SEVAK Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
SEVAK Bundle
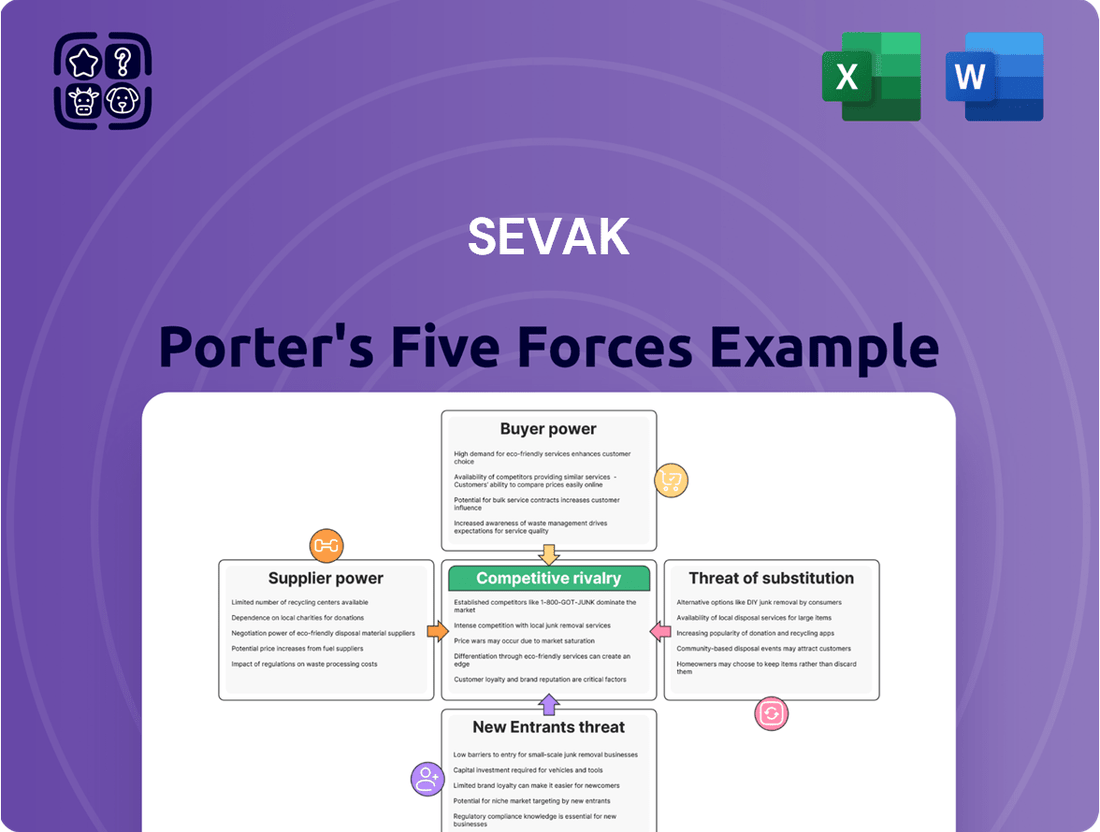
SEVAK's competitive landscape is shaped by five critical forces: the bargaining power of its buyers, the influence of its suppliers, the threat of new entrants, the availability of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing players. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating SEVAK's market effectively. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore SEVAK’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
SEVAK's bargaining power with its suppliers is significantly influenced by the concentration of key infrastructure providers, particularly telecom carriers. These entities, which control the essential networks for SMS and voice communications, are few in number. This limited pool of critical suppliers means SEVAK has fewer alternatives for sourcing these fundamental services, placing considerable leverage in the hands of the carriers.
The reliance on a small group of major telecom carriers for direct routes and service quality directly impacts SEVAK's operational expenses and the dependability of its CPaaS offerings. For instance, in 2023, global telecom carrier revenue reached trillions of dollars, highlighting their substantial market power. When only a handful of these large players can provide the necessary connectivity, SEVAK’s ability to negotiate favorable terms is curtailed, potentially leading to higher input costs and impacting profitability margins.
Switching costs for SEVAK to change its core telecom carriers or infrastructure providers are substantial, impacting its bargaining power. These costs encompass the intricate technical integration required to adapt SEVAK's systems to a new provider, alongside the administrative burden of renegotiating complex service agreements. For instance, in 2024, a major European telecom provider reported that onboarding a new enterprise client with integrated services could cost upwards of €1 million in integration and setup alone.
Beyond initial integration, SEVAK faces potential service disruptions during a transition, which could affect customer experience and revenue. Ensuring seamless global coverage with a new provider adds another layer of complexity and expense. These multifaceted challenges mean that SEVAK cannot easily switch suppliers, thereby granting existing providers considerable leverage in contract negotiations.
While basic SMS and voice services are largely commoditized, suppliers offering specialized network APIs, advanced routing capabilities, or unique global reach can command greater bargaining power. For instance, telecommunication companies are actively expanding their Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) offerings and exposing 5G network APIs. These differentiated services, such as guaranteed low latency, significantly enhance their value proposition and strengthen their position with buyers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Telecom carriers are increasingly demonstrating a threat of forward integration by building or acquiring their own Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS) offerings. This strategic move allows them to capture more value within the communication ecosystem.
Companies such as Ericsson, through its acquisition of Vonage, and Nokia, with its rapid acquisition strategy, are actively integrating CPaaS capabilities. Proximus also acquired Route Mobile, further solidifying this trend among major telecommunications players.
These integrations can potentially disintermediate or bypass independent CPaaS providers like SEVAK, especially in specific market segments where carriers can leverage their existing infrastructure and customer base more effectively.
For instance, the global CPaaS market size was estimated to be around $26.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, with carriers aiming to capture a larger share of this expanding market through direct CPaaS offerings.
- Carrier Integration: Telecom giants are investing heavily in CPaaS technology to offer direct services.
- Acquisition Strategies: Companies like Ericsson (Vonage) and Nokia are acquiring CPaaS providers to gain capabilities.
- Market Disruption: Direct carrier offerings could reduce the need for third-party CPaaS platforms in certain areas.
- Market Growth: The expanding CPaaS market presents an opportunity for carriers to vertically integrate and increase revenue.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The bargaining power of suppliers for SEVAK is significantly influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. For SEVAK, which operates in the communication sector, its core needs revolve around access to SMS, voice, and messaging networks. These are not easily replaceable.
While alternative routing through aggregators exists, direct connections with mobile network operators are vital for maintaining service quality and managing costs effectively. This reliance on direct carrier relationships means that the options for securing these fundamental communication channels are quite limited, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of these network providers.
- Limited Substitutes for Core Communication: SEVAK's essential services rely heavily on SMS, voice, and messaging networks, for which viable substitutes are scarce.
- Importance of Direct Carrier Connections: Direct connections with mobile network operators are crucial for SEVAK, impacting both service quality and cost efficiency.
- Aggregators as a Partial Alternative: While aggregators can offer alternative routing, they do not fully negate the need for direct carrier access, especially for premium services.
- Supplier Leverage: The restricted availability of substitute inputs grants significant leverage to the suppliers of these essential communication networks.
SEVAK's suppliers, primarily telecom carriers, hold significant bargaining power due to industry concentration and high switching costs for SEVAK. These carriers control essential infrastructure for SMS and voice, limiting SEVAK's options. For example, the global CPaaS market was valued at approximately $26.7 billion in 2023, a sector where carriers are increasingly offering direct services, potentially disintermediating providers like SEVAK.
| Factor | Impact on SEVAK's Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Lowers SEVAK's power; few critical providers exist. | Global telecom infrastructure is dominated by a limited number of major carriers. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers SEVAK's power; integration and transition are costly. | Onboarding new enterprise clients with integrated services can exceed €1 million in setup costs for telecom providers (2024 data). |
| Supplier Differentiation | Increases supplier power; specialized services (e.g., 5G APIs) command higher value. | Telecom companies are actively exposing advanced network APIs as part of their CPaaS expansion. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Lowers SEVAK's power; carriers can bypass CPaaS providers. | Companies like Ericsson (via Vonage) and Nokia are acquiring CPaaS capabilities, and Proximus acquired Route Mobile. |
What is included in the product
SEVAK's Porter's Five Forces analysis examines the competitive intensity and attractiveness of its operating environment by evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
SEVAK's Porter's Five Forces Analysis swiftly identifies and quantifies competitive pressures, allowing you to pinpoint the most critical threats and opportunities for immediate strategic action.
Customers Bargaining Power
SEVAK's customer base spans a wide range, from major enterprises to smaller businesses. This diversity influences customer bargaining power. Large enterprise clients, who represent a substantial portion of SEVAK's Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS) revenue, possess significant leverage. Their substantial traffic volumes and the potential for customized service demands allow them to negotiate more favorable pricing and terms.
For instance, in 2024, large enterprise clients accounted for over 60% of SEVAK's CPaaS revenue, giving them considerable sway. This concentration means that retaining these key accounts is paramount, and their demands for tailored solutions or volume discounts directly impact SEVAK's profitability.
Conversely, while the small and medium-sized business (SME) segment is experiencing rapid growth for SEVAK, individual SMEs typically wield less bargaining power due to their smaller transaction volumes. Their collective impact grows, but their individual ability to dictate terms remains limited compared to the large enterprises.
Customers generally encounter moderate switching costs when considering a move from one Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) provider to another. While the nature of APIs encourages integration, the practicalities of shifting established communication workflows, reconfiguring existing business systems, and retraining personnel can indeed represent a significant investment of both time and capital. This can, in turn, temporarily temper a customer's immediate leverage.
However, the dynamic and competitive landscape of the CPaaS market, coupled with the inherent design of these platforms to simplify integration processes, works to keep these switching costs relatively contained. For instance, many CPaaS providers in 2024 offer robust documentation and support to ease migration, and the availability of readily adaptable SDKs further streamlines the transition. This environment ensures that while switching isn't entirely frictionless, it remains a manageable consideration for most businesses.
The Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) market is teeming with options, making it easier for customers to switch providers. Companies like Twilio, Infobip, Vonage, and Sinch are prominent players, but many smaller, specialized vendors also exist, offering niche solutions. This intense competition means businesses can often negotiate better terms or find more suitable features elsewhere.
In 2024, the CPaaS market continued its rapid expansion, with analysts projecting continued growth. This accessibility to a wide array of providers empowers customers significantly. They can easily shop around, compare pricing structures, service level agreements, and the breadth of features offered by different CPaaS vendors. For instance, a company looking for advanced SMS capabilities might find one provider excels, while another might be better for voice APIs, allowing them to piece together the best solution or demand better pricing from their current vendor.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor within the Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) market, especially when dealing with high volumes of messaging. Providers often find that customers, particularly those utilizing core services like SMS and Application-to-Person (A2P) messaging, make their selection based primarily on cost. This means even minor adjustments in pricing can lead to substantial shifts in customer loyalty and provider choice.
The competitive landscape further amplifies this sensitivity. For instance, by mid-2024, the CPaaS market continued to see intense competition, with pricing becoming a key differentiator. Some reports indicated that the average cost per SMS message had stabilized or even slightly decreased in certain regions due to this pressure, making it easier for customers to switch providers for marginal savings.
- High-Volume Messaging Focus: Customers in the CPaaS sector, particularly those sending millions of messages, exhibit strong price sensitivity.
- Cost-Driven Decisions: The selection of a CPaaS provider for services like SMS and A2P messaging is frequently a cost-driven decision.
- Impact of Price Changes: Even small incremental price changes can trigger significant customer migration, especially for foundational messaging functionalities.
- Market Dynamics: The CPaaS market’s competitive nature, with numerous providers vying for market share, intensifies price sensitivity as a key battleground.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, while not a primary concern for most businesses, can emerge with very large enterprises possessing substantial development capabilities. These entities might explore building certain communication functionalities internally, particularly for highly specialized or sensitive operational needs.
However, the significant complexity and ongoing cost associated with maintaining proprietary communication infrastructure often render the Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) model a more economically viable and attractive solution for these same large customers. For instance, a major global bank might consider developing its own secure messaging system, but the continuous investment in platform updates, security protocols, and compliance often outweighs the benefits compared to leveraging an established CPaaS provider.
Consider the case of a large e-commerce platform. While they have the resources to develop some customer communication tools, the agility and specialized features offered by CPaaS providers, such as real-time chat APIs or sophisticated SMS campaign management, are often more compelling. The global CPaaS market was projected to reach approximately $24.2 billion in 2024, indicating the widespread reliance on these specialized services rather than in-house development for many organizations.
- Customer Integration Costs: Building in-house communication solutions involves significant upfront investment in R&D, infrastructure, and skilled personnel.
- CPaaS Market Growth: The expanding CPaaS market, projected to exceed $24 billion in 2024, highlights the preference for external, specialized solutions.
- Specialized Needs: Backward integration is most likely for customers with unique security or functionality requirements not met by standard CPaaS offerings.
- Operational Burden: Maintaining complex communication systems adds an operational burden that many large enterprises prefer to outsource to specialized providers.
SEVAK's customer bargaining power is influenced by customer concentration and price sensitivity. Large enterprise clients, who accounted for over 60% of SEVAK's CPaaS revenue in 2024, hold significant sway due to their volume and custom demands, directly impacting pricing and terms.
Switching costs for CPaaS providers are moderate; while integration is key, the practicalities of workflow shifts and retraining can deter immediate changes, offering some temporary leverage. The competitive CPaaS market, with numerous providers and readily adaptable SDKs, keeps these costs manageable, empowering customers to negotiate or switch for better terms.
Customer price sensitivity is high, especially for high-volume messaging services like SMS and A2P. In 2024, pricing became a key differentiator, with some markets seeing a slight decrease in per-message costs, making customers more inclined to switch for marginal savings.
The threat of backward integration is low for most customers, though very large enterprises with significant development capabilities might consider it for highly specialized needs. However, the complexity and cost of maintaining proprietary systems generally make CPaaS solutions more economically viable, especially given the CPaaS market's projected growth to approximately $24.2 billion in 2024.
Same Document Delivered
SEVAK Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the identical, comprehensive SEVAK Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring complete transparency. You're not just seeing a sample; you're viewing the final, professionally formatted document ready for your strategic application. Every element, from the detailed analysis of competitive rivalry to the assessment of bargaining power, is present and accurate in this preview. Once you complete your purchase, you'll gain instant access to this exact file, empowering you with the insights needed to understand SEVAK's competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The CPaaS market is a hotbed of competition, with a vast array of companies vying for market share. This includes specialized CPaaS providers like Twilio, which reported $4.4 billion in revenue for 2023, alongside traditional telecommunications companies offering similar services and enterprise software giants integrating communication capabilities. This diversity ensures that competition is fierce across various customer segments and service offerings.
The sheer volume of players, from nimble startups to established behemoths, creates a dynamic and often aggressive competitive landscape. For instance, MessageBird, another significant CPaaS player, has also been actively expanding its global reach and product portfolio, directly challenging larger incumbents. This constant influx of innovation and strategic moves by numerous competitors keeps pricing under pressure and drives continuous service improvement.
The Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) market is booming, with projections showing it could reach hundreds of billions of dollars by 2029. Some estimates suggest a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 18.83%, while others point to over 30%. This rapid expansion creates a dynamic environment for competition.
While such high growth can initially ease competitive pressures by offering enough room for many companies, it also acts as a magnet for new entrants. Existing players, eager to capture a larger share of this expanding pie, often engage in aggressive strategies to grow their market presence.
This intense growth phase means companies are frequently investing heavily in product development and market expansion. The race to innovate and acquire customers can lead to price wars or increased marketing spend, intensifying rivalry among established and emerging CPaaS providers.
Product differentiation is key in the competitive Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) market. Leading providers are distinguishing themselves through AI-driven automation, seamless omnichannel experiences, robust analytics, and specialized solutions for specific industries. For instance, many CPaaS platforms now offer AI chatbots for customer service, a feature that was less common even a few years ago.
SEVAK needs to continuously enhance its SMS, voice, and messaging APIs to carve out a unique market position. While competitors may offer similar foundational services, those adding advanced intelligence and integrated platform features are gaining traction. The global CPaaS market was valued at approximately $25 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, highlighting the opportunity for well-differentiated players.
Switching Costs for Customers
While some effort is involved in migrating from one CPaaS provider to another, the actual costs are not a significant barrier. For instance, a significant portion of businesses, around 40% in recent surveys, are actively considering switching their CPaaS providers. This suggests that the financial, technical, and operational hurdles associated with changing vendors are manageable for most clients.
This low-to-moderate switching cost environment directly contributes to heightened competition within the CPaaS market. It means customers are more willing to explore alternatives if they find a provider offering superior features, better pricing, or enhanced service levels.
- Customer Inertia: While not insurmountable, some inertia exists due to integration efforts and potential downtime during migration.
- Provider Lock-in: Limited proprietary technology or unique API integrations can create minor lock-in effects, but these are often outweighed by broader market offerings.
- Market Volatility: With nearly 40% of companies evaluating CPaaS provider replacements, the market clearly indicates that switching costs are not a strong deterrent to seeking better value.
- Competitive Pressure: The ease with which customers can shift providers intensifies rivalry, pushing existing players to continuously innovate and offer competitive pricing.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) market present a complex dynamic that can influence competitive rivalry. For instance, companies that have made substantial investments in building out their network infrastructure, establishing crucial carrier relationships, and developing sophisticated platform technologies face significant hurdles when considering an exit. These sunk costs can make it exceedingly difficult to divest or shut down operations without incurring substantial financial losses.
This situation often leads to a scenario where even less profitable players continue to operate within the market. Their reluctance to exit, driven by the desire to recoup investments or avoid outright losses, means they remain active competitors. This sustained presence from potentially weaker entities can further intensify the overall rivalry within the CPaaS sector, as they continue to compete for market share and customer attention.
For example, in 2024, the CPaaS market saw continued investment in advanced features like AI-powered customer engagement and omnichannel solutions. Companies like Twilio, with its extensive global infrastructure and developer ecosystem, represent significant capital commitment. Similarly, Vonage, now part of Ericsson, had invested heavily in its API platform and enterprise solutions prior to its acquisition. These investments create high exit barriers, ensuring that even if profit margins narrow for some participants, they are likely to persist rather than withdraw.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs in infrastructure, software development, and securing carrier agreements create substantial sunk costs for CPaaS providers.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing agreements with telecommunication carriers and enterprise clients can lock companies into operations for extended periods, making early exit financially punitive.
- Specialized Assets: The proprietary nature of CPaaS platforms and specialized network equipment means these assets have limited resale value outside the specific industry context, increasing the cost of exit.
- Brand Reputation and Customer Relationships: Exiting a market can damage a company's reputation and sever established customer relationships, impacting future business ventures and making a clean break difficult.
The CPaaS market is characterized by intense rivalry due to a large number of diverse players, including specialized CPaaS providers like Twilio, which reported $4.4 billion in revenue for 2023, and traditional telecom companies. This dynamic landscape, fueled by rapid market growth and continuous innovation, forces companies to differentiate through advanced features like AI and omnichannel experiences to maintain a competitive edge.
Switching costs for CPaaS services are generally low to moderate, with around 40% of companies considering provider changes, indicating customers are readily exploring alternatives for better value. This ease of switching intensifies competition, compelling existing providers to consistently innovate and offer competitive pricing to retain their customer base and attract new ones.
High exit barriers, stemming from substantial investments in infrastructure and technology, mean even less profitable CPaaS players tend to persist rather than withdraw, further intensifying competition. This sustained presence from a broader range of competitors, including those with significant sunk costs like MessageBird, keeps pricing under pressure and drives ongoing service improvements across the sector.
| Key Competitor | 2023 Revenue (approx.) | Key Differentiators |
| Twilio | $4.4 billion | AI-powered automation, extensive developer ecosystem |
| MessageBird | Not publicly disclosed, but significant global expansion | Omnichannel capabilities, focus on enterprise solutions |
| Vonage (Ericsson) | Part of Ericsson's reported revenue, significant prior investments | API platform, enterprise-grade communication solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Businesses might bypass Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS) providers by striking direct deals with telecom carriers. This route, however, requires substantial upfront investment and deep technical know-how. For example, a large enterprise might find it cost-effective to manage its own SMS gateway, bypassing CPaaS fees, but this is a complex undertaking.
Another substitute is in-house development of communication features. While this grants maximum control and customization, it's a resource-intensive path. Developing and maintaining these systems demands significant capital expenditure and a dedicated team of engineers. This is a strategy typically pursued by major tech companies or financial institutions with very specific, high-volume communication needs, rather than smaller businesses.
In 2024, the global CPaaS market was valued at approximately $27.5 billion, demonstrating its significant adoption. Direct carrier agreements or in-house solutions represent a threat mainly to this established market by offering alternative pathways, though the barriers to entry for these alternatives remain high for most players.
Traditional communication methods like direct email, standard phone calls, or even physical mail act as basic substitutes for specific communication needs. These channels are less efficient for scalable, automated, or integrated messaging compared to modern solutions.
While these older methods can fulfill simple communication requirements, they lack the sophisticated features offered by platforms like Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS). For instance, businesses still relying on manual email campaigns or unintegrated phone systems face limitations in reach and personalization.
The threat from these substitutes is moderate because for many core business functions, especially those requiring direct customer engagement or transactional updates, CPaaS provides a significantly more effective and efficient alternative. The market for CPaaS solutions continues to grow, with projected revenues reaching approximately $20 billion in 2024, indicating a strong preference for advanced communication tools over traditional methods.
While UCaaS and CCaaS platforms are often seen as complementary, their evolving integrated functionalities present a threat. These platforms can bundle communication features, potentially lessening the demand for standalone CPaaS solutions. For instance, many UCaaS providers now offer robust messaging and presence capabilities that overlap with core CPaaS offerings.
The blurring of lines is further amplified as CPaaS providers themselves begin to incorporate UCaaS and CCaaS features. This strategic integration means some CPaaS vendors are becoming substitutes for broader communication needs, challenging the distinct market position of pure-play CPaaS providers. The global UCaaS market was valued at approximately $35.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $100 billion by 2030, indicating significant growth that could absorb some CPaaS functionalities.
Over-the-Top (OTT) Messaging Apps and Rich Communication Services (RCS)
The rise of Over-the-Top (OTT) messaging apps and the expansion of Rich Communication Services (RCS) present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional messaging services, impacting providers like SEVAK. These platforms offer more engaging and feature-rich communication alternatives. For instance, WhatsApp, with over two billion monthly active users globally as of early 2024, provides a robust channel for both personal and increasingly, business-to-consumer interactions, directly competing with SMS-based customer engagement strategies.
Furthermore, the development and adoption of RCS Business Messaging (RBM) offer enhanced capabilities over standard SMS, including rich media support, branding, and interactive elements. Businesses can leverage RBM to create more sophisticated customer journeys and marketing campaigns. This direct access to consumers through these advanced channels can reduce reliance on CPaaS platforms that might otherwise facilitate SMS integration, thereby acting as a direct substitute for traditional messaging functionalities.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by the following:
- Increasing User Preference: Consumers are increasingly opting for feature-rich messaging apps for their convenience and enhanced communication capabilities.
- Direct Business Integration: Companies are exploring direct integration with OTT platforms for customer service and marketing, bypassing traditional messaging channels.
- RCS Growth: The ongoing rollout and adoption of RCS by mobile carriers worldwide are making it a more viable and attractive alternative to SMS for businesses.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For certain use cases, OTT messaging can be more cost-effective for businesses compared to per-message SMS charges.
Manual Processes and Legacy Systems
For businesses still relying on manual processes or older legacy systems, these can function as inefficient substitutes. Think of paper-based customer service logs or outdated inventory management software instead of modern CRM or ERP systems. These manual methods are far from ideal, often leading to delays and errors.
The ongoing drive towards digital transformation is a major factor here. Companies are increasingly investing in cloud-based solutions and automated workflows to improve efficiency and customer experience. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 75% of businesses surveyed were actively implementing or expanding their digital transformation initiatives, directly addressing the weaknesses of manual substitutes.
The attractiveness of these manual or legacy system substitutes is significantly diminished by the benefits offered by digital alternatives. These benefits include faster processing times, better data accuracy, and improved customer engagement capabilities.
- Manual processes are inherently slower and more prone to human error compared to automated systems.
- Legacy systems often lack the integration capabilities needed for seamless data flow and real-time insights.
- The push for enhanced customer experience makes outdated methods less viable as customer expectations rise.
- Digital transformation efforts, supported by significant IT spending forecasts in 2024, further highlight the inferiority of manual substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for SEVAK's services arises from alternative communication channels and platforms that can fulfill similar customer engagement needs. These include direct carrier agreements, in-house development, and traditional communication methods like email and phone calls, though these often lack the efficiency and integration of modern solutions. The rise of Over-the-Top (OTT) messaging apps like WhatsApp, with over two billion monthly active users globally in early 2024, and the expansion of Rich Communication Services (RCS) offer more engaging, feature-rich alternatives that can bypass traditional messaging functionalities.
These substitutes, particularly OTT and RCS, directly compete by offering enhanced capabilities such as rich media, branding, and interactive elements, allowing businesses to create more sophisticated customer interactions. While the global CPaaS market was valued at approximately $27.5 billion in 2024, indicating strong adoption, these substitutes leverage growing consumer preferences for convenience and advanced features. The UCaaS market, valued at approximately $35.4 billion in 2023, also presents a threat as it increasingly bundles communication features that overlap with CPaaS offerings.
The attractiveness of these substitutes is amplified by increasing user preference for feature-rich messaging, direct business integration with OTT platforms, and the ongoing rollout of RCS by mobile carriers. For instance, businesses might find OTT messaging more cost-effective than per-message SMS charges for certain use cases. Furthermore, the push for digital transformation, with over 75% of businesses surveyed in 2024 implementing or expanding such initiatives, further diminishes the viability of manual or legacy system substitutes.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on SEVAK | 2024 Market Context |
| OTT Messaging Apps (e.g., WhatsApp) | High user penetration, rich media, interactive features | Direct competition for customer engagement, potential bypass of CPaaS | Over 2 billion monthly active users globally (early 2024) |
| RCS Business Messaging (RBM) | Enhanced SMS, branding, interactive elements | Offers advanced customer journey capabilities, reducing reliance on traditional messaging | Growing adoption by mobile carriers |
| Direct Carrier Agreements/In-house Solutions | Requires significant investment and technical expertise | Threat to CPaaS providers by offering alternative infrastructure access | High barrier to entry for most businesses |
| UCaaS/CCaaS Platforms | Bundled communication features, integration | Can absorb standalone CPaaS functionalities, blurring market lines | UCaaS market valued at $35.4 billion (2023) |
| Traditional Methods (Email, Phone, Mail) | Basic functionality, less efficient for scale | Inefficient for automated or integrated messaging compared to CPaaS | Still used for simple needs but less effective for core business functions |
Entrants Threaten
Launching a Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) operation necessitates significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in creating sophisticated software platforms, building out global network infrastructure, and forging direct agreements with mobile carriers. For instance, establishing a reliable CPaaS backbone can easily run into millions of dollars, a sum that deters many smaller players from even considering entry.
The threat of new entrants into the CPaaS market is significantly moderated by substantial regulatory hurdles. Companies must navigate a labyrinth of evolving telecommunications regulations, stringent data privacy laws such as GDPR and HIPAA, and a patchwork of country-specific fees. For instance, in 2024, the global compliance burden for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions continues to increase, with many new entrants finding the cost and complexity of global regulatory adherence prohibitive.
Established Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS) providers hold a significant advantage due to their deeply entrenched direct carrier connections. These relationships are crucial for ensuring reliable and cost-effective delivery of SMS and voice communications globally. For instance, Twilio, a major player, has cultivated partnerships with over 2,000 carriers worldwide.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in replicating these extensive carrier networks. Building these relationships from scratch is time-consuming and capital-intensive. This lack of direct access can lead to lower quality of service, increased latency, and higher operational costs for newcomers, making it difficult to compete on core service delivery.
Furthermore, network effects amplify this barrier. As more users and businesses adopt existing CPaaS platforms, their value increases for everyone involved through greater reach and improved service quality. This creates a powerful moat, as new entrants must overcome not only carrier access issues but also the established user base of incumbents, a challenge that is particularly acute in the highly competitive 2024 CPaaS market.
Brand Loyalty and Switching Costs for Customers
Brand loyalty and the associated switching costs for customers present a significant barrier for new entrants in many industries. While direct financial switching costs might be moderate, the deeper challenge lies in overcoming established customer relationships built on trust and proven performance.
Companies that have operated for years have cultivated strong brand recognition and a loyal customer base. For instance, in the competitive smartphone market, Apple's ecosystem and brand loyalty, evidenced by a significant portion of its users upgrading to new iPhones year after year, make it difficult for new players to gain substantial market share. Similarly, in the software sector, businesses often hesitate to switch from established providers like Microsoft Office due to the integration, training, and potential data migration costs, even if newer alternatives offer advanced features.
- Established brand recognition acts as a powerful deterrent, making customers less receptive to unfamiliar alternatives.
- Customer trust, built over time through consistent service and product quality, is a difficult asset for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Switching costs, while sometimes not purely monetary, include the time, effort, and potential disruption involved in adopting a new solution or supplier.
- In 2024, industries with high levels of customer engagement, such as e-commerce and subscription services, often see loyalty programs and personalized experiences further solidifying existing customer bases.
Technological Complexity and Talent Acquisition
Developing and maintaining a sophisticated Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) platform demands considerable technical prowess. This includes expertise in areas like API development, cloud infrastructure management, the integration of artificial intelligence, and handling real-time communication protocols. For instance, companies like Twilio and Vonage invest heavily in R&D, with Twilio reporting $547 million in R&D expenses in 2023, highlighting the ongoing need for technological advancement.
The ability to attract and retain highly specialized talent presents a significant barrier to entry for new players in the CPaaS market. The demand for skilled software engineers, cloud architects, and AI specialists is intense, leading to competitive salaries and recruitment challenges. In 2024, the average software engineer salary in the US, particularly those with cloud and AI experience, can range from $120,000 to $180,000 annually, making talent acquisition a costly endeavor.
- High R&D Investment: CPaaS providers must continuously innovate, requiring substantial and ongoing investment in research and development to stay competitive.
- Specialized Skill Sets: Expertise in API design, cloud computing, AI/ML, and real-time data processing is crucial, creating a niche talent market.
- Talent Scarcity & Cost: The limited pool of qualified professionals drives up recruitment costs and retention efforts, acting as a barrier for new entrants.
- Platform Complexity: Building a robust, scalable, and secure CPaaS platform involves intricate architectural design and continuous maintenance.
The threat of new entrants in the CPaaS sector is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements for platform development and carrier agreements. Significant investments are needed for robust software, global infrastructure, and direct carrier partnerships, making it difficult for smaller companies to enter. For instance, establishing a functional CPaaS backbone can easily cost millions in 2024.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our SEVAK Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating information from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key players, and regulatory filings to ensure comprehensive insights.
