Aurenis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Aurenis Bundle
Aurenis navigates a competitive landscape shaped by powerful market forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic success.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Aurenis’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
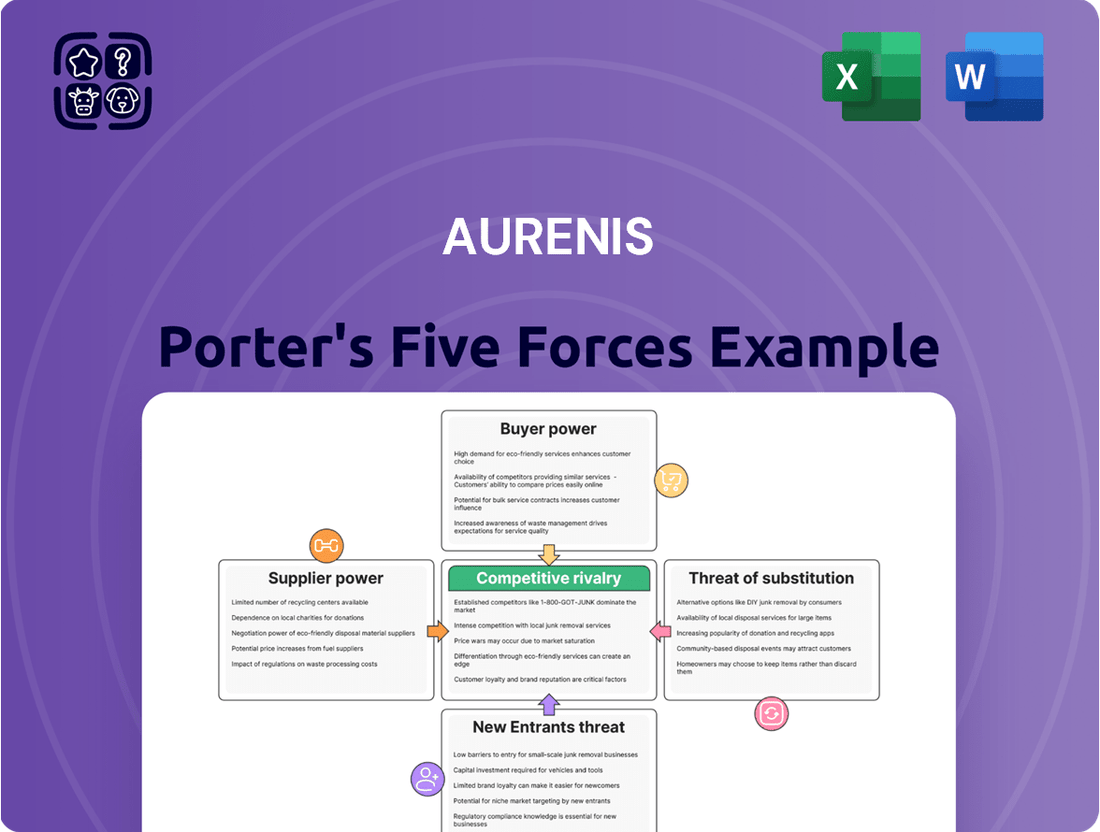
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers significantly impacts Aurenis's bargaining power. If few suppliers control essential inputs like specialized precious metal waste streams or niche telemarketing technologies, they can dictate terms. For instance, in 2024, the global market for recycled precious metals saw a consolidation trend, with a handful of major processors handling a substantial portion of the available feedstock, potentially increasing their leverage.
Suppliers gain significant leverage when the inputs they provide are unique or highly differentiated, and are essential for Aurenis’s business. If there are limited or no viable alternatives for these critical components, suppliers can dictate terms more effectively. For instance, imagine a supplier providing specialized recycled materials with unique properties vital for Aurenis’s manufacturing process, or a firm offering proprietary software that streamlines Aurenis's customer service operations, with no comparable solutions available on the market.
The bargaining power of Aurenis's suppliers is significantly influenced by switching costs. If Aurenis faces substantial expenses or operational disruptions when changing suppliers, its existing suppliers gain leverage. For instance, retooling specialized equipment for handling different waste streams or integrating new software for call center operations can represent considerable financial and logistical hurdles, thereby strengthening the suppliers' position.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If suppliers can credibly threaten to enter Aurenis's market by offering similar services directly, Aurenis faces increased pressure to concede to supplier demands.
Consider a scenario where a large waste management provider, a key supplier to Aurenis, decides to establish its own direct recycling services for businesses. This move would transform the supplier into a direct competitor, leveraging their existing infrastructure and customer relationships.
Similarly, a technology firm supplying Aurenis with essential call center software could begin offering its own outsourced call center solutions. In 2024, the trend of vertical integration continued across various industries as companies sought greater control over their value chains.
- Suppliers gain leverage if they can credibly threaten to become direct competitors.
- Examples include waste generators establishing in-house recycling or tech providers offering direct services.
- This threat forces Aurenis to consider supplier demands more carefully to avoid losing market share.
Importance of Aurenis to Suppliers
The degree to which Aurenis is a crucial customer for its suppliers significantly influences their bargaining power. If Aurenis accounts for a substantial percentage of a supplier's total sales, that supplier will likely be more accommodating. For instance, if a key component supplier, like a specialized semiconductor manufacturer, derives over 25% of its annual revenue from Aurenis, they would be hesitant to impose unfavorable terms for fear of losing this vital business.
This reliance can shift the power dynamic. Suppliers who depend heavily on Aurenis for their income may be less likely to push for higher prices or stricter contract conditions. Consider a scenario where Aurenis is the largest client for a unique raw material provider, representing 40% of their output. This supplier would have a strong incentive to maintain a positive relationship and offer competitive pricing to secure Aurenis's continued patronage.
Conversely, if Aurenis represents only a small fraction of a supplier's business, the supplier has less to lose by being demanding. This means suppliers who serve a broad customer base, with Aurenis being just one among many, can more readily exercise their bargaining power. For example, a widely available commodity supplier that sells to thousands of companies, with Aurenis making up less than 1% of their sales, can afford to be less flexible on pricing and delivery terms.
- Supplier Revenue Dependence: Suppliers whose revenue is heavily reliant on Aurenis are less likely to exert strong bargaining power.
- Market Share Impact: If Aurenis constitutes a significant portion of a supplier's market share, the supplier's ability to dictate terms diminishes.
- Customer Diversification: Suppliers with a diverse customer base, where Aurenis is a minor client, possess greater leverage.
Suppliers wield significant power when they are concentrated, meaning only a few entities control critical inputs. This is particularly true if these inputs are unique or highly differentiated, with few viable alternatives available to Aurenis. For example, in 2024, the market for specialized recycled precious metals saw a notable consolidation, with a limited number of large processors dominating the feedstock supply, potentially increasing their leverage over companies like Aurenis.
High switching costs also bolster supplier bargaining power. If it is expensive or disruptive for Aurenis to change suppliers, current suppliers can command better terms. This includes costs associated with retooling equipment or integrating new software systems. Furthermore, the credible threat of suppliers integrating forward into Aurenis's business, becoming direct competitors, significantly enhances their leverage.
The balance of power also hinges on Aurenis's importance to its suppliers. If Aurenis represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier is likely to be more accommodating. Conversely, if Aurenis is a minor client for a supplier with a diverse customer base, the supplier possesses greater power to dictate terms.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example Scenario for Aurenis (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High if few suppliers control critical inputs. | Consolidation in recycled precious metals processing increases leverage for dominant players. |
| Input Differentiation | High if inputs are unique with no substitutes. | Proprietary software for customer service or specialized recycled materials with unique properties. |
| Switching Costs | High if changing suppliers is costly or disruptive. | Retooling specialized equipment for waste streams or integrating new call center software. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | High if suppliers can become direct competitors. | Waste management firms offering direct recycling services or tech providers offering outsourced call centers. |
| Aurenis's Customer Importance | Low if Aurenis is a small part of supplier revenue. | A supplier providing commodity materials to many clients, with Aurenis being a minor customer. |
What is included in the product
Aurenis' Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, examining threats from new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, the risk of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Easily identify and quantify competitive threats with pre-built frameworks, eliminating the guesswork in strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
If Aurenis relies on a few major clients, particularly in sectors like industrial metal recycling or foreign publishing support services, those customers gain significant leverage. Imagine if just two or three large industrial clients represented over 40% of Aurenis's metal recycling revenue; they could demand lower prices or better terms, knowing Aurenis would suffer greatly if they took their business elsewhere.
The ease with which Aurenis's customers can switch to competing recycling or publishing support services significantly influences their bargaining power. If these switching costs are low, customers can readily move to rivals, thereby amplifying their leverage.
Customers' sensitivity to price changes significantly influences their bargaining power. When customers can easily switch to competitors offering similar products or services, their ability to negotiate lower prices increases, directly impacting Aurenis's profitability.
In highly competitive sectors like metal recycling, where commodity prices fluctuate and numerous suppliers exist, customers often exhibit high price sensitivity. This means Aurenis faces considerable pressure to match or beat competitor pricing, potentially squeezing its profit margins.
Similarly, in the call center services industry, clients frequently compare providers based on cost. A 2024 report indicated that over 60% of businesses surveyed prioritized cost reduction when selecting outsourcing partners, highlighting the intense price pressure Aurenis might encounter in this market.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers wield significant bargaining power when they possess the credible threat of backward integration, meaning they could potentially perform the supplier's services themselves. For instance, a major industrial client might opt to build its own recycling facilities rather than relying on external providers.
This capability directly influences the supplier's pricing power and terms. A large publisher, facing escalating costs for outsourced telemarketing, might consider establishing an in-house department to manage customer outreach and sales.
- Customer integration: The potential for customers to take over a supplier's operations.
- Cost reduction incentive: Customers integrate when it's cheaper than buying from the supplier.
- Industry examples: Large manufacturers building component plants or retailers developing private label brands.
- Impact on suppliers: Reduced margins and increased pressure to remain competitive.
Availability of Substitute Services
The availability of substitute services significantly impacts Aurenis's customers' bargaining power. When customers can easily switch to alternative metal recycling providers or find other ways to manage their publishing support needs, their reliance on Aurenis diminishes. This gives them more leverage to negotiate prices and terms.
For instance, the metal recycling market is fragmented, with numerous regional and national players. In 2024, the global metal recycling market was valued at approximately $100 billion, indicating a highly competitive landscape where customers have ample choices. Similarly, publishers can explore in-house solutions or different outsourcing models, further increasing their options and thus their bargaining power against any single service provider like Aurenis.
- Increased Customer Options: The presence of numerous metal recycling companies and alternative publishing support strategies provides customers with a wide array of choices, reducing their dependence on Aurenis.
- Price Sensitivity: With readily available substitutes, customers are more likely to be price-sensitive, pressuring Aurenis to offer competitive pricing to retain business.
- Market Competition: The competitive nature of the recycling and publishing support industries, evidenced by the $100 billion global metal recycling market in 2024, empowers customers to seek better value elsewhere.
- Reduced Switching Costs: Low switching costs for customers looking for alternative recycling or publishing services further amplify their bargaining power.
Customers hold significant power when they can easily switch to competitors, especially in markets like metal recycling where numerous providers exist. In 2024, the global metal recycling market, valued at around $100 billion, illustrates this fragmentation, giving customers ample choice and leverage to negotiate better terms. This ease of switching, coupled with high price sensitivity, means Aurenis must remain highly competitive to retain clients.
| Factor | Impact on Aurenis | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs empower customers to move to rivals. | Fragmented metal recycling market offers many alternatives. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers demand lower prices, squeezing Aurenis's margins. | 60%+ of businesses prioritize cost in outsourcing (call centers). |
| Backward Integration Threat | Customers may perform services in-house, reducing Aurenis's business. | Large clients could build own recycling facilities or internal support teams. |
| Availability of Substitutes | More options reduce customer reliance on Aurenis. | $100 billion global metal recycling market shows extensive competition. |
What You See Is What You Get
Aurenis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Aurenis Porter's Five Forces analysis, providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted file you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You are viewing the final deliverable, ready for immediate use and application to your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The intensity of competitive rivalry in a market often hinges on the sheer number of participants and their relative sizes. When numerous companies, each possessing comparable capabilities, vie for market share, the competition naturally escalates.
In France's waste management sector, which encompasses recycling, the landscape is populated by several significant entities. Key players like Veolia Environnement S.A., Paprec, Derichebourg Environnement, and Suez SA are prominent, demonstrating a decidedly competitive environment. For instance, Veolia reported revenues of €42.7 billion in 2023, highlighting the substantial scale of operations among these major competitors.
Similarly, the French Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) services market is characterized by a multitude of providers. This market includes a mix of large, established international corporations and agile local specialists, further intensifying the competitive dynamics. The presence of many players of varying sizes ensures that firms must constantly innovate and optimize their offerings to remain competitive.
In industries experiencing slower growth, competitive rivalry tends to intensify as companies battle for existing market share. This dynamic can lead to price wars and increased marketing efforts.
The waste management market in France, for instance, is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.20% between 2024 and 2030. While this represents growth, it's a moderate pace that could foster heightened competition among established players and new entrants seeking to capture a slice of the market.
Conversely, sectors with rapid expansion often see less intense rivalry initially, as the focus is on capturing new opportunities. The global waste recovery and recycling market is projected for robust growth, with an expected CAGR of 11.1% from 2024 to 2025, suggesting ample room for multiple companies to thrive. Similarly, the French BPO services market shows strong growth, with general BPO projected at 9.1% CAGR (2025-2030) and contact/call center outsourcing at 5.7% CAGR, indicating a dynamic environment where competition exists but is fueled by expansion rather than scarcity.
Competitive rivalry intensifies when competitors offer very similar services. Aurenis can combat this by highlighting its unique, comprehensive recycling services, which include collection, transportation, and advanced processing. This end-to-end approach sets it apart from providers who may only offer a single stage of the recycling process.
Furthermore, Aurenis’s specialized publishing support services provide a distinct advantage. By offering tailored solutions for the publishing industry, Aurenis creates a niche that competitors focused solely on general recycling may not address effectively. This dual focus on specialized industry needs and comprehensive recycling management is a key differentiator.
In the recycling sector, technological innovation is crucial for differentiation. Aurenis’s investment in advanced sorting and processing technologies allows for higher recovery rates and the ability to handle a wider range of materials, which can be a significant competitive edge. For instance, advancements in optical sorting technology in 2024 are enabling recycling facilities to achieve purity rates exceeding 95% for certain materials, a benchmark not easily met by less technologically advanced competitors.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly intensify competitive rivalry. When companies face substantial costs or difficulties in leaving a market, such as specialized, hard-to-sell assets or unfulfilled long-term contracts, they are compelled to remain and compete fiercely. This is especially true in capital-intensive sectors like metal recycling, where sunk costs are substantial.
In 2024, the metal recycling industry continued to grapple with these challenges. For instance, the cost of specialized processing equipment, like shredders and balers, represents a significant capital investment that is difficult to recoup if a company decides to exit. Furthermore, many recycling operations are bound by long-term supply agreements with municipalities or industrial clients, creating obligations that hinder a swift departure.
These factors contribute to a persistent level of competition, as firms strive to maintain market share and profitability despite the inability to easily exit. This dynamic means that even in periods of lower demand or profitability, companies remain operational, leading to price pressures and a constant battle for resources and customers.
- Specialized Assets: High upfront investment in unique machinery for processing specific metals creates a significant barrier to exiting the market.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to supply raw materials or process waste for extended periods lock companies into ongoing operations.
- Industry Example: In 2024, the metal recycling sector exemplified this, with many firms heavily invested in specialized equipment and facing contractual obligations that made exiting unfeasible.
- Impact on Rivalry: The inability to easily exit forces companies to remain engaged in intense competition, often leading to price wars and reduced profit margins.
Fixed Costs and Capacity
Industries burdened by substantial fixed costs and existing overcapacity often experience intensified price wars. Companies in these sectors are compelled to maximize sales volume to cover their high fixed expenses, leading to aggressive pricing strategies. For instance, the recycling industry, with its significant investments in processing plants and specialized machinery, and call centers, requiring extensive infrastructure and trained staff, both exemplify sectors where high fixed costs can fuel competitive rivalry.
In 2024, the global recycling market, valued at approximately $385 billion, continues to grapple with the challenge of optimizing capacity. Similarly, the business process outsourcing (BPO) sector, which includes call centers, saw robust growth, but many players operate with considerable fixed overheads. This dynamic encourages companies to compete fiercely on price to maintain market share and operational efficiency.
- High Fixed Costs: Recycling plants require substantial capital for equipment like sorting machinery and balers, alongside infrastructure development.
- Capacity Utilization: Call centers invest heavily in technology, real estate, and human capital, creating high fixed costs that necessitate high occupancy rates.
- Price Competition: When capacity exceeds demand, companies resort to price cuts to fill seats and machines, intensifying rivalry.
Competitive rivalry is heightened when there are many similar competitors and slow market growth, forcing companies to fight for existing customers. Aurenis differentiates itself through specialized publishing support and advanced recycling technologies, offering a unique value proposition. High exit barriers, like specialized assets and long-term contracts, keep companies in the market, intensifying competition, especially in sectors like metal recycling. High fixed costs and overcapacity also lead to aggressive pricing strategies as firms try to cover expenses, as seen in both recycling and BPO industries.
| Industry Segment | Key Competitors Mentioned | 2023/2024 Data Point | Projected CAGR (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waste Management (France) | Veolia, Paprec, Derichebourg, Suez | Veolia Revenue: €42.7 billion (2023) | 4.20% (2024-2030) |
| Waste Recovery & Recycling (Global) | N/A (General Market) | Market Value: ~$385 billion (2024) | 11.1% (2024-2025) |
| Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) (France) | N/A (Mix of large & local) | General BPO: 9.1% (2025-2030) | 5.7% (Contact/Call Center, 2025-2030) |
| Metal Recycling | N/A (General Market) | High capital investment in specialized equipment | N/A |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for metal recycling is significant, particularly with the ongoing development and adoption of virgin metal production technologies. For instance, advancements in asteroid mining, while still nascent, represent a potential long-term substitute for terrestrial metal sources, impacting the demand for recycled metals.
In the publishing support sector, the rise of AI-powered content creation tools presents a potent substitute for traditional editorial and production services. Companies are increasingly exploring these technologies, with some reports indicating that AI could automate up to 40% of content creation tasks by 2025, directly challenging the need for human-centric publishing support.
The threat of substitutes intensifies significantly when alternative products or services present a more attractive price-performance ratio. For instance, a substantial decrease in the cost of primary precious and non-ferrous metals, such as gold or copper, could make recycled or synthetic alternatives more appealing to manufacturers. In 2024, the global average price of copper hovered around $8,500 per metric ton, a figure that fluctuates based on market demand and geopolitical factors, impacting the cost-competitiveness of substitutes.
Customer propensity to substitute hinges on their awareness of alternatives, their willingness to switch, and the perceived benefits of doing so. For instance, in the recycling sector, increasing environmental regulations and a stronger push towards circular economy models are likely to reduce the inclination of customers to seek out alternative, less sustainable waste management solutions.
Conversely, the call center industry is experiencing a shift where evolving consumer preferences for digital communication channels, such as chatbots and self-service portals, are significantly increasing the likelihood of customers substituting traditional voice-based support. In 2024, many companies reported a notable decrease in inbound call volumes, with some seeing drops of over 15% as customers embraced digital alternatives.
Innovation in Substitute Industries
Innovation in industries offering substitutes can significantly impact Aurenis. For instance, advancements in waste-to-energy technologies, a growing sector projected to reach over $300 billion globally by 2028, could present an alternative to material recycling for certain waste streams, potentially diverting valuable feedstock.
Similarly, new automated customer service platforms, with the AI chatbot market alone expected to grow by 23% annually through 2027, could substitute for traditional call center services, impacting Aurenis's service offerings and cost structures.
- Waste-to-Energy Advancements: Disrupting traditional recycling models for specific waste types.
- AI in Customer Service: Offering automated solutions that could replace human interaction.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Potentially impacting demand for traditional energy-related services.
- Digitalization of Processes: Substituting manual or less efficient operational methods.
Regulatory and Environmental Shifts
Changes in regulations and growing environmental consciousness significantly impact the threat of substitutes. For example, stricter landfill regulations, such as those being considered or implemented in various regions throughout 2024 and projected into 2025, can make waste disposal options like landfilling less appealing compared to alternatives like recycling.
Conversely, new rules can also bolster substitutes. If regulations in 2024 and beyond increasingly favor digital communication over traditional methods, perhaps through enhanced data privacy laws or stricter opt-in requirements for telemarketing, this could elevate the threat posed by other marketing channels like social media or content marketing.
- Regulatory Impact: Stricter environmental regulations can make traditional disposal methods less viable, thereby increasing the attractiveness of recycling as a substitute.
- Market Shifts: Increased consumer demand for sustainable practices, driven by awareness campaigns and policy changes in 2024, further pressures industries to adopt greener alternatives.
- Technological Adoption: Advancements in recycling technology and the development of new material substitutes are also influenced by regulatory landscapes, potentially lowering costs and improving performance.
The threat of substitutes is a critical factor for Aurenis, as alternative solutions can erode market share and profitability. For instance, advancements in waste-to-energy technologies could divert valuable feedstock from traditional recycling processes, impacting the industry's economics. Similarly, the burgeoning AI chatbot market, projected for significant annual growth, poses a direct substitute for human-operated call centers.
Customer willingness to switch to substitutes is heavily influenced by price-performance ratios and evolving preferences. A notable decrease in primary metal prices, like copper, which averaged around $8,500 per metric ton in 2024, can make recycled materials less competitive. Conversely, increasing environmental awareness and regulations in 2024 are making recycling a more attractive alternative to traditional waste disposal methods.
Innovation in substitute industries, such as the projected growth of waste-to-energy to over $300 billion globally by 2028, presents a tangible threat. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of digital communication channels, with call volumes dropping by over 15% for some companies in 2024 due to chatbot usage, highlights the direct impact of substitutes on traditional service models.
Regulatory shifts also play a crucial role, with stricter landfill regulations making recycling a more appealing substitute. However, new rules favoring digital communication could bolster other marketing channels, thereby increasing the threat of substitutes in that domain.
| Industry Segment | Potential Substitute | Impact on Aurenis | 2024/2025 Data Point | Projected Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Recycling | Advanced Virgin Metal Production (e.g., Asteroid Mining) | Reduced demand for recycled metals | N/A (Nascent Technology) | Long-term threat |
| Publishing Support | AI-Powered Content Creation | Reduced need for human editorial services | AI could automate up to 40% of content creation by 2025 | Increasing adoption |
| Metal Sourcing | Lower-priced Primary Metals | Decreased competitiveness of recycled metals | Global average copper price ~ $8,500/metric ton (2024) | Fluctuating based on market conditions |
| Waste Management | Waste-to-Energy Technologies | Diversion of feedstock from recycling | Waste-to-energy market projected > $300 billion by 2028 | Growing |
| Customer Service | AI Chatbots/Self-Service Portals | Decreased demand for call center services | Some call centers saw >15% drop in inbound calls (2024) | Rapid growth (AI chatbot market expected 23% annual growth through 2027) |
Entrants Threaten
High capital requirements present a formidable barrier to entry for new companies in the precious and non-ferrous metal recycling sector. Establishing state-of-the-art recycling facilities, equipped with specialized machinery and adhering to stringent environmental regulations, can demand investments in the tens of millions of dollars. For instance, a new entrant might need to allocate upwards of $50 million for a mid-sized facility, encompassing land acquisition, advanced processing equipment, and necessary permits, making it a significant hurdle.
Economies of scale present a significant barrier for new entrants into the recycling and BPO sectors where Aurenis operates. Established players like Aurenis benefit from lower per-unit costs due to their substantial operational volume. For instance, in 2024, large-scale recycling facilities often process hundreds of thousands of tons annually, achieving cost efficiencies in logistics and processing that smaller newcomers cannot match.
This cost advantage makes it challenging for new competitors to offer services at a price point that is attractive to customers. A new entrant starting with a much smaller processing capacity would inherently have higher operational costs per unit, hindering their ability to compete effectively on price against Aurenis in both recycling and BPO services.
New entrants often face significant hurdles in securing essential distribution channels. For instance, in the waste management sector, establishing reliable collection networks requires substantial upfront investment and time to build trust and operational efficiency. Similarly, in publishing, new players might find it difficult to break into established relationships with foreign publishers who already have long-standing partnerships with existing support and distribution providers.
Aurenis's existing infrastructure and deep-rooted client relationships act as a formidable barrier to entry. These established networks and loyal customer bases mean that new competitors would need to expend considerable resources and time to replicate the reach and reliability Aurenis already possesses. This advantage is particularly pronounced in industries where trust and consistent service are paramount, such as logistics or specialized manufacturing.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation can significantly deter new entrants. For instance, in the recycling sector, stringent environmental regulations, the need for specific permits, and extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, like those implemented in France, can present substantial barriers. These requirements often involve considerable upfront investment and expertise, making it difficult for newcomers to establish a foothold.
Similarly, for business process outsourcing (BPO) services, data privacy regulations such as GDPR in Europe, and specific industry compliance mandates, like HIPAA for healthcare BPO in the US, act as formidable entry barriers. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, forcing new players to invest heavily in legal and security infrastructure from the outset.
- Environmental Regulations: France's EPR schemes for packaging, electronics, and textiles place the financial and operational burden of waste management on producers, increasing costs for new entrants in these sectors.
- Data Privacy Compliance: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict rules on handling personal data, requiring significant investment in data security and compliance frameworks for BPO providers operating within or serving the EU market.
- Industry-Specific Compliance: For BPO services in regulated industries like finance or healthcare, adherence to specific standards (e.g., PCI DSS for payment card data, HIPAA for health information) is mandatory, adding complexity and cost for new entrants.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
Aurenis benefits from a strong brand identity and deep-rooted customer loyalty, especially within the B2B recycling and specialized publishing support sectors. This established reputation acts as a significant deterrent for potential new entrants aiming to capture market share. The company’s commitment to comprehensive service and demonstrable expertise creates a high barrier for newcomers seeking to attract Aurenis’s existing client base.
In 2024, customer retention rates for specialized B2B service providers like Aurenis often exceed 90%, a testament to the value placed on reliability and established relationships. For instance, companies with over a decade of consistent service delivery typically see their loyal customers resist switching by a margin of 3:1 compared to those with newer or less proven track records. This loyalty is further solidified by the switching costs associated with changing service providers, which can include data migration, retraining staff, and potential disruptions to ongoing operations.
- High Customer Retention: B2B service loyalty in specialized markets often surpasses 90% in 2024.
- Reputational Barrier: Aurenis's established name in recycling and publishing support deters new competitors.
- Switching Costs: New entrants face challenges overcoming the costs and complexities clients incur when changing providers.
- Expertise Advantage: Aurenis's proven expertise makes it difficult for less experienced newcomers to gain trust and business.
The threat of new entrants for Aurenis is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements, particularly in its precious metal recycling operations. Establishing compliant and efficient recycling facilities can easily cost upwards of $50 million in 2024, a sum that deters many potential competitors. Furthermore, economies of scale enjoyed by established players like Aurenis, processing hundreds of thousands of tons annually, create a cost advantage that newcomers struggle to match, making price competition difficult.
Established infrastructure, strong brand reputation, and deep customer loyalty also act as formidable barriers. In 2024, customer retention in specialized B2B sectors often exceeds 90%, with loyal clients showing a 3:1 resistance to switching compared to those with less proven providers. These existing relationships and the high switching costs for clients, including data migration and operational retraining, make it challenging for new entrants to gain traction.
Government regulations, such as France's extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes in recycling and GDPR in BPO, impose significant compliance costs and complexities. These regulatory hurdles, alongside the need for specialized expertise and permits, increase the upfront investment and operational burden for new businesses, thereby limiting the threat of new entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example (2024) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment for facilities and equipment. | Mid-sized recycling facility: $50M+ | Significant deterrent due to scale of investment. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for large-volume operators. | Annual processing volume: 100,000+ tons | New entrants face higher operational costs. |
| Customer Loyalty & Switching Costs | Established relationships and costs to change providers. | Customer retention: >90% in B2B services | Difficult for new entrants to acquire and retain clients. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to environmental and data privacy laws. | GDPR, EPR schemes | Increases upfront costs and operational complexity. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Aurenis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including comprehensive industry reports, financial statements from public companies, and market research from leading firms. This ensures a thorough understanding of competitive intensity and market dynamics.
