Mainland Headwear Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Mainland Headwear Holdings Bundle
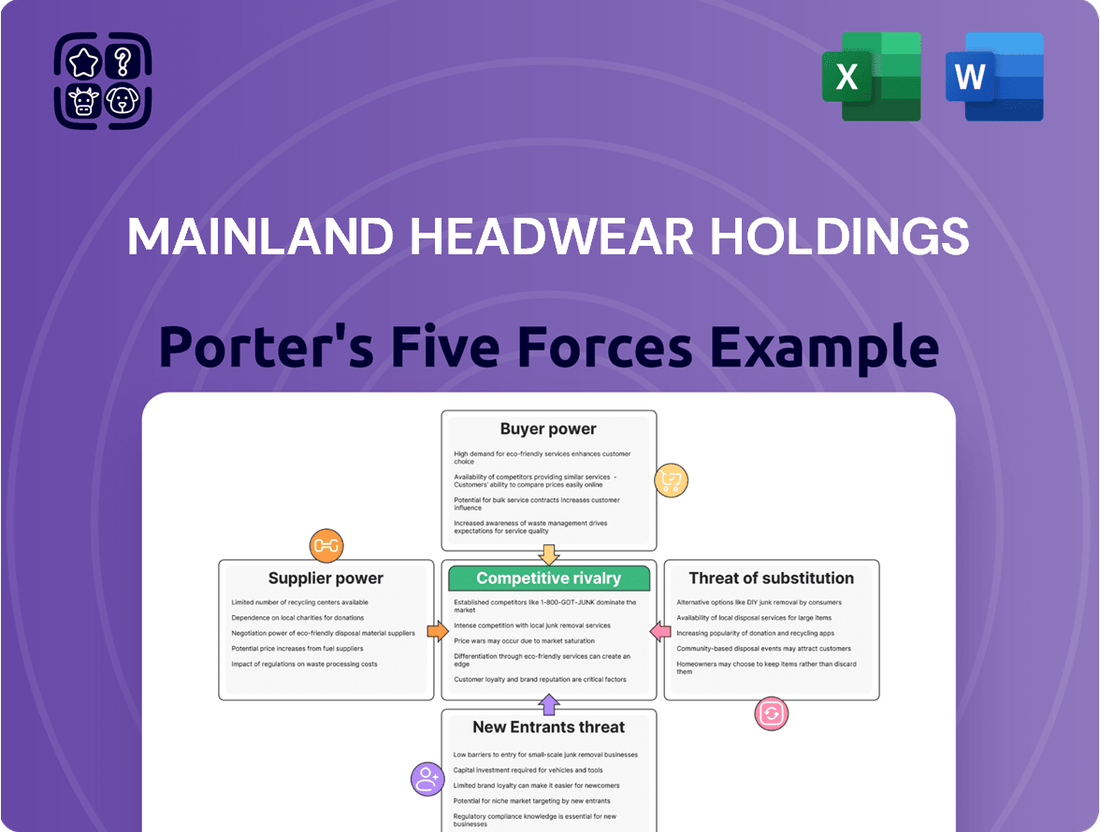
Mainland Headwear Holdings navigates a competitive landscape shaped by several critical forces. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for assessing profitability within the headwear industry. The threat of new entrants and the intensity of rivalry among existing players significantly impact market dynamics.
Furthermore, the presence of substitute products poses a constant challenge to Mainland Headwear Holdings's market share. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Mainland Headwear Holdings’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The headwear industry's dependence on specific inputs like high-quality cotton, wool, or specialized synthetic fibers means that if only a few suppliers offer these materials, their power naturally grows. This is especially evident in the burgeoning market for sustainable and eco-friendly fabrics, where the limited number of certified producers grants them considerable leverage.
For Mainland Headwear Holdings, the bargaining power of suppliers is a significant factor, particularly concerning the quality and timely delivery of raw materials. These inputs are absolutely critical for the company to uphold its reputation and successfully meet its original equipment manufacturer (OEM) and original design manufacturer (ODM) contracts. When a supplier's product is essential and lacks readily available substitutes, their leverage increases considerably.
This dynamic is further amplified by the increasing global demand for more sustainable materials, such as certified organic and recycled fabrics. In 2023, the global sustainable fashion market was valued at over $6.5 billion and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer preference. This trend means suppliers offering these specialized materials are in a stronger negotiating position with manufacturers like Mainland Headwear.
Switching suppliers for Mainland Headwear can be a costly endeavor, particularly when dealing with specialized or sustainably sourced materials. These costs can manifest as expenses for rigorous testing of new material samples, potential disruptions to ongoing production schedules, and even risks to the company's established brand reputation if the quality of incoming goods falters.
In 2024, for instance, the textile industry has seen increased volatility in raw material prices, meaning new supplier onboarding could involve not just qualification but also price renegotiation, adding to the switching burden. For a company like Mainland Headwear, which relies on consistent material quality for its product lines, the investment in validating new suppliers for even a single component could run into tens of thousands of dollars, encompassing laboratory analysis and pilot production runs.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into headwear manufacturing is a key consideration. If suppliers can effectively move into producing finished headwear products themselves, they gain significant bargaining power over companies like Mainland Headwear Holdings.
However, the apparel manufacturing industry, particularly for headwear, is characterized by its competitiveness and substantial capital requirements. This makes forward integration a challenging proposition for many raw material suppliers. It demands considerable investment in production facilities, technology, and the establishment of robust distribution networks.
For instance, the global apparel market, a broad category that includes headwear, saw significant investment in automation and advanced manufacturing techniques in 2024. Companies integrating forward would need to match these advancements to remain competitive. This high barrier to entry generally keeps the threat of forward integration low for raw material suppliers in this sector.
Consider these points regarding the threat:
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers must possess not only raw materials but also the manufacturing expertise and capital to produce headwear efficiently and at scale.
- Market Dynamics: The cost and complexity of establishing a manufacturing and distribution presence in the headwear market must be weighed against potential returns.
- Competitive Landscape: New entrants, including suppliers, would face established players with existing brand recognition and market share.
- Capital Investment: Significant upfront investment in machinery, labor, and marketing is required, potentially exceeding the financial capacity of many raw material providers.
Impact of Global Supply Chain Dynamics
Global supply chain disruptions, particularly those exacerbated by geopolitical tensions and persistent inflationary pressures through 2024, have notably amplified the bargaining power of suppliers. These factors directly translate into increased raw material costs and considerable logistics challenges for manufacturers like Mainland Headwear Holdings.
The fashion supply chain, as projected for 2025, is anticipated to grapple with ongoing difficulties in both raw material procurement and intricate logistics. This environment grants suppliers greater leverage, enabling them to dictate terms more favorably.
- Increased Input Costs: The cost of key materials, such as cotton and synthetic fibers, saw significant volatility in 2024. For instance, cotton prices experienced fluctuations driven by weather patterns and trade policies, impacting manufacturers' cost structures.
- Logistical Hurdles: Shipping container costs and port congestion remained persistent issues in 2024, extending lead times and increasing freight expenses for companies relying on global sourcing.
- Geopolitical Influence: Trade disputes and regional conflicts have disrupted traditional supply routes, forcing companies to seek alternative, often more expensive, sourcing options, thereby strengthening the position of available suppliers.
- Supplier Concentration: In specific segments of the headwear industry, a limited number of key suppliers for specialized fabrics or manufacturing components can exert considerable influence over pricing and availability.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Mainland Headwear Holdings is heightened by the industry's reliance on specific, high-quality raw materials like cotton and specialized synthetics. Limited availability of sustainable or certified fabrics, a growing market trend, further empowers these suppliers. For example, the global sustainable fashion market exceeded $6.5 billion in 2023, underscoring the demand for such materials and the leverage they provide to their producers.
Switching suppliers involves significant costs for Mainland Headwear, including rigorous testing, potential production delays, and brand reputation risks if new materials underperform. In 2024, raw material price volatility and the expense of validating new suppliers, which can reach tens of thousands of dollars per component, exacerbate this switching burden.
Global supply chain disruptions in 2024, driven by geopolitical issues and inflation, have amplified supplier leverage, leading to higher input costs and logistical challenges. For instance, cotton prices fluctuated significantly due to weather and trade policies, while shipping costs and port congestion persisted, extending lead times and increasing freight expenses.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into headwear manufacturing is generally low due to substantial capital requirements and the competitive landscape, which demands significant investment in advanced manufacturing and distribution networks to compete with established players.
| Factor | Impact on Mainland Headwear Holdings | 2024/2025 Context |
| Supplier Concentration | Limited suppliers for specialized/sustainable materials increase their power. | Growing demand for sustainable fabrics grants leverage to certified producers. |
| Switching Costs | High costs for material testing, production disruption, and quality risk. | Validation costs can be tens of thousands per component; price volatility adds complexity. |
| Input Cost Volatility | Fluctuations in raw material prices impact manufacturing costs. | Cotton prices saw significant swings in 2024 due to weather and trade policies. |
| Logistical Challenges | Disruptions increase lead times and freight expenses. | Persistent port congestion and high container costs continued through 2024. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Mainland Headwear Holdings' position in the global headwear industry.
Easily visualize competitive intensity across all five forces, highlighting the most significant threats to Mainland Headwear Holdings' profitability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Mainland Headwear Holdings caters to a wide array of global brands and retailers, many of which are significant players in the fashion and sports sectors. These substantial clients, particularly those placing large original equipment manufacturer (OEM) and original design manufacturer (ODM) orders, wield considerable influence due to the sheer volume of their business.
The substantial purchasing volume allows these major customers to negotiate more advantageous pricing and contractual terms. For instance, a single large order could represent a significant portion of Mainland Headwear's revenue, giving the customer leverage. In 2023, the company reported that its top five customers accounted for approximately 45% of its total revenue, highlighting the concentration and the resulting bargaining power.
For global brands and retailers sourcing headwear, switching manufacturers presents moderate switching costs. These typically involve the time and resources needed to re-establish supply chain relationships, implement new quality assurance protocols, and manage potential delays in product launches. While these hurdles exist, they are not prohibitive, and customers are inclined to switch if they find better pricing or superior quality elsewhere.
In the competitive headwear market, especially for mass-produced items through Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) agreements, customers, including brands and retailers, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are constantly on the lookout for manufacturers who can provide competitive pricing while still maintaining a good quality standard. For instance, in 2024, the global apparel and accessories market experienced intense competition, with many brands actively negotiating with suppliers to secure the best possible rates, directly impacting profit margins for manufacturers like Mainland Headwear.
Customers' Threat of Backward Integration
Customers, particularly large brands and retailers, typically lack the inclination and resources to venture into headwear manufacturing. The production process for headwear involves specialized machinery and expertise, making backward integration a significant undertaking. This inability or unwillingness to produce their own headwear limits the direct threat they pose to manufacturers like Mainland Headwear Holdings.
Consequently, the bargaining power derived from the threat of backward integration is somewhat diminished for these customers. While they possess other levers of power, their capacity to bypass manufacturers by producing headwear internally is minimal. This dynamic slightly softens their overall negotiating stance regarding pricing or other terms.
- Complexity of Manufacturing: Headwear production requires specialized equipment and skilled labor, deterring most large buyers from vertical integration.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing and maintaining manufacturing facilities represents a substantial financial commitment, often outweighing the perceived benefits for customers.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Major brands and retailers typically concentrate on design, marketing, and distribution, rather than engaging in the manufacturing of niche products like headwear.
- Limited Impact on Bargaining Power: The reduced threat of backward integration means customers rely more on other strategies, such as volume purchasing or sourcing from multiple suppliers, to exert influence.
Availability of Alternative Manufacturers
The availability of numerous alternative manufacturers, especially in Asia, significantly bolsters customer bargaining power in the OEM and ODM clothing sector. This competitive landscape means buyers, like those sourcing from Mainland Headwear, can easily switch suppliers if terms aren't favorable. For instance, a report from Statista in 2024 indicated that the global apparel manufacturing market comprises thousands of active factories, creating a buyer's market.
This abundance allows customers to compare pricing, quality, and lead times across many potential partners. Consequently, Mainland Headwear faces pressure to offer competitive pricing and maintain high service levels to retain clients. The sheer volume of choices means customers can negotiate more aggressively, driving down margins for individual manufacturers.
- Global Competition: Thousands of apparel manufacturers worldwide, particularly in Asia, offer extensive alternatives.
- Buyer's Market: The high supply of manufacturers creates a buyer's market, empowering customers.
- Price Negotiation: Customers can leverage multiple options to negotiate better pricing with manufacturers like Mainland Headwear.
- Supplier Switching: The ease of switching suppliers increases pressure on manufacturers to remain competitive.
The bargaining power of customers for Mainland Headwear Holdings is considerable, driven primarily by their significant purchasing volume and the availability of numerous alternative suppliers. Major clients, often global brands, represent a substantial portion of revenue, allowing them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. For example, in 2023, Mainland Headwear's top five customers contributed approximately 45% of its total revenue, underscoring their leverage.
Customers' ability to switch manufacturers is facilitated by moderate switching costs, primarily related to establishing new supply chain relationships rather than prohibitive technical barriers. This ease of switching, coupled with intense price sensitivity in the 2024 apparel market, pushes manufacturers to remain competitive. The global market in 2024 featured thousands of apparel factories, creating a buyer's market where customers can easily compare and negotiate.
| Customer Characteristic | Impact on Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Volume | High | Top 5 customers represented ~45% of revenue in 2023. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Thousands of apparel manufacturers globally, particularly in Asia (2024 market observation). |
| Switching Costs | Moderate | Primarily logistical and relationship-based, not prohibitive. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Intense competition in 2024 apparel market leads to aggressive negotiation. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low | Customers focus on core competencies, not headwear manufacturing. |
Same Document Delivered
Mainland Headwear Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Mainland Headwear Holdings meticulously examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the headwear industry. The preview accurately reflects the depth and detail of the insights you will gain into Mainland Headwear Holdings' competitive landscape, providing actionable intelligence for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The headwear manufacturing sector is characterized by a moderate level of concentration, with several large players coexisting with a multitude of smaller, specialized, and emerging companies. Mainland Headwear navigates this landscape, encountering competition not only from dedicated large-scale Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) providers but also from niche manufacturers focusing on specific styles or materials.
This diversity means Mainland Headwear must contend with competitors ranging from those capable of massive production runs to those offering highly customized or artisanal headwear. For instance, while some competitors might be global giants with extensive supply chains, others could be agile, design-led firms that can quickly adapt to emerging fashion trends.
The presence of brands that also possess their own manufacturing capabilities further intensifies rivalry. These vertically integrated companies can often exert greater control over production costs and lead times, presenting a competitive challenge. In 2024, the global headwear market was valued at approximately $25 billion, indicating a substantial market size that attracts a wide array of participants.
The global headwear market is anticipated to experience robust growth, with projected compound annual growth rates (CAGRs) ranging from 4.88% to 8.3% starting from 2025. This expansion is fueled by increasing fashion awareness, rising participation in sports and outdoor activities, and the continued dominance of e-commerce channels.
A growing market environment generally tempers competitive rivalry. With more opportunities for sales and expansion, companies may focus less on aggressively stealing market share from competitors and more on capturing new customers within the expanding pie.
While headwear might seem like a basic item, companies like Mainland Headwear Holdings can carve out a competitive edge through distinct product offerings. This means focusing on unique designs, superior quality materials, and practical features like sweat absorption or sun protection. The industry is seeing a surge in innovation, with manufacturers exploring new fabrics and even incorporating smart technology into their products, compelling rivals to keep pace.
Exit Barriers
High capital investments in manufacturing facilities and specialized machinery act as significant exit barriers for headwear companies. For instance, a typical modern apparel manufacturing plant, which includes specialized stitching and finishing equipment, could easily require an investment upwards of $5 million. This substantial financial commitment means that even when market conditions are unfavorable, firms may continue operating to recoup their investment, thereby prolonging competitive intensity.
These embedded costs discourage companies from leaving the industry, even if profitability dwindles. Consequently, Mainland Headwear Holdings and its peers might find themselves competing against businesses that are essentially running on a break-even or slightly loss-making basis, solely to avoid the sunk costs associated with shutting down operations. This situation can lead to aggressive pricing strategies and a prolonged fight for market share.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized machinery for headwear production, like automated cutting and embroidery machines, represents a significant upfront cost, potentially running into hundreds of thousands of dollars per unit.
- Sunk Costs: Once invested, these capital expenditures are largely irrecoverable if a company exits the market, creating a strong incentive to remain operational.
- Market Saturation: In a market with many players already facing these barriers, the pressure to maintain sales volume can intensify, leading to increased price competition.
- Extended Competition: Companies may stay in the market longer than economically rational, simply to avoid the financial penalty of exiting, thus perpetuating rivalry.
Strategic Importance and Industry Consolidation
The headwear industry, though a niche within the larger fashion and apparel sector, holds significant strategic importance. This strategic value means that many companies are reluctant to leave the market, fostering a competitive environment where rivalry remains intense. This unwillingness to exit contributes to the sustained pressure among existing players.
Despite a generally fragmented market structure, there's a noticeable trend towards consolidation. Larger companies are actively pursuing mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances. For instance, in 2023, the global sportswear market, which often includes headwear as an accessory, saw significant M&A activity as brands sought to expand their reach and customer demographics.
- Sustained Rivalry: The strategic importance of headwear in fashion and apparel limits market exits, keeping competition high.
- Market Fragmentation: The industry is characterized by numerous smaller players alongside larger entities.
- Consolidation Trend: Mergers and acquisitions are increasing as major companies aim to strengthen their market position.
- Strategic Partnerships: Companies are forming alliances to broaden their customer bases and operational capabilities.
Competitive rivalry in the headwear sector is significant due to a fragmented market with both large OEMs/ODMs and niche manufacturers, alongside vertically integrated brands. In 2024, the global headwear market, valued around $25 billion, is expected to grow robustly, which typically tempers rivalry, but high capital investment and sunk costs create substantial exit barriers, compelling companies to stay in the market even if unprofitable. This prolongs competitive intensity, leading to aggressive pricing and a continuous fight for market share, further exacerbated by a trend towards industry consolidation through mergers and acquisitions.
| Market Factor | Impact on Rivalry | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | Moderate to High | Coexistence of large players and numerous smaller, specialized firms. |
| Exit Barriers | High | Capital investment in specialized machinery (e.g., automated cutting, embroidery) can exceed hundreds of thousands of dollars per unit. |
| Market Growth | Tempering | Projected CAGR of 4.88%-8.3% from 2025 for the global headwear market (valued at ~$25 billion in 2024). |
| Industry Trends | Intensifying | Consolidation via M&A in related apparel sectors (e.g., sportswear in 2023) suggests similar pressures in headwear. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Alternative head coverings such as scarves, bandanas, and integrated hoods in clothing present a notable threat to Mainland Headwear Holdings. These items offer comparable functional benefits, like protection from the elements or as fashion accessories, but they often lack the distinct style and brand identity associated with specialized hats and caps. For example, while a scarf can provide warmth, it doesn't offer the same structured look or the potential for logo visibility that a branded baseball cap does.
The threat of substitutes from other fashion accessories is significant for Mainland Headwear Holdings. Consumers have a wide array of choices beyond headwear, like jewelry, eyewear, and handbags, to showcase their personal style and make fashion statements. This broad competitive landscape means that discretionary spending on fashion items can easily shift away from headwear towards these alternative accessories.
For instance, spending on fashion accessories globally is projected to reach approximately $340 billion by 2025, indicating a substantial market where consumers can allocate their disposable income. If a consumer decides to purchase a new designer handbag instead of a stylish hat, this directly impacts the demand for Mainland Headwear's products. This diversion of consumer spending poses a considerable challenge to maintaining and growing market share within the headwear segment.
For many situations, especially casual ones, consumers have the option to simply forgo headwear altogether. This 'do nothing' alternative is a powerful substitute for Mainland Headwear Holdings. It represents zero cost and is the default choice when headwear isn't perceived as essential for style, sun protection, or participating in an activity.
The prevalence of this option is significant. In 2024, surveys indicated that for informal social gatherings and everyday errands, a substantial percentage of individuals opt out of wearing hats or caps. This trend suggests that the market for headwear faces a constant challenge from the basic decision to wear nothing, impacting potential sales volume.
Technological Advancements in Apparel
Technological advancements in the apparel industry present a significant threat of substitutes for headwear manufacturers like Mainland Headwear Holdings. Innovations such as jackets with integrated, protective, or stylish hoods can directly diminish the demand for separate headwear items like caps or beanies. For example, the increasing sophistication of weatherproof and temperature-regulating fabrics in outerwear means consumers may find their needs met without purchasing additional head coverings.
Furthermore, the rise of smart apparel, incorporating features like biometric sensors or communication capabilities, could further erode the market for specialized headwear. As apparel becomes more functional, it may absorb some of the utility previously provided by items like sports headbands or even fashion-oriented hats. This trend suggests that consumers might opt for a single, multi-functional garment rather than discrete headwear accessories.
- Growing Smart Apparel Market: The global smart clothing market was valued at approximately $3.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $10 billion by 2028, indicating a strong trend towards integrated apparel functionality.
- Hooded Outerwear Popularity: Data from apparel market research firms consistently shows a high percentage of outerwear sales featuring integrated hoods, reflecting consumer preference for all-in-one solutions.
- Material Innovation: Ongoing research and development in textile technology are leading to lighter, more protective, and more versatile fabrics, enhancing the substitute potential of apparel.
DIY and Customization Trends
The growing trend of do-it-yourself (DIY) fashion and highly customized apparel poses a moderate threat to headwear manufacturers like Mainland Holdings. As consumers increasingly seek unique self-expression, they may opt for personalized clothing items that bypass the need for traditional, off-the-shelf headwear. This shift could lead to a reduction in demand for standardized products.
For instance, the global custom t-shirt printing market was valued at approximately USD 3.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a broader consumer interest in personalized apparel. This trend suggests that consumers might be more inclined to create their own headwear accessories or integrate headwear into their custom outfits, potentially reducing reliance on mass-produced options.
- DIY Fashion Growth: The increasing popularity of DIY fashion allows consumers to create unique apparel, potentially impacting demand for standardized headwear.
- Customization Demand: Consumers' desire for personalized clothing extends to accessories, with some opting for custom-designed headwear.
- Market Indicators: The robust growth in markets like custom apparel printing (e.g., t-shirts) suggests a wider consumer appetite for personalized items across the fashion spectrum.
- Potential Impact: This trend could divert consumer spending from ready-made headwear towards bespoke or self-made alternatives.
Alternative head coverings like scarves and integrated hoods in clothing offer functional substitutes for Mainland Headwear Holdings, though they may lack the specific style and branding of traditional headwear. The "do nothing" option remains a powerful substitute, especially in casual settings, as consumers may forgo headwear entirely rather than purchase a product.
The increasing sophistication of apparel, particularly with integrated hoods and smart fabric technology, directly competes with the need for separate headwear items. Furthermore, the growing DIY and custom apparel market suggests consumers might create their own headwear or integrate it into personalized outfits, potentially reducing reliance on mass-produced options.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Impact on Mainland Headwear | 2024/2025 Relevance |
| Alternative Coverings | Scarves, bandanas, integrated hoods | Offers similar basic protection; lacks specific style/branding | Continued popularity of versatile fashion items |
| "Do Nothing" Option | Forgoing headwear | Zero cost; default choice when headwear is not perceived as essential | Significant in casual settings, impacting potential sales volume |
| Smart/Functional Apparel | Jackets with integrated hoods, advanced fabrics | Absorbs utility of headwear; consumers may prioritize multi-functional garments | Global smart clothing market projected to exceed $10 billion by 2028 |
| DIY/Custom Apparel | Personalized clothing, custom headwear | Reduces demand for standardized products; shifts spending to bespoke alternatives | Custom apparel printing market growing, indicating broad consumer appetite for personalization |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a headwear manufacturing business, particularly one targeting global original equipment manufacturer (OEM) and original design manufacturer (ODM) clients, demands significant upfront capital. This includes investments in specialized machinery for various production processes, setting up or leasing factory facilities, and acquiring a skilled workforce. For example, a modern, automated knitting machine for caps can cost upwards of $50,000, and a full production line can easily run into millions of dollars.
These substantial capital requirements act as a formidable barrier to entry for new companies looking to enter the headwear manufacturing sector. Potential entrants face the challenge of securing financing for these high initial costs, which can deter many from even attempting to compete with established players who have already made these investments.
Established players like Mainland Headwear Holdings leverage significant economies of scale. For instance, in 2024, large-scale manufacturers often achieve production costs that are 10-20% lower per unit compared to smaller operations due to bulk purchasing of raw materials and optimized factory utilization.
This cost advantage presents a substantial barrier for new entrants. Without the volume to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers or invest in highly efficient, large-scale machinery, newcomers would likely face higher per-unit production expenses, hindering their ability to compete on price in the headwear market.
Sourcing and distribution efficiencies also contribute to this barrier. Mainland Headwear's established logistics networks and supplier relationships, built over years, allow for lower transportation and inventory management costs. New entrants would need considerable time and investment to replicate these operational efficiencies.
New companies entering the headwear market face significant hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels and nurturing strong customer relationships. Mainland Headwear Holdings, for instance, leverages its extensive global network of brands and retailers. This existing infrastructure is a substantial barrier, as new entrants would need considerable time and resources to replicate these connections, which are vital for widespread product availability and sales volume.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
While Mainland Headwear Holdings operates primarily on a business-to-business (B2B) model, its consistent delivery of quality products and innovative designs through Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) arrangements fosters a strong client relationship, akin to brand loyalty. New entrants would face a significant hurdle in replicating this established trust and proven track record, requiring substantial time and investment to build credibility within the industry.
The threat of new entrants is therefore mitigated by the established reputation and client relationships Mainland Headwear Holdings has cultivated. New competitors would need to overcome this entrenched loyalty, which is built on years of reliable service and product excellence.
- Established Relationships: Mainland Headwear's long-standing OEM/ODM partnerships provide a stable customer base resistant to new entrants.
- Quality and Design Reputation: A proven history of delivering high-quality, well-designed headwear builds a competitive advantage.
- High Switching Costs: For clients, changing suppliers involves significant effort in vetting, quality assurance, and potential design adaptation.
- Lack of Proven Track Record for Newcomers: New companies must invest heavily in marketing and building trust to compete with established players.
Regulatory and Trade Barriers
The global apparel and headwear sector is heavily influenced by international trade regulations, tariffs, and labor laws. For instance, in 2023, the average tariff on imported apparel into the United States ranged from 11.7% to 32.3%, depending on the item and country of origin. Newcomers must invest substantial resources to understand and comply with these diverse and often changing rules across sourcing and distribution channels. This compliance burden can be a significant deterrent, especially when compared to established players who have existing infrastructure and expertise in navigating these regulatory landscapes.
Established companies often benefit from pre-existing relationships with customs brokers and legal teams, streamlining the import/export process. For example, a new headwear company would need to factor in the costs and time associated with obtaining various certifications and adhering to country-specific product safety standards. The World Trade Organization’s Trade Facilitation Agreement, implemented in 2017 and continually updated, aims to simplify customs procedures, but the underlying complexities remain substantial for those without prior experience. Mainland Headwear Holdings, as an established entity, likely possesses the necessary frameworks to manage these challenges efficiently.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating international trade regulations and tariffs in the apparel sector is a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to diverse labor laws and product safety standards across different regions requires substantial investment.
- Established Infrastructure: Existing companies benefit from established compliance frameworks and expertise in customs procedures.
- Trade Agreements: While agreements like the WTO's Trade Facilitation Agreement aim to simplify processes, inherent complexities remain for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants into the headwear manufacturing sector is considerably low due to high initial capital requirements, estimated to be millions of dollars for a fully equipped production line. Furthermore, established players like Mainland Headwear Holdings benefit from significant economies of scale, achieving production costs 10-20% lower per unit in 2024 compared to smaller operations. Navigating complex international trade regulations and compliance costs also presents a substantial barrier for newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in machinery, facilities, and skilled labor. | Deters entry due to financing needs. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for large-volume manufacturers. | New entrants face higher production expenses. |
| Brand Reputation & Relationships | Established trust and client loyalty in OEM/ODM partnerships. | New entrants struggle to replicate credibility and secure clients. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating international trade laws, tariffs, and labor standards. | Requires significant investment in expertise and infrastructure. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Mainland Headwear Holdings leverages data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific trade publications. We also incorporate insights from market research reports and competitor financial filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
