TTEC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
TTEC Bundle
TTEC operates in a dynamic market shaped by several key forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among competitors, the bargaining power of buyers, and the influence of suppliers is crucial for grasping TTEC's strategic landscape. Furthermore, the threat of new entrants and the availability of substitute services significantly impact TTEC's long-term viability and profitability.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore TTEC’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
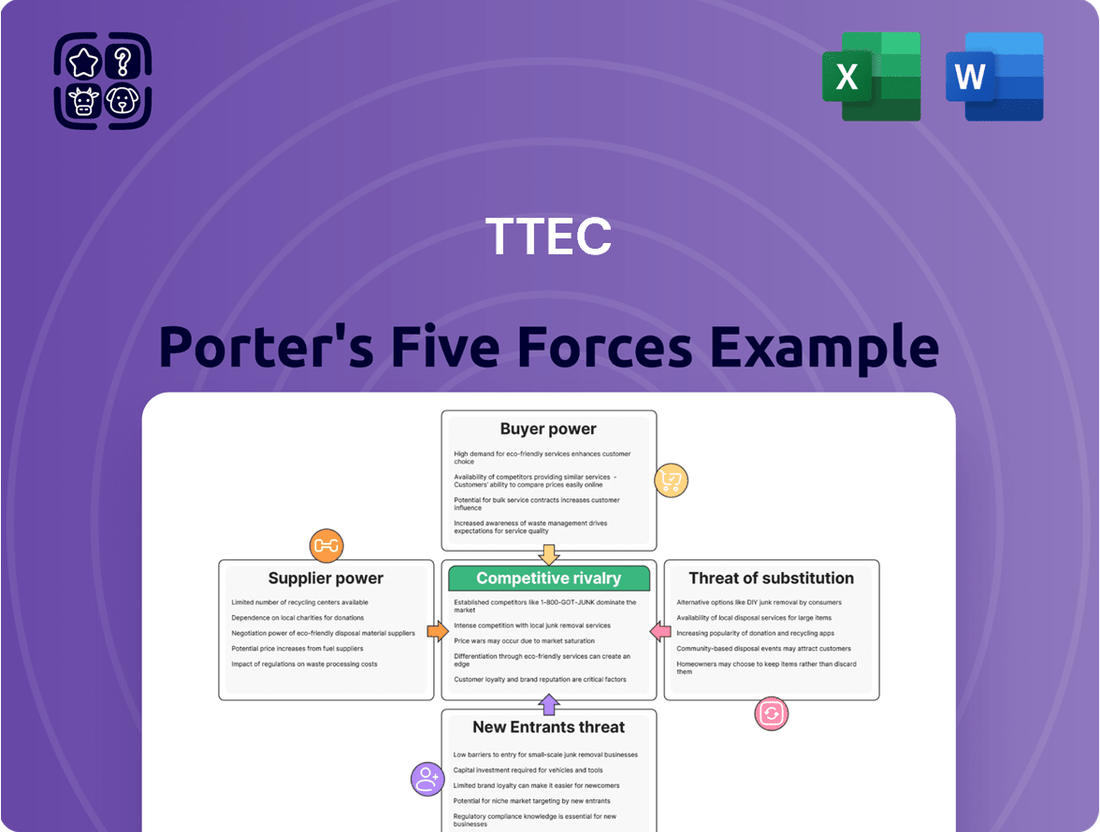
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The customer experience (CX) industry heavily relies on sophisticated technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), cloud infrastructure, and advanced CRM software. Key providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) collectively dominated over 70% of the global cloud infrastructure market in Q1 2024, according to Synergy Research Group. This market concentration gives these specialized suppliers significant leverage over pricing and terms. For TTEC, the high switching costs associated with integrating new core technology systems, including data migration and retraining, further strengthen the position of these essential providers.
TTEC's digital services heavily rely on platforms from major software vendors for critical CRM, analytics, and automation functionalities. This deep integration with a concentrated set of key partners, such as Microsoft and Salesforce, elevates their bargaining power. For instance, increased licensing fees or stricter service-level agreements from these essential suppliers can directly impact TTEC's operational costs and profitability for 2024. Such dependencies also influence TTEC's technology roadmap, potentially limiting its flexibility in adopting new solutions.
TTEC relies heavily on a large, skilled, and multilingual workforce for its customer experience services. In 2024, specialized talent like licensed healthcare professionals or advanced tech support faced tight labor markets, enhancing employee negotiation power. This dynamic directly impacts TTEC's largest operational cost, as wages and benefits constitute a significant portion of expenses. For instance, compensation and benefits typically represent over 70% of a BPO company's operating costs. This supplier power can lead to increased labor costs, affecting profitability.
Dependence on Third-Party Data Providers
TTEC's ability to deliver personalized CX solutions significantly depends on third-party data providers for crucial analytics and insights. The quality, accuracy, and cost of this external data are paramount to the effectiveness and competitiveness of TTEC's service offerings. Suppliers possessing unique or proprietary datasets, especially those leveraging advanced AI and machine learning capabilities, can exert considerable bargaining power. This influence directly impacts TTEC's operational costs and the overall quality of its client solutions, particularly as data privacy regulations continue to evolve in 2024.
- Dependency on unique data sources.
- Impact on service quality and cost structures.
- Market value of specialized data providers.
- Regulatory changes affecting data access and cost.
Real Estate and Infrastructure Suppliers
Despite the remote work trend, TTEC maintains a global footprint of physical contact centers, necessitating substantial real estate and infrastructure. In key urban markets, landlords and providers of essential utilities and telecom services wield significant bargaining power. Long-term lease agreements, often spanning 5-10 years for commercial spaces, coupled with the high cost of relocating established facilities, can create supplier lock-in for TTEC. For instance, commercial real estate rents in prime global business districts saw continued increases into 2024, impacting operational overhead.
- Real estate and utility providers hold leverage in prime locations.
- TTEC’s reliance on physical centers creates dependency on these suppliers.
- High relocation costs and long-term leases limit TTEC’s flexibility.
- Commercial real estate trends in 2024 show sustained high rental costs.
TTEC faces strong supplier bargaining power from concentrated technology providers and essential software vendors, driven by high switching costs and deep integration. The tight 2024 labor market for specialized talent significantly impacts wage costs, while reliance on unique data and rising commercial real estate rents further elevate supplier leverage. These dependencies directly influence TTEC's operational expenses and strategic flexibility.
| Supplier Type | Key Leverage | 2024 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud/Tech Vendors | Market Concentration (70%+) | Increased Infrastructure Costs |
| Software Vendors | Deep Integration | Higher Licensing Fees |
| Labor | Tight Talent Market | Rising Compensation (70%+ of Opex) |
| Real Estate | Long Leases, Prime Locations | Continued Rent Increases |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability potential for TTEC by examining industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive threats to inform strategic pivots and mitigate risks.
Customers Bargaining Power
TTEC faces high customer bargaining power due to significant client concentration. The company derives a large portion of its revenue from a limited number of major enterprise clients. As of 2022, TTEC's top 50 clients represented over 83% of its total revenue, granting these substantial customers considerable leverage. This concentration means the potential loss of even one key client could materially impact TTEC’s financial performance. Consequently, TTEC often needs to be flexible with pricing and contractual terms.
The Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) and Customer Experience (CX) market, including major players like Concentrix and Teleperformance, is highly competitive with numerous service providers as of 2024. This crowded landscape means clients face relatively low switching costs, making it simple to move to a competitor if TTEC’s pricing or service quality falters. The commoditization of many core BPO services further empowers buyers. Clients can easily leverage this broad market choice, strengthening their bargaining position against TTEC.
Price Sensitivity in a Competitive Market
Many clients view outsourced customer experience services as a significant operational expense, making them highly sensitive to pricing. The intensely competitive landscape in 2024, with numerous providers, often leads to substantial pricing pressure as clients can easily solicit bids from multiple vendors to drive down costs. This market dynamic forces TTEC to continuously prioritize operational efficiency and implement robust cost-saving measures across its service delivery. Maintaining a competitive edge in such an environment is crucial for TTEC to protect its profit margins and secure new contracts, reflecting a strong buyer influence on service pricing.
Demand for Integrated and High-Value Solutions
The bargaining power of customers intensifies as clients increasingly seek integrated, high-value solutions beyond basic call center operations. Sophisticated clients now demand end-to-end digital customer experience capabilities, pushing TTEC to continuously innovate. This shift means customers can leverage their demand for advanced features, including AI-driven analytics and comprehensive omnichannel support.
- Clients expect advanced AI integration, with market data from early 2024 showing a 30% year-over-year increase in enterprise demand for AI-powered CX solutions.
- The push for seamless omnichannel experiences requires providers like TTEC to invest heavily in unified platforms, a key client expectation in 2024.
- Customers prioritize partners capable of driving significant digital transformation, impacting TTEC's service offerings and strategic partnerships.
- This elevated demand for comprehensive solutions enables clients to negotiate more favorable terms, influencing TTEC's 2024 contract structures.
Use of AI as a Bargaining Tool
Clients are increasingly aware of the significant efficiencies AI and automation bring to customer experience operations. This knowledge empowers them to leverage AI as a bargaining tool during contract negotiations, pushing for lower prices from providers like TTEC. The expectation is that TTEC will utilize AI to reduce its own service delivery costs, putting pressure on profit margins despite necessary technology investments. For instance, clients in 2024 often expect CX cost reductions of 20-30% from AI integration.
- Clients demand lower prices, expecting AI-driven cost savings from providers.
- TTEC faces margin pressure despite investing heavily in new AI technologies.
TTEC faces significant customer bargaining power due to client concentration; its top 50 clients drove over 83% of 2022 revenue. The highly competitive 2024 CX market, with low switching costs, enables clients to demand lower prices and integrated AI solutions. Clients expect 20-30% cost reductions from AI in 2024, pressuring TTEC's margins despite innovation.
| Factor | 2024 Impact | Client Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Client Concentration | Top 50 clients: >83% revenue (2022) | High |
| Market Competition | Numerous providers, low switching costs | High |
| AI Cost Expectations | 20-30% expected CX cost savings | High |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
TTEC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete TTEC Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape within the business process outsourcing industry. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be delivered to you instantly upon purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. This comprehensive analysis details the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products/services, all as relevant to TTEC's operations. Rest assured, the document you see is the final deliverable, ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global Customer Experience (CX) and Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) market remains intensely competitive and highly fragmented, featuring a mix of large global players and numerous specialized niche providers. TTEC directly competes with industry giants such as Teleperformance, which reported over €8.3 billion in revenue in 2023, and Concentrix, with 2023 revenue exceeding $6.5 billion. This intense rivalry, amplified by the ongoing drive for digital transformation in 2024, leads to persistent price pressure and a continuous demand for service differentiation among all market participants.
Major competitors to TTEC, such as Concentrix + Webhelp and Teleperformance, offer broad service portfolios encompassing customer care, technical support, digital transformation, and consulting, leading to significant market overlap. This competitive landscape means TTEC often faces direct challenges across multiple service lines, intensifying the rivalry. As of early 2024, the lack of substantial differentiation in core offerings pushes competition heavily towards pricing strategies and operational scale. For instance, in the global customer experience (CX) services market, firms with over $5 billion in annual revenue, like TTEC, frequently vie for the same large enterprise contracts. This similarity in service scope necessitates continuous innovation to avoid becoming a commodity.
The customer experience (CX) industry is undergoing significant consolidation, with strategic acquisitions driving competitive rivalry. In 2024, companies like TTEC face heightened pressure as rivals expand capabilities; for instance, Concentrix completed its merger with Webhelp in 2023, creating a global CX giant with over 440,000 employees. This trend sees competitors acquiring smaller tech firms to bolster AI and digital offerings, directly challenging TTEC's market position. Such moves necessitate TTEC to innovate rapidly or pursue similar strategic partnerships to maintain its competitive edge and global footprint in a consolidating market.
Competition from In-House Operations
TTEC faces significant competitive rivalry from potential clients opting to manage their customer experience operations internally. Companies often weigh the costs and benefits of outsourcing against maintaining in-house control, demanding TTEC demonstrate clear advantages in efficiency, service quality, and advanced technological capabilities. This constant threat of clients insourcing their CX functions, rather than renewing or initiating contracts, represents a persistent competitive pressure. For instance, a 2024 industry report noted that approximately 35% of large enterprises considered bringing previously outsourced IT/CX functions back in-house to enhance data control and brand consistency.
- In-house operations offer greater control over data security and brand messaging.
- Clients assess outsourcing providers like TTEC based on tangible cost savings and quality improvements.
- The potential for insourcing creates a continuous need for TTEC to innovate and demonstrate value.
- Approximately 35% of large enterprises considered insourcing IT/CX functions in 2024 for enhanced control.
Emergence of AI-Driven Tech Firms
The emergence of AI-driven tech firms significantly intensifies competitive rivalry for TTEC. The rise of generative AI introduces new, technology-focused competitors specializing in AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants. Companies like Zendesk, with its Q3 2024 revenue reaching approximately $410 million, are increasingly competing in the CX solutions space, challenging the traditional labor-intensive models of BPO providers. This shift demands TTEC to rapidly integrate advanced AI capabilities to maintain its market position.
- Global AI in CX market projected to grow over 25% annually through 2024.
- Leading AI CX software providers saw revenue growth exceeding 20% in early 2024.
- Customer service interactions handled by AI are expected to rise significantly by 2025.
- Digital-first CX solutions are attracting substantial investment in 2024.
TTEC faces intense rivalry in the fragmented CX/BPO market, competing with giants like Teleperformance and Concentrix, which reported 2023 revenues of €8.3B and >$6.5B. This rivalry, amplified by market consolidation and the 2024 digital transformation push, drives price pressure and demands constant differentiation. The threat of clients insourcing operations (35% considered it in 2024) and the rise of AI-driven competitors further intensify the landscape, compelling TTEC to innovate rapidly.
| Metric | 2023 (B) | 2024 Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teleperformance Revenue | €8.3 | Digital focus | ||
| Concentrix Revenue | $6.5+ | Consolidation | ||
| Clients Considering Insourcing | N/A | ~35% |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute threat for TTEC comes from the increasing sophistication of AI-powered self-service tools, including intelligent chatbots and virtual agents. These technologies are becoming highly capable of handling complex customer queries, directly replacing the need for human agents. For example, the global conversational AI market is projected to reach over $18 billion by 2024, indicating a rapid adoption rate. As businesses increasingly automate customer interactions, a core part of TTEC's service offerings faces direct substitution, potentially reducing demand for their human-centric solutions.
A primary substitute for TTEC clients is establishing in-house customer experience operations. Companies often opt for this path to ensure greater brand alignment, tighter control over processes, and enhanced data security, especially given the rising focus on data privacy in 2024. This internal capability represents a constant and fundamental alternative, capping the growth potential for the entire Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) industry. Even with the global BPO market projected to reach approximately $300 billion in 2024, the in-house option remains a competitive consideration for enterprises.
The rise of direct-to-consumer engagement platforms presents a growing substitute threat to TTEC. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) providers, notably Salesforce and Zendesk, offer comprehensive tools that empower businesses to manage customer interactions directly. These platforms allow companies to build their own customer service infrastructure, reducing the dependency on full-service outsourcing partners like TTEC. For instance, the global customer experience management market, including these platforms, continues its strong growth into 2024, emphasizing this shift towards in-house capabilities.
Gig Economy Customer Service Platforms
The rise of the gig economy introduces a significant threat of substitution for TTEC, as platforms now directly connect businesses with freelance customer service agents. This model provides substantial flexibility and a potentially lower-cost alternative, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises or those with fluctuating service demands, effectively bypassing the need for a traditional, large-scale BPO provider. In 2024, the global gig economy market reached an estimated $455 billion, reflecting its growing appeal for agile staffing solutions.
- Cost savings: Businesses can often reduce customer service expenses by 30-50% using gig platforms versus traditional BPO.
- Flexibility: Access to on-demand agents scales easily with peak or off-peak business cycles.
- Market share: Smaller businesses often opt for gig solutions due to lower barriers to entry.
- Talent pool: Broad access to specialized customer service skills globally without long-term commitments.
Peer-to-Peer Support Communities
Peer-to-peer support communities present a growing threat of substitution for TTEC. In industries like technology and gaming, companies can cultivate online forums where customers assist each other with issues, reducing the need for traditional outsourced support. While not a complete replacement, these well-managed communities can significantly deflect a substantial volume of routine inquiries, acting as a partial substitute for TTEC's services. This trend impacts TTEC's potential revenue streams by reducing the scope of outsourced customer interactions.
- By 2024, many tech companies emphasize self-service and community forums to manage common customer queries.
- These platforms can handle up to 20-30% of typical support requests, lessening reliance on external providers.
- The rise of AI-powered chatbots further enhances the efficiency of these community-driven support models.
- For TTEC, this means a shrinking pool of basic support tasks, pushing focus towards complex, high-value interactions.
TTEC faces significant substitute threats from advanced AI self-service tools and direct-to-consumer SaaS platforms, enabling businesses to manage customer interactions internally. The gig economy offers flexible, lower-cost freelance support, while peer-to-peer communities deflect routine inquiries. These alternatives, often leveraging 2024 market trends, reduce reliance on traditional BPO services, capping TTEC's growth.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Market Data | Impact on TTEC |
|---|---|---|
| Conversational AI | >$18B | Replaces human agents |
| Gig Economy | ~$455B | Offers flexible, low-cost labor |
| In-House BPO | ~$300B (BPO Market) | Preferred for control/security |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a global customer experience operation like TTEC's demands substantial capital, acting as a significant barrier for new entrants. Building and equipping contact centers, investing in secure, scalable IT infrastructure, and recruiting a workforce of thousands requires immense upfront investment. For instance, the global customer experience management market was projected to reach over $11 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of necessary technology and infrastructure spending. New players would need significant capital to compete with established giants like TTEC, which reported over $2.4 billion in revenue in 2023, showcasing their operational scale.
Established players like TTEC benefit significantly from economies of scale, which allows them to offer competitive pricing and maintain profitability. New entrants face substantial hurdles matching the optimized cost structures of incumbents, refined over decades through process efficiency and global resource allocation. For instance, TTEC’s reported revenue for Q1 2024 was $561.4 million, showcasing their operational scale. This cost advantage makes it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to compete effectively on price in the customer experience (CX) sector.
TTEC, as an established incumbent, benefits from decades of building strong brand recognition and deep relationships with large enterprise clients. New entrants face significant hurdles in replicating this trust, especially when major corporations seek stability for multi-year contracts. For instance, TTEC's average client tenure often extends beyond five years, with many relationships lasting over a decade, reflecting the difficulty for new providers to secure such long-term commitments. Building the necessary track record and proven performance to win over Fortune 500 companies, which prioritize reliability, is a substantial barrier to entry in 2024.
Access to a Skilled Global Labor Pool
New entrants face a significant hurdle in accessing a skilled global labor pool, a complex operational challenge involving sourcing, training, and managing a diverse workforce across many countries and languages. Established players like TTEC have well-developed recruitment and training processes, alongside a presence in key labor markets, giving them a distinct advantage. A new entrant would need to build this intricate human resource infrastructure from scratch, demanding substantial time and investment. For example, the global talent shortage remained a concern in 2024, with various sectors reporting difficulty in finding qualified personnel.
- Global talent acquisition presents high initial costs for new firms.
- Established firms possess robust training and development programs.
- Building a global HR infrastructure requires significant time and capital.
- Expertise in diverse labor laws and cultural nuances is essential.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The customer experience (CX) industry faces significant regulatory and compliance hurdles, making it tough for new companies to enter. Established players like TTEC navigate a maze of complex data privacy and security regulations, including the stringent GDPR and various industry-specific rules, such as those in healthcare.
New entrants must build substantial legal and operational expertise to manage these diverse requirements across multiple jurisdictions. For instance, cumulative GDPR fines exceeded €4 billion by early 2024, highlighting the severe penalties for non-compliance. This regulatory burden necessitates significant upfront investment in compliance infrastructure and specialized staff.
- GDPR fines surpassed €4 billion by early 2024.
- Average data breach cost was $4.45 million in 2023.
- Compliance requires deep legal and operational expertise.
- Industry-specific regulations (e.g., healthcare) add complexity.
New entrants face significant hurdles due to the high capital required for global infrastructure and technology, exemplified by the $11 billion CX market in 2024. Established firms like TTEC benefit from economies of scale and deep client relationships, with average client tenures often exceeding five years. Navigating complex global regulatory compliance, including GDPR fines over €4 billion by early 2024, adds substantial cost and expertise barriers for newcomers. Building a skilled global workforce from scratch is also a major challenge.
| Barrier Type | Key Metric (2024) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Global CX Market: >$11 Billion | High upfront costs for infrastructure & tech. |
| Client Relationships | TTEC Client Tenure: >5 Years | Difficulty in securing long-term contracts. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Cumulative GDPR Fines: >€4 Billion | Significant legal and operational burden. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our TTEC Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of robust data, drawing from TTEC's annual reports, investor presentations, and publicly available financial statements. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and competitive intelligence from reputable sources.
