AirBnB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AirBnB Bundle
AirBnB navigates a complex competitive landscape, significantly shaped by the bargaining power of its diverse customer base and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp AirBnB's strategic positioning.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves deeper, quantifying the intensity of each force and revealing the underlying dynamics that influence AirBnB's profitability and growth potential. Unlock actionable insights to navigate this dynamic market effectively.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hosts who offer truly unique, highly sought-after, or perfectly situated properties wield considerable influence. These aren't just places to stay; they're experiences that Airbnb itself struggles to replicate, making these listings cornerstones of the platform's appeal. In 2024, the demand for distinctive stays continued to grow, with unique properties often commanding premium pricing, giving their hosts a stronger negotiating position.
Hosts can easily list their properties on various platforms, including rival sites like Vrbo and Booking.com, or even their own direct booking websites. This low switching cost means they aren't locked into Airbnb, significantly boosting their leverage. For instance, a host with a property in a popular tourist destination can readily compare commission rates and booking volumes across multiple platforms to maximize their earnings.
Airbnb benefits from a highly fragmented supply of individual hosts, meaning no single host has significant leverage. This decentralization of supply is a key strength for the platform.
However, this dynamic can shift. Consider the rise of professional property managers who aggregate numerous listings. If these managers, or even large groups of independent hosts, coordinate their actions, they could collectively bargain for better terms, especially if their properties represent a significant portion of desirable inventory. For instance, if a cluster of high-end properties in a popular tourist destination were to collectively threaten to delist, Airbnb might be compelled to negotiate.
Dependence on Airbnb's Network Effects
Hosts often find their bargaining power diminished due to a significant dependence on Airbnb's vast network of users and its powerful marketing engine. This reliance means that most hosts need Airbnb to achieve optimal occupancy rates and revenue, a dynamic that inherently constrains their ability to negotiate terms.
While hosts can list their properties on multiple platforms, Airbnb's sheer volume of potential guests frequently positions it as the most lucrative and efficient channel. This creates a strong, mutually beneficial relationship, as the platform's scale directly translates into greater opportunities for hosts.
- Network Effects: Airbnb's user base, numbering in the hundreds of millions of active guests, provides hosts with unparalleled access to demand.
- Marketing Reach: Airbnb invested heavily in marketing, driving significant bookings for hosts that would be difficult to replicate independently.
- Switching Costs: While not a direct financial cost, the effort and potential loss of bookings involved in shifting focus from Airbnb to smaller competitors can be a deterrent for hosts.
Airbnb's Commission Structure and Policies
Airbnb's commission structure significantly shapes the bargaining power of its suppliers, the hosts. The service fees, which can range from 3% for hosts to 14.2% or more for guests, directly impact host earnings. Hosts have limited ability to negotiate these fees, as they are set by the platform. This dependence on Airbnb's pricing model can reduce their leverage, especially for those with fewer alternative booking channels.
The transparency of Airbnb's fee structure and the perceived value of its services are crucial factors influencing host satisfaction and their willingness to accept the terms. For instance, in 2024, Airbnb continued to refine its fee display to be more upfront with both guests and hosts. However, the ability of hosts to absorb these costs, particularly smaller or less experienced ones, remains a key determinant of their bargaining power.
- Host Fees: Airbnb typically charges hosts a flat service fee of 3% on bookings, though this can be higher for certain types of listings or in specific regions.
- Guest Fees: Guests often pay a service fee, which can vary but commonly falls between 10% and 14.2% of the booking subtotal.
- Impact on Profitability: These combined fees directly reduce the net income hosts receive from their bookings, influencing their ability to remain profitable.
- Limited Negotiation: Hosts generally have little to no power to negotiate these standard service fees directly with Airbnb.
While individual hosts generally have low bargaining power due to Airbnb's vast network and marketing reach, the situation can change for those with unique or highly desirable properties. These hosts can command higher prices and have more leverage, especially as demand for distinctive stays grew in 2024. However, the ability for hosts to collectively bargain is limited by the platform's decentralized supply model, though coordinated actions by large property managers could shift this balance.
| Factor | Impact on Host Bargaining Power | Example/Data (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Uniqueness of Property | High | Properties in prime locations or offering unique experiences often see higher occupancy and can negotiate better terms or pricing. |
| Alternative Platforms | Moderate to High | Hosts can list on Vrbo, Booking.com, or direct sites, reducing dependence on Airbnb and increasing leverage. |
| Airbnb's Network Effects | Low | Hundreds of millions of active guests provide unparalleled demand, making it difficult for hosts to replicate this reach independently. |
| Host Fees | Low | Standard 3% host fees are generally non-negotiable, impacting net income and limiting host leverage. |
What is included in the product
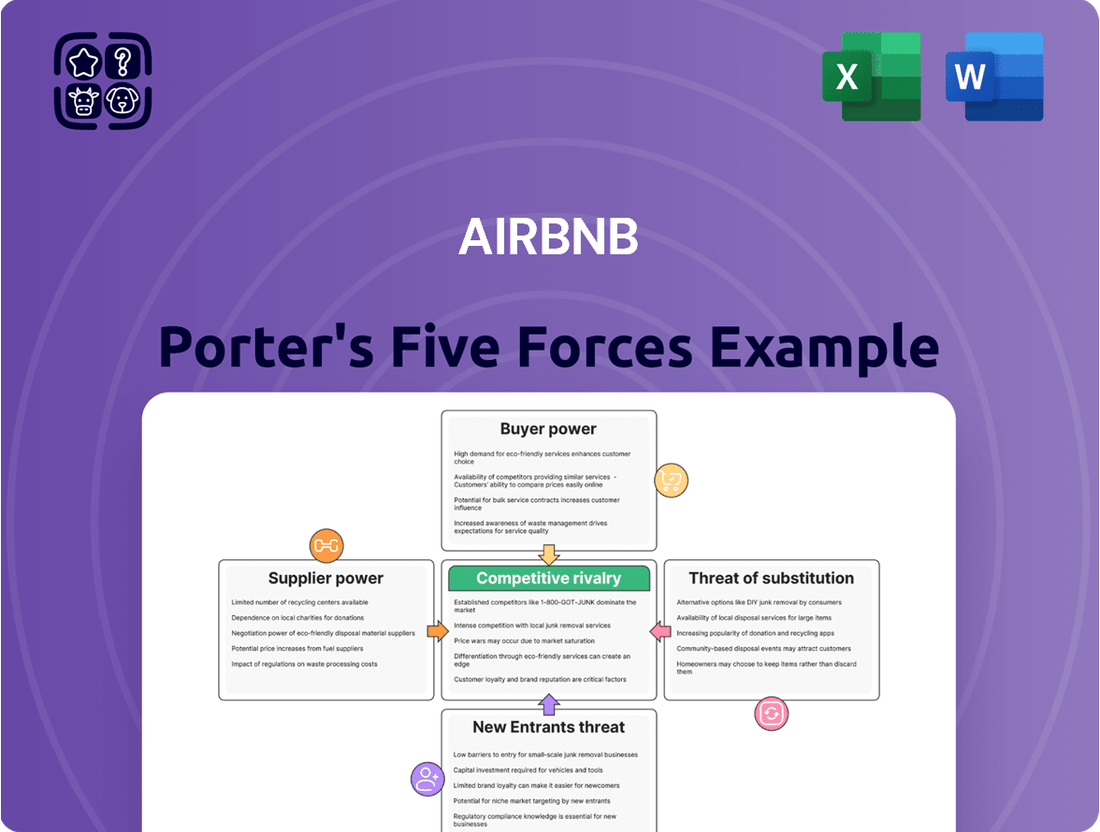
This analysis examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the short-term rental market, specifically for Airbnb.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force on Airbnb's market landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Guests, especially those traveling for leisure, often keep a close eye on their spending and will readily compare prices for accommodations. They look at different websites and even consider hotels or other lodging options before booking. This makes them quite sensitive to the overall cost.
This price sensitivity gives customers significant leverage. If they feel that Airbnb's prices or the fees associated with a booking are too high, they have the freedom to choose a less expensive option. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated that a substantial portion of travelers, upwards of 60%, consider price as their primary decision-making factor when booking accommodation, directly impacting Airbnb's pricing power.
The bargaining power of customers is notably high for Airbnb due to low switching costs for travelers. Guests can effortlessly compare and book accommodations across numerous platforms, including traditional hotels, other online travel agencies, and competing short-term rental sites, without incurring significant financial penalties or facing complex procedures. This accessibility means travelers are not tied to Airbnb, giving them considerable leverage.
The sheer volume of accommodation options available to travelers significantly boosts customer bargaining power. Guests can easily compare prices, amenities, and locations across not only Airbnb listings but also traditional hotels, hostels, and other short-term rental platforms. For instance, in 2024, the global hotel market alone is projected to reach over $620 billion, indicating a massive competitive landscape beyond just Airbnb.
Access to Information and Reviews
Guests can easily access extensive information about Airbnb listings, including detailed descriptions, high-quality photos, and crucially, reviews from past travelers. This transparency empowers them to thoroughly compare different options and make well-informed decisions.
The wealth of readily available data on Airbnb significantly boosts customer bargaining power. Travelers can scrutinize property details, amenities, and host responsiveness, leading them to expect higher quality accommodations and better value for their money.
- Informed Decision-Making: Guests can filter and sort listings based on price, location, amenities, and review scores, directly impacting their choices.
- Price Sensitivity: With easy price comparisons across numerous similar properties, guests can negotiate or opt for more affordable alternatives, putting pressure on hosts to remain competitive.
- Reputation Management: The public nature of reviews means hosts are incentivized to maintain high standards to attract future bookings, as negative feedback can deter potential customers.
Impact of Guest Reviews on Hosts
The review system on platforms like Airbnb grants guests substantial indirect bargaining power. A host's livelihood hinges on positive feedback, as guest reviews directly shape their reputation and influence future booking potential. This dynamic incentivizes hosts to prioritize exceptional service and promptly address any guest concerns to maintain high ratings.
This influence empowers guests to collectively shape the quality and standards of the entire platform. For instance, in 2024, listings with an average rating below 4.5 stars often experienced a significant drop in booking rates compared to their highly-rated counterparts. This data underscores the tangible impact of guest sentiment on a host's business success.
- Reputation Management: Guest reviews are the primary driver of a host's online reputation, directly affecting visibility and desirability.
- Service Incentives: High ratings are crucial for attracting guests, compelling hosts to offer superior experiences and amenities.
- Quality Control: The collective feedback acts as an informal quality control mechanism, pushing all hosts to meet elevated standards.
- Booking Impact: In 2024, data indicated that listings with average ratings of 4.7 stars or higher saw booking rates up to 30% higher than those with ratings below 4.0 stars.
The bargaining power of Airbnb customers is substantial due to the ease of price comparison and the availability of numerous alternatives, including hotels and other rental platforms. This ease of switching, coupled with a strong emphasis on value, allows travelers to exert significant influence over pricing and service quality.
In 2024, the vast array of lodging options available globally, with the hotel market alone exceeding $620 billion, means travelers are rarely constrained by a single provider. This broad competitive landscape directly amplifies customer leverage against platforms like Airbnb, as guests can readily find comparable or superior offerings elsewhere.
The transparency provided by detailed listings and extensive guest reviews further empowers customers. They can meticulously compare options, scrutinize amenities, and assess host responsiveness, leading to heightened expectations for quality and value, which in turn pressures hosts to deliver exceptional experiences to secure bookings.
| Factor | Impact on Airbnb Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High; customers readily compare prices and seek value. | Over 60% of travelers prioritize price in accommodation booking decisions. |
| Switching Costs | Low; easy to move between Airbnb, hotels, and other platforms. | Minimal financial or procedural barriers for travelers changing accommodation plans. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High; a wide range of lodging options exists globally. | Global hotel market projected over $620 billion in 2024, representing a massive competitive set. |
| Information Availability | High; detailed listings and reviews provide transparency. | Empowers informed decisions, driving expectations for quality and service. |
| Reputation and Reviews | Significant; positive reviews are critical for hosts. | Listings with ratings above 4.7 stars saw up to 30% higher booking rates than those below 4.0 stars in 2024. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
AirBnB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete AirBnB Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the short-term rental market. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can trust that the professionally formatted analysis, covering buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry, is ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Airbnb confronts significant competition from established Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) such as Booking.com and Expedia Group, which also operates Vrbo and HomeAway. These giants vie aggressively for dominance in the accommodation market, leveraging substantial marketing resources and widespread brand loyalty. Their offerings often encompass a broader spectrum, including traditional hotel bookings alongside vacation rentals, presenting a formidable challenge to Airbnb's model.
Traditional hotel chains, such as Marriott, Hilton, and Accor, are actively competing with Airbnb by expanding their own offerings. Many of these established brands now provide apartment-style accommodations or homes through their platforms, directly targeting guests who might otherwise choose Airbnb. This strategy leverages their existing brand recognition and operational expertise.
These hotel giants are also strengthening their direct booking channels and loyalty programs. For instance, Marriott Bonvoy and Hilton Honors offer exclusive perks and points for direct bookings, incentivizing travelers to bypass third-party platforms like Airbnb. This focus on customer retention and direct engagement presents a formidable challenge to Airbnb’s market share.
In 2024, the hotel industry continued to see robust recovery and growth, with major chains reporting strong occupancy rates and revenue per available room (RevPAR). This financial strength allows them to invest heavily in marketing, technology, and new property acquisitions, further intensifying their competitive stance against Airbnb.
While Airbnb initially defined the market for unique stays, the competitive landscape is rapidly evolving. Competitors are actively differentiating through specialized offerings, such as high-end luxury rentals, immersive eco-lodges, and unique themed accommodations, catering to distinct traveler preferences.
Emergence of niche platforms further intensifies rivalry. These platforms concentrate on specific travel segments, like adventure travel or pet-friendly stays, or particular property types, such as historic homes or beachfront villas. This specialization allows them to offer highly tailored experiences that can attract travelers seeking more curated options than a broad-based platform might provide.
For instance, platforms like Vrbo continue to focus on family-friendly vacation rentals, while others like Glamping Hub cater specifically to outdoor enthusiasts seeking unique camping experiences. This fragmentation means Airbnb faces pressure not just from direct, large-scale competitors but also from a growing number of specialized players, each vying for a distinct segment of the travel market.
Aggressive Marketing and Pricing Strategies
The short-term rental market, including players like Airbnb, sees intense competition driven by aggressive marketing and pricing. Companies frequently engage in promotional offers and pricing wars to capture market share from both hosts and guests.
Significant investments are made in digital advertising, loyalty programs, and seasonal discounts. For instance, Airbnb has historically utilized promotional offers and has seen its marketing expenses fluctuate, impacting its profitability. In 2023, Airbnb's marketing expenses were $3.7 billion, a notable increase from prior years, reflecting the competitive landscape.
- Aggressive Marketing Spend: Companies like Airbnb invest heavily in digital advertising and promotional campaigns to attract users.
- Pricing Wars: Frequent discounts and competitive pricing strategies are common tactics to gain an edge.
- Impact on Profitability: These aggressive strategies can compress profit margins across the industry.
- Loyalty Programs: Efforts to retain both hosts and guests through loyalty initiatives are a key competitive factor.
Technological Innovation and User Experience
Competitive rivalry within the online travel accommodation sector is intensely fueled by the relentless pursuit of technological innovation aimed at elevating user experience. Companies are pouring resources into developing advanced features that simplify booking, enhance discovery, and personalize travel planning for users.
This technological arms race is evident in competitors' investments in areas like AI-powered recommendations, immersive virtual property tours, and frictionless payment gateways. For instance, in 2024, many platforms are focusing on integrating generative AI to create more dynamic and tailored travel itineraries, a trend that directly pressures Airbnb to continuously upgrade its own offerings to maintain user engagement and market share.
- AI-Driven Personalization: Competitors are leveraging AI to offer highly customized travel suggestions, anticipating user needs and preferences.
- Virtual Tours: The adoption of virtual reality and 360-degree tours allows users to explore properties remotely, increasing confidence in bookings.
- Seamless Payment Systems: Innovations in payment processing aim to make transactions faster, more secure, and integrated across multiple devices.
- Feature Development: Continuous introduction of new functionalities, such as integrated local experience booking or enhanced communication tools, keeps the competitive landscape dynamic.
Competitive rivalry in the online travel accommodation market is fierce, with Airbnb facing strong challenges from established Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) like Booking.com and Expedia Group, which also own brands like Vrbo. Traditional hotel chains are also increasingly offering home-style accommodations, directly competing for Airbnb's customer base. This intense competition is further amplified by niche platforms specializing in specific travel types and the ongoing race for technological innovation, particularly in AI-driven personalization and virtual tours.
| Competitor Type | Key Players | Competitive Actions | Impact on Airbnb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Established OTAs | Booking.com, Expedia Group (Vrbo) | Aggressive marketing, broad offerings (hotels & rentals), loyalty programs | Market share pressure, need for differentiation |
| Traditional Hotels | Marriott, Hilton, Accor | Expanding home-sharing options, strengthening direct booking & loyalty programs | Direct competition for guests seeking home-like stays |
| Niche Platforms | Glamping Hub, specialized rental sites | Catering to specific traveler segments (e.g., adventure, luxury) | Fragmented market, targeting specific demand |
| Technological Innovation | Across the industry | AI recommendations, virtual tours, seamless payments | Necessity for continuous platform upgrades and feature development |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional hotels and resorts remain a significant substitute for Airbnb, particularly for business travelers or those prioritizing consistent amenities and professional service. In 2024, the global hotel industry is projected to see a strong recovery, with revenue per available room (RevPAR) expected to surpass pre-pandemic levels in many regions, indicating continued demand for this alternative.
Many travelers still value the predictability, loyalty programs, and on-site services like concierge and room service that hotels offer. This preference for a standardized and often more secure experience can limit Airbnb's appeal for certain segments of the travel market, especially those less inclined to venture into less regulated accommodation options.
For travelers prioritizing cost savings or a unique, localized experience, hostels, guesthouses, and bed and breakfasts present a significant threat to Airbnb. These alternatives often cater to budget-conscious individuals or those seeking a more communal or intimate lodging environment, directly competing for a segment of the travel market.
The appeal of these substitutes lies in their distinct offerings. Hostels, for instance, are known for their social atmosphere and affordability, with a global market valued in the billions. Guesthouses and B&Bs, on the other hand, frequently provide a more personalized service and a glimpse into local culture, which can be a strong draw for certain traveler demographics.
For travelers needing accommodation for extended periods, such as those relocating, on temporary work assignments, or students, traditional long-term rental apartments and corporate housing present significant substitutes to Airbnb. These options often offer more predictable costs and established lease terms, which can be appealing for stays exceeding a few weeks.
In 2024, the demand for long-term rentals remained robust, with national average rents for one-bedroom apartments hovering around $1,400 per month, according to various real estate data providers. Corporate housing, while typically more expensive, provides a fully serviced alternative that directly competes with Airbnb for business travelers seeking consistent amenities and services.
Camping, RVs, and Experiential Travel
For travelers prioritizing outdoor adventure or budget-conscious trips, camping and RV travel present a significant substitute to Airbnb. These options offer a different kind of immersion in nature that even Airbnb's experiences can't fully match. For instance, the U.S. National Park Service reported over 170 million recreation visits in 2023, indicating a strong demand for nature-focused travel.
These alternatives appeal to a distinct travel ethos, focusing on self-sufficiency and direct engagement with the environment. While Airbnb has expanded into experiences, the fundamental nature of staying in a tent or a mobile home provides a unique value proposition. The RV Industry Association reported a 17% increase in RV shipments in 2023 compared to 2022, signaling robust growth in this segment.
- Camping and RVs offer a more immersive outdoor experience than typical Airbnb stays.
- Budget-conscious travelers often find camping and RVing more affordable.
- The growing popularity of outdoor recreation fuels the threat from these substitutes.
- National Park visits and RV shipments show increasing consumer interest in these alternatives.
Staying with Friends and Family
The most basic substitute for paid lodging is staying with friends and family. This option carries no direct financial cost and often offers a deeply personal and comfortable experience for travelers. While not a traditional competitor, this informal arrangement effectively shrinks the pool of potential customers for all paid accommodation services, including Airbnb.
This fundamental substitute significantly impacts the addressable market for platforms like Airbnb. In 2023, a substantial portion of travel, particularly for younger demographics and budget-conscious individuals, likely still involves leveraging personal networks for accommodation. While precise figures for this specific substitute are difficult to quantify due to its informal nature, surveys consistently show that a significant percentage of travelers prioritize cost savings, making "free" lodging a powerful consideration.
- No Monetary Cost: This is the primary advantage, eliminating direct expenses for accommodation.
- Personalized Experience: Offers comfort and familiarity often unavailable in commercial settings.
- Reduced Addressable Market: Directly impacts the potential customer base for paid lodging providers.
- Demographic Appeal: Particularly attractive to younger travelers and those prioritizing budget.
The threat of substitutes for Airbnb is multifaceted, encompassing traditional hotels, hostels, long-term rentals, and even informal lodging with friends and family. While Airbnb offers unique experiences and often lower prices, these substitutes cater to different traveler needs and preferences, impacting Airbnb's market share.
Traditional hotels remain a strong substitute, especially for business travelers seeking predictability and amenities. In 2024, the global hotel industry's revenue per available room (RevPAR) is projected to exceed pre-pandemic levels, indicating sustained demand for this alternative. Hostels and guesthouses also compete, particularly with budget-conscious travelers seeking social or intimate experiences.
Long-term rentals and corporate housing serve as substitutes for extended stays, offering stability and often lower per-night costs over longer periods. For instance, national average rents for one-bedroom apartments in 2024 remained a significant factor for those needing accommodation for weeks or months. Even camping and RV travel, with a 17% increase in RV shipments in 2023, offer a distinct, nature-focused alternative that bypasses traditional lodging altogether.
| Substitute Type | Key Appeal | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Traditional Hotels | Predictability, amenities, loyalty programs | Global hotel RevPAR projected to surpass pre-pandemic levels in 2024. |
| Hostels & Guesthouses | Affordability, social atmosphere, local experience | Billions in global market value for hostels. |
| Long-Term Rentals | Cost-effectiveness for extended stays, predictable leases | National average rent for 1-bedroom apt ~$1,400/month (2024). |
| Camping & RV Travel | Immersive outdoor experience, self-sufficiency | 17% increase in RV shipments in 2023. |
| Friends & Family | No direct cost, personal comfort | Significant portion of travel, especially for budget-conscious, leverages informal lodging. |
Entrants Threaten
Building a globally recognized short-term rental marketplace, even with a digital core, demands significant capital. This investment is crucial for developing sophisticated technology, executing broad marketing campaigns to attract both hosts and guests, and establishing a reliable customer support system. For instance, Airbnb's marketing and sales expenses in 2023 were $3.9 billion, illustrating the scale of investment needed to maintain market presence.
Airbnb benefits from powerful network effects; the more hosts and guests join, the more valuable the platform becomes for everyone, a cycle challenging for new entrants to break. As of early 2024, Airbnb boasted over 5 million active hosts globally, a testament to this growing ecosystem.
The company's strong brand recognition, built on years of operation and millions of satisfied users, acts as a significant barrier. This established trust means new platforms must invest heavily in marketing and building credibility to attract users away from a familiar and reliable service.
The short-term rental market faces a growing web of regulations, from local occupancy taxes to national safety standards. For instance, in 2024, many cities continued to implement stricter rules on short-term rentals, requiring new operators to obtain specific licenses and adhere to zoning laws, which can significantly increase startup costs and operational complexity.
Difficulty in Attracting Quality Supply (Hosts)
New entrants to the short-term rental market face a significant hurdle in attracting quality hosts, particularly those offering unique or highly sought-after properties. Building a diverse and appealing inventory is crucial for competing with established players like Airbnb.
Established platforms have invested considerable time and resources in fostering host relationships and developing supportive tools. This makes it difficult for newcomers to quickly replicate the trust and value proposition that attracts top-tier hosts.
- Host Acquisition Costs: New platforms may face higher initial costs to onboard quality hosts compared to established competitors who benefit from network effects and brand recognition.
- Property Differentiation: Attracting hosts with unique properties is key, as these differentiate offerings and draw in a wider range of travelers.
- Trust and Reputation: Hosts often prioritize platforms with a proven track record and robust support systems, which new entrants lack.
Challenges in Building Trust and Safety Infrastructure
New entrants face a significant hurdle in establishing trust and safety, which is paramount in the short-term rental market. Building confidence between hosts and guests requires substantial investment in robust verification processes, comprehensive insurance policies, and responsive customer service. For instance, in 2024, platforms continue to grapple with ensuring host identity and property legitimacy, a costly but necessary endeavor to mitigate fraud and enhance user security.
The threat of new entrants is amplified by the substantial capital required to build and maintain effective trust and safety infrastructure. Without this, a new platform would struggle to attract users, especially in a market where Airbnb, a dominant player, has spent years cultivating user loyalty through its established safety protocols and dispute resolution systems. For example, the cost of implementing advanced background checks and providing adequate insurance coverage can run into millions of dollars annually for a growing platform.
- Verification Processes: New entrants must invest in rigorous identity verification for both hosts and guests, including ID checks and potentially background screenings, to build a secure environment.
- Insurance and Guarantees: Offering robust insurance for property damage and host liability is crucial, as demonstrated by industry standards that often cover millions in damages.
- Dispute Resolution: Establishing efficient and fair mechanisms for resolving conflicts between hosts and guests is vital for maintaining user satisfaction and platform reputation.
- Customer Support: Providing 24/7 customer support to handle emergencies and inquiries is a significant operational cost that new entrants must absorb to compete.
The threat of new entrants into the short-term rental market, while present, is significantly mitigated by substantial barriers to entry. These include the immense capital required for technology development, global marketing, and robust customer support, as evidenced by Airbnb's $3.9 billion in marketing and sales expenses in 2023. Furthermore, strong network effects, where more users increase platform value, and established brand loyalty, built on years of trust, make it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
The regulatory landscape also presents a considerable challenge, with increasing complexity in licensing and zoning laws in 2024, adding to startup costs and operational burdens for new players. Building a critical mass of quality hosts and differentiating property offerings requires significant investment in host relationships and supportive tools, areas where incumbents like Airbnb have a distinct advantage.
Establishing trust and safety is another major hurdle, necessitating investment in verification, insurance, and dispute resolution systems. For instance, the costs associated with comprehensive background checks and insurance coverage can easily reach millions annually, a substantial barrier for nascent platforms aiming to compete with established, trusted brands.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Developing technology, marketing, and customer support demands significant investment. | High barrier, requiring substantial funding to compete. |
| Network Effects | More hosts and guests increase platform value, creating a self-reinforcing cycle. | Difficult for new platforms to achieve critical mass and compete on value. |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Established brands have built user loyalty and confidence over time. | New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and building credibility. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Navigating diverse and evolving local and national regulations is costly and time-consuming. | Increases startup costs and operational complexity, deterring new entrants. |
| Host Relationships | Established platforms have cultivated strong ties with quality hosts. | New entrants struggle to attract and retain desirable property owners. |
| Trust & Safety Infrastructure | Robust verification, insurance, and dispute resolution are essential but expensive. | Significant ongoing investment required to ensure user security and confidence. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Airbnb leverages data from industry reports, market research firms, and competitive intelligence platforms. We also incorporate insights from financial filings, news articles, and user reviews to comprehensively assess competitive pressures.
