Ameren Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ameren Bundle
Ameren navigates a complex utility landscape where buyer power from large industrial customers and regulatory bodies significantly shapes pricing and service offerings. The threat of substitutes, though historically low for essential energy, is evolving with distributed generation and energy efficiency solutions. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ameren’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ameren, a major utility, sources a wide range of essential inputs, from natural gas and coal for power generation to sophisticated transmission and distribution equipment. While many of these inputs come from competitive markets, the concentration of suppliers for specialized generation components or critical maintenance services can be a significant factor. For example, a limited number of manufacturers for advanced turbine technologies could grant those suppliers considerable leverage.
Switching costs for Ameren are substantial, particularly concerning essential infrastructure and long-term fuel agreements. For instance, replacing major power generation equipment or transmission line components involves not just the purchase price but also the costs of potential operational downtime, employee retraining, and navigating complex regulatory approvals.
These high switching costs translate into a significant dependence on established suppliers for critical, high-value inputs. In 2023, Ameren's capital expenditures were approximately $4.1 billion, with a considerable portion allocated to infrastructure upgrades and new generation capacity, highlighting the scale of investment tied to supplier relationships.
Ameren's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. While the company utilizes a mix of energy sources, the substitutability of specific raw materials like coal or natural gas can be limited by existing infrastructure. For instance, specialized transportation and processing facilities are often required for different fuel types.
The ongoing transition to renewable energy sources is reshaping Ameren's supplier landscape. New suppliers for solar panels and wind turbines are emerging, diversifying the input market. However, this also introduces new dependencies on these specialized manufacturers, potentially altering supplier leverage.
Supplier's Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Ameren's core utility operations, such as electricity or natural gas distribution, is generally considered low. This is primarily because suppliers of fuel, specialized equipment, or maintenance services typically operate in distinct business models that do not align with the complex regulatory landscape and capital-intensive nature of utility provision.
For instance, a coal supplier's expertise lies in extraction and logistics, not in managing a regulated power grid or customer billing systems. Similarly, equipment manufacturers focus on product development and sales, not on operating and maintaining the infrastructure that delivers energy to millions of customers. The significant capital investment and the stringent regulatory oversight required to operate as a utility present substantial barriers to entry for most suppliers.
- Low Likelihood of Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers of fuel (coal, natural gas), equipment, and services to Ameren typically lack the strategic inclination and regulatory capacity to enter the highly regulated utility distribution sector.
- Distinct Business Models: The core competencies of Ameren's suppliers are centered around resource extraction, manufacturing, or specialized services, which are fundamentally different from the operational and regulatory demands of a utility.
- Regulatory and Capital Barriers: Entering the utility market requires substantial capital investment and navigating complex regulatory frameworks, posing significant deterrents for suppliers whose primary focus is elsewhere.
- Ameren's 2023 Revenue: Ameren reported total operating revenues of approximately $7.9 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale and complexity of its operations that suppliers would need to replicate.
Importance of Ameren to Supplier
Ameren's substantial purchasing volume makes it a critical client for many of its specialized suppliers, particularly those involved in large-scale infrastructure projects and long-term service agreements. For instance, in 2023, Ameren invested approximately $3.7 billion in capital expenditures, a significant portion of which flowed to suppliers of equipment, construction services, and technology.
The potential loss of Ameren as a customer can represent a considerable financial impact for these key suppliers, thereby granting Ameren a degree of bargaining power. This is especially true for suppliers whose revenue streams are heavily reliant on utility contracts.
However, for suppliers of more standardized or commoditized goods and services, Ameren's individual purchasing power might be less pronounced. These suppliers often serve a broader market, diminishing the impact of losing a single large client.
- Significant Customer Base: Ameren's substantial capital expenditure, such as the $3.7 billion in 2023, highlights its importance to specialized infrastructure suppliers.
- Leverage Through Dependence: Suppliers heavily reliant on Ameren's business can be influenced by the utility's purchasing decisions.
- Market Saturation Impact: The bargaining power dynamic shifts for suppliers serving a wider market with less dependence on any single utility client.
The bargaining power of Ameren's suppliers is a nuanced factor, influenced by the concentration of specialized input providers and the high switching costs associated with critical components and fuel. While Ameren's significant purchasing volume, exemplified by its $3.7 billion in capital expenditures in 2023, grants it leverage over key suppliers, the availability of substitutes for essential resources like specific fuels can be limited by existing infrastructure.
The emergence of new suppliers in the renewable energy sector is diversifying the market, but also creating new dependencies. The threat of supplier forward integration into Ameren's core utility operations remains low due to significant regulatory and capital barriers, as well as distinct business models.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Ameren |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited number of manufacturers for specialized generation components. | Can grant suppliers considerable leverage. |
| Switching Costs | High costs for replacing major equipment, downtime, retraining, and regulatory approvals. | Creates significant dependence on established suppliers. |
| Input Substitutability | Limited substitutability for specific raw materials like coal or natural gas due to infrastructure needs. | Reduces Ameren's ability to switch suppliers easily for certain inputs. |
| Purchasing Volume | Ameren's substantial capital expenditures ($3.7 billion in 2023). | Provides leverage over key suppliers reliant on its business. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low due to regulatory hurdles and distinct business models of suppliers. | Minimizes a potential competitive threat from suppliers. |
What is included in the product
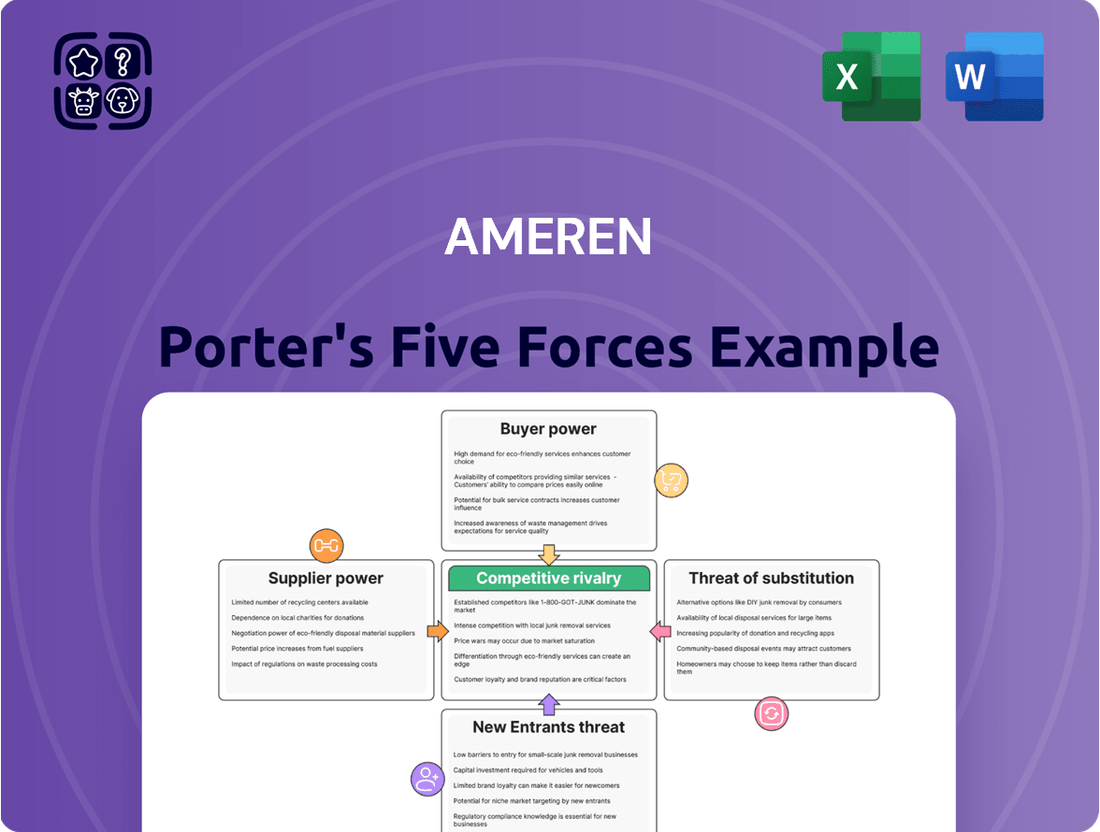
Analyzes the intensity of competition, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes impacting Ameren's utility operations.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of each force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ameren serves a massive customer base, including millions of residential, commercial, and industrial users across Missouri and Illinois. For individual residential customers, their bargaining power is practically nil. They have no individual leverage to negotiate rates or terms of service.
However, the landscape shifts for large industrial clients or major energy consumers like data centers. These entities, due to their substantial energy consumption, can exert some influence. Their sheer volume of demand gives them a degree of leverage, potentially allowing for direct negotiations or even the threat of relocating if energy costs become prohibitive.
In 2023, Ameren's electric utility operating revenue was approximately $10.5 billion. While the majority of this revenue comes from a broad base of smaller customers, the concentration of demand from a few large industrial users can still represent a significant portion of revenue from a smaller customer segment, thereby increasing their potential bargaining power.
Customer switching costs for Ameren's electricity and natural gas services are exceptionally high, effectively locking customers into their current provider. This is primarily due to the regulated, monopolistic nature of utility infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, Ameren Illinois reported serving over 1.2 million electric customers and 800,000 natural gas customers, highlighting the vast customer base reliant on their established network.
The significant investment required to establish and maintain the physical infrastructure for electricity and gas distribution means that customers cannot simply choose a different company to supply their power without substantial disruption and cost. This lack of viable alternatives severely limits the bargaining power of individual customers, as they are inherently dependent on Ameren for essential services, a situation reinforced by regional regulatory frameworks that prevent easy market entry for competitors.
While customers are largely tied to Ameren for their traditional electricity and gas supply due to regulated service territories, the availability of substitutes significantly impacts their bargaining power. These substitutes allow customers to reduce their reliance on Ameren's core offerings.
Customers can opt for rooftop solar installations, which directly compete with grid-supplied electricity. In 2023, the U.S. solar industry saw a significant growth, with residential solar capacity additions increasing by 42% year-over-year, reaching over 6.4 gigawatts. Energy efficiency measures, like improved insulation and LED lighting, also reduce demand for Ameren's services.
Furthermore, the rise of battery storage solutions, often paired with solar, provides customers with greater control over their energy consumption and the ability to store power for later use, thereby diminishing their dependence on the utility. Ameren itself acknowledges this shift by offering programs like incentives for smart thermostats, encouraging customers to actively manage their energy usage and costs.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity for Ameren is a significant factor, particularly for residential customers where energy costs represent a substantial portion of household budgets. This sensitivity often leads to robust regulatory oversight of Ameren's rate adjustments.
Large industrial and commercial clients, especially those with substantial energy demands such as data centers, exhibit high price sensitivity. Fluctuations in energy costs can directly impact their operational expenses and even influence their decisions regarding facility location and expansion.
- Residential Customer Sensitivity: In 2024, the average monthly residential electricity bill for Ameren Illinois customers was approximately $130, making price increases a notable concern for households.
- Industrial Customer Sensitivity: For large industrial users, energy costs can represent 10-20% of their total operating expenses, underscoring their keen attention to electricity pricing.
- Impact on Location Decisions: Companies considering new facilities or expansions often factor in long-term energy price stability and competitiveness when choosing a service territory.
Customer Information Availability
Customers increasingly have access to information about their energy usage and Ameren's energy efficiency initiatives. This empowers them to make more informed choices regarding their consumption patterns.
However, the bargaining power of customers is somewhat constrained by the limited availability of detailed financial and operational data from Ameren. Information regarding Ameren's specific operational costs, profit margins, and the precise cost of alternative energy supplies is not typically disclosed to individual consumers. This asymmetry of information makes it difficult for customers to engage in truly effective price negotiations or to gauge the fairness of Ameren's pricing structures.
- Limited Access to Cost Data: Customers generally cannot access Ameren's detailed operational costs or profit margins.
- Information on Efficiency Programs: Customers are informed about energy efficiency programs, potentially reducing their overall consumption.
- Asymmetric Information: The lack of transparency on Ameren's side hinders customers' ability to negotiate from a position of equal knowledge.
While individual residential customers possess very little bargaining power due to high switching costs and regulated monopolies, large industrial clients can exert influence. These major energy consumers, by virtue of their significant demand, can negotiate terms or threaten relocation, especially given that in 2024, Ameren Illinois served over 1.2 million electric and 800,000 gas customers, making these large users a concentrated segment.
The threat of substitutes, such as rooftop solar which saw a 42% year-over-year increase in residential capacity additions in the US in 2023, and energy efficiency measures, slightly empowers customers. However, Ameren's vast customer base and the high infrastructure costs for alternative energy delivery limit the overall impact of these substitutes on their core business.
Customer price sensitivity is notable, particularly for residential users where electricity bills, averaging around $130 monthly for Ameren Illinois customers in 2024, are a significant household expense. For industrial users, energy costs can represent 10-20% of operating expenses, making them highly attentive to pricing, which is a key factor in location decisions for new facilities.
Information asymmetry remains a challenge, as customers lack access to Ameren's detailed operational costs and profit margins, hindering their ability to effectively negotiate pricing despite being informed about energy efficiency programs.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | Low (High switching costs, regulated monopoly) | Approx. $130 average monthly bill (Ameren IL) |
| Industrial/Large Commercial | Moderate (High energy consumption, price sensitivity, potential relocation) | Energy costs can be 10-20% of operating expenses |
| Substitutes | Emerging (Rooftop solar, energy efficiency) | US residential solar capacity grew 42% YoY in 2023 |
Same Document Delivered
Ameren Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Ameren's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitute products. This comprehensive framework provides actionable insights into the strategic positioning of Ameren within the energy sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
In its primary service areas of Missouri and Illinois, Ameren functions as a regulated monopoly for electricity and natural gas transmission and distribution. This structure significantly limits direct competition for the same customer base within these regulated territories, meaning Ameren faces very few, if any, direct rivals for its core services.
The utility sector, where Ameren operates, generally sees steady but modest growth. However, the landscape is shifting. Electrification trends, the burgeoning demand from AI-driven data centers, and the reshoring of manufacturing are creating substantial opportunities for infrastructure upgrades and expansion.
In 2024, the U.S. electric power sector is projected to grow by approximately 1.5% to 2.0%, a solid, albeit not explosive, rate. Ameren's strategic investments in grid modernization and renewable energy integration are well-positioned to capitalize on these demand surges, potentially outperforming the industry average.
For essential utility services like electricity and natural gas, product differentiation is inherently low. Customers are primarily focused on securing reliable and affordable energy to power their homes and businesses. This means Ameren, like its competitors, competes on factors beyond the core product itself.
Ameren actively works to differentiate itself through superior service reliability and significant investments in its infrastructure. For instance, in 2023, Ameren Illinois invested approximately $1.7 billion in its energy delivery system, aiming to enhance reliability and reduce outages. These efforts, alongside a growing emphasis on sustainability initiatives, help distinguish Ameren in a market where the fundamental energy product is largely undifferentiated.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers for a large, established utility like Ameren are exceptionally high, making a complete withdrawal from its service territories practically unfeasible.
The sheer scale of capital invested in its extensive infrastructure, including power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks, represents a sunk cost that cannot be easily recouped. For instance, Ameren's 2024 capital expenditure plan alone is substantial, focusing on grid modernization and renewable energy integration, further cementing these long-term investments.
Regulatory obligations and the essential nature of providing electricity and gas services also create significant hurdles. These include franchise agreements, environmental compliance, and the societal expectation of continuous service delivery, all of which bind Ameren to its operational areas.
- Immense Capital Investment: Ameren's utility infrastructure represents billions of dollars in sunk costs, making divestiture extremely difficult.
- Regulatory Entrenchment: Franchise agreements and strict regulatory oversight prevent easy exit from service territories.
- Essential Service Nature: The critical need for reliable utility services discourages market abandonment by providers.
Diversity of Competitors
While Ameren operates in a sector with limited direct utility competitors, the landscape is increasingly shaped by indirect competition. Companies offering distributed generation, such as rooftop solar providers, and those specializing in energy storage solutions are gaining traction. These alternatives can reduce customer reliance on Ameren's traditional grid services.
Furthermore, advanced energy management systems and demand response providers represent another layer of competition. These firms help customers optimize their energy consumption, potentially lowering overall demand for Ameren's electricity supply. For instance, by 2024, the distributed solar market continued its expansion, with residential solar installations showing consistent growth year-over-year, impacting the load profiles of traditional utilities.
- Indirect Competition: Alternative energy solutions like distributed generation and energy storage.
- Energy Service Companies: Providers of advanced energy management and demand response.
- Market Trends: Growth in residential solar installations impacting traditional utility load.
- Impact: Reduced reliance on traditional grid services for consumers.
While Ameren operates as a regulated monopoly in its core transmission and distribution services, it faces indirect competition from distributed generation, such as rooftop solar, and energy storage solutions. These alternatives allow customers to reduce their reliance on traditional grid services. For example, the U.S. distributed solar market continued its expansion in 2024, with residential installations showing consistent year-over-year growth. Energy service companies offering advanced energy management and demand response also present a competitive force by helping customers optimize consumption.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Impact on Ameren | 2024 Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distributed Generation | Rooftop Solar Providers | Reduced demand for grid electricity | Continued market expansion |
| Energy Storage | Battery Storage Solutions | Customer energy independence | Growing adoption for grid services |
| Energy Service Companies | Demand Response Aggregators | Lowered peak load requirements | Increased focus on efficiency |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The improving price-performance ratio of substitutes like rooftop solar and battery storage presents a significant threat to Ameren. As the cost of these technologies continues to decline, they become increasingly competitive with traditional grid-supplied electricity.
For instance, the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) for residential solar photovoltaic (PV) systems in the US saw a notable decrease in 2023, making it a more viable option for consumers. This trend is expected to continue, further eroding the cost advantage Ameren historically held.
While these alternatives may not completely replace grid power for every customer, they can effectively reduce a customer's reliance on Ameren's services, particularly during periods of high demand. This shift can lead to decreased sales volumes and potentially lower revenue for the utility.
Customer propensity to substitute for Ameren's services is on the rise, fueled by a growing awareness of renewable energy options and a desire for greater energy independence. Government incentives further encourage this shift, making alternative solutions more attractive. For instance, the U.S. solar market saw significant growth in 2023, with residential solar installations increasing by 5% year-over-year, reaching over 6 gigawatts according to the Solar Energy Industries Association.
Ameren is proactively addressing this trend by implementing robust energy efficiency programs. These initiatives aim to help customers reduce their overall energy consumption, thereby mitigating the appeal of switching to alternative providers or self-generation. By fostering customer loyalty through cost savings and improved service, Ameren seeks to manage the threat of substitution effectively.
While the upfront cost of installing distributed generation like solar panels can be substantial, Ameren customers considering this switch often find the long-term operational savings make the initial investment a worthwhile endeavor. For instance, a residential solar installation in 2024 could range from $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives, but with potential savings on electricity bills over 25 years, the effective switching cost diminishes.
Furthermore, Ameren itself is actively working with regulators to develop frameworks that better integrate these distributed energy resources into the existing grid infrastructure. This collaboration aims to streamline the process and potentially reduce some of the technical and administrative barriers that might otherwise deter customers from adopting substitutes.
Availability of Alternative Energy Technologies
The threat of substitutes for Ameren's traditional energy services is growing due to the increasing availability and adoption of alternative energy technologies. Options like rooftop solar, wind power, and advanced battery storage systems offer consumers and businesses the ability to generate their own electricity or reduce reliance on the grid.
Ameren is actively addressing this threat by investing in its own renewable generation and energy storage projects. For instance, as of early 2024, Ameren Illinois reported significant progress in its smart grid investments, which include integrating distributed energy resources and enhancing grid resilience to accommodate these evolving technologies. This strategic move aims to capture value from the transition to cleaner energy sources and maintain its market position.
- Growing Rooftop Solar Adoption: Residential and commercial solar installations continue to rise, providing a direct substitute for grid electricity.
- Advancements in Battery Storage: Improved battery technology makes energy storage more feasible and cost-effective, enabling greater energy independence.
- Ameren's Renewable Investments: Ameren is developing projects such as the Latitude 2 Wind Farm and investing in battery storage to diversify its energy mix and compete with substitutes.
- Grid Modernization Efforts: By upgrading its infrastructure, Ameren aims to better manage distributed energy resources, potentially mitigating some of the direct substitution threat.
Regulatory and Policy Support for Substitutes
Government incentives and policies are significantly bolstering the appeal of substitutes for traditional utility services. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 provides substantial tax credits and rebates for renewable energy installations and energy efficiency upgrades, making these alternatives more financially viable for consumers and businesses. This regulatory tailwind directly encourages exploration and adoption of options that bypass or supplement conventional utility offerings.
The impact of these policies is measurable. By the end of 2023, the U.S. saw a record 39 GW of solar capacity added, a testament to the effectiveness of such support. Similarly, investments in energy efficiency programs are projected to save consumers billions annually, further enhancing the attractiveness of these substitutes.
- Government incentives, like the Inflation Reduction Act, directly lower the cost of renewable energy and efficiency solutions.
- These policies make alternatives to traditional utility services more competitive and accessible.
- The 2022 Inflation Reduction Act is a key driver, spurring significant investment in clean energy technologies.
- Increased customer adoption of these substitutes can reduce demand for Ameren's core services.
The increasing affordability and performance of distributed energy resources, particularly rooftop solar and battery storage, pose a significant threat to Ameren's traditional electricity sales. As these technologies become more cost-effective, customers have a greater incentive to generate their own power or reduce their reliance on the grid.
The levelized cost of energy for residential solar PV systems in the US continued to decline in 2023, making it a more attractive alternative. This trend is expected to accelerate, directly impacting Ameren's customer base and revenue streams.
While these substitutes may not fully displace grid power, they can significantly reduce a customer's consumption from Ameren, especially during peak demand periods. This erosion of demand is a key concern for the utility's future growth.
| Technology | 2023 US Residential Solar LCOE (approx.) | Projected 2024 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Rooftop Solar PV | $0.08 - $0.15 per kWh | Continued cost reduction, increased adoption |
| Residential Battery Storage | $0.15 - $0.30 per kWh (including installation) | Enhanced grid independence, reduced reliance on utility |
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to enter the utility sector, especially for electricity generation, transmission, and distribution, is immense. For instance, building a new large-scale solar farm can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, and a new transmission line project can easily run into billions. This massive upfront investment acts as a formidable barrier, deterring potential new competitors from entering the market.
Ameren, like other established utility companies, benefits from substantial economies of scale. This means their large operational size allows them to spread fixed costs like infrastructure and generation facilities over a vast customer base, significantly lowering the per-unit cost of electricity. For instance, in 2023, Ameren Illinois's electric delivery revenue was $3.9 billion, supporting a massive network.
New companies entering the utility market would face immense difficulty matching these cost efficiencies. Building out a comparable generation, transmission, and distribution network requires massive upfront capital investment, estimated in the billions of dollars, which is a significant barrier. Without this scale, new entrants would operate at a cost disadvantage, making it hard to compete on price with incumbents like Ameren.
Access to Ameren's established grid infrastructure is a significant hurdle for potential competitors. As of the end of 2023, Ameren Illinois reported operating over 120,000 miles of distribution lines, a vast network that new entrants would need to replicate or gain access to.
This existing infrastructure represents a substantial capital investment and a regulatory advantage, making it exceedingly difficult for new companies to deliver electricity to customers without substantial new build-outs or favorable regulatory decisions mandating grid access.
Government Policy and Regulation
The utility sector, including companies like Ameren, faces significant hurdles due to government policy and regulation. These include stringent licensing, environmental protection mandates, and operational standards that new entrants must meet. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency continued to enforce regulations like the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) for power plants, requiring substantial capital investment for compliance.
This complex regulatory environment acts as a formidable barrier. New companies must invest heavily in legal expertise and lobbying efforts to navigate the intricate web of federal, state, and local laws. The lengthy and costly process of obtaining necessary permits and approvals deters many potential competitors from entering the market.
- High Capital Requirements: Complying with environmental and safety regulations often necessitates massive upfront investments in technology and infrastructure, making it difficult for smaller firms to compete.
- Licensing and Permitting: Obtaining the necessary operating licenses and permits can be a protracted and expensive process, often involving extensive public hearings and environmental impact assessments.
- Rate Regulation: State public utility commissions have the authority to approve or deny rate increases, which can limit the profitability and return on investment for new entrants, thereby discouraging market entry.
- Environmental Compliance Costs: In 2024, the ongoing transition to cleaner energy sources meant companies faced increasing costs associated with carbon capture technologies and renewable energy integration, further raising the barrier to entry for traditional power generation.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
While customers typically don't exhibit strong brand loyalty to a specific utility due to limited choices, Ameren benefits from its established presence as a provider of essential services. Building trust and reliability in this sector, where these attributes are critical, presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. For instance, in 2023, Ameren Illinois reported a customer satisfaction score of 80%, indicating a solid foundation of trust.
New entrants would need substantial investment to replicate Ameren's infrastructure and operational track record. This includes overcoming regulatory barriers and demonstrating a commitment to service reliability, which is paramount for customers. The capital expenditure for grid modernization alone is substantial; Ameren invested over $1.7 billion in its electric and gas infrastructure in 2023.
- Established Infrastructure: Ameren operates a vast network of transmission and distribution systems, requiring immense capital to replicate.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gaining approval from state utility commissions is a lengthy and complex process for new market participants.
- Customer Trust: Decades of service build a level of trust that new companies must earn, which is time-consuming and costly.
- Reliability Expectations: Customers expect uninterrupted service, a standard that new entrants must consistently meet from day one.
The threat of new entrants for Ameren is generally low due to extremely high capital requirements and significant regulatory barriers. Building new power generation facilities or transmission lines can cost billions, a sum few new companies can readily access. Furthermore, the extensive licensing, permitting, and compliance with environmental standards, such as those enforced by the EPA in 2024, create substantial hurdles. For instance, Ameren Illinois’s 2023 capital expenditures exceeded $1.7 billion, illustrating the scale of investment needed to maintain and expand utility operations.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for Ameren (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Massive upfront investment for infrastructure (generation, transmission, distribution). | Over $1.7 billion capital expenditure by Ameren in 2023 for infrastructure. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Stringent licensing, permits, and compliance with environmental/safety standards. | Ongoing EPA regulations (e.g., NESHAP) impacting power plant operations in 2024. |
| Economies of Scale | Established companies benefit from lower per-unit costs due to large operational size. | Ameren Illinois’s $3.9 billion electric delivery revenue in 2023 supports a vast network. |
| Infrastructure Access | Replicating or gaining access to existing grid networks is difficult. | Ameren Illinois operates over 120,000 miles of distribution lines (end of 2023). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ameren is built upon a foundation of publicly available data, including Ameren's annual reports (10-K filings), investor presentations, and industry-specific reports from organizations like the Edison Electric Institute. We also incorporate data from financial news outlets and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
