ACNB Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ACNB Bank Bundle
ACNB Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape, facing pressures from rivals, customer demands, and the constant evolution of banking services. Understanding these forces is crucial for any strategic decision.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping ACNB Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of core banking technology, like Fiserv, Temenos, and Finastra, wield considerable influence over ACNB Bank. Their platforms are fundamental to daily operations and ACNB's pursuit of digital advancement, meaning ACNB relies heavily on these specialized providers.
The complexity and expense associated with migrating from one core banking system to another significantly limit ACNB's ability to switch suppliers. This high switching cost reinforces the bargaining power of these technology vendors, as they offer integrated solutions crucial for improving performance and customer engagement.
The global market for banking and financial services software is robust, with key players like Fiserv and Temenos holding substantial market shares. For instance, Fiserv reported over $17 billion in revenue for 2023, highlighting their significant market presence and the critical nature of their offerings to financial institutions.
The availability of skilled financial professionals, especially those adept in digital banking, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence, acts as a significant supplier constraint for ACNB Bank. As the financial industry rapidly adopts advanced technologies to maintain a competitive edge and bolster security, the demand for specialized talent intensifies, thereby increasing the bargaining power of these skilled employees.
Community banks such as ACNB must actively compete for this limited pool of talent. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals in the banking sector saw a notable surge, with average salaries for entry-level positions in major financial hubs often exceeding $90,000 annually, reflecting the high value placed on these skills.
Depositors, essentially suppliers of capital, wield influence over banks through their ability to seek higher returns elsewhere. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Reserve maintained interest rates at elevated levels, prompting depositors to demand more competitive rates, thereby increasing a bank's cost of funds. This dynamic directly impacts a bank's net interest income, a key profitability metric.
Midsize and regional banks, in particular, have grappled with persistently high deposit costs throughout 2024. This situation squeezes their margins, as the interest paid out on deposits rises, while the income generated from loans may not keep pace. This elevated cost of capital is a significant factor in assessing the bargaining power of these capital suppliers.
ACNB Bank's strategy of utilizing brokered time deposits highlights its proactive approach to managing its funding mix. Brokered deposits, while offering flexibility, can also signal a reliance on external capital sources, which may come with higher costs compared to core retail deposits. This indicates that ACNB Bank, like many peers, is navigating the power of capital suppliers by diversifying its funding channels.
Regulatory and Compliance Service Providers
Regulatory and compliance service providers hold significant bargaining power over banks like ACNB Bank, especially given the increasingly intricate and ever-changing regulatory environment. Banks are under immense pressure to ensure adherence to new rules, particularly concerning third-party vendor management and robust data security protocols, making expert advice from these specialized firms essential. For instance, in 2024, the financial services industry continued to grapple with evolving data privacy regulations, such as those impacting cross-border data flows, directly increasing the reliance on and thus the leverage of compliance consultants.
The necessity for banks to navigate complex legislation, including new mandates on areas like digital asset regulation and cybersecurity resilience, further amplifies the bargaining power of these niche service providers. Their specialized knowledge is not easily replicated, and the penalties for non-compliance can be severe, often running into millions of dollars. In 2023, fines for regulatory breaches in the banking sector globally exceeded $5 billion, underscoring the critical need for expert guidance.
- Specialized Expertise: Regulatory and compliance service providers possess unique, in-demand skills.
- Increasing Regulatory Burden: Banks face growing complexity and scrutiny in compliance.
- High Cost of Non-Compliance: Penalties for regulatory failures are substantial.
- Data Security and Privacy Focus: New rules in these areas boost provider leverage.
Cybersecurity and Data Security Vendors
The bargaining power of cybersecurity and data security vendors is significant for ACNB Bank. Given the escalating costs and frequency of data breaches within the financial sector, companies offering robust cybersecurity and data privacy solutions hold considerable sway. For instance, the average cost of a data breach in the financial sector reached $5.90 million in 2023, according to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report.
Community banks like ACNB are increasingly focusing their investments on critical areas such as AI-driven threat detection, zero-trust security models, and comprehensive end-to-end encryption. These technologies are not just beneficial but essential for protecting sensitive customer information and preserving the bank's reputation and customer trust. The demand for these specialized services means vendors can command premium pricing and favorable contract terms.
- Rising Data Breach Costs: The financial services industry faced an average data breach cost of $5.90 million in 2023.
- Key Investment Areas: Banks are prioritizing AI-powered monitoring, zero-trust architectures, and end-to-end encryption.
- Vendor Importance: Cybersecurity vendors are crucial for safeguarding customer data and maintaining trust in the financial sector.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical factor for ACNB Bank, particularly concerning core banking technology providers and skilled labor. High switching costs for core banking systems mean ACNB is often locked into existing relationships, giving vendors significant leverage. The intense competition for specialized talent, especially in areas like cybersecurity and AI, further empowers these suppliers, driving up labor costs for the bank.
Depositors also act as suppliers of capital, and their bargaining power increased in 2024 due to elevated interest rates, forcing banks like ACNB to offer more competitive deposit rates. This directly impacts the bank's cost of funds and net interest income. Furthermore, regulatory and cybersecurity service providers wield considerable influence due to the complex and evolving compliance landscape, with substantial penalties for non-compliance amplifying their leverage.
| Supplier Type | Key Influencing Factors | Impact on ACNB Bank | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Core Banking Tech | High switching costs, system integration | Limited flexibility, reliance on vendors | Fiserv 2023 Revenue: >$17 billion |
| Skilled Labor (Cybersecurity) | High demand, specialized skills | Increased labor costs, talent acquisition challenges | 2024 Entry-level cybersecurity salaries in finance: >$90,000 |
| Depositors (Capital) | Interest rate environment, alternative returns | Higher cost of funds, pressure on margins | Federal Reserve rates elevated in 2024 |
| Regulatory Services | Complex regulations, penalties for non-compliance | Necessity for expert advice, increased service costs | 2023 global banking regulatory fines: >$5 billion |
| Cybersecurity Vendors | Rising data breach costs, essential security needs | Premium pricing for critical services | 2023 average financial sector data breach cost: $5.90 million |
What is included in the product
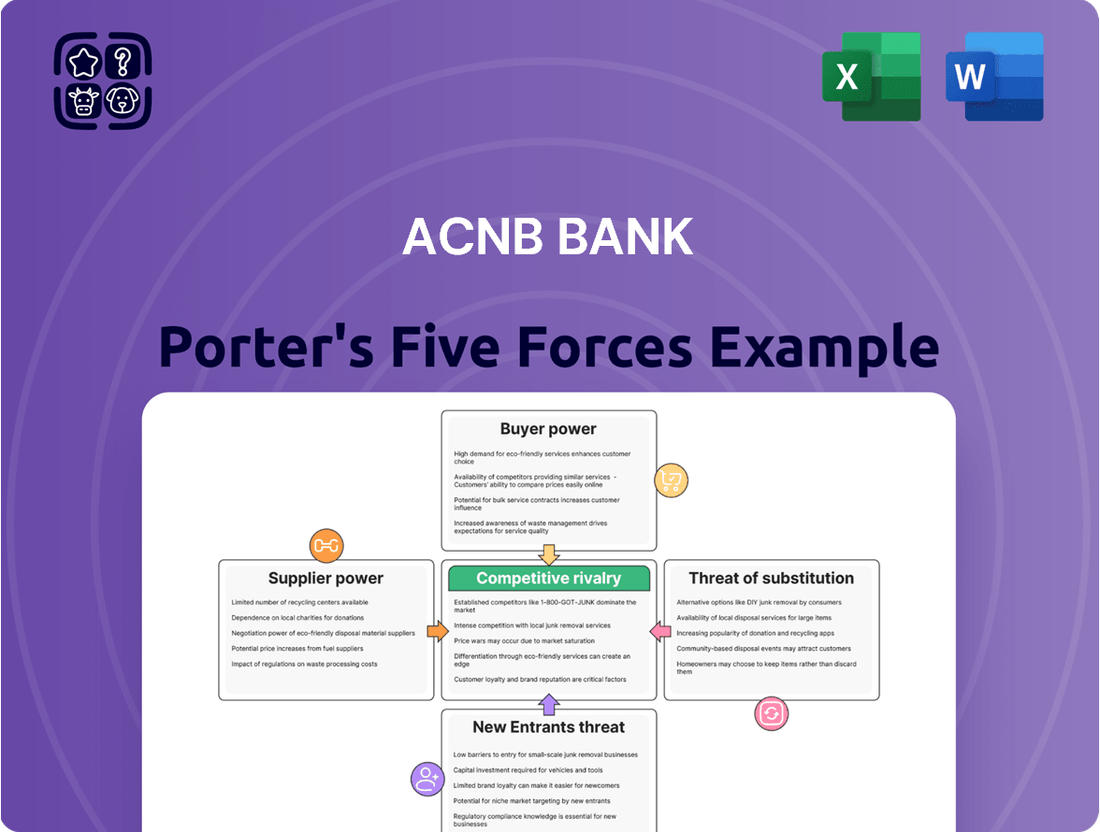
Tailored exclusively for ACNB Bank, this analysis dissects the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its market position.
Instantly identify and address competitive pressures by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces for ACNB Bank.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by low switching costs in digital banking. Traditional banking often involved significant hurdles to changing institutions, but the rise of digital-first neobanks and user-friendly online platforms has drastically reduced these barriers.
Customers can now readily transfer their accounts to banks offering better digital features or more competitive rates, directly increasing their leverage. This is especially noticeable in the current account market, where digital challengers are successfully attracting and retaining customers through superior online experiences, as evidenced by the growing market share of neobanks in many developed economies throughout 2024.
Customers now have a wealth of information at their fingertips, allowing them to easily compare financial products, services, and pricing across numerous institutions. This ease of access to data, often facilitated by online comparison platforms and readily available fee schedules, significantly strengthens their ability to negotiate favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, the growth of financial comparison websites and apps has made it simpler than ever for consumers to find the best interest rates on savings accounts or the most competitive loan terms. This transparency inherently pressures banks like ACNB Bank to maintain competitive offerings to attract and retain customers.
A significant trend is the growing customer preference for digital-first banking services. Data from 2024 indicates that a substantial percentage of consumers, especially younger demographics like millennials, actively seek out and favor digital-only banking options. This shift in preference directly increases the bargaining power of customers, as they can more easily switch to financial institutions that offer superior digital platforms.
ACNB Bank's customer base, mirroring broader industry trends, anticipates intuitive, rapid, and secure digital interactions. The expectation for seamless online and mobile banking experiences is now a baseline requirement. For ACNB Bank, meeting these evolving digital demands is crucial to retaining its customer base and mitigating the risk of losing them to competitors that are more adept at providing these digital solutions.
Hybrid Model Preference in Wealth Management
The bargaining power of customers in wealth management is amplified by a strong preference for hybrid service models. Many high-net-worth individuals in the U.S. increasingly expect a blend of personalized human advice and accessible digital tools. This demand grants them greater leverage, allowing them to select financial institutions that effectively integrate both components.
This trend means that wealth management clients can more easily switch providers if their expectations for integrated digital and personal service are not met. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of affluent investors prefer a hybrid approach, seeking both the reassurance of a human advisor and the efficiency of digital platforms. This directly translates to increased customer power, as they can shop around for the best combination of services.
- Hybrid Model Demand: A significant portion of U.S. high-net-worth individuals favor a wealth management approach that combines human financial advisors with digital tools.
- Customer Leverage: This preference empowers customers, as they can choose providers that offer seamless integration of personalized advice and convenient digital access.
- Competitive Pressure: Financial institutions like ACNB must adapt their wealth management offerings to meet this evolving client demand, facing pressure to provide comprehensive, digitally-enabled services.
- Market Shift: The growing expectation for hybrid solutions signifies a shift in client priorities, increasing their bargaining power in the wealth management sector.
Community Relationship Value vs. Price Sensitivity
ACNB Bank's community focus cultivates strong customer relationships, potentially mitigating price sensitivity. However, customers can still exert significant bargaining power if ACNB's pricing isn't competitive or if its digital services don't match those of larger banks or fintech competitors. This dynamic highlights the critical need to balance relationship value with price competitiveness.
In 2024, the banking sector continued to see heightened customer expectations for digital convenience and competitive rates. Community banks like ACNB face the challenge of meeting these demands while preserving their personalized service advantage. For instance, while ACNB might excel in personalized financial advice, a customer might still switch for a 0.50% higher interest rate on a savings account, especially if digital account management is cumbersome.
The bargaining power of ACNB Bank's customers is influenced by several factors:
- Relationship Loyalty: ACNB's emphasis on local ties and personalized service can create customer loyalty, reducing their inclination to switch purely based on price.
- Price Sensitivity: Despite loyalty, customers remain sensitive to pricing. If ACNB's loan rates or deposit yields are significantly out of step with market averages, customer bargaining power increases. For example, if the average savings account rate in ACNB's market is 2.00% and ACNB offers 1.50%, customers have a strong incentive to seek better rates elsewhere.
- Digital Competition: The rise of digital-only banks and enhanced online platforms from larger institutions means customers have more options for convenient, rate-competitive banking, thereby increasing their bargaining power against community banks.
- Switching Costs: While switching banks can involve some effort, the availability of user-friendly online onboarding processes from competitors can lower these costs, empowering customers to demand better terms.
Customers' ability to switch banks easily due to low switching costs and readily available information significantly enhances their bargaining power. This is particularly evident in the digital banking space, where neobanks and improved online platforms offer competitive rates and user-friendly experiences, as seen with the growing market share of digital challengers in 2024.
The increasing demand for hybrid wealth management models, blending personalized advice with digital tools, further empowers clients. In 2024, over 60% of affluent investors preferred this approach, enabling them to seek providers that offer the best integration of both services, thereby increasing their leverage.
While ACNB Bank benefits from strong customer relationships, price sensitivity remains a factor. If ACNB's rates lag behind market averages, such as offering 1.50% on savings when the market average is 2.00%, customers gain leverage to seek better terms elsewhere, especially with the ease of digital banking options.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Lower switching costs increase power. | Digital onboarding processes reduce effort to change banks. |
| Information Availability | Easy access to pricing and product comparisons amplifies power. | Growth of financial comparison websites and apps. |
| Digital Preference | Preference for digital services shifts power to digitally adept banks. | Substantial consumer, especially millennial, favor for digital-only banking. |
| Hybrid Service Demand (Wealth Management) | Demand for integrated human and digital advice increases client leverage. | Over 60% of affluent investors prefer hybrid models. |
| Price Sensitivity | Discrepancies in rates (e.g., savings accounts) empower customers to seek better offers. | Customers may switch for a 0.50% higher interest rate if digital management is cumbersome. |
What You See Is What You Get
ACNB Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete ACNB Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the banking industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholders. You're looking at the actual document, ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. banking sector, especially in Pennsylvania, continues to be highly fragmented. Despite a significant trend of consolidation, with a notable number of community banks merging, being acquired, or closing, ACNB Bank still contends with a large number of competitors. In 2023, the number of U.S. commercial banks fell to 4,142, a decrease from previous years, yet this still represents a substantial competitive landscape.
ACNB Bank faces rivalry not only from other community banks but also from larger regional and national financial institutions. This diverse competitive set means banks are constantly vying for customer deposits and loans, leading to intense pressure on pricing and service offerings. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, the average net interest margin for U.S. commercial banks hovered around 3.15%, a figure that can be squeezed by aggressive competition.
This ongoing consolidation, while reducing the sheer number of players, has also intensified the battle for market share among the remaining institutions. Banks are forced to innovate and operate efficiently to maintain their position. The drive for scale through mergers means that larger, more resource-rich competitors can often exert greater influence on pricing and product development, amplifying the rivalry for banks like ACNB.
Net interest margins are under significant strain, with projections for 2025 indicating a downturn driven by falling interest rates and the ongoing challenge of elevated deposit costs. This environment forces banks into a competitive battle, pushing them to offer more aggressive loan pricing and attractive deposit rates to secure and keep valuable customers.
ACNB Bank's 2024 financial performance reflects this trend, with the bank reporting a noticeable decline in its net interest income for the year.
Banks are locked in a fierce competition to excel in digital offerings, driven by customer expectations for effortless, speedy, and secure banking interactions. This ongoing pursuit of digital advancement, encompassing AI-driven personalization and instant payment solutions, heightens competitive pressures as financial institutions pour resources into staying ahead. For instance, in 2024, the global banking sector saw significant investment in digital transformation initiatives, with many banks allocating over 15% of their IT budgets to these areas to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
Competitive Landscape in Wealth Management
The wealth management arena is intensely competitive, with a diverse array of players including established banks, independent financial advisors, and increasingly, sophisticated robo-advisors. This dynamic environment means that entities like ACNB Bank must constantly adapt.
Innovation is a key driver, with artificial intelligence and predictive analytics rapidly becoming essential tools. By mid-2024, many wealth management firms reported significant investment in these technologies to enhance client service and operational efficiency.
- Intense Competition: Traditional banks, independent advisors, and robo-advisors all compete for market share.
- Rapid Innovation: AI and predictive analytics are becoming industry standards, necessitating continuous service enhancement.
- Differentiation is Key: Firms like ACNB Bank must actively differentiate their offerings to attract and retain clients.
Local Market Dynamics in South Central Pennsylvania and Maryland
ACNB Bank operates in a competitive landscape within South Central Pennsylvania and Maryland. While community banks focus on building local relationships, they contend with larger national banks that possess greater resources and broader product offerings. In 2024, credit unions continued to gain traction, appealing to consumers with their member-centric models and often lower fees, further intensifying the rivalry.
The economic health of areas like the Lehigh Valley directly impacts competitive pressures. A robust economy can attract more financial institutions and encourage existing players to compete more aggressively on pricing and services to capture market share. For instance, in 2024, the Lehigh Valley’s GDP growth of approximately 3.5% fueled increased competition among banks and credit unions vying for deposits and lending opportunities.
- Community Banks vs. Large Institutions: Local banks like ACNB emphasize personalized service, while national banks offer wider networks and digital capabilities.
- Credit Union Growth: Member-owned credit unions are increasingly attracting customers, posing a significant competitive threat.
- Regional Economic Impact: Economic vitality in areas such as the Lehigh Valley can amplify competitive intensity as more institutions seek to capitalize on growth.
ACNB Bank faces intense competition from a fragmented U.S. banking sector, particularly within its Pennsylvania and Maryland markets. This rivalry extends beyond community banks to include larger regional and national institutions, as well as growing credit unions. The drive for scale and digital innovation among competitors means ACNB must continuously adapt its services and pricing to remain competitive.
The pressure on net interest margins, exacerbated by falling interest rates and rising deposit costs, intensifies this rivalry. Banks are compelled to offer more aggressive loan pricing and attractive deposit rates to retain customers, as evidenced by ACNB Bank's reported decline in net interest income for 2024.
Digital offerings are a key battleground, with significant investments made by financial institutions in 2024 to enhance customer experience through AI and instant payment solutions. In the wealth management sector, competition is fierce, with AI and predictive analytics becoming crucial for client service and operational efficiency, a trend observed by many firms by mid-2024.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on ACNB Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Community Banks | Local relationships, personalized service | Direct competition for local market share |
| Regional/National Banks | Broader product offerings, larger resources, digital capabilities | Price competition, pressure on service breadth |
| Credit Unions | Member-centric, often lower fees | Growing threat, appeals to price-sensitive consumers |
| Robo-Advisors | Automated investment, lower overhead | Disruption in wealth management, requires digital investment |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of fintech companies and neobanks poses a substantial threat of substitutes for traditional banks like ACNB. These digital-first entities offer streamlined services, often with lower overhead and therefore lower fees, directly competing for customer deposits and transactions. For instance, neobanks like Chime have attracted millions of customers by focusing on user-friendly mobile apps and fee-free services, demonstrating a clear alternative for consumers seeking convenience and cost savings.
Credit unions are becoming a more significant threat to traditional banks like ACNB. As member-owned, nonprofit entities, they are attracting customers by offering comparable services such as checking, savings, and loans, often with more appealing rates and a focus on community engagement. This makes them a strong substitute, particularly in ACNB's local operating areas.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by credit unions expanding their reach. For instance, some credit unions have been actively acquiring banks in different states, demonstrating a growth strategy that directly challenges the market presence of established banking institutions. This trend suggests that the substitute threat is not static but is actively evolving and growing.
Alternative lending platforms, including non-bank lenders and digital innovators, present a significant threat of substitution for traditional bank loans. These platforms often provide faster loan origination and approval processes by leveraging advanced technology, appealing to borrowers who prioritize speed and convenience over established banking relationships. For instance, the online lending market saw substantial growth, with some reports indicating origination volumes in the hundreds of billions of dollars annually in recent years, demonstrating their increasing appeal.
Embedded Finance Solutions
The rise of embedded finance presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services like those offered by ACNB Bank. Digital banking functionalities are increasingly being woven directly into non-financial platforms, meaning customers can manage finances within apps they already use for shopping, travel, or healthcare, bypassing direct engagement with a bank.
This integration offers a more convenient, contextualized financial experience. For instance, a user might be able to make a purchase and arrange financing directly within an e-commerce checkout flow, or manage payments related to a travel booking without ever visiting a bank's website or app. This shift means that the need to interact with a dedicated banking interface diminishes significantly.
The market for embedded finance is growing rapidly. By 2025, it's projected that embedded finance solutions will generate over $7 trillion in global transaction volume. This indicates a substantial portion of financial activity could occur outside traditional banking channels, directly impacting customer acquisition and retention for institutions like ACNB Bank.
- Embedded finance allows consumers to access financial services within non-financial applications.
- This trend substitutes traditional banking channels by offering integrated financial solutions.
- Embedded finance is expected to reach over $7 trillion in global transaction volume by 2025.
Investment and Wealth Management Alternatives
The threat of substitutes in investment and wealth management is significant for ACNB Bank. Alternatives like independent financial advisors, robo-advisors, and direct investment platforms offer comparable services, often at lower price points.
Robo-advisors, a key substitute, are rapidly gaining traction. By 2024, the global robo-advisory market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating their appeal to a wide range of investors seeking automated, cost-effective solutions.
- Independent Financial Advisors: Offer personalized, high-touch service but can be more expensive.
- Robo-Advisors: Provide automated, algorithm-based portfolio management with lower fees, attracting digitally-savvy investors.
- Direct Investment Platforms: Allow individuals to manage their own investments without advice, appealing to self-directed investors.
- DIY Investing Apps: Further democratize access to markets, increasing the competitive landscape.
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking services remains high for ACNB Bank, driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. Fintechs and neobanks continue to offer streamlined, often lower-cost alternatives, capturing market share through user-friendly digital experiences. Credit unions are also expanding their reach, presenting a community-focused substitute with competitive offerings.
Alternative lending platforms and embedded finance solutions further diversify the substitute landscape. These options provide faster, more contextualized financial services, potentially bypassing traditional banking interactions altogether. The investment and wealth management sectors also face significant substitution threats from robo-advisors and direct investment platforms, which appeal to cost-conscious and digitally-inclined investors.
| Substitute Category | Key Players/Examples | Impact on Traditional Banks | Market Trend/Data (2024/2025 Projections) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech & Neobanks | Chime, Revolut, N26 | Customer acquisition, transaction volume | Neobanks projected to capture significant deposit market share. |
| Credit Unions | Local and regional credit unions | Deposit and loan competition, community banking | Continued growth in membership and assets. |
| Alternative Lending | Online lenders, P2P platforms | Loan origination, business financing | Online lending market volume in hundreds of billions annually. |
| Embedded Finance | BNPL providers, integrated payments | Disintermediation of banking services | Projected over $7 trillion in global transaction volume by 2025. |
| Investment & Wealth Management | Robo-advisors (Betterment, Wealthfront), Independent Advisors | Asset management, financial planning | Global robo-advisory market projected to reach hundreds of billions by 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like ACNB Bank, faces significant threats from new entrants due to high regulatory barriers and substantial capital requirements. Obtaining a bank charter is a complex and lengthy process, demanding extensive documentation and adherence to stringent compliance standards. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Reserve continued to scrutinize applications for new bank charters, with only a handful approved annually, underscoring the difficulty of entry.
Established brand loyalty and trust represent a significant barrier to entry for new banks. ACNB Bank, for instance, has cultivated decades of customer relationships, fostering a deep sense of reliability and security. This hard-won trust is not easily replicated; new entrants face the daunting task of building a comparable reputation, which requires substantial time and investment. For example, in 2024, the average customer tenure at established regional banks often exceeds ten years, a testament to the loyalty ACNB Bank likely enjoys.
Established banks like ACNB Bank often leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can spread their fixed costs, such as technology investments and branch networks, across a much larger customer base and a wider array of services than a new entrant could initially manage. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to invest billions in digital transformation, a cost that is more easily absorbed by institutions with substantial existing assets and revenue streams.
New entrants struggle to match these cost advantages. They must invest heavily to build comparable operational efficiency and market presence, often at a higher per-unit cost. This makes it difficult for them to compete on price or offer the same breadth of integrated financial solutions that incumbents can readily provide, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
Fintech Partnerships and Regulatory Scrutiny
Fintech companies often partner with established banks to navigate complex regulations, rather than entering the market independently. This collaborative approach, while common, is now under increased regulatory examination. For instance, in 2024, regulators globally continued to focus on safeguarding consumer data and ensuring fair practices within these bank-fintech arrangements.
The heightened scrutiny on these partnerships acts as a barrier for new entrants. Concerns around data privacy, cybersecurity, and compliance with evolving financial regulations mean that a purely fintech-driven entry requires significant investment in legal and compliance infrastructure. This complexity can deter potential competitors who lack the resources to meet these stringent requirements.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating financial regulations remains a significant challenge for new entrants, often necessitating partnerships.
- Increased Scrutiny: Bank-fintech collaborations face growing oversight concerning data handling and consumer protection.
- Compliance Costs: Meeting regulatory demands requires substantial investment, potentially limiting new market participants.
- Data Ownership Concerns: Ambiguities in data ownership within partnerships add another layer of regulatory complexity.
Limited New Bank Charters in Local Markets
The threat of new entrants for ACNB Bank is significantly mitigated by the scarcity of new bank charters in its primary operating regions. Specifically, in Pennsylvania, no new traditional bank has been chartered since 2013, indicating extremely high barriers to entry. This regulatory environment strongly favors established institutions like ACNB Bank.
This trend suggests that new, traditional banking competitors are unlikely to emerge and challenge ACNB Bank's market position. Instead, the banking landscape in these areas tends to see consolidation among existing players rather than the influx of new entities.
- Limited New Bank Charters: No new bank has opened in Pennsylvania since 2013.
- High Barriers to Entry: The difficulty in obtaining new bank charters creates substantial hurdles for potential competitors.
- Consolidation Favored: The market trend leans towards consolidation among existing banks rather than new market entrants.
- Established Market Position: This environment protects ACNB Bank's existing market share and stability.
The threat of new entrants for ACNB Bank is low, primarily due to the stringent regulatory environment and the high capital requirements inherent in the banking industry. Obtaining a bank charter is a complex, time-consuming process, with regulators carefully vetting applicants. For instance, in 2024, the number of new bank charters issued remained exceptionally low across the United States, reflecting these significant entry barriers.
Established brand loyalty and economies of scale further deter new competitors. ACNB Bank benefits from decades of customer trust and the ability to spread fixed costs over a larger operational base, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price or service breadth. In 2024, the average customer tenure at established regional banks often exceeded ten years, highlighting the loyalty incumbents like ACNB Bank enjoy.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex chartering process, strict compliance standards. | High difficulty and cost to enter. |
| Capital Requirements | Substantial initial investment needed. | Limits the pool of potential entrants. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Decades of customer relationships. | New entrants struggle to gain market share. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established banks. | New entrants face higher operating costs. |
| Limited New Charters (PA) | No new traditional banks chartered since 2013. | Virtually eliminates new traditional competition. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for ACNB Bank leverages data from their annual reports, investor relations disclosures, and SEC filings. We also incorporate industry-specific reports from financial analysis firms and market research data to understand competitive dynamics.
