Asure Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Asure Bundle
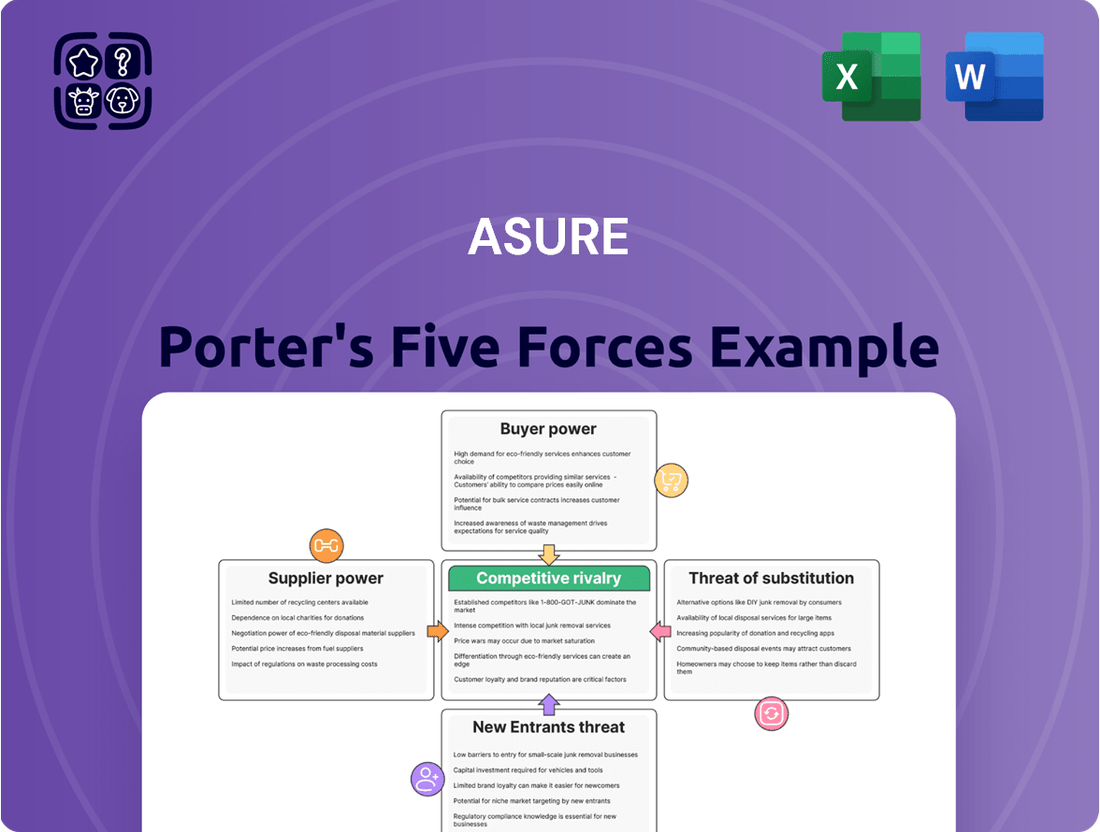
Asure's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Asure’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration in the Human Capital Management (HCM) software market generally indicates a fragmented landscape. This means Asure likely sources components and services from a wide array of providers, diluting the power of any single supplier. For instance, as of early 2024, the HCM software market is characterized by numerous vendors, with the top players holding only single-digit market shares, underscoring this fragmentation.
However, certain specialized technology providers, particularly those offering advanced AI capabilities or niche compliance solutions, may wield more influence. These specialized suppliers, crucial for differentiating Asure's offerings, could command higher prices or more favorable terms due to their unique expertise and limited alternatives.
Furthermore, Asure's reliance on major cloud infrastructure providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), presents a different dynamic. AWS, a critical backbone for many cloud-based HCM solutions, holds significant bargaining power due to its essential role and market dominance in cloud computing services. This dependence means Asure, like many SaaS companies, is subject to AWS's pricing and service level agreements.
Asure's reliance on deeply integrated core technology components, potentially tied to specific vendor APIs or proprietary systems, could create significant switching costs. This integration means that if a supplier were to increase prices or reduce service quality, Asure might face substantial expense and operational disruption to change providers.
Conversely, if Asure utilizes more generic infrastructure or widely adopted open-source components, the ability for suppliers to exert power through high switching costs would be diminished. This flexibility allows for easier transitions if better terms or technologies become available from alternative sources.
The strategic partnership with Amazon Web Services (AWS) highlights a dependency on a major cloud provider. Should Asure decide to migrate its operations to a different cloud platform, the associated costs and complexities of data transfer, re-architecting applications, and retraining staff could be substantial, thereby increasing AWS's bargaining power.
Suppliers providing highly specialized AI capabilities, advanced security features, or niche compliance updates that are difficult for Asure to replicate can wield considerable bargaining power. For instance, if a key AI algorithm provider for Asure's HR compliance services experiences a surge in demand for its unique technology, it could command higher prices or more favorable terms.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Asure's business is generally low for software component providers. They would need to build entire Human Capital Management (HCM) platforms and create their own sales networks to directly challenge Asure. This is a significant barrier to entry.
However, major cloud infrastructure providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, represent a potential, albeit theoretical, threat. These companies could expand their service offerings to encompass more aspects of HCM, potentially competing with certain Asure functionalities. For instance, in 2024, cloud infrastructure spending continued to grow significantly, with AWS and Microsoft Azure holding substantial market shares, indicating their capacity for expansion into adjacent service areas.
- Low Threat from Software Component Suppliers: Developing full HCM platforms and sales channels is a substantial undertaking, making direct competition unlikely for most.
- Potential Threat from Cloud Giants: Large cloud providers have the resources and market presence to theoretically expand into competing HCM services.
- Market Dynamics: The continued growth in cloud infrastructure spending in 2024 highlights the financial capacity of major players to diversify their offerings.
Importance of Asure to Suppliers
Asure's prominent standing as a leading provider of Human Capital Management (HCM) solutions for small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) positions it as a key client for many of its suppliers. This substantial customer base means Asure can wield considerable influence in its dealings with suppliers, particularly if it accounts for a significant percentage of their overall sales. For instance, if a supplier's business is heavily reliant on Asure's orders, Asure's bargaining power increases, potentially leading to more favorable terms and pricing.
The company's scale within the SMB HCM sector translates into considerable purchasing power. This leverage allows Asure to negotiate better pricing, service level agreements, and other terms with its suppliers. By consolidating its procurement or demonstrating the value of its partnership, Asure can effectively reduce the supplier's incentive to charge premium rates or offer less competitive service. For example, in 2023, Asure reported revenue of $337.7 million, indicating a substantial volume of business that suppliers would want to secure.
- Asure's market leadership in SMB HCM makes it a crucial client for its suppliers.
- Significant revenue contribution from Asure grants it leverage in supplier negotiations.
- The company's substantial purchasing volume can secure more favorable terms and pricing.
- Asure's $337.7 million in 2023 revenue underscores its importance to its supply chain partners.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Asure is generally moderate, influenced by market fragmentation and the specialized nature of certain inputs. While many component providers operate in a fragmented market, limiting their individual power, those offering unique AI or compliance solutions can command higher prices.
Asure's significant revenue, such as its $337.7 million in 2023, positions it as a key client for many suppliers, enhancing its negotiation leverage. However, reliance on dominant cloud providers like AWS introduces a counterbalancing force, as these platforms are critical and offer limited alternatives for many cloud-based operations.
| Factor | Asure's Position | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Generally fragmented, with some specialized providers | Low for most, moderate for specialized tech |
| Importance of Supplier to Asure | High for critical tech, moderate for generic components | High for specialized inputs, low for commoditized ones |
| Asure's Purchasing Power | High due to significant revenue ($337.7M in 2023) | Lowers supplier leverage |
| Switching Costs for Asure | Can be high for integrated systems | Increases supplier leverage |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low from software vendors, theoretical from cloud providers | Low from most, potential from cloud giants |
What is included in the product
Asure's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive landscape by examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry, providing a strategic roadmap for Asure's market positioning.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual, easy-to-understand breakdown of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Asure's customer base is largely comprised of small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs). This fragmentation means that no single customer typically accounts for a substantial portion of Asure's overall revenue, which inherently limits the bargaining power of any individual client. For instance, as of early 2024, Asure reported serving tens of thousands of clients, underscoring the dispersed nature of its customer relationships.
Switching Human Capital Management (HCM) software providers presents significant hurdles for Asure's clients. These challenges include the complex process of data migration, the necessity of retraining staff on new systems, and the inherent risk of disrupting crucial HR and payroll operations. These factors contribute to moderately high switching costs.
This customer "stickiness," a common characteristic of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models, plays a vital role in reinforcing Asure's competitive standing. For instance, in 2024, businesses often face lengthy implementation cycles for new HCM systems, sometimes extending over six months, further increasing the perceived cost and effort of a switch.
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) often exhibit a notable sensitivity to pricing, particularly within the crowded Human Capital Management (HCM) software sector. Many SMBs operate on tighter budgets and actively seek cost-effective solutions.
However, the inherent value proposition of HCM software, which includes streamlining HR processes and ensuring regulatory compliance, can significantly offset this price sensitivity. For instance, by automating payroll and benefits administration, businesses can reduce administrative overhead, potentially saving thousands annually.
In 2024, the average SMB spent approximately $1,500 to $5,000 per year on HCM software, with pricing often scaling based on employee count and feature sets. Despite this, the demonstrable ROI through efficiency gains and reduced compliance risks makes many SMBs willing to invest in robust solutions.
Customer Information Availability
Customers today have unprecedented access to information about Human Capital Management (HCM) solutions. This readily available data, sourced from online reviews, specialized comparison websites, and in-depth industry reports, significantly boosts their bargaining power. For instance, by mid-2024, platforms like G2 and Capterra hosted millions of user reviews, providing detailed insights into vendor performance and product features.
This increased transparency empowers customers to conduct thorough comparisons of various HCM offerings. They can readily assess features, compare pricing structures, and evaluate customer service quality across different providers. This ability to benchmark solutions means vendors face greater pressure to offer competitive pricing and superior service to win and retain business.
- Increased Information Access: Customers can easily find detailed reviews and comparisons of HCM solutions online.
- Enhanced Benchmarking: Buyers can effectively compare features, pricing, and support across multiple vendors.
- Price Sensitivity: Greater information availability often leads to more price-sensitive purchasing decisions by customers.
- Vendor Accountability: Vendors are held more accountable for their product quality and customer service due to public feedback.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, particularly for Human Capital Management (HCM) software providers, is generally low. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are unlikely to possess the resources or expertise to develop their own complex HCM software solutions. The significant investment in research and development, coupled with the ongoing need for maintenance and updates, makes this an impractical endeavor for most.
Consider the substantial costs involved. Developing a robust HCM system can easily run into millions of dollars, a prohibitive expense for the average SMB. For instance, a custom-built HRIS platform could require over $100,000 in initial development alone, not to mention the continuous expenditure on software engineers, cloud infrastructure, and security. This financial barrier significantly mitigates the threat of customers integrating backward.
Furthermore, the technical complexity of modern HCM software, which often includes features like payroll processing, benefits administration, talent management, and advanced analytics, demands specialized skill sets.
- Low Likelihood for SMBs: It is highly improbable for small and medium-sized businesses to develop their own sophisticated HCM software.
- High Development Costs: The financial outlay for creating and maintaining such systems is prohibitive for most customers.
- Technical Complexity: The intricate nature of HCM functionalities requires specialized expertise that SMBs typically lack.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Businesses generally prefer to outsource non-core functions like software development to focus on their primary operations.
Asure's customer base, primarily small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), limits individual customer bargaining power due to its dispersed nature. With tens of thousands of clients served as of early 2024, no single entity represents a significant revenue share, thereby reducing the leverage any one customer holds.
Switching HCM providers is challenging for Asure's clients, involving complex data migration, staff retraining, and the risk of operational disruption, leading to moderately high switching costs. This customer stickiness, common in SaaS, is reinforced by lengthy implementation cycles, often exceeding six months in 2024, further deterring clients from switching.
While SMBs can be price-sensitive, often spending $1,500-$5,000 annually on HCM software in 2024, the value proposition of streamlining HR and ensuring compliance justifies the investment. The demonstrable return on investment (ROI) through efficiency gains and reduced compliance risks makes many SMBs willing to pay for robust HCM solutions.
The threat of backward integration by customers is low because SMBs lack the resources and expertise to develop their own HCM software. The substantial costs, easily running into millions of dollars and requiring specialized skills, make this an impractical endeavor for most businesses, which prefer to focus on their core competencies.
What You See Is What You Get
Asure Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The preview you see is the exact Asure Porter's Five Forces Analysis document you'll receive immediately after purchase. This comprehensive report details the competitive landscape, including threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitute products, and intensity of rivalry within the industry. You can trust that what you preview is precisely what you'll download, fully formatted and ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The human capital management (HCM) software market, especially for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), is quite crowded. You'll find a wide array of companies competing, from giants like ADP and Workday to many smaller, niche players.
This sheer number of competitors, coupled with their varying sizes, means there's a constant push and pull. It often leads to pressure on pricing as companies try to win over customers, and it also fuels a rapid pace of innovation as everyone tries to stand out.
For instance, in 2024, the HCM market is projected to reach over $30 billion globally, showcasing the significant demand but also the intense battle for market share among hundreds of vendors.
The global Human Capital Management (HCM) software market is a dynamic space, and its impressive growth rate is a key factor influencing competitive rivalry. Projections show this market expanding significantly, with expectations of continued robust expansion through 2029 and beyond. This upward trend, especially within the small and medium-sized business (SMB) segment, can actually temper some of the intense competition by creating ample room for various providers to thrive.
Asure stands out by offering a robust, cloud-based Human Capital Management (HCM) platform. This suite integrates payroll, HR management, time and attendance, and benefits administration, specifically designed to simplify complex HR tasks and ensure compliance for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs).
A key element of Asure's differentiation is its strategic integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology. This AI capability enhances the platform's efficiency and provides advanced insights, setting it apart from competitors who may offer more basic HR solutions.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for customers in the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) sector can be a significant factor in competitive rivalry. These costs often arise from the complexities of data migration, the need for employee retraining on new platforms, and the potential disruption to ongoing business operations. For instance, a company heavily reliant on a specific CRM system might face substantial expenses and time investment to move its customer data and re-educate its sales team on a competitor's offering.
Despite these inherent switching barriers, the dynamic nature of the SaaS market compels providers to constantly prove their worth. Continuous innovation and the delivery of superior value are paramount for client retention. Many SaaS agreements are structured as long-term contracts, which inherently increases customer stickiness, making it more challenging for competitors to lure away established client bases without offering a compelling advantage.
- High Switching Costs: Data migration and retraining are key drivers of customer inertia, often representing significant financial and operational hurdles for businesses looking to change providers.
- Value Demonstration: Providers must continuously showcase enhanced features, better performance, or cost savings to justify their pricing and prevent customer churn.
- Contractual Lock-in: Long-term SaaS contracts, common in the industry, create a natural barrier to switching, contributing to customer retention for incumbent providers.
- Market Pressure: Despite high switching costs, intense competition forces providers to remain competitive, as customers can still be attracted by demonstrably better offerings.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can really make the competition tougher. Think about it: if it's really hard or expensive to leave a market, companies tend to stick around, even if things aren't great. This means more players fighting for the same customers, which can drive down prices and profits.
In the Software as a Service (SaaS) sector, these barriers are often quite significant. Companies invest heavily in building their platforms, and once that's done, those costs are pretty much sunk. Plus, acquiring customers in SaaS can be a long and costly process, creating another reason why businesses are hesitant to just pack up and go.
Consider the sheer investment in proprietary technology and the ongoing costs of maintaining and updating complex systems. These are major fixed assets that are difficult to repurpose or sell off easily. For instance, many SaaS providers in 2024 continue to pour billions into cloud infrastructure and specialized AI development, making a clean exit a daunting prospect.
- Sunk Costs: In 2024, the average cost for a company to develop a robust SaaS platform can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, representing a significant barrier to exit.
- Specialized Technology: Many SaaS solutions rely on unique, proprietary algorithms and infrastructure that have little to no resale value outside of the specific business context.
- Long-Term Contracts: Customer contracts, often spanning multiple years, create an obligation that makes abrupt market departure financially punitive and operationally complex.
- Brand Reputation: Companies invest years in building trust and brand loyalty; exiting abruptly can damage this reputation, impacting future ventures.
The competitive rivalry within the HCM software market is intense, driven by a large number of providers, including established players and emerging niche companies. This crowded landscape often leads to price competition and a continuous drive for innovation as vendors strive to differentiate themselves.
The significant global HCM market size, projected to exceed $30 billion in 2024, attracts numerous competitors. While this growth offers opportunities, it also intensifies the battle for market share, pushing companies to offer compelling value propositions and advanced features.
Switching costs in the SaaS HCM sector are a considerable factor, with data migration, retraining, and potential operational disruptions acting as deterrents. However, despite these barriers, the need to retain customers forces providers to constantly innovate and demonstrate superior value.
High exit barriers, such as substantial sunk costs in technology development and long-term customer contracts, contribute to sustained competition. Companies are hesitant to leave the market due to the difficulty in recouping investments and the potential damage to brand reputation.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Asure's comprehensive Human Capital Management (HCM) software is moderate. While many businesses still rely on manual processes, in-house developed systems, or a patchwork of different software for various HR functions, these alternatives often fall short in terms of integration and overall efficiency compared to a unified platform like Asure's.
For instance, a significant portion of small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) in 2024 might still be using spreadsheets for payroll and employee data management, a clear substitute that Asure aims to replace. However, the increasing complexity of compliance regulations and the demand for streamlined employee experiences are pushing more companies towards integrated solutions.
The cost and effort required to integrate multiple disparate software solutions can also make them less attractive substitutes than a single, comprehensive HCM platform. This is especially true as Asure continues to enhance its offerings, making the value proposition of a unified system increasingly compelling for businesses looking to optimize their HR operations.
While manual processes or basic spreadsheets might seem cheaper upfront, they present a significant performance deficit. These alternatives severely lag in efficiency, accuracy, and compliance, especially as businesses grow. For instance, a small business with just 10 employees might manage payroll manually, but scaling this to 50 employees in 2024 would likely introduce errors and consume excessive time, costing more in lost productivity than a dedicated solution.
The increasing complexity of HR and payroll for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) makes these manual or spreadsheet-based methods increasingly less viable. In 2024, regulatory changes and the need for robust data security mean that companies relying on outdated systems face higher risks of penalties and data breaches. Asure's integrated HCM solution offers a stark contrast, providing automated compliance and enhanced security, which are critical for long-term operational health.
The tendency for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) to switch to alternative solutions is diminishing. This shift is driven by a growing understanding of the advantages offered by integrated Human Capital Management (HCM) systems, particularly as regulatory landscapes become more intricate and the demand for data-backed HR decisions intensifies. For instance, in 2024, 65% of SMBs reported that the complexity of compliance was a primary driver for adopting more robust HR technology, up from 52% in 2022.
While larger SMBs are increasingly consolidating their HR functions into comprehensive platforms, smaller businesses may still lean towards more basic, less integrated tools to manage their workforce. This segment, representing roughly 20% of the SMB market, often prioritizes cost-effectiveness and simplicity over advanced features. However, even within this group, there's a noticeable trend towards cloud-based payroll and benefits administration services, which offer a degree of integration without the full commitment of an all-encompassing HCM suite.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements, particularly in artificial intelligence and automation, are a significant driver in the emergence of new substitutes. These innovations can create highly specialized, AI-driven point solutions capable of performing specific HR tasks with exceptional efficiency. For instance, AI-powered recruitment platforms can automate candidate sourcing and initial screening, potentially reducing the reliance on traditional HR software for these functions.
While these advanced substitutes offer enhanced capabilities, their integration into existing broader HR systems often remains a necessity. This means that while they can substitute for certain functions, they may not entirely replace the need for comprehensive HR management solutions. For example, an AI chatbot handling employee queries might be a substitute for a human HR representative for routine questions, but it still needs to integrate with the company's core HRIS for accurate information retrieval.
The threat posed by these evolving substitutes is amplified by their potential to disrupt established market dynamics. Consider the rapid development in AI-powered payroll processing, which can offer greater accuracy and speed compared to manual or less sophisticated systems. Companies are increasingly evaluating these advanced solutions, with the global HR tech market projected to reach over $38 billion by 2027, indicating a strong appetite for innovative HR tools.
- AI-driven recruitment platforms can automate candidate sourcing and initial screening.
- AI chatbots can handle routine employee queries, substituting for human HR representatives.
- The global HR tech market is expected to exceed $38 billion by 2027, highlighting the growth of substitute technologies.
- Integration with existing HR systems remains a key factor for the adoption of these advanced substitutes.
Switching Costs to Substitutes
Switching from a comprehensive Human Capital Management (HCM) platform like Asure to less integrated solutions or manual processes would incur substantial switching costs. These costs stem from the operational disruption, loss of efficiency, and heightened risk of non-compliance that accompany such a transition. For instance, migrating data, retraining staff on new, fragmented systems, and potentially re-establishing workflows represent significant investments of time and resources.
The integration and automation provided by a unified HCM platform like Asure are difficult and costly to replicate with disparate tools. Businesses that have invested in Asure's capabilities, such as streamlined payroll processing, benefits administration, and HR compliance management, would face considerable expenses in rebuilding these functionalities. This includes the cost of acquiring new software, implementing it, and ensuring data integrity across multiple systems.
The threat of substitutes is therefore mitigated by the high switching costs associated with leaving a robust HCM solution. Consider that in 2024, companies are increasingly prioritizing efficiency and compliance. A study by Gartner in late 2023 indicated that over 60% of organizations are looking to consolidate their HR technology stack, highlighting a trend away from fragmented solutions and towards integrated platforms like Asure, further solidifying the barrier to substitutes.
- Operational Disruption: Transitioning away from an integrated HCM platform necessitates significant changes to daily HR operations, impacting payroll, onboarding, and employee record management.
- Loss of Efficiency: Manual processes or basic software cannot match the automation and workflow efficiencies offered by comprehensive HCM systems, leading to increased labor costs and slower processing times.
- Increased Compliance Risk: Integrated HCM platforms often include built-in compliance features and updates, reducing the risk of penalties. Moving to substitutes can expose businesses to greater regulatory risks.
- Data Migration and Integration Costs: The expense and complexity of moving data from a centralized HCM system to multiple, less compatible platforms represent a substantial financial barrier.
The threat of substitutes for Asure's HCM solutions is currently moderate, largely due to the significant switching costs involved in moving away from an integrated platform. These costs encompass operational disruption, potential loss of efficiency, and increased compliance risks. For instance, in 2024, companies are increasingly focused on streamlining operations, making the disruption of switching from a consolidated system like Asure particularly unappealing.
Replicating the integration and automation Asure provides with disparate tools is both complex and expensive. Businesses utilizing Asure's payroll, benefits, and compliance management features would face substantial expenses to rebuild these functionalities. This includes software acquisition, implementation, and ensuring data integrity across multiple, less compatible systems.
The high switching costs associated with leaving robust HCM solutions like Asure's effectively mitigate the threat of substitutes. A late 2023 Gartner report indicated that over 60% of organizations aim to consolidate their HR technology, underscoring a move away from fragmented solutions and towards integrated platforms, thereby strengthening the barrier against substitutes.
The difficulty and expense of replicating Asure's integrated functionalities with separate tools are considerable. Companies that have invested in Asure's capabilities, such as streamlined payroll, benefits administration, and HR compliance, would incur significant costs to rebuild these functions. This involves acquiring new software, implementing it, and ensuring data integrity across various systems.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the Human Capital Management (HCM) software market, particularly with advanced cloud-based solutions, demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development for robust software, secure cloud infrastructure, and extensive sales and marketing efforts to gain traction. For instance, building a competitive SaaS HCM platform can easily require tens of millions of dollars in initial investment.
New entrants often struggle to secure reliable distribution channels, a critical hurdle in reaching customers. Established companies, like Asure, have already built strong relationships with suppliers and retailers, making it difficult for newcomers to gain access. In 2024, many industries saw continued consolidation of distribution networks, further limiting opportunities for new players.
Asure benefits significantly from its established sales channels and the trust it has cultivated with its small and medium-sized business (SMB) clientele. This existing infrastructure and brand recognition provide a substantial barrier to entry for potential competitors seeking to replicate its market presence.
Asure benefits from strong brand loyalty and significant customer switching costs in the human capital management (HCM) sector. Existing relationships with clients and the inherent difficulties in migrating data and retraining staff on new systems create a substantial hurdle for potential new competitors. This stickiness is further reinforced by Asure's recurring revenue model, which ensures consistent income streams and deepens integration with client operations.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Established players like Asure leverage significant economies of scale, which can be a major barrier for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, Asure’s operational efficiency, driven by its large customer base, likely translated into lower per-unit costs for service delivery and technology development compared to a startup. This scale allows for more competitive pricing and the ability to invest heavily in product innovation and marketing, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction without substantial upfront capital.
Economies of scope also play a role, enabling Asure to offer a wider range of integrated services, such as payroll, HR, and benefits administration, at a lower combined cost than if a new entrant tried to build each service independently. This bundled offering creates a more compelling value proposition for customers. By 2024, many businesses sought consolidated solutions, a trend that favors established providers with broad service portfolios.
- Economies of Scale: Asure's large operational footprint in 2024 likely allowed for substantial cost reductions per customer in areas like software development, data center operations, and customer service, creating a pricing advantage.
- Economies of Scope: The integration of payroll, HR, and benefits services by Asure in 2024 offered a cost-effective, one-stop solution, a difficult and expensive proposition for new, specialized entrants to replicate.
- Capital Investment: New entrants would need to invest heavily to match Asure's existing infrastructure, technology, and brand recognition, a significant hurdle in the competitive landscape of 2024.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Expertise
The Human Capital Management (HCM) sector faces significant threats from new entrants, largely due to the intricate web of regulations surrounding payroll and tax compliance. New companies entering this space must invest heavily in understanding and adhering to these complex legal frameworks, a task that requires specialized expertise and substantial resources. This regulatory burden acts as a formidable barrier, deterring many potential competitors.
Asure's strategic advantage lies in its deep-rooted commitment to compliance. The company has built a robust infrastructure and cultivated extensive knowledge to manage these intricate requirements effectively. This focus on navigating the regulatory landscape is a core strength that differentiates Asure and solidifies its position against emerging players who may struggle with these initial hurdles.
- Regulatory Complexity: The HCM industry is subject to extensive and evolving regulations, especially concerning payroll processing, tax filings, and labor laws.
- Compliance Expertise: New entrants need to develop significant in-house expertise or acquire specialized knowledge to ensure accurate and timely compliance, a costly and time-consuming endeavor.
- Barrier to Entry: The need for deep understanding and continuous adaptation to regulatory changes creates a substantial barrier, limiting the number of viable new competitors.
- Asure's Strength: Asure's established focus on and investment in compliance provides a competitive moat, making it difficult for new, less experienced companies to challenge its market position.
The threat of new entrants in the HCM market is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements for technology development and infrastructure. Established players like Asure benefit from significant economies of scale and scope, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price or breadth of services. Furthermore, strong brand loyalty and customer switching costs, coupled with the complexity of regulatory compliance, create substantial barriers to entry.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Asure's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High (R&D, Cloud Infrastructure, Sales & Marketing) | Established infrastructure and brand recognition |
| Distribution Channels | Challenging to secure access to customers | Strong existing relationships and SMB clientele |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Difficult to overcome customer inertia | Recurring revenue model and deep integration |
| Economies of Scale/Scope | Higher per-unit costs, limited service bundles | Lower operating costs, integrated service offerings |
| Regulatory Complexity | Requires significant expertise and resources for compliance | Robust compliance infrastructure and knowledge |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and expert analyst opinions to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
