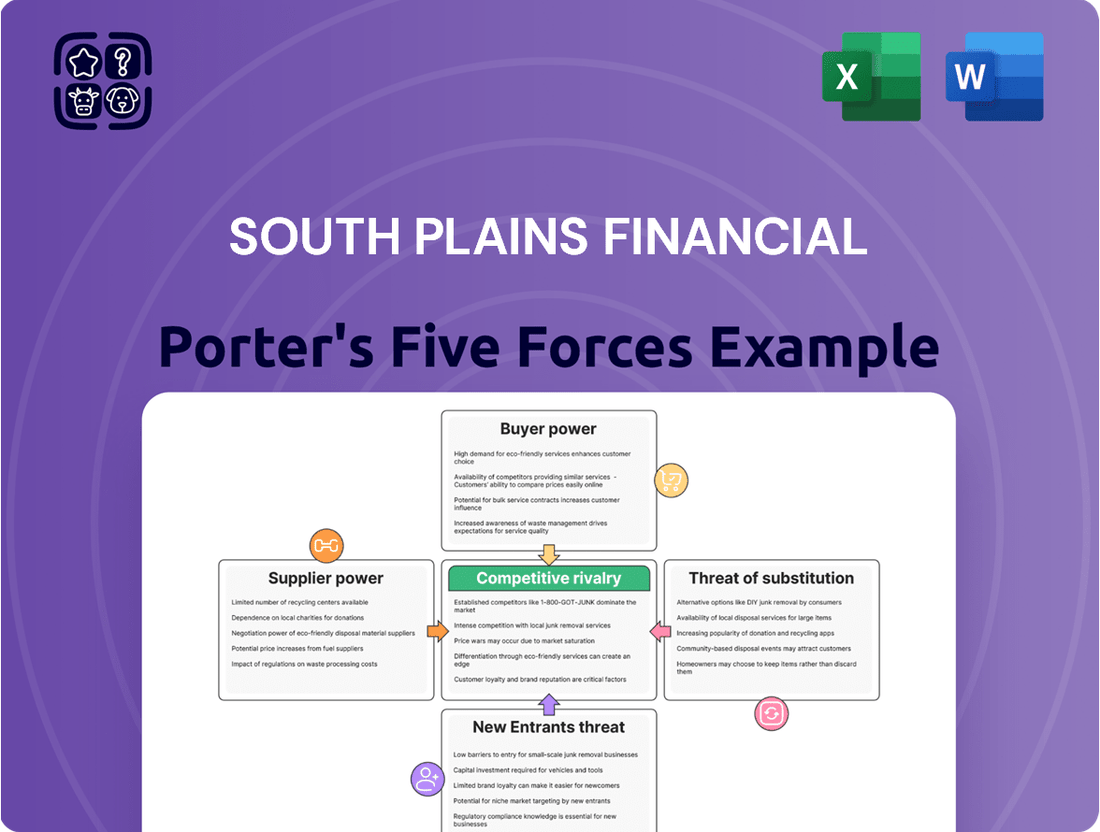
South Plains Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
South Plains Financial Bundle
South Plains Financial operates in a dynamic banking sector where customer loyalty is a key battleground, influencing pricing power. The threat of new entrants, while present, is somewhat mitigated by regulatory hurdles and capital requirements. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing banks is crucial for anticipating strategic moves and potential margin pressures.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping South Plains Financial’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
South Plains Financial, like many banks, depends on technology and software providers for essential operations. Core banking systems, cybersecurity, and FinTech solutions are critical. The bargaining power of these suppliers is often moderate to high, particularly for highly specialized or deeply integrated software that is costly and time-consuming to replace.
For instance, a 2024 industry report highlighted that community banks are significantly increasing their technology budgets, with a focus on automation and advanced fraud detection. This heightened reliance on specific technology vendors, especially those offering unique AI capabilities or real-time security, can amplify their negotiating leverage.
South Plains Financial, like many community banks, relies on wholesale funding markets beyond customer deposits to manage liquidity and capital. These markets, including interbank lending and debt issuance, are sensitive to broader economic conditions. In 2025, ongoing high interest rates and potential liquidity crunches amplify the influence of those providing this capital, as the cost and accessibility of these funds are directly impacted.
The banking industry, especially regional players like those in the South Plains, heavily relies on a skilled workforce across lending, compliance, IT, and customer service. A noticeable scarcity of qualified talent, particularly in cutting-edge digital and cybersecurity fields, significantly bolsters the bargaining power of these employees.
Community banks are currently grappling with persistent talent shortages, exacerbated by the dynamic shifts in the modern work landscape. This ongoing challenge directly contributes to upward pressure on labor costs as institutions compete for essential expertise.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Services
Regulatory bodies, while not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, exert considerable bargaining power over financial institutions like South Plains Financial through stringent compliance requirements. These mandates often necessitate significant investments in specialized services, advanced software solutions, and dedicated personnel to ensure adherence. For instance, the ongoing evolution and implementation of Basel III, with its potential adjustments through 2024 and beyond, directly impacts capital adequacy ratios and operational complexity for banks, increasing the demand for compliance expertise.
The increasing regulatory burden effectively raises the cost of doing business for banks, indirectly empowering those entities that offer specialized compliance and consulting services. These service providers, by helping navigate complex and ever-changing frameworks, gain leverage by making adherence possible and efficient. This dynamic can be seen in the growing market for regulatory technology (RegTech), which is projected to reach substantial figures. For example, the global RegTech market was valued at approximately $11.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow significantly through 2024 and beyond, reflecting the substantial investments financial firms are making.
- Increased Compliance Costs: Financial institutions must allocate resources for compliance services, technology, and staff, driven by regulations like Basel III.
- Demand for Expertise: The complexity of regulatory frameworks creates demand for specialized knowledge, boosting the bargaining power of compliance service providers.
- RegTech Market Growth: The global RegTech market, valued at around $11.5 billion in 2023, highlights the significant financial commitment to regulatory adherence.
- Operational Complexity: Evolving regulations directly influence a bank's operational costs and strategic planning, giving regulatory bodies indirect influence.
Payment Network Providers
Payment network providers like Visa and Mastercard wield significant bargaining power over financial institutions such as South Plains Financial. Their extensive infrastructure, global acceptance, and strong brand recognition make them indispensable for processing debit and credit card transactions. These networks can influence the fees and terms of service, directly impacting a bank's operational costs and profitability. In 2024, interchange fees remained a key revenue driver for these networks, and their ability to set these rates gives them considerable leverage.
South Plains Financial, like other banks, relies heavily on these established payment networks to offer essential services to its customers. The sheer ubiquity of Visa and Mastercard means that alternative processing solutions often lack the necessary scale and consumer adoption to be viable replacements. This dependency allows payment networks to dictate terms, as switching costs and the risk of disrupting customer services are substantial. For instance, the continued dominance of these networks in the digital payment landscape in 2024 underscores their strong market position.
- Dominant Market Share: Visa and Mastercard collectively process a vast majority of global card transactions, giving them immense market power.
- Network Effects: The more consumers and merchants use a particular network, the more valuable it becomes, creating a strong barrier to entry for competitors.
- Infrastructure Investment: These providers have made massive investments in secure and reliable transaction processing technology, which banks leverage.
- Brand Loyalty and Trust: Consumers are familiar with and trust major payment brands, making it difficult for banks to steer customers to less-known networks.
The bargaining power of suppliers for South Plains Financial is a multifaceted issue. Critical technology providers, especially those offering specialized FinTech or cybersecurity solutions, often hold significant sway due to the complexity and cost of replacement. Furthermore, wholesale funding markets and skilled labor, particularly in digital and compliance roles, represent areas where supplier influence is amplified, especially in the current economic climate of 2024-2025 with its focus on liquidity and talent scarcity.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on South Plains Financial | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers | Specialization, integration costs, uniqueness of solutions | Increased costs for essential software and IT services | Rising tech budgets for community banks in 2024, focus on AI/security |
| Wholesale Funding Markets | Liquidity availability, interest rate environment, counterparty risk | Higher cost of capital, potential liquidity constraints | Ongoing high interest rates in 2025 impacting fund accessibility |
| Skilled Labor | Talent scarcity, demand for specialized skills (digital, compliance) | Upward pressure on wages and benefits, recruitment challenges | Persistent talent shortages in banking, especially for digital roles |
| Payment Networks (Visa/Mastercard) | Market dominance, network effects, infrastructure investment | Influence on transaction fees, essential for customer services | Continued dominance in digital payments, interchange fees as key revenue |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for South Plains Financial, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitutes, and competitive rivalry.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model, allowing for rapid assessment of South Plains Financial's strategic positioning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual retail customers generally experience low costs when moving their deposit or basic loan accounts between financial institutions. This ease of movement significantly enhances their bargaining power.
The widespread availability of digital banking tools and a diverse array of financial products from numerous providers simplify the process for customers to shop around and switch. In 2024, the rise of digital-only banks continues to attract customers with attractive deposit rates and reduced fees, further empowering consumers.
Customers now have vast amounts of information at their fingertips, readily comparing interest rates, fees, and service quality across various financial institutions via online platforms and comparison websites. This transparency significantly boosts their bargaining power, compelling banks to maintain competitive offerings. For instance, in 2024, a significant percentage of consumers actively used comparison tools before making financial decisions, directly impacting pricing strategies.
For standardized financial products like basic checking accounts, savings accounts, and conventional loans, customers often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are more likely to switch to a competitor offering better rates or lower fees, especially if the added benefits of their current provider don't justify the cost. In 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts hovered around 4.35%, making even small differences in APY a deciding factor for many consumers.
Diversified Customer Base
South Plains Financial benefits from a diverse customer base, encompassing both individual retail clients and small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs). While individual depositors and borrowers can exert some influence, their impact is generally diffused across a large customer pool. The bank's strategy of serving various segments, from personal banking to commercial lending and cash management, means that the leverage of any single customer or small group of customers is somewhat mitigated.
The bank's geographic diversification across Texas and New Mexico further strengthens its position against customer bargaining power. This broad market presence means South Plains Financial is not overly reliant on a single community or industry. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, South Plains Financial reported total assets of approximately $3.9 billion, serving a wide array of clients across its operational footprint.
- Diversified Customer Segments: Serves retail individuals and SMBs, spreading reliance.
- Commercial Relationships: SMBs often depend on banks for multiple services, moderating their individual bargaining power.
- Geographic Reach: Operations in multiple Texas and New Mexico markets reduce concentration risk from any single customer group.
- Asset Base: With $3.9 billion in assets as of Q1 2024, the bank's scale helps absorb individual customer leverage.
Personalized Service as a Differentiator
Despite the increasing prevalence of digital banking, a significant segment of customers, particularly small businesses, continue to place a high value on personalized service and local relationships with their financial institutions. For community banks like City Bank, this presents a powerful opportunity to differentiate themselves.
By offering tailored financial solutions and cultivating strong, personal customer relationships, City Bank can reduce the likelihood of customers switching solely on the basis of price. This emphasis on relationship banking is a cornerstone of community banking's appeal.
For example, in 2024, community banks reported that over 70% of their small business clients cited relationship as a primary reason for choosing and staying with their bank, even when competing with larger, potentially cheaper national options.
- Personalized service builds loyalty among small business clients.
- Local relationships mitigate price sensitivity for banking services.
- Community banks can leverage personal touch as a competitive advantage.
- Customer retention is strengthened through tailored solutions and strong rapport.
Individual retail customers possess considerable bargaining power due to low switching costs and readily available information, as evidenced by the 2024 trend of consumers actively using comparison tools. While South Plains Financial serves a diverse client base, mitigating individual leverage, the bank's substantial asset base of $3.9 billion as of Q1 2024 and its geographic diversification across Texas and New Mexico further reduce its vulnerability to customer power.
| Factor | Impact on South Plains Financial | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs (Retail) | Low, increasing customer power | Widespread digital banking adoption |
| Information Availability | High, enabling price comparison | Prevalence of financial comparison websites |
| Customer Diversification | Mitigates individual customer power | Serves both retail and SMB segments |
| Geographic Reach | Reduces reliance on single markets | Operations across Texas and New Mexico |
| Asset Size | Aids in absorbing customer leverage | $3.9 billion in total assets (Q1 2024) |
Preview Before You Purchase
South Plains Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete South Plains Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within its industry. You'll receive this exact, professionally formatted document immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate usability. The analysis details the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes, providing actionable insights. What you see here is precisely the document you will download, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
South Plains Financial faces significant competition in Texas and New Mexico from large national and super-regional banks. These competitors, such as Regions Financial, boast extensive resources, wider branch networks, and larger marketing budgets, allowing them to offer a comprehensive suite of products and potentially more attractive pricing on loans and deposits. Regions Financial, for instance, is actively enhancing its digital capabilities within the Texas market, further sharpening the competitive landscape.
The financial sector is seeing a surge of digital-only banks and FinTechs, offering specialized services with lower costs and slick user experiences. These newcomers are directly challenging traditional banks for deposits, payments, and loans, especially from younger, tech-forward customers. This competitive pressure is compelling established institutions to speed up their digital upgrades.
For instance, by the end of 2023, neobanks like Chime had amassed over 14 million customers in the U.S., demonstrating substantial inroads into the market. These digital players are not just gaining customers; they are also growing their assets and revenue at a pace that necessitates a strategic response from incumbent banks.
Credit unions are a substantial competitive force, particularly for individual consumers and smaller enterprises. Their member-focused approach often allows them to offer more attractive interest rates and lower fees compared to traditional banks. In 2023, credit unions in the U.S. served over 135 million members, demonstrating their significant market penetration and influence.
Beyond credit unions, specialized lenders further intensify competition. For instance, mortgage lenders, dedicated online small business loan providers, and even peer-to-peer lending platforms carve out specific market segments. This fragmentation means that community banks like those within South Plains Financial's operating regions must constantly innovate to retain customers across various financial product categories.
The competitive landscape is further complicated by the rise of fintech companies and the continued dominance of larger national banks. Fintechs offer digital-first solutions that are often more agile and user-friendly, while large banks leverage economies of scale and broader product offerings to attract and retain customers. This dual pressure challenges community banks to maintain their market share and adapt to evolving customer expectations.
Market Concentration and Geographic Overlap
South Plains Financial faces significant competitive rivalry due to its presence across multiple Texas and New Mexico markets. This geographic overlap means direct competition with numerous other financial institutions vying for the same customer base.
The intensity of this rivalry is not uniform. Densely populated urban centers, such as those City Bank serves in Dallas, El Paso, and Houston, typically exhibit a higher degree of competition compared to more rural areas. This concentration of economic activity draws more players, intensifying the fight for market share.
- Market Presence: South Plains Financial operates in both Texas and New Mexico, creating direct competitive scenarios.
- Urban Competition: Cities like Dallas, El Paso, and Houston, where competitors like City Bank are also active, see heightened rivalry.
- Geographic Overlap: The shared operational regions amplify the pressure from other banks targeting similar demographics and business clients.
Interest Rate Environment and Deposit Competition
The current interest rate environment, with rates remaining elevated through early 2025, is significantly fueling competition for deposits. Banks are actively seeking to secure funding, leading them to offer more compelling deposit rates to retain existing customers and attract new ones. This heightened competition for deposits is a particularly pronounced challenge for community banks as they navigate funding costs.
This intensified rivalry means banks must differentiate their deposit offerings to stand out. Strategies include offering tiered interest rates, promotional bonuses, or specialized accounts catering to specific customer needs. The ongoing pressure to manage funding costs in a high-rate environment directly translates into more aggressive deposit-gathering tactics among financial institutions.
- Deposits are a critical funding source for banks, especially community banks.
- High interest rates increase the cost of acquiring and retaining deposits.
- Competition for deposits is expected to remain a key strategic focus for financial institutions throughout 2025.
- Banks are responding with more attractive deposit rates and product features.
South Plains Financial contends with intense competitive rivalry, particularly from larger national and super-regional banks like Regions Financial, which possess greater resources and broader market reach. The financial sector's ongoing digital transformation also introduces formidable competition from agile FinTechs and digital-only banks, such as Chime, which had over 14 million U.S. customers by late 2023, challenging traditional players for customer acquisition and digital services.
Credit unions, serving over 135 million members in the U.S. as of 2023, represent another significant competitive force, often offering more favorable terms to consumers and small businesses. Furthermore, specialized lenders in areas like mortgages and small business loans fragment the market, compelling community banks to continuously innovate to retain clients across a spectrum of financial products.
The heightened competition for deposits, fueled by elevated interest rates through early 2025, forces financial institutions to offer more attractive rates and product features to secure funding. This dynamic is particularly challenging for community banks, directly impacting their funding costs and strategic responses.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech companies present a significant threat of substitutes for South Plains Financial's core payment and lending services. Platforms like PayPal and Venmo offer increasingly popular digital payment alternatives, bypassing traditional banking channels. In 2023, the global digital payments market was valued at over $8.5 trillion, demonstrating the widespread adoption of these substitutes.
For lending, peer-to-peer platforms and online lenders provide accessible alternatives for both consumers and small businesses. These fintech solutions often boast faster approval times and more flexible terms compared to traditional banks. For instance, the online lending market in the U.S. saw substantial growth in 2024, with billions of dollars facilitated through these alternative channels, directly impacting demand for traditional bank loans.
Larger small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) are increasingly bypassing traditional bank loans by accessing capital directly through private placements, crowdfunding platforms, or other non-bank financial institutions.
This trend signifies a growing substitute for core banking services, particularly for businesses that might otherwise rely on commercial bank lending. In 2023, private placement issuance for U.S. SMEs reached an estimated $1.2 trillion, demonstrating the significant scale of this alternative capital-raising channel.
This direct access reduces businesses' dependence on commercial banks, impacting the traditional lending market. While community banks like South Plains Financial often focus on smaller businesses, a substantial portion of their potential larger SME clients may opt for these more direct financing routes.
Platforms like Nasdaq Private Market reported a 25% increase in transaction volume in 2024 for private securities, highlighting the growing appetite for these alternative capital solutions.
Customers seeking to save and invest have a vast array of options beyond traditional bank deposit accounts. These include money market funds, brokerage accounts, mutual funds, and direct investments in stocks and bonds, all offering varying levels of risk and return.
The attractiveness of bank deposit accounts is directly tied to the interest rates they offer. For instance, in early 2024, while some banks offered competitive yields on high-yield savings accounts and CDs, money market funds were also yielding around 5%, making them a strong contender for depositors.
This availability of diverse, often higher-yielding alternatives puts pressure on banks like South Plains Financial to remain competitive with their deposit rates. If bank rates lag significantly behind market alternatives, customers are likely to move their funds elsewhere, impacting the bank's deposit base.
Robo-Advisors and Digital Wealth Management
Robo-advisors and digital wealth management platforms present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services, especially in investment and trust management. These platforms offer automated, algorithm-driven investment strategies at a considerably lower cost than human advisors. For instance, many robo-advisors charge annual management fees around 0.25%, a stark contrast to the 1% or more often seen with traditional wealth managers.
This trend is particularly impactful for younger demographics and tech-savvy individuals who are comfortable with digital solutions and prioritize cost-effectiveness. The convenience and accessibility of these online services can easily replace the need for a bank's established trust and investment departments. As of early 2024, the assets under management for robo-advisors have surpassed hundreds of billions of dollars globally, demonstrating their growing market penetration.
- Lower Fees: Robo-advisors typically charge 0.25% to 0.50% annually, compared to 1% or more for traditional advisors.
- Accessibility: Digital platforms allow for easy account setup and management online or via mobile apps, often with lower minimum investment requirements.
- Growing Adoption: The market for robo-advisory services has seen substantial growth, with assets under management projected to reach trillions in the coming years.
- Targeting Younger Investors: These digital solutions appeal strongly to millennials and Gen Z, who are increasingly seeking financial advice but are often more cost-sensitive and digitally inclined.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-Based Services
While still in their early stages for widespread banking adoption, cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms present a potential threat of substitution. These technologies could eventually replace traditional banking services such as payment processing, loan origination, and secure asset holding, especially for cross-border transactions or niche customer groups. For instance, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization reached approximately $2.5 trillion in early 2024, indicating growing user interest and adoption of these alternative financial mechanisms.
Blockchain technology itself is also a significant factor, not just as a platform for cryptocurrencies but as a tool to improve security within open finance frameworks. This means that while not a direct substitute for the entire banking model, specific blockchain applications could chip away at current banking revenue streams. By mid-2024, the value locked in DeFi protocols exceeded $100 billion, demonstrating a tangible shift of assets and activities away from traditional financial institutions.
The threat is amplified by the increasing efficiency and lower transaction costs offered by some blockchain-based payment systems compared to traditional international wire transfers. Furthermore, the growing integration of blockchain for digital identity and asset tokenization could bypass traditional intermediaries. As of late 2024, several major financial institutions are actively exploring or piloting blockchain solutions for various operational efficiencies.
- Growing Market Acceptance: The global cryptocurrency market cap fluctuating around $2.5 trillion in early 2024 signifies increasing user adoption.
- DeFi Value Locked: Over $100 billion was locked in DeFi protocols by mid-2024, indicating a significant migration of financial activity.
- Blockchain for Security: Blockchain technology is being implemented to enhance security in open finance, potentially reducing reliance on traditional security measures.
- Cost Efficiency: Blockchain-based payment systems offer potential cost savings for international transactions compared to conventional methods.
The threat of substitutes for South Plains Financial is multifaceted, encompassing digital payment platforms, alternative lending channels, diverse investment vehicles, and emerging financial technologies like crypto and DeFi. These substitutes often offer greater convenience, lower costs, or higher yields, directly challenging traditional banking services.
Fintech payment solutions like PayPal and Venmo saw significant adoption, with the global digital payments market exceeding $8.5 trillion in 2023. Similarly, online lending platforms facilitated billions in credit in the U.S. during 2024, offering faster alternatives to bank loans.
Customers have numerous options beyond bank deposits, with money market funds yielding around 5% in early 2024, competing directly with bank savings accounts. Robo-advisors, charging fees as low as 0.25%, manage hundreds of billions globally as of early 2024, attracting younger, cost-conscious investors.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Market Size/Adoption (Approx.) | Key Advantage |
| Digital Payments | PayPal, Venmo | Global market > $8.5 trillion (2023) | Convenience, Speed |
| Alternative Lending | P2P platforms, Online lenders | Billions facilitated in U.S. (2024) | Faster approvals, Flexibility |
| Investment Alternatives | Money Market Funds, Robo-advisors | Money Market Funds yielding ~5% (Early 2024); Robo-advisors AUM > $100 billion (Early 2024) | Higher yields, Lower fees |
| Emerging Technologies | Cryptocurrencies, DeFi | Crypto market cap ~ $2.5 trillion (Early 2024); DeFi value locked > $100 billion (Mid-2024) | Decentralization, Potential cost savings |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the banking sector, particularly as a chartered institution, presents formidable regulatory obstacles. These include substantial capital requirements, complex licensing processes, and continuous adherence to evolving compliance mandates. For instance, New Mexico statutes detail specific requirements for establishing branch banks, such as obtaining director approval and paying investigation fees, underscoring the significant investment and administrative burden.
Establishing a new bank, like South Plains Financial, demands a significant capital investment. This includes costs for physical branches, advanced banking technology, skilled personnel, and crucially, meeting stringent regulatory capital requirements.
This substantial financial barrier effectively deters many potential new entrants from entering the banking sector. For perspective, South Plains Financial reported total assets exceeding $4.2 billion as of December 31, 2024, illustrating the immense scale of resources necessary to operate as a regional financial institution.
Established brand reputation and trust represent a significant hurdle for new entrants looking to compete with incumbent financial institutions. Traditional banks, for instance, have cultivated decades of customer loyalty and name recognition, making it challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold quickly. This is particularly true for older demographics and businesses that prioritize stability and a proven track record. South Plains Financial, for example, was honored on Forbes Best In State Banks 2024, a testament to its strong and enduring reputation within the market, which acts as a powerful deterrent for potential new competitors.
Economies of Scale and Scope for Incumbents
Existing financial institutions like South Plains Financial enjoy significant advantages due to economies of scale and scope. They can process transactions, manage risk, and invest in technology more efficiently by spreading these costs over a vast customer base and a broad range of products. This makes it difficult for new entrants to compete on cost alone, as they lack the established infrastructure and customer volume.
South Plains Financial, for instance, provides a wide spectrum of services including commercial banking, diverse deposit accounts, and various loan solutions. This integrated offering allows them to capture more customer wallet share and create cross-selling opportunities, a feat that is challenging for newcomers who often start with a more limited product set.
In 2023, South Plains Financial reported total assets of approximately $4.5 billion. This scale enables them to negotiate better terms with vendors and invest more heavily in digital platforms, further solidifying their competitive position against smaller, less-established entities. New entrants would need substantial capital to replicate this level of operational efficiency and product breadth.
- Economies of Scale: Banks like South Plains Financial benefit from lower per-unit costs in operations due to their large asset base.
- Economies of Scope: Offering a wide range of financial products (loans, deposits, wealth management) allows for cost synergies and enhanced customer relationships.
- Capital Requirements: New entrants face high initial capital needs to build comparable infrastructure and achieve necessary scale.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: Established banks have existing customer relationships, reducing the cost of acquiring new business compared to startups.
Technological Advancements Lowering Some Barriers
While the hurdles to establishing a full-service traditional bank remain substantial, technological innovations have certainly lowered some entry barriers, particularly within specific financial service niches. The proliferation of FinTech companies exemplifies this trend, enabling new players to offer specialized services with greater agility.
Digital-only banks, for instance, can operate with a significantly reduced physical footprint compared to legacy institutions. This can translate into lower overhead costs, a key advantage for new entrants. For example, many neobanks have minimal branch networks, allowing them to allocate capital more strategically towards technology and customer acquisition rather than real estate.
Despite these advantages, new entrants still face considerable challenges. Building brand recognition and, crucially, customer trust in the financial sector takes time and significant investment. The competitive landscape is also intensely crowded, with established players and other innovative startups vying for market share.
FinTech startups are frequently seeking strategic partnerships with incumbent financial institutions. This collaboration allows them to leverage existing infrastructure and customer bases while offering their cutting-edge technology solutions. In 2024, we've seen numerous such alliances, as both established banks and agile FinTechs recognize the mutual benefits of innovation through integration.
- Lowered Overhead: Digital banks can operate with fewer physical branches, reducing capital expenditure on real estate and associated costs.
- FinTech Disruption: The rise of financial technology has enabled specialized service providers to enter markets previously dominated by traditional banks.
- Partnership Opportunities: FinTechs often collaborate with established institutions to gain market access and customer reach, demonstrating a dynamic competitive environment.
- Trust as a Barrier: Despite technological advancements, gaining and maintaining customer trust remains a significant challenge for new financial service providers.
The threat of new entrants in the banking sector, particularly for institutions like South Plains Financial, is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements and stringent regulatory oversight. These factors demand substantial upfront investment and ongoing compliance, creating a formidable barrier. For example, as of December 31, 2024, South Plains Financial held total assets exceeding $4.2 billion, underscoring the scale of resources required to operate effectively in this market.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for South Plains Financial leverages data from SEC filings, annual reports, and industry-specific research from sources like S&P Global Market Intelligence. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape and strategic positioning.
