Astrana Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Astrana Health Bundle
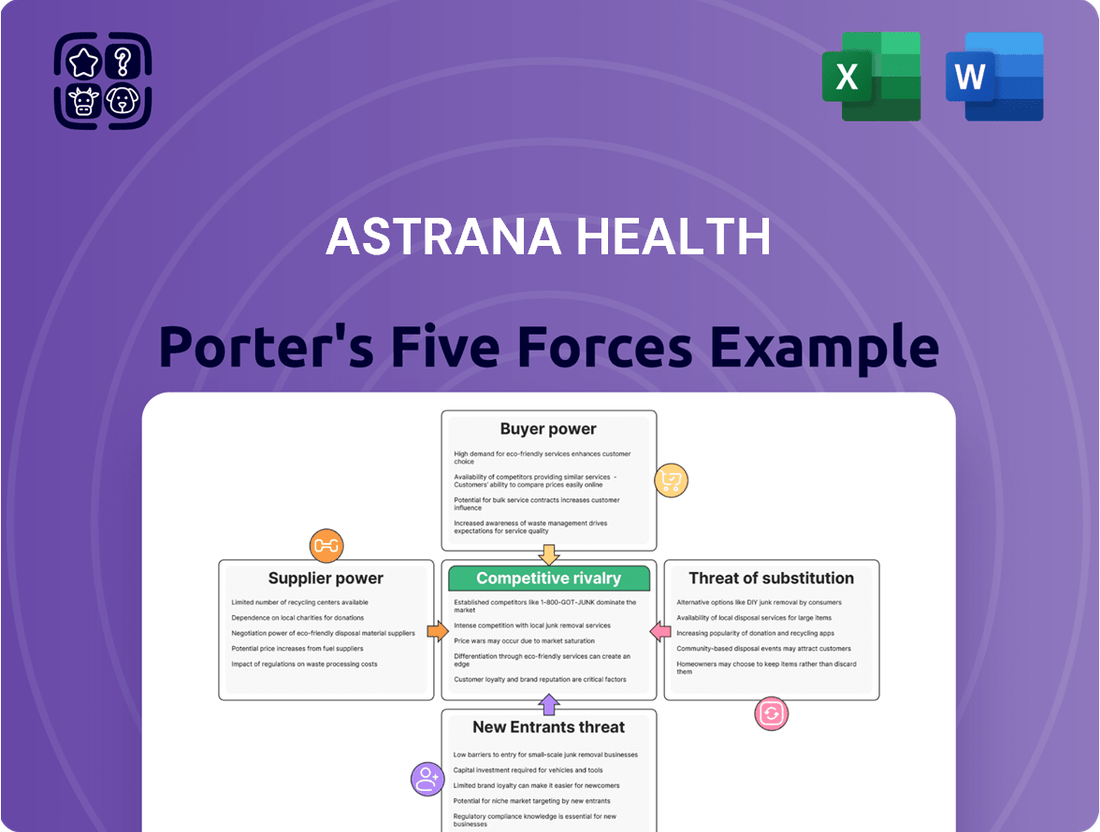
Astrana Health faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with moderate bargaining power from both buyers and suppliers, and a notable threat from substitute healthcare solutions. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the industry effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Astrana Health’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Astrana Health's reliance on a network of primary care physicians and specialists means these professionals hold significant supplier power. The growing momentum of physician unionization, especially among employed doctors, is projected to strengthen their collective bargaining leverage in 2024-2025, impacting compensation and work environment negotiations.
Astrana Health's reliance on specialized technology, particularly for its AI and data analytics platforms, significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. The unique and evolving nature of these healthcare technologies means suppliers offering proprietary or cutting-edge solutions can command considerable leverage. For instance, the global AI in healthcare market was valued at approximately $15.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a high demand for specialized tech where key providers hold sway.
Switching core technology platforms or significantly altering its provider network can impose substantial switching costs on Astrana Health. These costs can include complex integration challenges, the arduous process of data migration, and the potential for significant disruption to ongoing patient care. For instance, a major health system transition in 2024 involved an estimated $50 million in IT integration costs alone.
These high switching costs effectively increase the bargaining power of Astrana Health's entrenched suppliers. When it is costly and disruptive to change, suppliers can leverage this to negotiate more favorable terms, potentially impacting Astrana Health's operational efficiency and profitability.
Uniqueness of Supplier Services/Products
Suppliers providing highly specialized medical devices, unique pharmaceutical products, or niche healthcare management software with few substitutes can exert significant bargaining power over Astrana Health. This is particularly true if these offerings are critical to Astrana's service delivery or competitive advantage. For instance, a supplier of a proprietary robotic surgery system or a breakthrough gene therapy drug would command considerable leverage.
The increasing trend towards personalized medicine further bolsters supplier power. As treatments become more tailored to individual patient needs, the specialized nature of the components or therapies required can limit the available supplier pool. Astrana Health's reliance on such unique inputs means suppliers can potentially dictate terms, including pricing and supply volume, impacting Astrana's operational costs and flexibility.
In 2024, the global market for specialized medical devices saw robust growth, with some niche segments experiencing double-digit increases. This demand, coupled with ongoing supply chain complexities for advanced materials, means suppliers of these critical items are well-positioned to negotiate favorable terms. Astrana Health, like its peers, must manage these supplier relationships carefully to ensure continuity and cost-effectiveness.
- Supplier Specialization: Suppliers offering unique or highly specialized products/services, such as advanced diagnostic equipment or proprietary software platforms, gain significant leverage.
- Limited Alternatives: When few other suppliers can provide comparable goods or services, their bargaining power increases substantially.
- Personalized Medicine Impact: The rise of personalized medicine amplifies supplier power due to the specialized nature of required components and therapies.
- Market Dynamics (2024): Growth in specialized medical device markets in 2024, alongside supply chain challenges, strengthens supplier negotiation positions.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant challenge to Astrana Health. Large physician groups or advanced technology companies that currently provide services to Astrana could potentially bypass Astrana and offer their coordinated care solutions directly to patients or payers. This move would diminish Astrana's role as an intermediary and reduce its leverage.
For instance, if a major health system that partners with Astrana for its care coordination platform were to develop its own proprietary patient engagement app and direct-to-consumer outreach, it would directly compete with Astrana's core offerings. This potential shift could be driven by a desire to capture a larger share of the revenue currently flowing through Astrana's services or to gain more direct control over patient relationships.
Consider the competitive landscape in 2024; many healthcare providers are investing heavily in digital health solutions. If a substantial portion of Astrana's supplier base, such as large accountable care organizations (ACOs) or integrated delivery networks (IDNs), were to pursue this forward integration strategy, it could significantly impact Astrana's market position. For example, if key partners representing 20% of Astrana's revenue decided to integrate forward, this would necessitate a strategic response from Astrana to maintain its value proposition.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers like large physician groups or tech firms may offer Astrana's services directly to patients or payers.
- Reduced Reliance: This action would lessen Astrana Health's dependence on its current supplier relationships.
- Competitive Pressure: Healthcare providers are increasingly investing in direct-to-consumer digital health, increasing this threat.
- Revenue Impact: A significant move by key suppliers to integrate forward could directly affect Astrana's revenue streams.
Astrana Health faces considerable supplier power due to the specialized nature of many of its inputs, from advanced medical technologies to niche pharmaceutical products. The growing trend of physician unionization, particularly among employed doctors, is expected to enhance their collective bargaining power in 2024-2025, potentially increasing labor costs for Astrana. Furthermore, the increasing demand for personalized medicine in 2024, as highlighted by the robust growth in specialized medical device markets, further empowers suppliers of unique components and therapies, as fewer alternatives exist.
The high switching costs associated with Astrana Health's core technology platforms and provider networks significantly bolster supplier leverage. These costs, which can easily reach tens of millions of dollars for IT integration alone as seen in major health system transitions during 2024, make it difficult for Astrana to change suppliers. This entrenched position allows suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms, impacting Astrana's operational efficiency and profitability.
The threat of forward integration by key suppliers, such as large physician groups or technology firms, presents a notable challenge. If these entities were to offer their services directly to patients or payers, bypassing Astrana, it would diminish Astrana's intermediary role and competitive standing. This risk is amplified by the 2024 trend of healthcare providers investing heavily in direct-to-consumer digital health solutions.
| Factor | Impact on Astrana Health | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Physician Bargaining Power | Increased leverage for doctors and specialists | Growing physician unionization in 2024-2025 |
| Technology Supplier Power | High due to proprietary AI and data platforms | Global AI in healthcare market valued at ~$15.4B in 2023, with strong projected growth |
| Switching Costs | Significant, increasing supplier leverage | Major IT integration projects in 2024 costing an estimated $50M+ |
| Specialized Inputs | Empowers suppliers of niche medical devices and therapies | Double-digit growth in some specialized medical device segments in 2024 |
| Forward Integration Risk | Potential for suppliers to bypass Astrana | Increased investment in direct-to-consumer digital health by providers in 2024 |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Astrana Health's competitive landscape dissects the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its market.
Astrana Health's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces—perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Patients, the ultimate consumers in healthcare, are wielding more influence due to readily available information. Digital health platforms and patient choice initiatives are empowering them to compare providers based on quality metrics and cost-effectiveness, directly impacting Astrana Health's customer bargaining power.
Astrana Health's reliance on value-based care models means its revenue is heavily influenced by its payers. These large organizations, including major managed care companies and government programs like Medicare Advantage, wield significant power. In 2024, Medicare Advantage enrollment continued its upward trend, representing a substantial portion of the senior healthcare market, directly impacting Astrana's reimbursement and the flexibility of its care models.
The increasing cost of healthcare is a significant factor influencing the bargaining power of customers. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. national health expenditure reached an estimated $4.7 trillion, a figure that puts immense pressure on individuals and payers to seek value. This trend empowers patients and insurance providers to scrutinize medical expenses and demand services that are both cost-effective and deliver demonstrable health outcomes.
Astrana Health's strategic emphasis on managing and reducing healthcare costs directly addresses this heightened customer demand. By focusing on efficiency and value-based care models, Astrana Health positions itself to meet the expectations of a more informed and cost-conscious customer base, thereby mitigating some of the inherent customer bargaining power.
Customer Segmentation (e.g., Medicare, Commercial, Medicaid)
Astrana Health navigates diverse customer segments, including Medicare, commercial insurance, and Medicaid beneficiaries. Each group exhibits distinct price sensitivities and a different range of available choices, directly impacting Astrana's approach to pricing and service customization.
For instance, Medicare beneficiaries often have more predictable healthcare needs and a greater reliance on government-sponsored plans, potentially leading to less price elasticity compared to commercially insured individuals who may have more employer-sponsored options and higher disposable income.
- Medicare: Beneficiaries often have limited choices of providers and plans, which can reduce their bargaining power.
- Commercial: This segment typically has more options and can switch plans or providers, increasing their bargaining power.
- Medicaid: Beneficiaries are highly price-sensitive due to program limitations, but their choices are often restricted by provider participation.
- Data Insight: In 2024, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) projected that approximately 67 million Americans would be enrolled in Medicare, highlighting the significant market share this segment represents.
Potential for Backward Integration by Payers
Health insurance companies, often referred to as payers, and large employer groups possess significant bargaining power when they can credibly threaten to integrate backward into healthcare provision. This means they might develop their own provider networks or directly contract with physician groups. This strategy directly reduces their dependence on third-party entities like Astrana Health, thereby increasing pressure on Astrana to offer more competitive pricing and favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, several large self-funded employers continued to explore direct contracting models to manage costs more effectively.
The ability of payers to build or acquire their own provider infrastructure poses a direct threat to Astrana Health’s market position. If payers can effectively replicate the services Astrana offers, they can internalize those functions, capturing any associated profits and potentially offering services at a lower cost due to reduced overhead or administrative layers. This potential for backward integration is a powerful lever for customers in negotiating contracts.
- Backward Integration Threat: Payers can develop proprietary provider networks, bypassing intermediaries like Astrana Health.
- Cost Control Incentive: Direct contracting allows payers to potentially reduce administrative costs and capture provider margins.
- Market Pressure: The credible threat of backward integration forces Astrana Health to be more competitive on price and contract terms.
- Employer-Led Initiatives: Large employers are increasingly exploring direct contracting models in 2024 to gain greater control over healthcare spending.
The bargaining power of customers in the healthcare sector, particularly payers like insurance companies and large employers, is substantial. Their ability to negotiate pricing and terms is amplified by the sheer volume of patients they represent and their increasing interest in controlling costs. This dynamic directly influences Astrana Health's revenue and operational flexibility.
In 2024, the healthcare landscape saw continued consolidation among payers, leading to larger entities with greater negotiating leverage. For instance, major health insurance providers continued to expand their networks and explore direct contracting arrangements with providers, aiming to bypass intermediaries and secure more favorable pricing. This trend puts direct pressure on companies like Astrana Health to demonstrate value and cost-efficiency.
The increasing transparency in healthcare pricing and quality metrics empowers patients, the ultimate consumers, to make more informed choices. As patients become more discerning, they can more effectively leverage their choices to demand better services at competitive prices, further influencing the bargaining power within the healthcare ecosystem.
Payers' potential for backward integration, meaning their ability to develop their own provider networks or directly employ healthcare professionals, represents a significant threat. This capability allows them to internalize functions previously outsourced to entities like Astrana Health, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations and potentially reducing Astrana's market share.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Payers (Insurance Companies, Employers) | Volume of patients, Cost control focus, Potential for backward integration | Continued payer consolidation; increased exploration of direct contracting models by large employers. |
| Patients (Individuals) | Information availability, Choice of providers, Price sensitivity | Growing use of digital health platforms for comparisons; increased demand for value-based care. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Astrana Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Astrana Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape of the healthcare industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the sector. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, offering a complete and accurate assessment for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Astrana Health faces intense competition from a multitude of healthcare providers. Major players like HCA Healthcare, with its extensive network of hospitals and facilities, and Intermountain Healthcare, known for its integrated delivery system, represent significant competitive threats. These large systems often possess greater resources and market share, directly impacting Astrana's ability to attract and retain patients and talent.
The healthcare services market is a dynamic arena, projected to reach $9.25 trillion by 2025, fueling intense competition. This substantial market size naturally draws in new players eager to capitalize on the opportunities, while existing companies fight harder to retain their customer base.
A major driver of this rivalry is the industry-wide shift towards value-based care. Providers are increasingly competing not just on the services they offer, but on the quality and outcomes they deliver at a competitive price. This focus on value means companies must innovate and differentiate themselves to stand out.
Astrana Health distinguishes itself by focusing on a provider-centric model, leveraging technology to empower healthcare providers in delivering accessible, high-quality, and value-based care. This approach aims to set it apart from competitors who may offer similar integrated or value-based care solutions.
The company's success hinges on effectively communicating and demonstrating the tangible benefits of its technological and operational differentiators to providers, especially in a competitive landscape where many players are vying for provider partnerships and patient engagement.
For instance, in 2024, the healthcare technology market saw significant investment, with companies emphasizing solutions that streamline workflows and improve patient outcomes, directly challenging Astrana Health's value proposition if its technology does not offer a clear advantage.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
Astrana Health, like many in the healthcare industry, faces substantial exit barriers for its competitors. High fixed costs associated with advanced medical technology, extensive regulatory compliance, and specialized facilities mean that exiting the market involves significant unrecoverable investments. For instance, the capital expenditure for a single state-of-the-art MRI machine can easily exceed $1 million, and building a new hospital wing can run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars.
These specialized assets, often tailored for specific medical procedures or patient care, have limited resale value outside the healthcare sector. This lack of alternative use further traps capital, making it difficult for companies to divest or pivot away from healthcare operations. Consequently, even when market conditions are unfavorable, competitors may be compelled to remain operational due to the sheer difficulty and cost of winding down.
Furthermore, long-term contracts with insurance providers, government agencies, and patient groups create an obligation that is not easily shed. These agreements often span multiple years and involve complex service level agreements. For example, a managed care contract might lock a provider into serving a specific patient population for three to five years, making immediate withdrawal impractical without incurring substantial penalties or reputational damage.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for medical equipment and facilities create a financial lock-in.
- Specialized Assets: Healthcare-specific infrastructure and technology have limited salvage value outside the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with payers and patients make rapid market exit challenging.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Decommissioning facilities and transferring patient records involve complex compliance procedures.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
Astrana Health's competitive rivalry is significantly shaped by its strategic acquisitions and partnerships. By acquiring companies like Prospect Health and Collaborative Health Systems, Astrana Health has effectively broadened its market reach and integrated new capabilities, thereby intensifying competition within the healthcare sector. These moves are not just about scale; they are about consolidating market share and creating a more formidable presence against rivals.
Furthermore, Astrana Health's strategic alliances, such as those with Anthem Blue Cross and Elation Health, bolster its competitive standing. These partnerships allow Astrana Health to leverage the strengths of its collaborators, enhancing its service offerings and expanding its network. For instance, by integrating with Anthem Blue Cross, a major health insurer, Astrana Health gains access to a larger patient base and potentially more favorable reimbursement rates, directly impacting its competitive advantage.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Astrana Health's acquisition of Prospect Health and Collaborative Health Systems in 2023 and 2024 respectively, aimed at expanding its network and service capabilities.
- Key Partnerships: Collaborations with Anthem Blue Cross and Elation Health are crucial for deepening market penetration and enhancing integrated care delivery.
- Market Consolidation: These strategic moves contribute to industry consolidation, increasing the intensity of competition as Astrana Health strengthens its position against other major healthcare providers.
- Competitive Footprint Expansion: The combined effect of acquisitions and partnerships allows Astrana Health to compete more effectively across a wider geographic and service spectrum.
Astrana Health operates in a highly competitive landscape, facing pressure from both established giants and emerging players. The healthcare industry’s substantial market size, projected to grow significantly, attracts continuous new entrants and intensifies existing rivalries. This rivalry is further amplified by the industry's pivot towards value-based care, where providers compete on quality and cost-effectiveness.
Astrana Health's strategy of a provider-centric model, bolstered by technology, aims to differentiate it. However, the company must clearly articulate the advantages of its technological solutions to attract and retain providers, especially as competitors also invest heavily in similar advancements. For example, the healthcare technology market saw substantial investment in 2024, with many companies focusing on workflow streamlining and patient outcome improvements, directly challenging Astrana's value proposition.
The competitive rivalry is also influenced by Astrana Health's strategic acquisitions and partnerships. Acquisitions of companies like Prospect Health and Collaborative Health Systems in 2023 and 2024, respectively, have expanded its market reach and capabilities. Key partnerships with entities such as Anthem Blue Cross and Elation Health enhance its service offerings and patient access, contributing to industry consolidation and a more intense competitive environment.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The enduring prevalence of the traditional fee-for-service (FFS) healthcare model presents a significant threat of substitutes for Astrana Health's value-based care initiatives. Despite increasing adoption of value-based payment models, a substantial portion of healthcare providers continue to operate primarily under FFS arrangements. In 2024, it's estimated that FFS still accounts for a majority of healthcare payments in many developed markets, making it a readily available and familiar alternative for both patients and providers.
The growing availability of direct-to-consumer digital health solutions presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional healthcare providers like Astrana Health. Platforms offering telehealth, remote patient monitoring, and even online prescription services allow individuals to manage certain health needs without engaging with established networks. This trend is amplified by increasing patient demand for convenience and accessibility, a sentiment reflected in the projected growth of the digital health market, which was valued at over $200 billion globally in 2023 and is expected to continue its upward trajectory.
Large corporations are increasingly exploring in-house healthcare solutions as a substitute for traditional external providers. For instance, many companies are investing in on-site clinics and comprehensive wellness programs to manage employee health proactively. This trend could potentially reduce the demand for Astrana Health's services among its corporate clients, impacting revenue streams from employer-sponsored health plans.
Self-Care and Preventive Health Initiatives
The increasing focus on self-care and preventive health presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional healthcare services. As individuals gain more control over their well-being through accessible tools and information, the demand for certain medical interventions may decline.
This shift is fueled by technological advancements and a growing awareness of personal health management. For instance, wearable fitness trackers and health monitoring apps are becoming commonplace, empowering users to proactively manage chronic conditions and general wellness. In 2024, the global digital health market was valued at over $300 billion, with a substantial portion dedicated to wellness and preventive solutions, indicating a strong consumer interest in these alternatives.
- Growing Adoption of Wearables: Over 100 million smartwatches were shipped globally in 2023, many with advanced health monitoring features.
- Telehealth Expansion: Telehealth services, which often facilitate preventive consultations and remote monitoring, saw continued growth in 2024, offering a convenient substitute for in-person visits.
- Wellness Program Investment: Companies are increasingly investing in employee wellness programs, reducing the need for reactive medical care.
- Patient Empowerment: Access to online health resources and patient portals enables individuals to make more informed decisions about their health, potentially bypassing traditional channels for minor concerns.
Retail Clinics and Urgent Care Centers
The increasing number of retail clinics and urgent care centers presents a significant threat of substitution for Astrana Health. These facilities often provide convenient, walk-in access for common ailments, directly competing with Astrana's primary care services. For instance, in 2024, the retail clinic sector saw continued expansion, with major players like CVS Health and Walgreens reporting increased patient visits for basic care needs.
- Convenience: Retail clinics offer extended hours and walk-in appointments, appealing to patients seeking immediate care without the need for pre-scheduling.
- Cost: Often, these substitute services are perceived as more affordable for routine check-ups and minor treatments compared to traditional physician visits.
- Accessibility: Their widespread presence in accessible retail locations makes them a readily available option for a broad patient base.
The traditional fee-for-service (FFS) model remains a potent substitute, with a significant portion of healthcare payments still operating under this familiar framework. This inertia means that while Astrana Health champions value-based care, many patients and providers are comfortable with and continue to utilize FFS, which still dominates many healthcare transactions in 2024.
Direct-to-consumer digital health solutions are increasingly offering convenient alternatives for managing specific health needs, bypassing traditional healthcare networks. The digital health market’s substantial growth, exceeding $300 billion globally in 2023, underscores the appeal of these accessible, tech-enabled substitutes.
Retail clinics and urgent care centers pose a direct substitution threat by offering convenient, walk-in access for common ailments, often at a perceived lower cost. Their expansion in 2024 means more patients can opt for these readily available services over traditional primary care appointments.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | 2024 Market Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Fee-for-Service (FFS) | Familiar, established payment model | Still accounts for a majority of healthcare payments in many markets. |
| Digital Health Solutions | Convenience, accessibility, remote monitoring | Global market valued over $300 billion in 2023, with strong growth in wellness and preventive tech. |
| Retail Clinics/Urgent Care | Walk-in access, extended hours, perceived affordability | Continued expansion of chains like CVS Health and Walgreens, reporting increased patient visits. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the healthcare provider services market, especially with an integrated, value-based model similar to Astrana Health's, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in physical infrastructure, advanced technology systems, and the development of a robust provider network. For instance, building out a comprehensive care management platform and securing necessary licenses can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars.
Furthermore, navigating the intricate web of healthcare regulations presents a considerable barrier. Compliance with HIPAA, Stark Law, Anti-Kickback Statute, and state-specific licensing requirements necessitates specialized legal and administrative resources. The ongoing cost of maintaining this compliance adds another layer of financial burden, effectively deterring many potential new entrants who lack the deep pockets and expertise to manage these complexities.
Established players like Astrana Health benefit from significant economies of scale in managing vast provider networks and utilizing advanced, proprietary technology platforms. This scale allows them to negotiate better rates with providers and spread the costs of technology development over a larger base, creating a substantial cost advantage that new entrants struggle to overcome.
The experience curve further solidifies this advantage. As Astrana Health and similar incumbents have operated for longer, they have refined their processes, optimized operations, and learned from past challenges, leading to greater efficiency and lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, major health insurers reported operating expense ratios in the low single digits, a benchmark difficult for new, smaller entities to match immediately.
Astrana Health faces a substantial threat from new entrants due to the immense difficulty in establishing robust distribution channels and provider networks. Building an extensive network of primary care physicians, specialists, and ancillary service providers, like diagnostic labs and rehabilitation centers, is a time-consuming and capital-intensive endeavor. For instance, in 2024, the average time to onboard a new physician group could extend to over six months, involving complex credentialing and contract negotiations.
Furthermore, securing contracts with a diverse range of payers, including government programs like Medicare and Medicaid, as well as numerous private insurance companies, poses a significant hurdle. These contracts are crucial for revenue generation and patient access. As of 2024, a new entrant would likely need to demonstrate a proven track record and a substantial patient base to even begin negotiating favorable terms with major payers, a feat that is incredibly challenging for a nascent organization.
Brand Loyalty and Patient Relationships
Astrana Health, like many established healthcare providers, benefits significantly from deeply ingrained brand loyalty and the enduring trust built through years of patient relationships. This makes it challenging for new market entrants to attract and retain patients, especially when the existing providers offer a continuity of care and familiarity that new entities struggle to replicate quickly. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of patients prioritize a known provider when choosing healthcare services, highlighting the power of established relationships.
The difficulty for new entrants is further amplified by the inherent nature of healthcare, where patient trust is paramount. Astrana Health's established reputation acts as a substantial barrier, as patients are often hesitant to switch to unfamiliar providers, even if offered competitive pricing or novel services. This loyalty is not just about convenience; it's often rooted in a perceived higher quality of care and a comfort level with the existing medical team.
New entrants face the uphill battle of not only proving their clinical competence but also building the same level of emotional connection and reliability that Astrana Health has cultivated. This requires substantial investment in marketing, community outreach, and patient experience initiatives to even begin to chip away at the loyalty enjoyed by established players. The 2024 healthcare market report showed that the average cost for a new healthcare provider to acquire a new patient was nearly double that of retaining an existing one.
- Established Brand Recognition: Astrana Health benefits from a recognized name, fostering immediate trust.
- Long-Standing Patient Relationships: Years of service have built deep patient loyalty and continuity of care.
- Patient Trust as a Barrier: Patients are often reluctant to switch to unfamiliar providers, prioritizing known entities.
- High Patient Acquisition Costs for New Entrants: The expense of building trust and attracting patients is significantly higher for new players.
Proprietary Technology and Data Advantages
Astrana Health's proprietary end-to-end technology platform, coupled with its advanced data analytics capabilities for population health management, presents a formidable barrier to entry for potential competitors. Replicating this sophisticated ecosystem requires substantial capital investment in research and development, as well as the acquisition of specialized talent in data science and health informatics.
New entrants would need to overcome the significant hurdle of developing or acquiring comparable technological infrastructure and data processing expertise. For instance, Astrana Health's platform integrates various data sources to provide actionable insights, a feat that demands considerable time and resources to build from scratch. As of early 2024, the healthcare technology sector continues to see substantial investment, with companies focusing on AI and data analytics, underscoring the high cost of entry for advanced solutions.
- High R&D Investment: New entrants must commit significant funds to develop comparable technology.
- Data Integration Complexity: Building a system to integrate diverse health data is technically challenging and costly.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: Securing skilled data scientists and health IT professionals is expensive and competitive.
- Scalability Challenges: Achieving the scale and efficiency of Astrana's platform requires substantial infrastructure investment.
The threat of new entrants for Astrana Health is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles. Building a comprehensive healthcare network and complying with stringent regulations like HIPAA demands substantial financial resources and specialized expertise, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively. For example, in 2024, the average cost to establish a new healthcare facility often exceeded $50 million, encompassing infrastructure, technology, and initial staffing.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Astrana Health Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and regulatory filings from healthcare authorities.
We leverage insights from health economics journals, competitor investor relations materials, and government healthcare databases to accurately assess the competitive landscape for Astrana Health.
