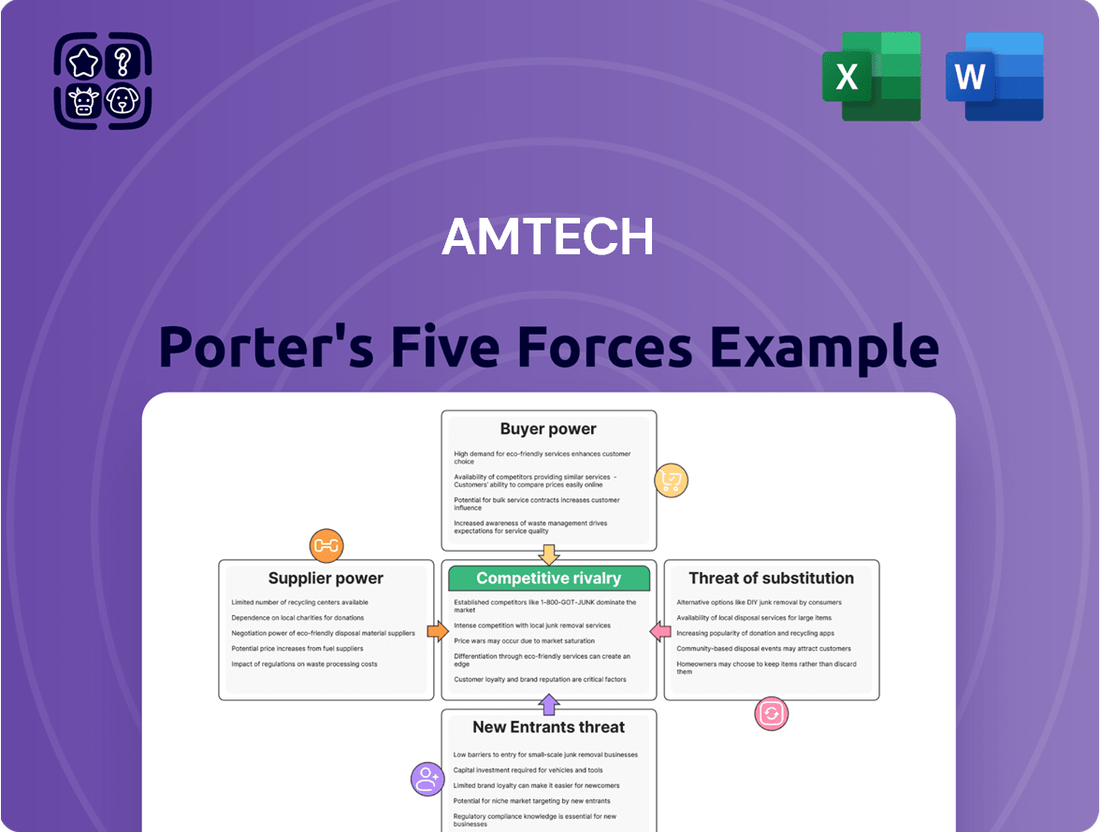
Amtech Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Amtech Bundle
Amtech's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five critical forces, revealing the intensity of rivalry and potential for profit. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Amtech’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Amtech Systems depends on suppliers for highly specialized components and materials essential for its advanced capital equipment. These include automation, coating, and thermal processing systems vital for industries like semiconductor, advanced packaging, and solar manufacturing.
The specialized and often proprietary nature of these components can concentrate power in the hands of a few suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor equipment market saw continued consolidation, with key material and component providers holding significant leverage due to the high R&D investment required for their specialized products.
Amtech faces significant switching costs when considering alternative suppliers for its capital equipment. The intricate design and integration of these specialized machines mean that changing providers for critical components can necessitate substantial investments in redesigning existing systems, retooling manufacturing processes, and rigorous qualification procedures. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor equipment sector saw average integration costs for new components range from 15% to 25% of the component's initial price, reflecting the complexity involved.
These substantial upfront expenses, coupled with the potential for production disruptions during the transition, grant suppliers considerable bargaining power. This is especially pronounced for highly engineered parts integral to Amtech's thermal processing and wafer polishing equipment, where specialized knowledge and precise manufacturing are paramount. In the fiscal year ending June 30, 2024, Amtech reported that nearly 40% of its cost of goods sold was attributable to specialized component suppliers, highlighting the critical nature of these relationships.
Amtech's reliance on specialized, high-precision components means suppliers of these critical inputs wield significant bargaining power. For instance, the intricate nature of semiconductor fabrication equipment demands inputs with extremely tight tolerances and exceptional purity, making it difficult for Amtech to switch suppliers without compromising product quality and performance. In 2024, the semiconductor equipment market saw continued demand for advanced materials, further solidifying the position of key component providers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Amtech's equipment manufacturing business, while theoretically present, is likely minimal. This is primarily due to the substantial capital investment and specialized technical knowledge required to compete in Amtech's core markets, such as semiconductor fabrication and advanced packaging. For example, the global semiconductor equipment market alone was valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023, demanding significant R&D and manufacturing capabilities.
Key suppliers in these high-tech sectors typically focus on their core competencies, like component manufacturing or material science, rather than venturing into complex capital equipment assembly. The sheer scale of expertise needed for designing, producing, and servicing sophisticated machinery for industries with stringent quality and performance demands acts as a significant barrier to entry for most suppliers.
However, if a supplier were to possess unique, proprietary technology that could be directly incorporated into a finished equipment product, the incentive for forward integration might increase. Nevertheless, the established players in the equipment manufacturing space, including Amtech, generally maintain strong relationships and contracts that secure component supply and mitigate such risks.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The bargaining power suppliers hold is significantly shaped by how easily Amtech can find alternative materials or components. If there are limited substitutes that can deliver the same functionality for Amtech's sophisticated systems, the suppliers of those crucial, unique inputs gain considerable leverage. This is especially true in sectors reliant on specialized or proprietary technologies, where finding comparable alternatives is difficult.
For instance, consider the semiconductor industry. In 2024, the global semiconductor market was valued at approximately $689 billion, with demand for advanced chips soaring. Companies like Amtech, relying on cutting-edge processing units or specialized memory modules, would find their suppliers' bargaining power amplified if these specific components have few direct replacements. This scarcity of substitutes allows suppliers to potentially dictate terms, including pricing and delivery schedules.
- Limited Substitutes: If Amtech's core technologies depend on unique, patented components with no readily available alternatives, supplier power increases.
- Technological Dependence: High reliance on suppliers for specialized, advanced materials or software critical to Amtech's product performance strengthens supplier leverage.
- Market Concentration: If only a few suppliers can provide the necessary inputs, especially those incorporating novel technologies, their bargaining power is enhanced.
- Cost of Switching: The expense and time involved in qualifying and integrating new suppliers for specialized inputs further solidify the position of existing suppliers.
Suppliers of specialized components for Amtech's advanced capital equipment, such as those used in semiconductor and solar manufacturing, hold significant bargaining power. This is due to the limited availability of substitutes and the high switching costs Amtech incurs when changing providers. For example, in 2024, the semiconductor equipment market saw continued demand for advanced materials, reinforcing the leverage of key component suppliers.
The specialized and often proprietary nature of these inputs means that a few suppliers can dominate the market, dictating terms. Amtech's reliance on these critical, high-precision components, which are integral to product performance, further amplifies supplier leverage. In fiscal year 2024, specialized components represented nearly 40% of Amtech's cost of goods sold, underscoring their importance.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Context |
| Limited Substitutes | High | Demand for advanced materials in semiconductor equipment market remained strong. |
| Switching Costs | High | Integration costs for new components in semiconductor equipment averaged 15-25% of component price. |
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate to High | Consolidation in semiconductor equipment market benefits key component providers. |
| Importance of Input | High | Specialized components accounted for ~40% of Amtech's COGS in FY24. |
What is included in the product
Amtech's Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Amtech Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a visual, interactive dashboard that simplifies complex competitive landscapes, allowing for rapid identification of key strategic pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Amtech's customer base includes major players in the semiconductor, advanced packaging, and solar sectors. These are often large foundries, integrated device manufacturers (IDMs), and substantial solar panel producers.
These key customers frequently procure high-value capital equipment in considerable quantities. For example, a leading semiconductor foundry might invest billions in new fabrication equipment annually, making them a critical supplier relationship.
This significant purchasing volume grants these customers substantial leverage in negotiating prices and favorable terms. Their ability to place large orders, or potentially shift their business to competitors, directly impacts Amtech's pricing power and profitability.
Customers investing in Amtech's specialized capital equipment, such as thermal processing or advanced packaging systems, encounter significant switching costs. These costs are incurred when a customer decides to move from one supplier to another.
Once Amtech's equipment is integrated into a customer's production lines, the process of switching involves substantial expenses. This includes the cost of re-qualifying new equipment, retraining personnel on different systems, and the potential for costly production downtime during the transition period. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, re-qualifying a new piece of equipment can take months and cost millions of dollars.
These high switching costs effectively reduce the bargaining power of Amtech's customers in the short term. Customers are less likely to switch suppliers if the financial and operational disruption is substantial, giving Amtech a degree of pricing power and customer retention.
Customers in the semiconductor and solar sectors, even with high switching costs, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is driven by the intense competition they face in their respective end markets, compelling them to relentlessly pursue cost optimization strategies.
This cost-consciousness directly translates into pressure on Amtech's pricing, particularly for equipment used in mature semiconductor nodes. Demand in these segments has shown weakness, making price a more critical factor for buyers looking to control their production expenses.
For instance, in 2024, the average selling price for certain types of mature node semiconductor manufacturing equipment saw a decline of up to 10% year-over-year due to softer demand and increased competition among equipment suppliers.
Customer's Ability to Backward Integrate
While large customers may possess significant R&D, backward integration into manufacturing specialized capital equipment is often impractical. The enormous capital outlay, intricate technology, and specialized knowledge needed create substantial barriers. For instance, the semiconductor equipment manufacturing sector, where Amtech operates, demands billions in investment for a single fabrication plant, a cost prohibitive for most end-users.
This difficulty in self-production significantly curtails the bargaining power of customers who might otherwise consider producing their own equipment. The high barriers to entry mean that customers are unlikely to become competitors by manufacturing the capital equipment themselves, thus limiting their leverage.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing a manufacturing facility for advanced capital equipment can cost billions of dollars, far exceeding the typical R&D budgets of most customer companies.
- Technological Complexity: The manufacturing processes for highly specialized equipment involve proprietary technologies and intricate engineering, requiring deep, specialized expertise that is difficult and time-consuming to acquire.
- Lack of Core Competency: Most customers' core businesses are not in equipment manufacturing. Venturing into this area would divert resources and focus from their primary operations, potentially harming their core business performance.
Access to Information and Product Standardization
Customers in sophisticated industries, like those Amtech serves, are often highly informed about pricing, product details, and what competitors offer. This knowledge empowers them significantly.
When Amtech's products become more standardized, or when customers can easily compare different options, their ability to negotiate better terms grows. For instance, in the semiconductor packaging sector, readily available datasheets and performance benchmarks allow buyers to pit suppliers against each other.
However, Amtech's strategic emphasis on advanced packaging solutions and specialized thermal processing creates a degree of product differentiation. This specialization can mitigate some of the customer bargaining power, as unique capabilities are harder to substitute.
- Informed Customer Base: Buyers in Amtech's target markets possess detailed knowledge of market pricing and product specifications.
- Impact of Standardization: Increased product standardization or easy access to comparative data amplifies customer negotiation leverage.
- Amtech's Differentiation: Advanced packaging and specialized thermal processing offer unique value, potentially reducing customer power.
Amtech's customers, primarily large semiconductor and solar companies, wield considerable bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the high switching costs associated with Amtech's specialized equipment. Despite these switching costs, intense market competition drives significant price sensitivity among these buyers, especially for equipment used in mature semiconductor nodes. For example, in 2024, the average selling price for certain mature node semiconductor manufacturing equipment decreased by up to 10% year-over-year due to weaker demand.
Customers' inability to backward integrate into manufacturing Amtech's complex, capital-intensive equipment further limits their leverage. While informed about market offerings, Amtech's differentiation in advanced packaging and thermal processing helps to temper customer power by offering unique, less substitutable capabilities.
| Factor | Impact on Amtech | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Volume & Size | High dependence on key accounts | Significant |
| Switching Costs | Moderate retention benefit | Reduced in short-term |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on margins, especially in mature segments | High |
| Backward Integration Potential | Very Low | Negligible |
| Customer Information & Differentiation | Mitigated by Amtech's specialization | Moderate |
What You See Is What You Get
Amtech Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Amtech Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and no hidden content. This professionally prepared analysis is ready for immediate download and application to your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Amtech faces a dynamic competitive landscape across its core markets: semiconductor, advanced packaging, and solar equipment. This means a wide array of players, from massive global corporations to highly specialized niche firms, are vying for market share.
The semiconductor equipment sector, for instance, is dominated by giants like ASML, Applied Materials, and Lam Research, but also features numerous smaller, innovative companies. In advanced packaging, competitors such as KLA Corporation and Onto Innovation are significant, alongside emerging players focused on specific technologies.
The solar equipment market, while perhaps more consolidated in certain areas, still includes a diverse set of manufacturers, including companies like CVD Equipment Corporation, EMAG, and Fujimi, each offering specialized solutions. This broad range of competitors, from established leaders to agile newcomers, underscores the intensity of rivalry Amtech navigates.
The semiconductor equipment market is poised for robust expansion, with projections indicating strong growth through 2025 and into the future. This upward trend is largely fueled by escalating demand for advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, high-performance memory, and sophisticated packaging solutions. Such broad market growth can potentially alleviate some of the intense competitive pressures among equipment manufacturers.
However, this positive outlook isn't uniform across all market segments. For instance, the market for mature node semiconductor equipment has experienced a notable slowdown, leading to heightened competition within these specific niches. Companies focusing on older technology nodes may find themselves in a more challenging environment as demand shifts towards cutting-edge capabilities.
Amtech stands out by offering specialized thermal processing, automation, coating, and wafer polishing systems. A prime example is the high demand for their advanced packaging reflow equipment, driven by the burgeoning AI sector, which highlights their product differentiation.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry, where Amtech operates, saw significant investment in advanced packaging technologies to support AI workloads. This focus on innovation is key, as companies like Amtech must continuously differentiate their offerings to avoid becoming mere suppliers of generic components in these fast-paced tech markets.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The capital equipment manufacturing sector, where Amtech operates, is inherently burdened by substantial fixed costs. These include significant investments in research and development, the establishment and maintenance of advanced manufacturing facilities, and the acquisition of highly specialized machinery. For instance, in 2024, the average R&D expenditure for leading capital equipment manufacturers reached approximately 6% of their revenue, a substantial commitment that cannot be easily recouped.
These high fixed costs, coupled with the specialized nature of assets, erect formidable exit barriers. Companies are essentially locked into the industry, as divesting specialized equipment or repurposing facilities often proves economically unfeasible. This forces players to continue competing fiercely, even when market demand softens, to spread their fixed cost base over a larger production volume.
Consequently, Amtech faces intense rivalry from established players who are similarly compelled to maintain operations. This dynamic can lead to price wars and aggressive market share battles, as companies strive to cover their substantial overheads. In 2023, the industry saw an average capacity utilization rate of 78%, indicating that many firms were pushing production to absorb fixed costs, thereby intensifying competitive pressures.
- High R&D Investment: Capital equipment firms in 2024 allocated an average of 6% of revenue to R&D, underscoring significant upfront costs.
- Specialized Assets: The industry relies on unique machinery and facilities, making asset liquidation difficult and costly.
- Forced Competition: High fixed costs and exit barriers compel companies to remain active and compete aggressively, even in slow economic periods.
- Capacity Utilization: In 2023, the sector operated at 78% capacity, highlighting the drive to cover fixed expenses through production.
Strategic Stakes and Aggressiveness of Competitors
The semiconductor and solar industries are critical for global technology advancement and energy independence, creating immense strategic stakes for all players. This high level of investment, often backed by government initiatives, fuels aggressive competition. For instance, in 2024, governments worldwide continued to pour billions into domestic semiconductor manufacturing, with the US CHIPS Act alone allocating over $52 billion to boost domestic production and research.
Competitors actively engage in aggressive tactics such as intense price wars to gain market share, particularly in the solar panel sector where margins can be thin. Rapid innovation is another hallmark, with companies constantly striving to develop more efficient chips and solar cells. Strategic alliances are also common, as seen in joint ventures for R&D or manufacturing capacity expansion, allowing firms to share costs and accelerate technological breakthroughs.
- Global Semiconductor Market Growth: Projected to reach over $700 billion in 2024, indicating intense competition for a larger share.
- Solar Energy Investment Surge: Global investment in solar power in 2023 surpassed $380 billion, driving competition among manufacturers and developers.
- Government Subsidies: Significant government support for domestic chip production and renewable energy creates a competitive landscape influenced by policy.
- R&D Expenditure: Leading semiconductor firms invest upwards of 20% of their revenue in research and development to maintain a competitive edge.
Amtech operates in highly competitive markets, facing rivals ranging from industry giants to specialized niche players. The semiconductor equipment sector, for example, is led by ASML and Applied Materials, while advanced packaging sees competition from KLA Corporation. This diverse competitive set necessitates continuous innovation and differentiation for Amtech to maintain its market position.
High fixed costs, including substantial R&D investments averaging 6% of revenue for capital equipment firms in 2024, create significant exit barriers. These costs, coupled with specialized assets, compel companies to compete aggressively to spread overheads, as seen in the 78% capacity utilization in 2023. This intensified rivalry can lead to price pressures and market share battles.
Strategic stakes are high in the semiconductor and solar industries, fueled by government initiatives like the US CHIPS Act, which allocated over $52 billion in 2024 to boost domestic chip production. Competitors employ tactics such as price wars and rapid innovation, with leading semiconductor firms investing up to 20% of revenue in R&D to gain an edge.
| Metric | 2023/2024 Data | Significance for Amtech |
| Semiconductor Equipment Market Growth | Projected robust expansion through 2025 | Opportunity for increased sales, but also intensified competition for market share. |
| Average R&D Expenditure (Capital Equipment) | ~6% of revenue in 2024 | Highlights Amtech's need for significant ongoing investment to stay competitive. |
| Capacity Utilization (Industry) | 78% in 2023 | Suggests companies are pushing production to cover fixed costs, leading to competitive pressure. |
| US CHIPS Act Funding | Over $52 billion | Indicates government support driving competition and investment in domestic semiconductor manufacturing. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Amtech's capital equipment is significant, arising from alternative manufacturing processes and materials that can achieve similar functional outcomes. For example, advancements in chip architectures or novel solar cell designs could necessitate entirely different types of processing equipment, rendering Amtech's current offerings less relevant.
Customers actively seek substitutes that deliver a better performance-to-price ratio. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, if a new chip technology offers a 15% performance increase at the same cost as Amtech's current offerings, it presents a significant threat. This constant drive for efficiency means Amtech must innovate to maintain its value proposition.
While Amtech’s customers face significant switching costs, such as re-tooling machinery and retraining staff, estimated to be in the tens of thousands of dollars for many, the allure of superior substitute technologies remains a persistent threat. For instance, advancements in additive manufacturing could potentially reduce the need for traditional CNC machining, a core area for Amtech, by offering faster prototyping and more complex part creation with lower upfront capital investment in some applications.
Technological Advancements and Disruptions
Rapid technological advancements in semiconductor and solar manufacturing pose a significant threat of substitutes for Amtech's current offerings. Innovations in materials science, for instance, could lead to entirely new methods of wafer polishing or thermal processing that bypass the need for Amtech's specialized equipment. Consider the ongoing research into advanced ceramics and composite materials that could offer superior performance characteristics in high-temperature applications, potentially displacing traditional silicon wafer processing.
Alternative energy conversion methods also represent a disruptive substitute. Breakthroughs in areas like perovskite solar cells, which can be manufactured using less energy-intensive processes than silicon-based cells, could reduce the demand for the sophisticated equipment Amtech provides for silicon wafer fabrication. For example, the global solar energy market, valued at over $240 billion in 2023, is increasingly exploring these next-generation technologies.
- Disruptive Technologies: New materials science advancements could offer alternative wafer polishing and thermal processing solutions.
- Alternative Energy: Innovations in solar cell technology, like perovskites, may reduce reliance on traditional silicon wafer processing.
- Market Impact: The growing solar market's shift towards new manufacturing methods could directly impact demand for Amtech's equipment.
Integrated Solutions by Customers or Competitors
Customers increasingly desire streamlined, end-to-end solutions. This means they might opt for a single provider offering comprehensive services or even bring certain capabilities in-house, thereby diminishing their reliance on specialized equipment suppliers like Amtech. For instance, in the industrial automation sector, a trend towards integrated robotic cells from one manufacturer reduces the need for separate component purchases.
Competitors who bundle Amtech's offerings with complementary products or services create a stronger substitute. If a rival can present a more holistic package, potentially at a competitive price point, it directly challenges Amtech's market position by offering a more convenient or cost-effective alternative for the customer's overall needs. This is particularly relevant in sectors where system integration is complex and time-consuming.
- Customer Integration: Businesses may develop internal solutions or partner with a single vendor for a complete package, bypassing specialized equipment providers.
- Competitor Bundling: Rivals offering broader product portfolios that encompass Amtech's specific systems can act as direct substitutes.
- Turn-key Solutions: The demand for ready-to-use, integrated systems reduces the market for individual, specialized components.
The threat of substitutes for Amtech's capital equipment is heightened by advancements in alternative manufacturing processes and materials. For example, new semiconductor fabrication techniques or novel solar cell designs could render Amtech's current machinery obsolete, impacting its market share. This dynamic is particularly evident in the rapidly evolving solar energy sector, where the global market reached over $240 billion in 2023, with significant investment in next-generation technologies like perovskite solar cells.
| Threat Factor | Description | Impact on Amtech | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Emergence of new materials and processes that bypass traditional equipment needs. | Reduces demand for Amtech's specialized machinery. | Additive manufacturing potentially replacing CNC machining. |
| Cost-Performance Ratio | Substitutes offering superior performance or lower cost. | Pressures Amtech to innovate or lower prices. | A new chip technology offering 15% better performance at the same cost. |
| Customer Integration Trends | Customers seeking end-to-end solutions or in-house capabilities. | Decreases reliance on specialized equipment suppliers. | Industrial automation customers opting for integrated robotic cells. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the capital equipment manufacturing space for semiconductor, advanced packaging, and solar industries demands immense capital. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development, build state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and secure a highly skilled workforce. For instance, setting up a new semiconductor fabrication equipment facility can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars.
Established players like Amtech leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, enabling lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, Amtech's production volume allowed it to negotiate bulk discounts on raw materials, a benefit inaccessible to smaller, nascent competitors. This cost advantage makes it difficult for new entrants to compete on price without substantial initial investment.
Amtech's long history and well-established brand names like BTU International, Entrepix, Inc., PR Hoffman™, and Intersurface Dynamics, Inc. are built upon a bedrock of proprietary technology and intellectual property. This deep well of innovation creates a significant barrier for potential new entrants.
Developing advanced thermal processing, automation, and coating systems comparable to Amtech's offerings demands substantial investment in research and development, often spanning many years and millions of dollars. Furthermore, navigating and overcoming existing patent protections held by Amtech and its subsidiaries presents a formidable challenge.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
Amtech's established global sales channels and deep-rooted relationships with key players in the semiconductor, advanced packaging, and solar industries present a formidable barrier to new entrants. These established connections, spanning Asia, North America, and Europe, are not easily replicated, requiring significant time and investment to build.
Securing access to these critical customer bases is a major hurdle. Newcomers must not only develop comparable technology but also invest heavily in sales infrastructure and marketing to even begin challenging Amtech's entrenched market position. For instance, Amtech’s 2023 annual report highlighted that over 85% of its revenue came from repeat customers, underscoring the strength of these relationships.
- Established Global Sales Network: Amtech boasts a comprehensive sales and support infrastructure across major manufacturing hubs, making it difficult for new entrants to match its reach.
- Long-Standing Customer Relationships: Decades of trust and collaboration with leading semiconductor, advanced packaging, and solar manufacturers create significant loyalty and switching costs for customers.
- Brand Reputation and Reliability: Amtech's reputation for quality and reliability, built over years of consistent performance, is a valuable intangible asset that new entrants struggle to build quickly.
- Access to Key Decision-Makers: Amtech has cultivated direct relationships with the key decision-makers within its target customer organizations, facilitating faster sales cycles and deeper integration.
Regulatory Hurdles and Industry Standards
The semiconductor and solar industries face significant regulatory hurdles and demanding industry standards. Companies looking to enter these markets must invest heavily in meeting stringent quality certifications and navigating complex compliance frameworks. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act continues to shape the semiconductor landscape, requiring adherence to specific manufacturing and R&D standards for companies seeking government funding. This can significantly slow down new entrants and increase their initial capital expenditure.
These regulatory and quality requirements act as a substantial barrier. Newcomers must dedicate considerable time and financial resources to ensure their products and processes align with established norms, such as those set by SEMI for semiconductors or IEC standards for solar panels. This upfront investment deters many potential competitors, thereby reducing the threat of new entrants.
- Stringent Quality Standards: Compliance with rigorous quality control is essential, impacting product reliability and market acceptance.
- Complex Regulatory Landscape: Navigating diverse national and international regulations, including those related to environmental impact and safety, is a significant challenge.
- Certification Costs: Obtaining necessary certifications, such as ISO standards or specific industry accreditations, can be a substantial financial burden for new players.
- Time-to-Market Delays: The process of meeting regulatory approvals and industry standards can extend the time it takes for new products to reach the market, impacting competitive timing.
The threat of new entrants for Amtech is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements in its target industries, particularly semiconductor equipment manufacturing. Setting up facilities can cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, creating a substantial financial barrier. Furthermore, Amtech's established economies of scale in 2024, enabling preferential raw material pricing, make it difficult for new players to compete on cost without massive initial investment.
Amtech's proprietary technology, protected by patents and years of R&D, along with its strong brand reputation for reliability, presents a formidable challenge for newcomers. These intangible assets, built through consistent performance and innovation, are not easily replicated. For instance, Amtech’s 2023 report indicated over 85% of revenue from repeat customers, highlighting customer loyalty.
The company's global sales network and deep-rooted customer relationships, cultivated over decades, act as a significant deterrent. Building comparable market access and trust requires substantial time and investment, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction. Navigating stringent industry regulations and quality standards, such as SEMI or IEC, also adds considerable cost and time to market entry in 2024.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Amtech Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and expert analyst commentary to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
