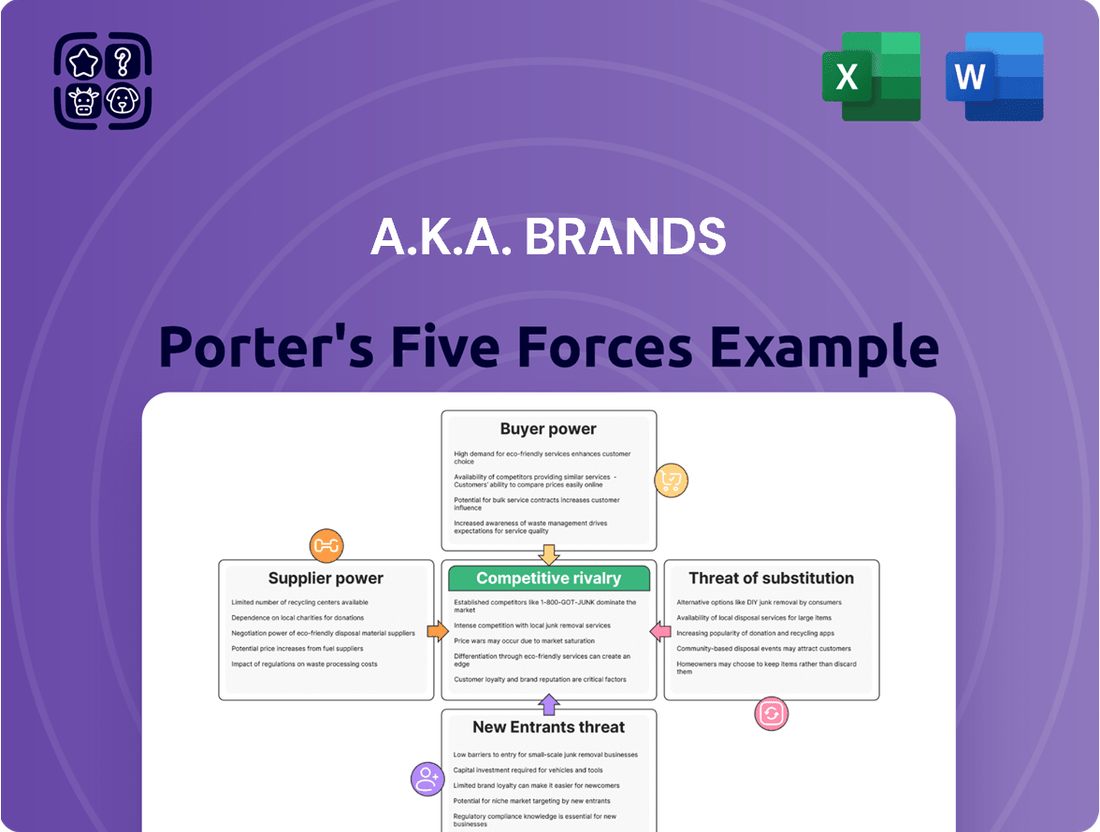
a.k.a. Brands Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
a.k.a. Brands Bundle
a.k.a. Brands faces a dynamic retail landscape, with intense competition and evolving consumer preferences. Understanding the power of buyers and the threat of new entrants is crucial for their success. Our full Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive deep dive into these pressures, offering actionable insights into a.k.a. Brands’s market position and strategic levers.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of a.k.a. Brands’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The fashion industry's intricate global supply chains, encompassing everything from raw material sourcing to final product delivery, inherently grant suppliers significant leverage. A.k.a. Brands, like many fashion retailers, navigates a complex network where specialized production needs and diverse geographical sourcing can amplify supplier bargaining power.
For instance, the reliance on specific, high-quality fabrics or unique manufacturing techniques can make it difficult to switch suppliers, thereby increasing their ability to dictate terms. In 2024, the ongoing global shipping disruptions and increased raw material costs further underscored this supplier strength, impacting lead times and production expenses for fashion companies.
a.k.a. Brands' reliance on specialized manufacturers for its fashion-forward product lines, particularly for items requiring unique materials or intricate designs, can significantly amplify supplier bargaining power. For instance, if a key manufacturer holds exclusive rights to a particular fabric or production technique crucial to a.k.a. Brands' seasonal collections, it gains considerable leverage in price negotiations and delivery timelines. This concentration of specialized capabilities among a few suppliers means a.k.a. Brands has fewer alternatives, increasing the suppliers' ability to dictate terms.
Suppliers of essential raw materials such as cotton, silk, and synthetic fibers often face significant price volatility due to global commodity market fluctuations and potential supply chain disruptions. These external forces can strengthen their negotiating position, allowing them to dictate higher prices to companies like a.k.a. Brands.
For instance, the price of cotton, a key material for many apparel brands, saw considerable swings in 2023 and early 2024, influenced by weather patterns and global demand. This volatility directly translates into increased costs for a.k.a. Brands, impacting their overall cost of goods sold and potentially their profit margins if they cannot pass these increases onto consumers.
Logistics and Technology Providers
Logistics and technology providers hold significant bargaining power over digitally-native companies like a.k.a. Brands. As a platform reliant on seamless e-commerce operations and timely delivery, a.k.a. Brands' dependence on these specialized services is substantial. For instance, in 2024, global shipping costs saw an average increase of 5-10% due to fuel price volatility and capacity constraints, directly impacting e-commerce businesses. Similarly, the demand for advanced digital marketing and platform technologies means providers of these critical services can command higher prices or dictate terms.
Key technology vendors and shipping companies, particularly those offering integrated or unique solutions, can leverage their position. This power can manifest through pricing structures, service level agreements (SLAs), and the ability to prioritize certain clients. Companies that can offer specialized logistics for fashion items or advanced e-commerce platform features can therefore exert considerable influence over a.k.a. Brands' operational costs and efficiency.
- Dependence on Specialized Services: a.k.a. Brands’ reliance on efficient logistics and cutting-edge e-commerce platforms makes it vulnerable to supplier power.
- Impact of 2024 Market Trends: Increased global shipping costs in 2024, driven by factors like fuel prices, directly translate to higher operational expenses for digitally-native retailers.
- Vendor Influence: Providers of integrated technology solutions and specialized logistics can negotiate favorable terms due to their critical role in the company's digital operations.
Switching Costs for Suppliers
Switching primary manufacturing partners for a.k.a. Brands can involve substantial costs. These costs can include expenses related to retooling, quality control recalibration, and the potential loss of established supplier relationships and their associated efficiencies. For instance, a significant shift in manufacturing could necessitate investments in new equipment or extensive training for a new workforce, impacting production timelines and budgets.
The operational disruptions associated with changing suppliers also play a critical role. A disruption can lead to temporary halts in production, delayed product launches, and a potential impact on inventory levels. This can be particularly challenging in the fast-paced fashion industry where timely delivery is crucial for meeting consumer demand and maintaining brand relevance.
- High Switching Costs: Significant financial outlay is often required to transition to new manufacturing or technology partners, including potential investments in new machinery or quality assurance processes.
- Operational Disruptions: Changing suppliers can lead to production delays, impacting inventory management and the ability to meet market demand, potentially affecting sales and customer satisfaction.
- Supplier Leverage: The presence of high switching costs empowers established suppliers, as a.k.a. Brands may be hesitant to change partners due to the associated financial and operational risks, giving suppliers more negotiating power.
Suppliers of raw materials and specialized manufacturing services hold considerable sway over a.k.a. Brands. This leverage is amplified when these suppliers possess unique capabilities or control essential inputs, making it costly and disruptive for a.k.a. Brands to switch. For example, the price of cotton, a fundamental material in apparel, experienced volatility in 2023 and early 2024, directly impacting production costs for brands like a.k.a. Brands.
The bargaining power of logistics and technology providers is also significant for digitally-native fashion retailers. a.k.a. Brands' reliance on efficient e-commerce operations and timely delivery means these service providers can command higher prices or dictate terms, especially given the 5-10% average increase in global shipping costs observed in 2024.
High switching costs, both financial and operational, further empower suppliers. The expense of retooling, recalibrating quality control, and the potential loss of established efficiencies mean a.k.a. Brands may be reluctant to change partners, thus strengthening the suppliers' negotiating position.
| Factor | Impact on a.k.a. Brands | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Price Volatility (e.g., Cotton) | Increased cost of goods sold, potential margin pressure | Observed price swings influenced by weather and demand |
| Specialized Manufacturing Capabilities | Limited supplier alternatives, increased negotiation leverage for suppliers | Reliance on unique production techniques for fashion-forward items |
| Global Shipping Costs | Higher operational expenses for e-commerce fulfillment | Average increase of 5-10% due to fuel prices and capacity constraints |
| E-commerce Platform Dependence | Vulnerability to pricing and service terms from technology providers | Critical for seamless digital operations and customer experience |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to a.k.a. Brands' direct-to-consumer fashion model.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces for a.k.a. Brands.
Customers Bargaining Power
Gen Z and millennial consumers, a.k.a. Brands' core demographic, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they actively seek value and are more likely to switch brands if a better price is available.
Data from 2024 indicates that a substantial portion of these younger demographics actively compare prices across retailers before making a purchase. For instance, a significant percentage of Gen Z shoppers reported using price comparison apps regularly in their fashion buying decisions.
This high price sensitivity empowers customers, as they can exert considerable pressure on brands like a.k.a. Brands to maintain competitive pricing or offer frequent discounts, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
The direct-to-consumer online fashion market is incredibly crowded, with countless brands and retailers vying for attention. This abundance of choice means customers can easily find very similar items from different sellers, making it simple for them to switch if they aren't satisfied.
In 2024, the global online fashion market reached an estimated $900 billion, highlighting the sheer volume of competition. With so many alternatives readily available, customers face minimal barriers to switching to a competitor, significantly increasing their bargaining power.
Customers wield considerable influence in the digital era, largely thanks to social media and online review platforms. A single negative post can go viral, impacting a brand's reputation almost instantaneously. For instance, in 2024, brands faced increasing pressure to respond to customer complaints shared on platforms like X (formerly Twitter) and Instagram, often within hours, to mitigate reputational damage.
This heightened visibility means brands must consistently deliver on quality, price, and service to satisfy customer expectations. Failure to do so can lead to widespread negative sentiment, directly affecting sales and market share. Studies from 2024 indicated that over 80% of consumers read online reviews before making a purchase, underscoring the power of peer recommendations and customer feedback.
Low Switching Costs for Consumers
For online fashion retailers like a.k.a. Brands, low switching costs for consumers significantly amplify the bargaining power of customers. The digital marketplace makes it incredibly easy for shoppers to move between different brands. In 2024, the average consumer spent approximately 2 hours and 30 minutes per day online, with a significant portion dedicated to browsing and shopping, highlighting the ease of comparison and switching.
This ease of transition means customer loyalty is a constant challenge. A.k.a. Brands must continuously offer compelling value propositions, whether through pricing, product quality, or customer experience, to retain its customer base. The ability for consumers to effortlessly compare options across numerous online platforms puts direct pressure on profit margins and necessitates agile marketing strategies.
- Minimal Effort to Switch: Consumers can change online fashion retailers with just a few clicks, eliminating significant barriers.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: Low switching costs often correlate with higher price sensitivity as consumers readily explore alternatives.
- Pressure on Loyalty Programs: Brands need robust loyalty programs to counteract the ease with which customers can defect.
- Data on Online Shopping Behavior: In 2024, e-commerce sales in the fashion sector continued to grow, underscoring the dynamic nature of online consumer behavior and the importance of customer retention.
Demand for Personalization and Experience
Modern consumers, especially younger demographics like Gen Z and millennials, are increasingly seeking personalized experiences and smooth online interactions. A 2024 study indicated that 71% of consumers expect companies to deliver personalized experiences, and 76% get frustrated when this doesn't happen. Brands that don't adapt to these demands find customers have more leverage to ask for customized products and better service.
This shift in consumer expectation directly impacts a.k.a. Brands by increasing the bargaining power of its customers. When individuals can easily find and switch to competitors offering tailored solutions, they can dictate terms more effectively. For instance, in the fashion apparel sector, where a.k.a. Brands operates, customers can readily compare offerings across numerous direct-to-consumer brands, amplifying their ability to demand unique styles and personalized attention.
- Personalization Expectation: 71% of consumers expect personalized experiences from brands in 2024.
- Frustration with Lack of Personalization: 76% of consumers express frustration when personalization is absent.
- Impact on Brand Loyalty: Failure to meet personalization demands can lead to customer attrition, increasing customer bargaining power.
- Competitive Landscape: The highly competitive direct-to-consumer fashion market allows consumers to easily switch, further empowering their demands.
Customers of a.k.a. Brands possess significant bargaining power due to the highly competitive online fashion market and their price sensitivity. The ease with which consumers can switch between brands, coupled with the influence of social media and review platforms, forces brands to maintain competitive pricing and high service standards.
In 2024, the global online fashion market's substantial size, estimated at $900 billion, underscores the intense competition. This environment allows customers to easily find alternatives, increasing their leverage to demand better prices or unique offerings.
Furthermore, a growing expectation for personalized experiences, with 71% of consumers in 2024 expecting personalization, empowers customers. Brands that fail to deliver tailored interactions face increased customer bargaining power, as consumers can readily switch to competitors who meet these demands.
| Factor | Impact on a.k.a. Brands | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Customer Price Sensitivity | High, leading to pressure on pricing and promotions. | Younger demographics actively use price comparison apps. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Low switching costs empower customers to easily move to competitors. | Global online fashion market valued at $900 billion in 2024, indicating vast choice. |
| Influence of Social Media & Reviews | Brands must manage online reputation to mitigate negative feedback. | Over 80% of consumers read reviews before purchasing in 2024. |
| Demand for Personalization | Brands need to offer tailored experiences to retain customers. | 71% of consumers expect personalization; 76% get frustrated without it (2024). |
Full Version Awaits
a.k.a. Brands Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact a.k.a. Brands Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive document delves into the competitive landscape of a.k.a. Brands, meticulously detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. You're looking at the actual document, ready for download and use the moment you buy.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The online fashion landscape is incredibly crowded, featuring a vast array of brands from massive fast-fashion retailers to small, specialized boutiques. This sheer volume of competitors means companies constantly battle for visibility and customer loyalty, making it a fiercely competitive arena.
In 2024, the global online fashion market is projected to reach over $800 billion, underscoring the intense competition as numerous entities strive to capture a piece of this lucrative, yet saturated, market. This high level of fragmentation naturally escalates rivalry, as differentiation and effective marketing become paramount for survival and growth.
Competitors in the direct-to-consumer (DTC) space, particularly those focusing on lifestyle and apparel like a.k.a. Brands, are locked in a fierce digital marketing and pricing war. Companies heavily invest in targeted social media advertising, influencer partnerships, and search engine optimization to capture consumer attention. For example, many DTC brands allocate over 30% of their revenue to marketing and customer acquisition costs.
This aggressive digital push often translates into frequent promotional pricing and flash sales. Brands use discounts and limited-time offers to drive immediate sales and build customer loyalty in a crowded online marketplace. This constant battle for visibility and sales volume can compress profit margins across the industry, forcing even well-established players to re-evaluate their cost structures and pricing models.
In many fashion segments, particularly for everyday wear and fast-fashion trends, the differences between brands are often minimal. This lack of distinctiveness means consumers can easily switch allegiance based on a lower price point or a slight variation in style, intensifying the rivalry among companies.
This low product differentiation fuels intense price competition. For instance, in 2024, the global apparel market, valued at over $1.7 trillion, sees numerous players vying for market share, with many basic apparel items being virtually interchangeable. This forces brands to compete heavily on cost, impacting profit margins.
Rapid Trend Cycles and Inventory Management
The fashion industry, a key sector for a.k.a. Brands, is characterized by extremely short trend cycles, demanding a swift response from retailers. This rapid pace means companies must constantly update their offerings to stay relevant, creating intense rivalry among players focused on speed-to-market. For instance, in 2024, many fast-fashion retailers aimed to introduce new collections weekly, a stark contrast to traditional apparel cycles.
This constant need for newness puts immense pressure on inventory management. Companies that fail to accurately forecast demand and quickly clear out older stock risk significant markdowns. The accumulation of unsold, out-of-season inventory can lead to aggressive price wars as businesses try to liquidate excess goods, directly impacting profitability and competitive positioning.
- Short Trend Lifecycles: Fashion trends can shift dramatically within months, requiring agile product development and sourcing.
- Inventory Obsolescence Risk: Holding onto last season's styles can result in substantial write-downs, as seen with many apparel retailers facing excess stock in early 2024.
- Speed-to-Market Competition: Brands are in a race to get new designs from concept to consumer, intensifying rivalry on delivery speed.
- Price Wars Triggered by Excess Stock: When inventory doesn't move, companies often resort to deep discounts, eroding margins and intensifying competitive pressures.
Emergence of New Business Models and Platforms
The fashion industry is seeing a significant shift with the emergence of new business models that directly impact competitive rivalry. Rental services and resale platforms, for instance, offer consumers alternatives to traditional purchasing, thereby intensifying competition for brands like a.k.a. Brands. These innovative models tap into growing consumer desires for sustainability and affordability.
Social commerce is another disruptive force, enabling direct-to-consumer sales through social media channels. This bypasses traditional retail structures and creates new avenues for brands and influencers to compete. For example, by mid-2024, the global social commerce market was projected to reach over $2.5 trillion, demonstrating its significant impact on retail competition.
These evolving consumption patterns challenge the established ownership-based model of fashion. Brands are compelled to innovate their strategies to remain relevant and competitive. This includes exploring their own rental or resale initiatives and enhancing their digital presence to engage with consumers on these new platforms.
- Rental Services: Companies like Rent the Runway have gained traction, offering access to designer clothing without ownership.
- Resale Platforms: Sites such as Depop and Poshmark facilitate the buying and selling of pre-owned fashion, extending product lifecycles.
- Social Commerce: Platforms like Instagram and TikTok are increasingly used for direct sales, fostering new competitive dynamics.
- Consumer Preference Shift: A 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of Gen Z consumers are interested in sustainable fashion options, including resale and rental.
The competitive rivalry within the online fashion sector, particularly for direct-to-consumer brands like a.k.a. Brands, is intense due to a highly fragmented market and the ease with which consumers can switch between numerous similar offerings. This dynamic is further fueled by rapid trend cycles and the necessity for constant product innovation, creating a high-stakes environment where speed and relevance are critical for survival.
In 2024, the global online fashion market, estimated to exceed $800 billion, reflects this fierce competition, with many brands heavily investing in digital marketing, often allocating over 30% of revenue to customer acquisition. The prevalence of price wars, driven by frequent promotions and the low differentiation of many apparel items, compresses profit margins across the industry, forcing companies to focus on cost efficiency and strategic pricing to maintain market share.
The emergence of rental services, resale platforms, and the growth of social commerce are also reshaping the competitive landscape, introducing new business models that challenge traditional ownership. These shifts, coupled with a growing consumer interest in sustainable and affordable fashion options, as indicated by over 60% of Gen Z consumers in a 2024 survey, compel brands to adapt their strategies and enhance their digital engagement to remain competitive.
| Metric | 2024 Data/Projection | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Global Online Fashion Market Size | >$800 billion | High fragmentation, intense competition for market share. |
| DTC Marketing Spend | >30% of revenue | Escalates rivalry through aggressive digital advertising and influencer marketing. |
| Trend Cycles | Weekly updates for some fast-fashion | Forces rapid product development and sourcing, intensifying speed-to-market competition. |
| Social Commerce Market Size | >$2.5 trillion | Creates new competitive avenues, bypassing traditional retail and intensifying direct-to-consumer battles. |
| Consumer Interest in Resale/Rental | >60% of Gen Z | Introduces alternative consumption models, intensifying rivalry for traditional purchasing-focused brands. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The burgeoning growth of second-hand and resale markets presents a significant threat of substitutes for brands like a.k.a. Brands. Platforms such as Depop, Poshmark, and Vestiaire Collective are increasingly popular, offering consumers, particularly Gen Z, more sustainable and budget-friendly options compared to purchasing new fashion items. This shift directly impacts demand for new products.
In 2024, the global secondhand apparel market was projected to reach $350 billion, demonstrating a substantial and growing alternative for consumers. This trend is fueled by a desire for both affordability and environmental consciousness, making it a powerful substitute for traditional retail, especially for younger demographics who are highly engaged with these platforms.
Fashion rental services, like Rent the Runway and Nuuly, present a significant threat to brands like a.k.a. Brands by offering a compelling alternative to purchasing new clothing. These platforms provide access to a wide array of garments, from everyday wear to designer pieces, on a subscription or per-rental basis. This caters to consumers who desire variety and trend-following without the commitment of ownership, directly impacting the demand for new apparel purchases.
The growing popularity of rental services is fueled by a desire for sustainability and a more budget-conscious approach to fashion. For instance, Nuuly, owned by Urban Outfitters (a.k.a. Brands' competitor), reported a significant increase in its subscriber base in recent years, indicating a strong market shift. This trend directly substitutes the need for a.k.a. Brands' customers to buy new items, especially for special occasions or to keep up with rapidly changing fashion cycles.
The rise of DIY and upcycling trends presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like a.k.a. Brands. Consumers are increasingly embracing the ability to create or modify their own apparel, a movement that gained considerable traction in 2023 and is projected to continue growing. This empowers individuals to bypass traditional retail channels, offering a personalized and often more cost-effective alternative to mass-produced fashion.
This trend directly impacts the demand for ready-to-wear clothing. For instance, a 2024 report indicated a 15% year-over-year increase in online searches for DIY fashion tutorials and upcycling techniques. This suggests a growing consumer base actively seeking to reduce reliance on brands and instead engage in creative self-expression through their wardrobes, thereby diminishing the perceived necessity of purchasing new items from traditional retailers.
Shift Towards Non-Fashion Spending
Consumers are increasingly diverting discretionary income towards non-fashion sectors like travel and technology. For instance, global spending on experiences, including travel and entertainment, saw robust growth in 2024, with many segments exceeding pre-pandemic levels. This trend means less disposable income is available for apparel and accessories, posing an indirect substitute threat.
This shift impacts the fashion industry by reducing the overall demand for new clothing purchases. Consider the rise of the wellness industry, which captured significant consumer spending in 2024, offering alternatives for discretionary budgets. This broadens the competitive landscape beyond traditional fashion rivals.
- Increased spending on experiences: Global spending on travel and leisure activities continued its upward trajectory in 2024.
- Growth in technology and wellness: These sectors are attracting substantial consumer investment, diverting funds from fashion.
- Reduced discretionary income for fashion: A larger portion of consumer budgets is allocated to these alternative categories.
Durability and Timelessness Over Fast Fashion
The growing consumer preference for durability and timelessness presents a significant threat to fast fashion brands like a.k.a. Brands. This counter-trend emphasizes quality and longevity over fleeting trends, directly challenging the core model of frequent, low-cost purchases.
Consumers increasingly choose fewer, more expensive, and long-lasting items, effectively substituting multiple fast fashion purchases with a single, sustainable investment. This shift can be seen in the rising popularity of capsule wardrobes and the resale market for high-quality apparel.
- Consumer Shift: A 2024 survey indicated that 65% of consumers are now prioritizing durability when making clothing purchases, a notable increase from previous years.
- Market Impact: The secondhand apparel market, a direct beneficiary of this trend, is projected to reach $350 billion globally by 2027, demonstrating a clear alternative to new fast fashion.
- Brand Response: Brands that fail to adapt by offering more sustainable and durable options risk losing market share to those catering to this evolving consumer demand.
The threat of substitutes for a.k.a. Brands is multifaceted, encompassing the growing secondhand market, rental services, DIY fashion, and shifts in consumer spending towards experiences and durable goods.
The secondhand apparel market's projected $350 billion valuation by 2027 highlights a significant alternative for consumers seeking value and sustainability. Rental platforms and DIY trends further fragment the market, offering consumers ways to access fashion without direct purchase.
Consumers are increasingly prioritizing durability and timelessness, a trend supported by data showing 65% of consumers valuing durability in 2024. This directly challenges the fast fashion model, pushing consumers towards fewer, higher-quality purchases or alternatives like the thriving resale market.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Data/Trend | Impact on a.k.a. Brands |
|---|---|---|
| Secondhand Apparel Market | Projected $350 billion by 2027 (growing) | Directly reduces demand for new purchases. |
| Fashion Rental Services | Increasing subscriber base (e.g., Nuuly) | Offers variety without ownership, impacting sales. |
| DIY & Upcycling | 15% YoY increase in related online searches (2024) | Empowers self-sufficiency, bypassing brands. |
| Spending on Experiences (Travel, Wellness) | Robust growth exceeding pre-pandemic levels in 2024 | Reduces discretionary income available for fashion. |
| Preference for Durability | 65% of consumers prioritize durability (2024 survey) | Shifts demand from fast fashion to long-lasting items. |
Entrants Threaten
Launching a digital-native fashion brand today demands significantly less upfront capital than traditional brick-and-mortar retail. This is because the costs associated with physical store leases, extensive staffing, and large-scale inventory procurement are largely bypassed. For example, in 2024, many successful DTC brands began with minimal inventory, utilizing pre-orders or dropshipping models to test market demand before committing to larger stock levels.
This lower capital requirement acts as a substantial magnet for new competitors. Entrepreneurs can establish an online presence, build a brand identity, and reach consumers globally with a fraction of the investment previously needed. This accessibility means that a steady stream of new, agile digital-native brands can emerge, directly challenging established players like a.k.a. Brands without needing to overcome massive financial hurdles.
The proliferation of accessible e-commerce platforms and digital marketing tools dramatically reduces the threat of new entrants. Companies like Shopify and BigCommerce empower entrepreneurs to launch online stores with minimal technical expertise, democratizing market access. In 2024, the global e-commerce market is projected to reach over $7 trillion, highlighting the vastness of the digital landscape now open to newcomers.
Social media platforms have significantly lowered the barrier to entry for new brands, offering cost-effective avenues for building awareness and customer bases. For instance, in 2024, the influencer marketing industry was projected to reach $21.1 billion, demonstrating the power of these channels in brand building without massive traditional advertising spends.
Micro-influencers, with their engaged niche audiences, and the potential for viral content, can rapidly establish brand presence. This accessibility allows new entrants to quickly gain traction, challenging established players by leveraging organic reach and community building.
Niche Market Opportunities and Specialization
The ability to target highly specific niche markets or demographics allows new entrants to sidestep direct competition with established, larger players. This focused approach enables new brands to build a strong initial presence in underserved segments before contemplating wider market penetration.
For example, in the rapidly evolving beauty industry, brands like Glossier, which began by focusing on a minimalist, digitally-native approach to skincare and makeup, successfully carved out a significant niche. By 2024, the direct-to-consumer beauty market continues to see growth, with specialized brands leveraging social media to connect with specific consumer groups, demonstrating the ongoing viability of this strategy.
- Niche Market Entry: New entrants can bypass established giants by concentrating on specialized customer segments.
- Digitalization Advantage: Online platforms and social media enable targeted outreach to niche demographics, reducing initial marketing overhead.
- Brand Loyalty: Successfully serving a niche can foster strong customer loyalty, providing a stable base for future growth.
- Market Share Acquisition: By focusing on unmet needs, new entrants can gradually capture market share without direct confrontation.
Challenges in Building Brand Loyalty and Supply Chain
Even with relatively low initial barriers to entry, new competitors find it tough to win over customers and build lasting brand loyalty in today's saturated consumer goods market. Brands like a.k.a. Brands have invested heavily in marketing and product differentiation to stand out, making it difficult for newcomers to capture significant market share quickly.
Establishing robust and ethical supply chains presents another major hurdle. New entrants must navigate complex logistics, ensure quality control, and often meet stringent sustainability standards, which require substantial capital and operational expertise to replicate the established networks of existing players.
- Brand Loyalty Challenges: Consumers often stick with brands they trust, making it hard for new entrants to gain traction without significant marketing investment or a truly disruptive offering.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Building reliable, cost-effective, and ethically sourced supply chains demands considerable upfront investment and ongoing management, a significant barrier for startups.
- Scaling Hurdles: Expanding production and distribution to meet demand while maintaining quality and competitive pricing is a persistent challenge for new companies entering established markets.
The threat of new entrants remains a significant consideration for a.k.a. Brands, although the digital landscape has lowered initial capital requirements. While it's easier than ever to launch an online store, building a recognizable brand and securing customer loyalty in a crowded market requires substantial effort and investment. For instance, the global digital advertising market was expected to exceed $800 billion in 2024, indicating the scale of spending needed to cut through the noise.
Newcomers can leverage accessible e-commerce platforms and social media marketing, as seen with the projected $21.1 billion influencer marketing industry in 2024. This allows for targeted outreach and brand building with less upfront cost compared to traditional retail. However, overcoming established brand recognition and the inherent trust consumers place in existing players is a considerable challenge.
Building a robust supply chain and achieving economies of scale are critical barriers. New entrants must invest heavily in logistics, quality control, and ethical sourcing to compete effectively. For example, the global fashion apparel market is vast, but achieving competitive pricing and consistent product availability requires significant operational expertise and capital, which can deter many potential new players.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Relevance to a.k.a. Brands |
|---|---|---|
| Low Capital Requirement (Digital) | Enables easier market entry for online-only brands. | Increases potential competition, but a.k.a. Brands benefits from existing infrastructure. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Difficult for new brands to acquire quickly. | A significant barrier for newcomers; a.k.a. Brands leverages its established customer base. |
| Supply Chain Complexity & Scale | Requires substantial investment and expertise to replicate. | A major hurdle for new entrants; a.k.a. Brands has existing supply chain relationships. |
| Marketing & Advertising Costs | High costs to gain visibility in a saturated market (e.g., digital ad spend >$800B in 2024). | a.k.a. Brands must continually invest, but new entrants face an even steeper climb. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our a.k.a. Brands Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse and reliable data sources, including company annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports.
We leverage insights from financial databases, competitor websites, and trade publications to thoroughly assess the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of a.k.a. Brands.
