making it challenging for new airlines to secure desirable times.
- Partnership Barriers: Establishing mutually beneficial partnerships with established airlines, travel agencies, and loyalty programs requires time, trust, and demonstrated value, which new entrants often lack.
- Avianca's Advantage: Avianca's established operational history and existing network of alliances provide a significant barrier to entry by offering preferential access and broader market reach.
Intense Competition from Existing Players
The threat of new entrants for Avianca Holdings is significantly mitigated by the intense competition already present in the airline industry. Established carriers frequently engage in aggressive pricing wars and adjust their capacity, making it exceptionally challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold and market share. For instance, in 2024, major Latin American airlines like LATAM Airlines Group and Copa Holdings reported robust load factors, demonstrating their ability to fill seats and maintain competitive pricing, which would be a formidable barrier for any new airline trying to enter.
New entrants would need substantial capital to compete effectively, not only for fleet acquisition but also for marketing and operational setup. The existing players, with their established brand recognition and operational efficiencies, can absorb initial losses more readily than a startup. This dynamic means that a new airline would likely face immediate price undercutting and route competition from incumbents determined to preserve their existing customer base and profitability.
- Existing rivalry: The airline sector is characterized by high fixed costs and intense competition, making it difficult for new players to enter profitably.
- Incumbent strategies: Established airlines often react to new entrants with price reductions and increased capacity, squeezing profit margins for all.
- Capital requirements: The substantial investment needed for aircraft, maintenance, and regulatory compliance acts as a significant barrier.
- Brand loyalty: Existing carriers benefit from established customer loyalty and route networks, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate.
The threat of new entrants for Avianca Holdings is considerably low due to the immense capital required to start an airline, estimated in the billions for fleet acquisition and infrastructure. Furthermore, the industry's stringent regulatory landscape and the difficulty in securing prime airport slots present substantial hurdles for any newcomer. Avianca's established brand loyalty and extensive network of partnerships, including over 100 destinations served in 2024, create significant barriers that newcomers would struggle to overcome quickly.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for aircraft, maintenance, and operations. | Deters potential entrants due to financial risk. | New wide-body aircraft cost >$300 million. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Strict safety standards and licensing. | Increases time and cost for market entry. | Complex compliance procedures. |
| Brand Loyalty & Network | Established customer trust and route reach. | Difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly. | Avianca served >100 destinations in Latin America. |
| Airport Slot Scarcity | Limited access to prime takeoff/landing times. | Hinders operational efficiency and accessibility. | Major airports operate at near-full capacity. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Avianca Holdings leverages a comprehensive blend of data, including Avianca's annual and quarterly reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate industry-specific data from aviation consulting firms and market intelligence platforms to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
