nima Educação Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
nima Educação Bundle
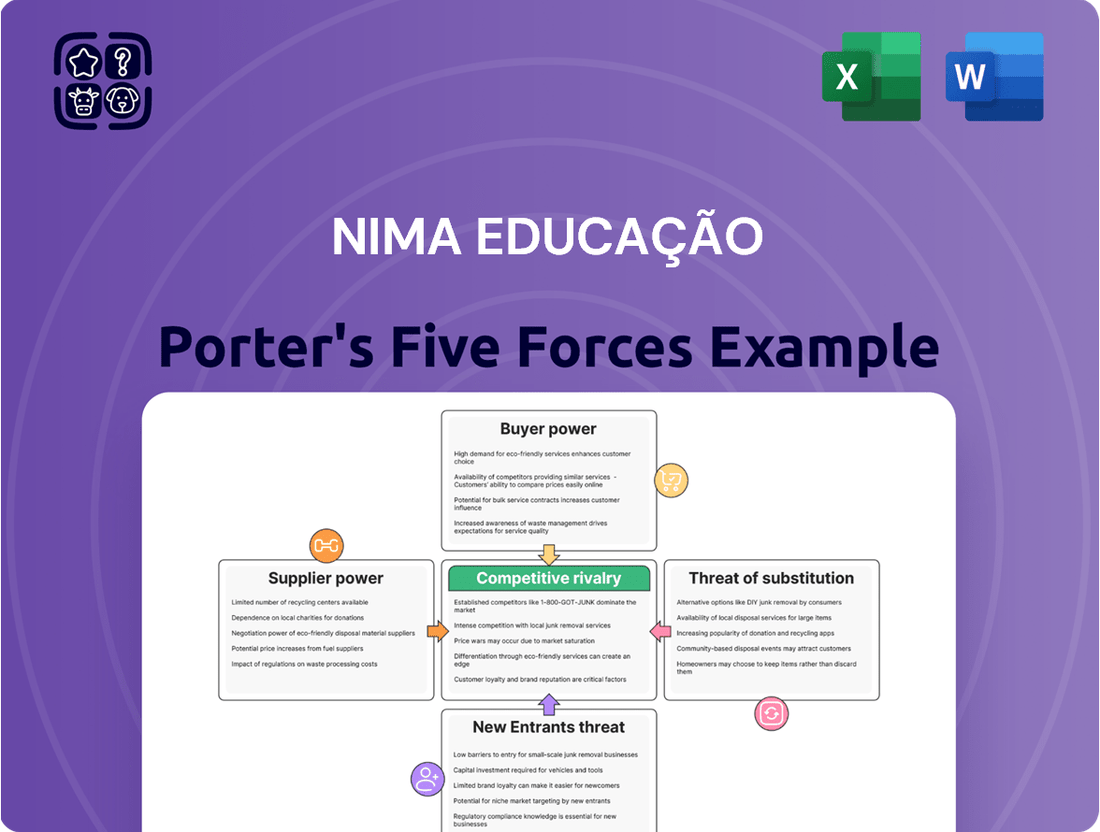
nima Educação operates within a dynamic educational landscape, where understanding the interplay of competitive forces is paramount. Our analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the ever-present threats of new entrants and substitutes.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of nima Educação’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
nima Educação operates within an educational landscape that, by its nature, requires a broad spectrum of suppliers. This includes everything from content creators and digital platform providers to those managing physical campuses and administrative services. The sheer variety of available options generally keeps any single supplier's leverage in check.
As a substantial entity in the education sector, nima Educação is well-positioned to capitalize on this diverse supplier ecosystem. This allows the company to negotiate more effectively, securing better pricing and service level agreements by not being overly dependent on a limited number of providers. For instance, in 2024, the edtech market saw numerous new entrants offering specialized learning management systems, providing nima with more choices for its technological infrastructure.
This extensive network of suppliers significantly mitigates risks associated with price hikes or interruptions in service. Should one supplier become uncompetitive or unreliable, nima Educação can more readily pivot to alternative providers, ensuring continuity in its educational offerings and operational efficiency.
While specialized faculty in high-demand areas like medicine, a key focus for nima's Inspirali, can command greater leverage, the broader availability of educators across Brazil generally tempers the bargaining power of this supplier group. The substantial pool of teaching professionals, coupled with the growing embrace of distance learning, offers nima considerable flexibility in staffing and managing costs.
The bargaining power of technology and content providers for nima Educação is moderate, influenced by the dynamic ed-tech market. While specialized platforms may have few direct competitors, the overall sector offers diverse solutions, allowing nima to negotiate favorable terms. In 2024, the global ed-tech market was valued at approximately $127.2 billion, showcasing a competitive environment where providers vie for institutional clients.
Infrastructure and Real Estate
For on-campus learning, real estate and infrastructure providers hold significant sway. However, nima Educação's strategic shift towards a blended learning model, incorporating distance education, lessens its reliance on physical spaces. This diversification, especially with the expansion of EAD, allows nima to manage its infrastructure needs more flexibly.
The company's increasing investment in distance learning directly impacts the bargaining power of landlords and construction firms. By optimizing its physical footprint and expanding its digital presence, nima can negotiate more favorable terms for its real estate and infrastructure requirements.
- Reduced Dependence: nima's mixed modality approach dilutes the bargaining power of traditional real estate suppliers.
- EAD Growth: The expansion of distance learning allows for a more optimized physical infrastructure, mitigating landlord leverage.
- Negotiating Power: Flexibility in physical space needs enhances nima's ability to negotiate with construction and real estate companies.
Regulatory and Accreditation Bodies
Regulatory and accreditation bodies, while not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, hold considerable sway over educational institutions like nima Educação. These entities establish the benchmarks for educational quality and operational standards, directly impacting how institutions function and what they can offer. nima Educação, for instance, must meticulously follow the directives set forth by Brazil's Ministry of Education (MEC). These guidelines cover everything from curriculum design to faculty qualifications, and failure to comply can result in significant penalties or even the inability to operate certain programs. This mandatory adherence grants these bodies substantial power, as they dictate the fundamental rules of engagement within the educational sector.
The MEC's influence is a critical factor in nima Educação's operational strategy. For example, in 2024, the MEC continued to emphasize the importance of digital learning infrastructure and pedagogical innovation. Institutions that fail to meet evolving MEC standards for course delivery, particularly in hybrid or online formats, may face limitations on student enrollment or program accreditation. This regulatory oversight can necessitate substantial investments in technology, faculty training, and curriculum development, thereby increasing operational costs for nima Educação.
- MEC Accreditation: nima Educação's programs require accreditation from the MEC, ensuring adherence to national educational standards.
- Operational Compliance: Non-compliance with MEC regulations can lead to sanctions, impacting enrollment and program viability.
- Investment in Quality: Meeting MEC standards often requires ongoing investment in faculty development and technological infrastructure.
nima Educação generally faces moderate bargaining power from its suppliers due to the diverse nature of the educational sector and its own significant market presence. While specialized content or technology providers might hold some leverage, the availability of alternatives across most categories limits any single supplier's ability to dictate terms. For instance, the Brazilian ed-tech market in 2024 offered numerous platform options, allowing nima to negotiate competitive pricing for its digital learning tools.
The company's strategic expansion into distance learning, or EAD, has also been instrumental in reducing its reliance on traditional physical infrastructure suppliers. This shift allows nima to optimize its real estate needs, thereby lessening the bargaining power of landlords and construction firms. By embracing a blended learning model, nima gains greater flexibility in managing its operational footprint and associated costs.
While highly specialized faculty, particularly in fields like medicine for its Inspirali brand, can exert more influence, the broader availability of educators across Brazil, coupled with the growing acceptance of online instruction, helps to balance this. This diverse talent pool provides nima with options, mitigating the risk of excessive salary demands from any single group of academic staff.
The bargaining power of suppliers for nima Educação is largely kept in check by the company's scale and its strategic diversification into online and blended learning models. This approach allows for greater negotiation flexibility across various supplier categories, from technology and content providers to real estate and faculty, ensuring cost efficiencies and operational continuity.
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the five competitive forces impacting nima Educação, providing a strategic overview of its market position and potential challenges.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the impact of each force on your business.
Customers Bargaining Power
Brazilian students face a wealth of choices in higher education, with numerous private institutions offering both on-campus and online programs. This abundance of options directly fuels their bargaining power.
Compounding this, economic headwinds such as elevated unemployment rates and household debt in Brazil make students acutely aware of tuition costs. For instance, Brazil's unemployment rate hovered around 7.8% in late 2023, impacting household disposable income and reinforcing price sensitivity among prospective students.
Consequently, nima Educação must actively differentiate itself not just on academic quality but also on competitive tuition fees and a compelling value proposition to attract and retain its student base in this dynamic market.
The expansion of distance learning (EAD) in Brazil has significantly boosted customer bargaining power. Students now have access to a wider array of flexible and often more economical educational options, breaking down geographical barriers to higher education. nima's strong presence in EAD means it directly competes in a market where customers can easily compare online programs, increasing their leverage.
Government programs like FIES (Fundo de Financiamento Estudantil) and ProUni (Programa Universidade para Todos) significantly impact the bargaining power of customers in Brazil's education sector. These initiatives provide financial aid, making education more accessible and influencing student enrollment decisions.
By offering subsidized loans and scholarships, these government programs effectively centralize a portion of the purchasing power. This means institutions may have less flexibility in setting tuition fees, as student choices are often guided by the availability and terms of these government-backed financial options, thus increasing customer bargaining power in a collective sense.
For instance, in 2024, FIES continued to be a crucial funding source for many students pursuing higher education, with millions of contracts actively supporting enrollment. Similarly, ProUni awarded thousands of scholarships to students in private institutions. These figures highlight the substantial influence the government, as a collective financier, wields over student demand and institutional pricing strategies.
Student Debt and Inadimplência
The significant burden of student debt and high rates of inadimplência, or default, in Brazil's education sector grants students considerable indirect bargaining power. Educational institutions feel pressure to be more accommodating with payment plans and offer discounts to secure and keep students enrolled.
This financial strain on students means companies like nima must remain competitive with their pricing and financial aid packages. Failing to do so risks lower enrollment numbers and higher student attrition rates, directly impacting revenue and stability.
- Student Debt Impact: In 2023, the total outstanding student loan debt in Brazil continued to be a significant factor for potential and current students.
- Inadimplência Rates: While specific recent figures for the education sector's default rates fluctuate, general economic conditions often correlate with higher inadimplência, pressuring institutions.
- Competitive Landscape: nima's ability to attract and retain students is directly tied to its financial offerings compared to competitors, especially given the cost of higher education.
- Strategic Response: Institutions are increasingly exploring innovative financial models and support systems to mitigate student financial distress and maintain enrollment stability.
Quality and Reputation as Differentiators
While price is certainly a consideration for students, the quality of education and the institution's overall reputation play a significant role in their decision-making. nima Educação's commitment to high educational standards, evidenced by its strong performance in metrics like the Índice Geral de Cursos (IGC), helps to mitigate the bargaining power of customers. For instance, in the 2023 evaluation, nima's institutions achieved an average IGC score of 3.83, placing them in the top tier of Brazilian educational institutions, which can command premium pricing and loyalty.
This focus on quality and reputation acts as a key differentiator, making it harder for students to simply switch to competitors based on price alone. However, this advantage is not absolute. Should nima's perceived educational quality falter, or if competitors significantly improve their offerings and reputation, students' willingness to pay a premium could diminish, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
- Student Choice Factors: Price, educational quality, institutional reputation, and future career prospects are primary drivers for student enrollment.
- nima's Competitive Edge: A strong emphasis on quality and positive performance in indicators like the IGC (e.g., average IGC of 3.83 in 2023) can reduce customer bargaining power.
- Reputation Risk: A decline in perceived quality or a stronger competitive offering could erode nima's differentiation, increasing student bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers, particularly students, is substantial for nima Educação. This is driven by the sheer volume of educational providers in Brazil, coupled with students' heightened price sensitivity due to economic pressures like unemployment and debt. For example, Brazil's unemployment rate was around 7.8% in late 2023, directly impacting students' ability to afford tuition.
Government financial aid programs like FIES and ProUni further amplify this power by centralizing funding and influencing enrollment decisions, effectively limiting institutions' pricing flexibility. In 2024, millions of FIES contracts and thousands of ProUni scholarships continued to underscore this influence.
While nima's commitment to quality, evidenced by its 2023 average IGC score of 3.83, helps mitigate this power, it's not a permanent shield. Any perceived decline in quality or significant improvement by competitors could easily shift the balance back towards students, increasing their leverage.
Preview Before You Purchase
nima Educação Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for nima Educação, offering a detailed examination of industry competition and profitability. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no hidden surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Brazilian private education sector is a mixed bag, featuring both many small players and a trend towards larger entities absorbing them. This means competition is fierce, as smaller schools fight for students, and bigger ones like Ânima Educação actively acquire others to grow. This constant activity means a move by one company, like launching a new program, can quickly force others to react, perhaps by acquiring a competitor or introducing their own new courses.
The distance learning (EAD) sector has seen remarkable growth, significantly intensifying competition for institutions like Ânima Educação. This expansion breaks down geographical limitations, allowing universities to reach students far beyond their physical campuses. For instance, by the end of 2023, the number of students enrolled in distance learning programs in Brazil had surpassed 10 million, a substantial increase from previous years, highlighting the sector's dynamism.
This surge in EAD means Ânima Educação now faces a much wider array of competitors. It's no longer just about local universities; national players with robust online offerings are directly vying for the same student pool. This broader competitive field necessitates a constant focus on differentiation and value proposition to attract and retain students in an increasingly crowded digital classroom.
Competitive rivalry in the Brazilian education sector, particularly for Ânima Educação, is fierce. This intensity frequently triggers price wars, especially in the more standardized areas of higher learning. For instance, in 2023, the average tuition fee for undergraduate courses in Brazil saw fluctuations, with private institutions often adjusting prices to remain competitive.
The constant drive to attract students, many of whom are highly sensitive to the cost of education, directly translates into downward pressure on tuition prices. This, in turn, squeezes profit margins for companies like Ânima. The company's strategic diversification, including its focus on higher-margin medical programs and the growing distance learning (EAD) segment, is a key approach to mitigating these profitability pressures inherent in a highly competitive market.
Differentiation through Specialization and Quality
Educational institutions are increasingly differentiating themselves by specializing in high-demand areas and focusing on quality. For instance, Ânima Educação's Inspirali unit targets the medical field, a sector known for consistent demand. This specialization allows institutions to carve out unique market positions.
Ânima's emphasis on quality is evident in its reported leadership in IGC (General College Performance Index) scores. In 2023, Ânima maintained its position as a leader in the Brazilian private education sector, with several of its institutions achieving top-tier IGC ratings, reflecting a commitment to academic excellence and innovation. This focus on a distinctive value proposition helps to lessen the intensity of direct price competition.
- Specialization in High-Demand Fields: Ânima Educação's Inspirali unit focuses on medicine, a consistently sought-after program.
- Quality and Innovation Emphasis: The company highlights its strong performance in IGC scores, aiming to stand out.
- Ecosystem of Education Investment: Ânima invests in a comprehensive educational ecosystem to enhance its unique offering.
- Mitigating Price Rivalry: Differentiation through specialization and quality reduces pressure for direct price competition.
Macroeconomic Factors Impacting Enrollment
The economic climate in Brazil significantly shapes competitive rivalry within the education sector. When the economy is robust, with low unemployment and rising incomes, more individuals can afford higher education, expanding the potential student base. However, a downturn, characterized by higher unemployment and increased household debt, forces educational institutions to vie more intensely for a reduced number of students. This economic pressure can lead to price wars and a greater focus on differentiation to attract and retain students.
For instance, Brazil's unemployment rate hovered around 7.8% in early 2024, a figure that, while showing some improvement from previous periods, still represents a considerable portion of the workforce potentially limiting discretionary spending on education. Similarly, household indebtedness levels can impact families' ability to pay tuition fees. When economic conditions are tight, institutions may find themselves competing not just on academic quality but also on affordability and flexible payment options.
- Economic Health Impact: Brazil's overall economic performance, including GDP growth and inflation rates, directly influences consumer confidence and disposable income available for education.
- Unemployment and Income: Higher unemployment rates and stagnant income levels in 2024 can reduce the pool of eligible and willing students, intensifying competition among educational providers.
- Indebtedness Factor: Elevated household debt levels can make students and their families more price-sensitive, forcing institutions to offer more competitive pricing or financial aid.
- Market Share Competition: In a challenging economic environment, educational institutions must work harder to capture and maintain market share, often through aggressive marketing and program adjustments.
Competitive rivalry in Brazil's education sector is intense, driven by a fragmented market and the rise of distance learning (EAD). Ânima Educação faces pressure from numerous smaller players and larger institutions alike, particularly as EAD expands geographic reach. This necessitates constant innovation and differentiation to attract students, often leading to price adjustments.
The drive to attract students, who are often price-sensitive, puts downward pressure on tuition. For instance, in 2023, tuition fees for undergraduate courses saw fluctuations, with private institutions frequently adjusting prices. Ânima's strategy to mitigate this includes specializing in high-demand areas like medicine and focusing on quality, as evidenced by its strong IGC scores in 2023, aiming to reduce direct price competition.
Economic conditions significantly impact this rivalry. In early 2024, Brazil's unemployment rate around 7.8% and household debt levels mean students are more price-conscious. This forces institutions to compete not just on academics but also on affordability and payment flexibility, intensifying the fight for market share.
| Indicator | Value (Early 2024/2023) | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Brazilian Unemployment Rate | ~7.8% | Increases price sensitivity, intensifies competition for students. |
| EAD Student Growth | Exceeded 10 million enrollments (end of 2023) | Broadens the competitive landscape beyond physical locations. |
| Ânima's IGC Performance | Leader in private education (2023) | Supports differentiation strategy, lessening direct price wars. |
| Tuition Fee Fluctuations | Observed in 2023 | Indicates ongoing price adjustments to remain competitive. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing demand for practical, job-ready skills is making vocational and technical courses a significant substitute for traditional university degrees. These programs offer a quicker path to employment, often at a lower cost, attracting students who prioritize immediate career entry over extended academic pursuits. For instance, in 2024, the global online vocational training market was projected to reach over $30 billion, indicating strong student interest in these alternatives.
The growing availability of online certifications and micro-credentials poses a substantial threat of substitutes for traditional educational offerings. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity, along with specialized bootcamps, provide accessible and often more affordable pathways to acquire in-demand skills. For instance, a data science bootcamp might cost a fraction of a university degree, delivering job-ready competencies in months rather than years.
This trend directly challenges institutions like Ânima Educação by offering alternative routes to career advancement. Individuals seeking specific skill sets, such as digital marketing or cloud computing, can bypass lengthy degree programs for quicker, more focused training. This can diminish the perceived value of traditional degrees if they are not perceived as providing a distinct advantage in the job market.
Ânima Educação needs to consider how to integrate or compete with these flexible learning formats. This could involve developing its own micro-credential programs, partnering with online platforms, or ensuring its degree programs offer unique advantages, such as deeper theoretical understanding, broader networking opportunities, or stronger employer partnerships, to justify their cost and time commitment.
The threat of substitutes for traditional corporate training programs is growing. Many companies are investing in in-house training or collaborating with specialized firms to develop tailored upskilling initiatives. This shift away from relying solely on external educational institutions for professional development is a significant challenge.
For example, in 2023, the global corporate e-learning market was valued at approximately $23.4 billion and is projected to grow significantly. This indicates a strong demand for flexible and company-specific learning solutions that can be delivered efficiently, potentially bypassing traditional university continuing education offerings.
Ânima Educação, through its HSM and HSMu brands, is well-positioned to address this evolving market by offering programs that cater to the specific needs of corporations and their employees, recognizing the increasing importance of lifelong learning and strategic partnerships in the education sector.
Self-Learning and Open Educational Resources (OER)
The proliferation of free and low-cost educational content, such as YouTube tutorials and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs), presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional educational institutions like Ânima Educação. These platforms empower individuals to acquire knowledge and skills independently, potentially bypassing formal degree programs for specific learning objectives.
For instance, platforms like Coursera and edX reported millions of enrollments in 2023, with many courses offering foundational knowledge in areas previously exclusive to university curricula. This accessibility allows self-directed learners to gain practical skills without the financial commitment of higher education, thereby substituting for certain educational functions.
- Widespread Availability: Platforms like YouTube and open educational resource repositories offer a vast library of free learning materials.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many OER and MOOCs are free or significantly cheaper than traditional tuition fees.
- Skill-Based Learning: Substitutes often focus on practical skills directly applicable to the job market, appealing to career-oriented individuals.
- Growing User Base: The user base for online learning platforms continues to expand, indicating a strong demand for alternative educational pathways.
International Online Education Providers
The increasing accessibility of international online education platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for local institutions like Ânima Educação. These global providers, including established universities and specialized online learning platforms, offer a vast array of courses and degree programs directly to Brazilian students, bypassing traditional geographical limitations.
While language and cultural differences can be a hurdle, the continuous globalization of education is diminishing these barriers. For instance, many international platforms now offer content in Portuguese or provide robust translation services. This global reach expands student choice considerably, intensifying the competitive pressure on domestic educational providers.
- Increased Global Online Enrollment: In 2023, global online education enrollment saw a significant uptick, with projections indicating continued growth through 2025.
- Accessibility of Foreign Degrees: Many international online programs in 2024 offer flexible payment plans and are often priced competitively against comparable Brazilian offerings.
- Language Support Growth: Platforms like Coursera and edX have been actively expanding their multilingual content and support, making foreign education more accessible to Portuguese speakers.
The rise of vocational training, online certifications, and micro-credentials directly challenges traditional degrees by offering faster, more cost-effective routes to job readiness. These alternatives are gaining traction, particularly among students prioritizing immediate employment. For example, the global online vocational training market was projected to exceed $30 billion in 2024.
The availability of free and low-cost educational content, such as MOOCs and YouTube tutorials, further substitutes for formal education by enabling self-directed learning of specific skills. Platforms like Coursera and edX saw millions of enrollments in 2023, demonstrating a strong preference for accessible, skill-focused learning pathways.
International online education platforms also pose a threat by offering global access to degrees and courses, often with competitive pricing and growing language support. This global competition expands student options and intensifies pressure on local institutions to demonstrate unique value.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Traditional Education | Market Trend Example (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vocational Training & Bootcamps | Job-specific skills, shorter duration, lower cost | Reduced demand for lengthy degree programs | Global online vocational training market projected over $30 billion (2024) |
| Online Certifications & Micro-credentials | Targeted skills, flexibility, affordability | Challenges university credentialing, offers alternative career paths | Significant growth in specialized online learning platforms |
| Free/Low-Cost Online Content (MOOCs, YouTube) | Accessibility, self-paced learning, broad topic coverage | Empowers independent learning, bypasses formal institutions for specific knowledge | Millions of enrollments on platforms like Coursera and edX (2023) |
| International Online Education | Global access, diverse programs, competitive pricing | Increased competition for local institutions, broader student choice | Growing multilingual content and support on international platforms |
Entrants Threaten
The Brazilian education sector is heavily regulated, with the Ministry of Education (MEC) overseeing the establishment of new institutions and the accreditation of courses. These stringent requirements, including extensive documentation and adherence to quality standards, create substantial barriers for potential new entrants. For instance, in 2023, the MEC continued to refine its accreditation processes, emphasizing digital learning quality and institutional sustainability, which adds layers of complexity and cost for aspiring education providers.
Establishing a robust educational institution, particularly one like Ânima Educação with a broad curriculum and physical campuses, demands considerable upfront capital. This investment spans critical areas such as state-of-the-art infrastructure, advanced technological integration, and the recruitment of highly qualified faculty and staff.
The substantial financial barrier presented by these high initial costs acts as a significant deterrent for prospective new competitors. For instance, the average cost to build a new school in Brazil can range from R$10 million to over R$50 million, depending on size and facilities, making it challenging for smaller entities to enter the market.
Established players like Ânima Educação have cultivated strong brand recognition and a reputation for quality, a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, Ânima's extensive network of institutions and its long-standing presence in the Brazilian education market solidified its position, making it difficult for new entrants to quickly gain traction.
Newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and recruitment to build trust and attract students, as perceived quality and brand loyalty are paramount in enrollment decisions. The financial commitment required to establish a comparable brand presence and reputation can be substantial, potentially exceeding the resources of many aspiring competitors in the competitive educational landscape.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Large educational groups, such as Ânima Educação, leverage significant economies of scale, realizing cost efficiencies in shared administrative functions, robust technology infrastructure, and widespread marketing efforts. For instance, in 2023, Ânima reported a consolidated net revenue of R$3.6 billion, demonstrating the scale of its operations which allows for optimized resource allocation.
Furthermore, Ânima's broad portfolio, spanning K-12, higher education, and postgraduate programs, generates economies of scope. This diversification enables them to cross-sell services and share best practices across different educational segments, a feat difficult for new, specialized entrants to replicate. This integrated approach can lead to higher customer lifetime value and reduced operational redundancies.
New entrants often struggle to match these cost advantages and the comprehensive nature of established players' offerings. Without the benefit of existing scale or scope, they face higher per-unit costs and a more limited ability to compete on price or provide a full spectrum of educational services, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
- Economies of Scale: Reduced per-unit costs through large-scale operations in administration, technology, and marketing.
- Economies of Scope: Cost savings and enhanced value from offering a diverse range of educational products and services.
- Competitive Disadvantage for New Entrants: Lack of scale and scope makes it harder for new players to compete on price and breadth of offerings.
Market Saturation in Certain Segments
While the Brazilian education sector shows robust overall growth, some segments, particularly traditional on-campus undergraduate programs, are nearing saturation. This saturation can deter new entrants from targeting these established areas, pushing them towards niche markets or innovative educational models. Even these new approaches, however, will likely encounter competition from existing institutions looking to expand their offerings and market share.
For instance, in 2024, while the demand for higher education in Brazil continues to rise, the number of available spots in highly sought-after, traditional on-campus programs has led to increased competition for new institutions. This dynamic forces potential new entrants to consider alternative delivery methods like hybrid or fully online learning, or to focus on specialized vocational training where demand may still outstrip supply.
- Market Saturation: Traditional on-campus undergraduate programs in Brazil are experiencing increasing saturation, limiting opportunities for new entrants.
- Niche Market Focus: New competitors are compelled to explore specialized segments or innovative educational models to gain traction.
- Established Competition: Even in niche areas, new entrants face competition from established players seeking to broaden their reach.
- 2024 Data Insight: The high demand for higher education in Brazil contrasts with the limited capacity in popular on-campus programs, intensifying competition for new providers.
The threat of new entrants for Ânima Educação is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements for establishing new educational institutions, including infrastructure and technology. Stringent government regulations from the Ministry of Education (MEC) further complicate entry, demanding extensive documentation and adherence to quality standards, as seen in ongoing refinements to accreditation processes in 2023. These combined factors create substantial barriers, making it difficult for new players to compete effectively.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for infrastructure, technology, and faculty. | Deters smaller or less-funded entities. | New school construction costs can range from R$10 million to over R$50 million. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | MEC oversight, accreditation, and quality standards. | Increases complexity, time, and cost of entry. | MEC's 2023 focus on digital learning quality adds complexity. |
| Brand Reputation & Loyalty | Established trust and recognition of existing players. | Requires significant marketing investment for newcomers to build credibility. | Ânima's long-standing presence in 2024 solidifies its market position. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Nima Educação Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of reliable data, including industry-specific market research reports, government educational statistics, and publicly available financial disclosures from educational institutions.
