JSR Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
JSR Bundle
JSR Corporation operates within a dynamic market, shaped by critical competitive forces. Understanding these forces is key to navigating its strategic landscape. For instance, the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers significantly influence JSR's pricing and market share.
The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors and the availability of substitute products also present ongoing challenges and opportunities. Furthermore, the bargaining power of suppliers can impact JSR's cost structure and operational efficiency.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore JSR’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration is a significant factor in JSR's advanced materials sectors. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, the availability of highly specialized photoresists and other critical chemicals is often dominated by a few key global manufacturers. If JSR relies heavily on a limited number of suppliers for these essential components, those suppliers gain considerable leverage.
This limited supplier base means JSR has fewer options for sourcing, potentially leading to higher input costs or less favorable contract terms. For example, in the market for high-purity chemicals essential for advanced semiconductor fabrication, a handful of companies might control the majority of the global supply. This scarcity directly translates to increased bargaining power for those suppliers.
In 2024, the semiconductor materials market continued to see consolidation. Companies specializing in advanced lithography materials, for example, often operate with very high barriers to entry, limiting new competitors. This situation allows established players to command premium pricing and dictate terms, impacting JSR's procurement strategies and overall cost structure for critical inputs.
The bargaining power of suppliers for JSR is significantly influenced by high switching costs, particularly in the semiconductor industry. Developing and qualifying new materials for advanced chip manufacturing requires extensive research, development, and rigorous testing, making it a costly and time-consuming endeavor for JSR. For instance, a new photoresist formulation might take years of integration and validation within a chipmaker's process. This deep integration means that even minor changes can necessitate substantial re-engineering and re-certification, creating a strong lock-in effect for JSR with its existing material suppliers.
JSR's reliance on highly specialized and proprietary inputs, particularly for its advanced photoresists and life science materials, grants significant bargaining power to its suppliers. For instance, the development of next-generation semiconductor materials often involves unique chemical formulations or patented processes that only a handful of specialized chemical manufacturers can provide. These suppliers, by controlling access to critical, non-substitutable components, can command higher prices and dictate terms, impacting JSR's cost structure and production timelines.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into JSR's manufacturing processes, while not a primary concern, can nonetheless represent a significant bargaining chip. If a supplier possesses the technological know-how and financial resources, they could potentially enter JSR's market, thereby capturing more of the value chain.
However, this specific threat is considerably dampened by the inherent complexity and substantial capital investment required for JSR's operations. Such barriers make it unlikely for most suppliers to successfully undertake forward integration.
For instance, JSR's advanced materials production involves highly specialized equipment and extensive research and development, estimated to require billions in capital expenditure for new facilities.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing JSR's manufacturing capabilities necessitates significant upfront investment, acting as a deterrent to potential supplier integration.
- Technological Sophistication: The intricate production processes and proprietary technologies employed by JSR are difficult for suppliers to replicate.
- Market Complexity: Navigating JSR's established distribution channels and customer relationships presents another hurdle for aspiring integrated suppliers.
- Limited Supplier Incentive: Many suppliers focus on their core competencies, finding the risks and costs of forward integration into JSR's business outweigh the potential rewards.
Importance of JSR to Supplier's Business
JSR's significant presence in multiple advanced materials sectors positions it as a crucial customer for many of its raw material providers. This substantial purchasing volume naturally grants JSR a degree of leverage, as suppliers are keen to secure and retain such a large, consistent buyer for their products.
The bargaining power of suppliers to JSR is therefore moderated by JSR's own market standing. For instance, in the semiconductor materials market, where JSR is a leading supplier of photoresists, its demand represents a substantial portion of output for specialized chemical manufacturers. This mutual dependence can create a more balanced negotiation environment.
- JSR's Market Share: JSR holds a dominant position in several niche markets, such as semiconductor photoresists, where it is a top global player.
- Supplier Dependence: For certain high-purity chemicals and specialized polymers, JSR may account for a significant percentage of a supplier's total revenue.
- Relationship Stability: Maintaining a strong relationship with JSR is often a strategic priority for these suppliers, influencing their willingness to offer favorable terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers for JSR is amplified by the limited number of companies capable of producing highly specialized materials, particularly in the semiconductor sector. This concentration means JSR often has few alternatives for critical inputs like advanced photoresists.
High switching costs further bolster supplier leverage, as JSR faces significant expense and time delays in qualifying new materials due to rigorous R&D and validation processes. For example, integrating a new photoresist can take years.
In 2024, the semiconductor materials market continued to experience consolidation, with high barriers to entry for new players in advanced lithography materials. This allowed established suppliers to maintain pricing power and dictate terms, impacting JSR's procurement costs.
| Factor | Impact on JSR | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited options increase supplier leverage. | Dominance of few players in specialized semiconductor chemicals. |
| Switching Costs | High R&D and validation costs lock JSR in. | Years of qualification for new materials in chip manufacturing. |
| Proprietary Inputs | Control over unique formulations grants pricing power. | Few manufacturers can produce next-gen semiconductor materials. |
What is included in the product
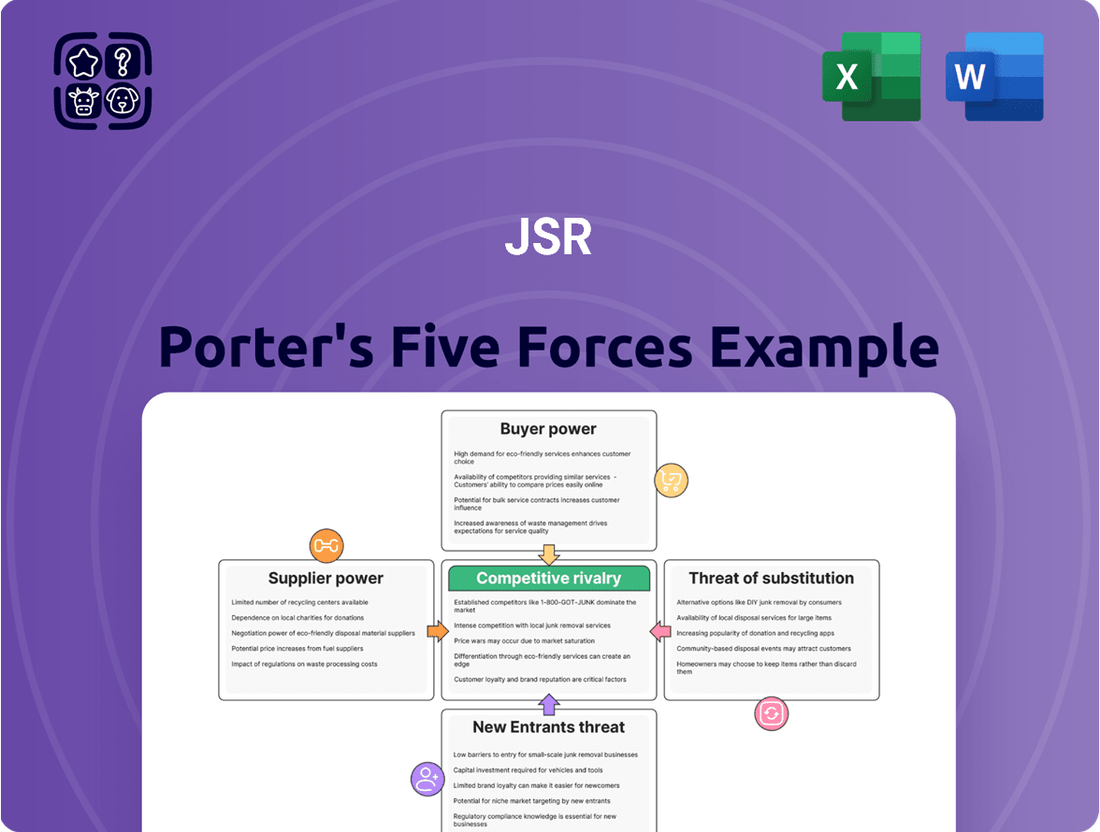
This analysis dissects the competitive intensity within JSR's operating environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual, interactive representation of all five forces.
Easily assess and adapt your strategy to changing market dynamics by seeing the impact of each force on your business.
Customers Bargaining Power
JSR's customer concentration with a few large, global players significantly influences its bargaining power. Major semiconductor manufacturers, for instance, represent substantial portions of JSR's revenue. In 2024, the top five semiconductor customers alone accounted for over 35% of JSR's sales in that segment, highlighting their considerable leverage.
These large clients, particularly in the high-volume semiconductor market, can often consolidate their orders, negotiate bulk discounts, and even threaten to switch suppliers if terms are not met. This concentrated customer base means JSR must carefully manage relationships and pricing to retain these key accounts.
Customers in the semiconductor and life sciences sectors often face significant hurdles when switching materials suppliers, directly impacting their ability to change vendors. For instance, qualifying new materials in semiconductor manufacturing is a lengthy and expensive process, often involving extensive testing and validation to ensure compatibility and performance. This can add months and millions of dollars to a new supplier's integration timeline.
This reliance on rigorous qualification and the demand for absolute consistency in performance means that even minor deviations from a current supplier's materials can lead to production disruptions or subtle quality degradation. For example, a semiconductor manufacturer might experience yield losses of 5-10% or more during an initial transition period due to these factors, making the perceived cost savings of switching suppliers often outweighed by the immediate financial and operational risks.
The potential for production delays and quality issues further solidifies customer loyalty to established suppliers like JSR. Companies have invested heavily in optimizing their processes around specific materials, and introducing new ones requires a complete re-evaluation and often recalibration of manufacturing lines. This intricate integration creates a high barrier to entry for competitors and significantly reduces the bargaining power of customers who wish to switch.
Customer price sensitivity for JSR can vary significantly. In segments like consumer electronics, where JSR offers synthetic rubbers and display materials, customers operating in highly competitive environments may push for lower prices, especially as these products become more standardized. For instance, the global automotive rubber market, a key sector for synthetic rubber, is projected to reach over $70 billion by 2027, indicating substantial volume where price negotiations can be intense.
However, for JSR's advanced, high-performance materials, which are crucial for specialized applications, customers are often less sensitive to price. These materials, vital for industries such as semiconductors or advanced displays, command higher prices due to their unique properties and the significant R&D investment involved. The semiconductor materials market alone is expected to grow substantially, with advanced materials being a key driver.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant challenge to JSR Corporation. Major clients, particularly those in the demanding semiconductor sector, possess the financial and technical capability to bring critical material production in-house if JSR's pricing becomes unfavorable or supply chains falter.
This risk is amplified because these materials are often indispensable to the customers' end products. For instance, a large semiconductor manufacturer might assess the cost-benefit of developing its own photolithography materials or advanced display chemicals if JSR's market position allows for significant price increases or if there are concerns about JSR's production stability.
- Semiconductor Industry Reliance: Key customers in semiconductors rely heavily on JSR's advanced materials, creating a strong incentive for them to explore internal production if costs or supply become unreliable.
- Strategic Importance of Materials: The materials JSR supplies are often critical components in high-value electronic devices, making their control a strategic imperative for large customers.
- Potential for Cost Savings: If JSR's profit margins are perceived as high, customers may find backward integration a viable route to reduce their own input costs.
- Supply Chain Control: Customers may also seek to integrate backward to gain greater control over their supply chain, mitigating risks associated with supplier disruptions or quality variations.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers to Customers
Customers in JSR's markets frequently encounter alternative suppliers, a situation that grants them a degree of negotiation power. While this is generally true, the landscape shifts for highly specialized materials, such as the EUV photoresists crucial for advanced semiconductor manufacturing. In these niche segments, the pool of qualified suppliers is considerably smaller, thereby tempering the bargaining leverage customers can exert.
For instance, in the cutting-edge semiconductor industry, where JSR is a key player, the development and production of EUV photoresists require immense research and development investment and stringent quality control. This high barrier to entry means that while customers might have options for less specialized chemicals, their choices for critical components like EUV photoresists are more constrained. This limited number of highly capable suppliers for these advanced materials can significantly influence pricing and contract terms.
- Limited Alternatives for High-Tech Materials: For specialized products like EUV photoresists, the number of suppliers capable of meeting the stringent quality and performance demands is significantly lower than for more commoditized chemicals.
- Customer Leverage Varies by Product: Customers generally possess more bargaining power when purchasing standard chemical products where multiple suppliers exist, but this power diminishes considerably for JSR's most advanced and proprietary offerings.
- Impact on Pricing Negotiations: The availability of alternatives directly influences JSR's ability to command premium pricing. When alternatives are scarce for critical components, JSR can often negotiate more favorable terms.
- Strategic Importance of Niche Markets: JSR's focus on high-value, specialized materials means that while the absolute number of customers might be lower, their dependence on JSR's unique products strengthens JSR's position.
The bargaining power of JSR's customers is a significant factor, primarily driven by the concentration of its client base in key industries like semiconductors and life sciences. In 2024, JSR's top five semiconductor customers represented over 35% of that segment's sales, indicating their substantial influence through consolidated orders and potential for bulk discounts.
These large clients often face high switching costs due to the rigorous qualification processes for specialized materials, a barrier that limits their ability to easily change suppliers. For instance, integrating new semiconductor materials can cost millions and take months, often outweighing perceived price savings due to risks of production delays and yield losses, which could reach 5-10% or more during transitions.
Customer price sensitivity varies; while synthetic rubber markets for automotive applications see intense price negotiations, JSR's advanced, high-performance materials for semiconductors and displays command higher prices due to their unique properties and R&D investment, with the semiconductor materials market showing robust growth driven by these advanced products.
The threat of backward integration by major clients, particularly in the semiconductor sector, is also a concern, as these companies have the financial and technical capacity to produce critical materials in-house if JSR's pricing or supply chain stability becomes unfavorable.
Same Document Delivered
JSR Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete JSR Porter's Five Forces Analysis, ensuring you receive the exact, professionally formatted document you see here immediately after purchase. There are no hidden sections or placeholder content; you get the full, ready-to-use analysis. This means you can confidently download and implement the strategic insights presented without any surprises. What you preview is precisely what you will own and utilize for your business planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
JSR Corporation navigates markets characterized by a significant number of global competitors, especially in its core semiconductor materials and life sciences divisions. Established players like Tokyo Ohka Kogyo and Shin-Etsu Chemical are prominent in the semiconductor materials space, presenting a concentrated competitive front in certain product categories.
While some specific segments exhibit high concentration, the broader competitive landscape for JSR includes a diverse array of companies. For instance, in the photoresist market, a key area for JSR, competition is intense with multiple global suppliers vying for market share. In 2023, the global semiconductor materials market was valued at over $60 billion, indicating the scale of operations and the numerous entities involved.
The semiconductor materials market is anticipated to rebound and expand, which could ease competitive pressures as firms shift focus to securing emerging demand rather than just fighting for current market share. This growth is crucial for companies like JSR, a key player in advanced materials.
Conversely, sectors such as plastics may see more subdued growth, potentially leading to fiercer competition as companies battle for limited market expansion opportunities within these segments.
JSR's competitive rivalry is significantly shaped by its commitment to product differentiation through relentless innovation, particularly in high-demand sectors like EUV photoresists and advanced life science solutions. This focus on cutting-edge materials, like their specialized semiconductor materials, allows JSR to command premium pricing and reduces the direct impact of price-based competition.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key market for JSR's photoresists, continued to see intense competition, yet JSR's advanced materials, such as those for next-generation lithography, maintained a strong market position due to their unique performance characteristics. For instance, the demand for EUV photoresists is projected to grow substantially, with the market expected to reach billions of dollars, a testament to the value of JSR's differentiated offerings.
The emphasis on innovation not only strengthens JSR's market standing but also creates barriers for competitors looking to replicate their specialized product lines. JSR's investment in research and development, often a significant portion of their revenue, fuels this differentiation, ensuring they remain at the forefront of material science and technology.
Exit Barriers
JSR Corporation operates in highly capital-intensive sectors like semiconductor materials and life sciences, where substantial investments in research and development (R&D) and advanced manufacturing facilities are crucial. For instance, JSR's semiconductor materials division, a significant contributor to its revenue, requires ongoing, massive R&D spending to keep pace with Moore's Law and the ever-evolving demands of chip manufacturers. This deep commitment to specialized infrastructure and continuous innovation creates formidable exit barriers.
The need to recoup these large upfront and ongoing investments means that companies like JSR are reluctant to exit even when market conditions are unfavorable. This reluctance can intensify competitive rivalry, as firms are compelled to remain in the market and fight for market share to justify their capital expenditure. In 2023, JSR reported R&D expenses amounting to approximately ¥52.7 billion, underscoring the continuous investment necessary to maintain its competitive edge.
- High R&D Investment: JSR's commitment to innovation, particularly in advanced materials for the semiconductor industry, necessitates substantial and continuous R&D expenditure.
- Specialized Manufacturing Assets: The company's manufacturing facilities are highly specialized and costly to build and maintain, making them difficult to repurpose or sell.
- Talent and Expertise: Acquiring and retaining highly skilled personnel with specialized knowledge in areas like photolithography and bioprocessing adds another layer to exit barriers.
- Downturn Resilience: These high exit barriers can force companies to remain competitive even during economic downturns, potentially leading to prolonged periods of intense price competition and margin pressure.
Strategic Stakes and Acquisitions
Competitive rivalry within the semiconductor materials industry is intense, driven by significant strategic investments and consolidation activities. JSR Corporation itself was acquired by JIC Capital in early 2024 for approximately ¥900 billion (around $6 billion USD at the time of announcement), a move aimed at bolstering its position in advanced semiconductor materials. This substantial investment highlights the high strategic stakes involved for major players seeking to enhance their capabilities and market share.
The ongoing pursuit of advanced materials and technologies fuels aggressive competition among established firms and emerging players. These strategic maneuvers, including acquisitions and joint ventures, are common as companies aim to secure critical intellectual property and production capacity. For instance, competitors are heavily investing in research and development for next-generation lithography materials and advanced packaging solutions. The semiconductor materials sector saw global market revenue reach an estimated $69.4 billion in 2023, with projections indicating continued growth, further intensifying the competitive landscape.
- Strategic Investments: JSR's acquisition by JIC Capital for roughly $6 billion underscores the capital-intensive nature and high strategic value of semiconductor materials.
- Consolidation Trends: The industry is experiencing consolidation as companies seek to gain scale, technological advantages, and market access through mergers and acquisitions.
- R&D Focus: Intense competition drives significant R&D spending on next-generation materials, such as those for advanced lithography and packaging, critical for future semiconductor advancements.
- Market Growth: The semiconductor materials market's projected growth, estimated at $69.4 billion in 2023, incentivizes aggressive competitive actions and strategic positioning.
JSR Corporation faces intense competition, particularly in its core semiconductor materials and life sciences sectors, from established global players like Tokyo Ohka Kogyo and Shin-Etsu Chemical. The semiconductor materials market, valued over $60 billion in 2023, sees fierce rivalry, especially for advanced products like EUV photoresists, where JSR's innovation provides a competitive edge. This differentiation, fueled by substantial R&D investments, helps mitigate direct price wars.
The high capital requirements for R&D and specialized manufacturing create significant barriers to exit, compelling companies to stay competitive even in challenging market conditions. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense rivalry as firms fight to justify their investments. JSR's own acquisition by JIC Capital in early 2024 for approximately ¥900 billion ($6 billion USD) highlights the strategic importance and capital intensity of these markets, as companies consolidate to gain technological advantages and market share.
| Key Competitors in Semiconductor Materials | JSR's Strategic Focus | Market Dynamics & Data |
| Tokyo Ohka Kogyo | Product Differentiation through Innovation (e.g., EUV Photoresists) | Global Semiconductor Materials Market: >$60 billion (2023) |
| Shin-Etsu Chemical | High R&D Investment (e.g., ¥52.7 billion in FY2023) | EUV Photoresist Market: Billions of dollars (projected growth) |
| Others (Global Suppliers) | Specialized Manufacturing Assets & Expertise | JSR Acquisition by JIC Capital: ~¥900 billion / $6 billion USD (early 2024) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
In JSR's digital solutions, the threat of substitutes is significant due to rapid technological evolution. New materials or processes can quickly emerge, potentially replacing current offerings. For example, advancements in alternative lithography techniques, such as directed self-assembly or nanoimprint lithography, pose a potential substitute threat to JSR's established photoresist technologies. The semiconductor industry's drive for smaller feature sizes and cost efficiencies fuels this innovation, meaning a breakthrough in a substitute technology could rapidly alter the market landscape.
The threat of substitutes for JSR's products hinges on their price-performance ratio. If alternative materials can deliver comparable or better performance at a lower cost, JSR could face significant customer attrition. For instance, in the semiconductor materials market, while JSR's advanced photoresists are highly specialized, the emergence of more affordable, yet sufficiently effective, alternatives could erode JSR's market share, especially among price-sensitive customers.
Customer willingness to adopt substitutes in high-tech sectors is often tempered by significant hurdles. The qualification process alone can take years and cost millions, as seen with semiconductor materials where even minor changes require extensive re-testing. For instance, a new dielectric material might need to pass hundreds of reliability tests before being approved for use in a new chip design.
Integration into existing, complex manufacturing lines presents another substantial barrier. Companies invest heavily in specialized equipment and process parameters tailored to current materials. Switching to a substitute often necessitates costly retrofits or entirely new machinery, a risk many are reluctant to take unless the benefits are overwhelmingly clear and quantifiable.
This inherent caution means substitutes must offer not just parity, but demonstrably superior performance, cost savings, or enable entirely new functionalities to overcome inertia. A 2024 report by Gartner indicated that for critical component suppliers, the average time to qualify a new material in the automotive electronics sector can exceed 24 months, underscoring the lengthy adoption cycles.
Technological Advancements in Other Industries
Innovation in industries adjacent to or even unrelated to JSR’s core markets can introduce disruptive technologies. These could offer entirely new methods to fulfill the same basic functions that JSR's materials currently address. For instance, progress in areas like advanced additive manufacturing or direct-write technologies might emerge as viable substitutes, potentially diminishing the demand for certain types of display materials or specialized coatings JSR currently provides.
This threat is particularly relevant given the rapid pace of technological evolution across diverse sectors. For example, breakthroughs in bio-integrated electronics, while seemingly distant, could eventually offer alternative solutions for flexible display technologies, a key market for JSR. The increasing convergence of materials science, digital fabrication, and biotechnology means that unforeseen substitutes can materialize with surprising speed, impacting established product categories.
Consider the potential impact of emerging quantum dot technologies or advanced photonic materials, which could offer superior performance characteristics in displays and lighting, thereby substituting for current liquid crystal or OLED materials. Companies investing heavily in these areas, even if not direct competitors today, represent a latent threat. The strategic advantage lies in anticipating and adapting to these technological shifts, rather than reacting to them after market disruption has occurred.
The financial implications are significant, as a substantial shift to substitute technologies could lead to reduced market share and pricing pressure for JSR's existing product lines. For instance, if a new, lower-cost manufacturing process for advanced semiconductors bypasses the need for specialized photoresists that JSR supplies, it represents a direct threat. Understanding these evolving technological landscapes is crucial for long-term strategic planning and investment in research and development.
- Technological Convergence: Advancements in fields like additive manufacturing could create direct substitutes for JSR's materials in certain applications.
- Emerging Display Technologies: Innovations such as quantum dots or photonic materials may replace current display components supplied by JSR.
- Cross-Industry Disruption: Breakthroughs in unrelated industries can unexpectedly yield alternative solutions, impacting JSR's markets.
- R&D Investment: Companies focusing on disruptive technologies, even in adjacent sectors, pose a potential long-term threat to JSR's material dominance.
Regulatory or Environmental Shifts
Increased environmental regulations and a growing emphasis on sustainability present a significant threat of substitution for JSR Corporation. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter rules on emissions and waste, encouraging a shift towards more eco-friendly materials. For instance, by 2024, many automotive manufacturers are targeting higher percentages of recycled or bio-based content in their vehicles, directly impacting demand for traditional synthetic rubbers used in tires and other components.
This regulatory push can lead industries to explore and adopt bio-based alternatives or novel materials that offer a reduced environmental footprint. Such shifts could directly substitute for JSR's established chemical products, particularly in sectors like advanced materials and elastomers, where performance and sustainability are increasingly weighed. For example, the development of plant-derived polymers is gaining traction as a potential replacement for petroleum-based plastics.
- Environmental regulations are tightening globally, pushing for sustainable material alternatives.
- Industries are actively seeking bio-based or recycled materials to meet new standards.
- This trend poses a direct substitution risk to JSR's traditional chemical and elastomer products.
- By 2024, automotive sector demand for greener materials is expected to rise significantly.
The threat of substitutes for JSR is amplified by the potential for entirely new technological paradigms to emerge, offering different ways to achieve desired outcomes. These substitutes don't necessarily compete directly on existing product features but rather redefine the problem or solution space. For instance, advancements in direct air capture technologies for carbon dioxide could, in the long term, reduce the demand for certain chemical processes that JSR supports.
In 2024, the market for advanced materials is highly dynamic, with significant investment flowing into research and development of novel solutions. Companies are actively exploring alternatives that promise enhanced performance, reduced costs, or improved sustainability. This environment means that even established product lines like JSR's advanced photoresists or display materials face a continuous risk from innovative substitutes that may not yet be widely recognized.
The financial impact of successful substitutes can be profound, leading to market share erosion and downward pressure on pricing for incumbent products. A 2024 market analysis highlighted that in the specialty chemicals sector, a single disruptive substitute innovation can shift market leadership within 3-5 years if adoption hurdles are overcome. JSR's revenue streams, particularly those tied to mature technologies, are thus susceptible to this threat.
The strategic challenge for JSR lies in anticipating these emerging threats and adapting its R&D and product development strategies accordingly. This includes monitoring not only direct competitors but also innovations in adjacent or seemingly unrelated fields that could eventually offer alternative solutions. For example, breakthroughs in organic electronics might offer new pathways for display technologies that bypass the need for some of JSR's current material offerings.
| Threat of Substitutes Impact | Description | Example Scenario | Potential Financial Impact | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technological Disruption | Emergence of entirely new technologies that fulfill the same need differently. | A new additive manufacturing process that eliminates the need for certain specialized coatings. | Reduced demand for existing products, pricing pressure. | Estimated 15% of specialty chemicals market vulnerable to disruptive tech by 2025. |
| Cost-Performance Advantage | Substitutes offering comparable or superior performance at a lower price point. | Development of a lower-cost, high-performance alternative to JSR's advanced photoresists. | Market share loss, margin compression. | Average customer cost savings target for new material qualification is 10-15%. |
| Sustainability Driven Substitution | Increased adoption of eco-friendly or bio-based materials due to regulations and consumer demand. | Shift towards biodegradable polymers replacing petroleum-based plastics in packaging applications. | Decreased demand for traditional materials, need for product reformulation. | Global sustainable materials market projected to reach $120 billion by 2027, with significant growth from 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the advanced materials sector, especially for semiconductors and life sciences, demands immense capital. Think about the costs for cutting-edge research and development, building highly specialized manufacturing plants, and securing crucial intellectual property. For instance, establishing a new semiconductor fabrication facility, or fab, can easily cost billions of dollars, with some estimates for advanced nodes exceeding $20 billion in the late 2020s. This financial hurdle significantly deters potential new players.
JSR's formidable portfolio of proprietary technology and patents, particularly in high-demand areas like advanced photoresists for semiconductor manufacturing and specialized biopharmaceutical materials, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. For instance, JSR's leadership in EUV photoresists requires substantial R&D investment and years of development, a steep climb for any newcomer. The sheer complexity and intellectual property protection around these core technologies mean that any new competitor would face immense challenges in replicating JSR's product performance and market position without extensive licensing or groundbreaking, independent innovation.
JSR Corporation has cultivated deeply entrenched brand loyalty and enduring customer relationships, acting as a significant barrier to new entrants. These partnerships, forged over years of dependable service and high-quality material supply, are particularly robust in demanding sectors where reliability is paramount.
For instance, in the semiconductor materials market, where JSR holds a leading position, switching suppliers can involve extensive re-qualification processes and carries substantial risks for manufacturers. This inertia favors incumbents like JSR, making it challenging for newcomers to gain traction, even with competitive pricing.
The trust built through consistent performance and a deep understanding of customer needs means that new entrants face a steep uphill battle to displace these established connections. Imagine a scenario where a critical component in a high-volume production line fails due to an unproven material from a new supplier; the cost of such a disruption would be immense.
This customer stickiness, evident in JSR's long-term supply agreements with major electronics manufacturers, effectively locks in market share and discourages potential competitors from entering markets where JSR's brand equity is a primary differentiator.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certifications
The semiconductor and life sciences sectors are heavily regulated, demanding rigorous certifications and adherence to compliance standards. Newcomers must navigate a complex and expensive journey to satisfy these requirements, significantly delaying their market entry.
For instance, in the semiconductor industry, compliance with standards like ISO 9001 and industry-specific quality management systems is often mandatory for suppliers to major players. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval process for medical devices, a segment often intertwined with advanced semiconductor technology, can take years and cost millions of dollars. In 2024, the average cost for bringing a new medical device to market, including regulatory submissions, was estimated to be in the tens of millions. Similarly, life sciences companies face extensive clinical trials and regulatory approvals, with the pathway to market for a new drug often exceeding a decade and costing over $2 billion.
- Regulatory Complexity: Semiconductor and life sciences industries require adherence to a vast array of national and international regulations.
- Certification Costs: Obtaining necessary certifications, such as those from the FDA or EMA (European Medicines Agency), involves substantial financial investment and time.
- Lengthy Approval Processes: New entrants must endure lengthy review periods for product approvals, which can span several years, hindering rapid market penetration.
- Impact on Competition: These high barriers to entry significantly reduce the threat of new companies easily entering the market, thus protecting existing players.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
The threat of new entrants in JSR's market is significantly mitigated by the substantial barriers to accessing crucial distribution channels and supply chains. Building efficient and reliable global supply chains and distribution networks for specialized materials, as JSR has done, is an inherently complex and time-consuming endeavor. New players would face immense difficulty in replicating JSR's established infrastructure, which has been developed over decades and represents a significant capital investment and operational expertise.
Consider the sheer scale: JSR operates a vast network of facilities and partnerships that ensure timely delivery of their advanced materials across diverse industries. For a new entrant to even begin competing, they would need to invest heavily in logistics, warehousing, and transportation, a task made even more daunting by the specialized handling requirements of many of JSR's products. In 2023, global logistics costs represented a significant portion of business expenses, and for specialized materials, this figure can be even higher, creating a substantial financial hurdle for newcomers.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants require massive upfront capital to establish global supply chain and distribution networks comparable to JSR's.
- Operational Complexity: Managing specialized material handling, international shipping regulations, and diverse customer needs across multiple regions is a significant operational challenge.
- Established Relationships: JSR benefits from long-standing relationships with suppliers and distributors, creating a loyalty that is difficult for new companies to break into.
- Time to Market: The time required to build a robust and efficient supply chain can delay a new entrant's market entry, allowing JSR to further solidify its position.
The threat of new entrants for JSR Corporation is considerably low due to extremely high capital requirements, particularly in advanced materials for semiconductors and life sciences. Establishing state-of-the-art R&D and manufacturing facilities, such as a semiconductor fab, can cost upwards of $20 billion by 2025, a formidable barrier for any potential competitor.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our JSR Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific data, including company financial statements, market research reports from leading firms, and government regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
