Insulet Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Insulet Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape for Insulet, particularly the bargaining power of buyers and the threat of new entrants, is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview highlights key industry pressures that shape Insulet's market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Insulet’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration is a key factor in assessing Insulet's bargaining power of suppliers. While Insulet utilizes a wide network of suppliers, its dependence on specialized components for its Omnipod system, potentially sourced from a limited number of critical providers, could significantly amplify supplier leverage. For instance, if a single supplier provides a unique sensor or pump mechanism, Insulet’s ability to negotiate favorable terms or switch suppliers would be severely constrained.
Insulet faces substantial switching costs if it needs to change suppliers for its critical diabetes management device components. These costs can include significant investments in re-tooling manufacturing equipment and the lengthy process of re-qualifying new suppliers to meet stringent regulatory and quality standards. For instance, the specialized nature of components for devices like the Omnipod likely means that finding and integrating a new supplier could take months, if not longer, impacting production timelines.
These high switching costs effectively bolster the bargaining power of Insulet's current suppliers. Because it is costly and time-consuming for Insulet to find alternatives, existing suppliers can leverage this situation to negotiate more favorable pricing or terms. This dynamic can put pressure on Insulet's cost of goods sold, impacting its overall profitability.
The uniqueness of Insulet's supplier offerings, particularly for its advanced Omnipod system, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. Suppliers providing highly specialized or proprietary components essential for Insulet's innovative technology may command higher prices or more favorable terms.
This reliance on unique, critical components limits Insulet's ability to switch suppliers easily, thereby increasing its dependence and potentially strengthening the suppliers' negotiating position. For instance, in 2023, Insulet reported significant research and development expenses, underscoring the importance of specialized input for its product pipeline.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while less prevalent in the medical device sector, poses a potential challenge for Insulet. If a critical supplier were to decide on entering the insulin delivery system market directly, it could shift negotiation power. This scenario would create a direct competitor, compelling Insulet to manage its supplier relationships carefully to avoid empowering a rival.
- Supplier Integration Risk: A supplier moving into Insulet's market could leverage its existing capabilities to compete, potentially impacting Insulet's market share and pricing power.
- Negotiation Leverage: Insulet would likely face increased pressure in negotiations with such a supplier, as the supplier could threaten to withhold supply or increase prices, knowing Insulet's dependence.
- Market Dynamics: While specific instances of major medical device component suppliers integrating forward into the end-product market are not widely publicized, the potential exists, especially for suppliers with significant technological or manufacturing expertise. For example, in 2024, many component manufacturers across various industries have been exploring diversification strategies to capture more value.
- Strategic Response: Insulet's strategy would need to account for this by diversifying its supplier base and potentially exploring vertical integration options itself to mitigate this threat.
Importance of Insulet to Suppliers
Insulet's substantial market presence as a pioneer in tubeless insulin pump technology likely translates to a significant portion of its suppliers' overall revenue. For instance, Insulet reported total cost of goods sold of $508.9 million in 2023. A supplier whose products are critical to Insulet's manufacturing process might find that Insulet represents a substantial percentage of their sales, making them less inclined to risk this lucrative relationship through aggressive pricing demands.
This dependency can significantly curb a supplier's bargaining leverage. If Insulet is a major client, a supplier's ability to dictate terms or raise prices is diminished, as they would be hesitant to jeopardize a substantial revenue stream.
- Insulet's Market Dominance: As a leader in its niche, Insulet's purchasing volume can make it a crucial customer for many suppliers.
- Supplier Revenue Dependence: Suppliers may rely heavily on Insulet for a significant portion of their income.
- Reduced Price Leverage: This reliance weakens a supplier's ability to demand higher prices or more favorable terms.
- Risk Aversion: Suppliers are less likely to risk losing a major client like Insulet by pushing for unfavorable conditions.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Insulet is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, switching costs, and the uniqueness of their offerings. While Insulet works with a broad supplier base, its reliance on specialized components for its Omnipod system means that a few critical providers could hold significant leverage. For example, if a single supplier provides a unique sensor, Insulet’s ability to negotiate or switch is limited.
High switching costs for Insulet further empower suppliers. Re-tooling manufacturing and lengthy supplier re-qualification processes, potentially taking months, make it difficult for Insulet to change providers. This situation allows existing suppliers to push for more favorable pricing, impacting Insulet's cost of goods sold, which was $508.9 million in 2023.
The uniqueness of components, especially those vital for Insulet's innovative diabetes technology, grants suppliers greater power. Suppliers of proprietary parts essential for the Omnipod system can command higher prices. In 2023, Insulet’s substantial R&D spending highlights the importance of these specialized inputs.
Insulet's position as a major customer for many suppliers can, however, temper supplier bargaining power. If Insulet represents a large portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier may be hesitant to risk the relationship with aggressive pricing demands.
| Factor | Impact on Insulet | Supporting Data/Example |
| Supplier Concentration | Potentially High Leverage for Critical Component Suppliers | Dependence on specialized sensors/pump mechanisms |
| Switching Costs | High, Strengthening Supplier Position | Re-tooling, re-qualification delays, estimated months |
| Uniqueness of Offerings | Increased Supplier Pricing Power | Proprietary components for Omnipod |
| Insulet's Revenue Contribution to Suppliers | Can Reduce Supplier Leverage | 2023 Cost of Goods Sold: $508.9 million |
What is included in the product
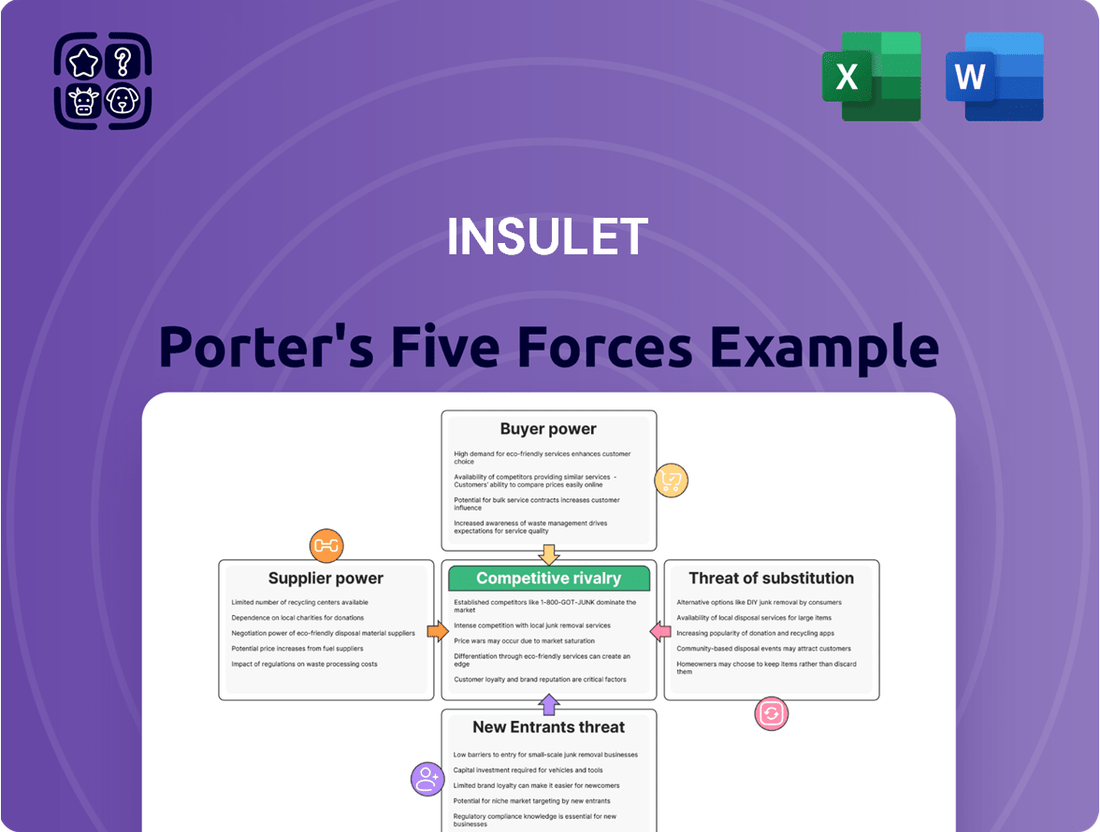
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Insulet, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the diabetes device market.
Effortlessly assess competitive pressures and identify strategic opportunities with pre-built templates for Insulet's Porter's Five Forces analysis.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts Insulet's market position. Individuals with diabetes, healthcare providers, and insurance companies all weigh the cost of Insulet's products, particularly the Omnipod system. For instance, the average out-of-pocket cost for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) supplies, which often pair with insulin delivery systems, can be a substantial concern for patients, influencing their brand choices.
When out-of-pocket expenses are high, or insurance coverage for advanced diabetes management tools is limited, customers become more attuned to pricing. This pressure compels Insulet to ensure its pricing remains competitive within the diabetes care market, balancing innovation with affordability to attract and retain users.
Customers considering insulin delivery systems have numerous alternatives to Insulet's Omnipod. These include traditional insulin pens and syringes, as well as a variety of other insulin pump manufacturers.
The presence of strong competitors like Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care, each offering distinct features and pricing structures, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the diabetes device market continues to see innovation, with companies vying for market share by offering integrated continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems and improved user interfaces, giving patients more leverage in their choices.
Switching from Insulet's Omnipod system to another insulin delivery method, like a traditional pump or injections, can present customers with significant switching costs. These costs aren't just monetary; they include the time and effort required to learn a new device, reorder different supplies, and potentially adjust their established diabetes management routines. For instance, a user accustomed to the tubeless design of the Omnipod might find the setup and cannula insertion of a different pump system to be a considerable hurdle.
Customer Information and Awareness
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, especially in the healthcare sector. Digital health solutions, patient forums, and readily available online medical education empower individuals to understand their conditions and treatment options better. This heightened awareness directly impacts their ability to negotiate with companies like Insulet.
Well-informed customers are more likely to question pricing, demand specific product features, and expect superior customer support. For instance, if a competitor offers a similar device with enhanced functionality or a more attractive price point, customers will leverage this knowledge to pressure Insulet. In 2023, the global digital health market was valued at approximately $234.3 billion, showcasing the widespread adoption of technologies that facilitate this information access.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by their ability to share experiences and research findings. Online communities and social media platforms allow users to collectively voice concerns and advocate for changes.
- Increased Information Access: Digital health platforms and online communities provide patients with detailed product information and peer reviews.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers can now compare Insulet's offerings against competitors based on features, efficacy, and cost.
- Pressure on Pricing and Features: Knowledgeable customers can demand better value, influencing Insulet's product development and pricing strategies.
- Influence of Online Communities: Patient advocacy groups and online discussions can shape market perceptions and drive demand for specific product attributes.
Influence of Healthcare Providers and Payers
Healthcare providers, such as endocrinologists and diabetes educators, wield considerable influence by recommending specific insulin delivery systems. Their endorsements can significantly shape patient choices, giving them substantial bargaining power over Insulet. For instance, a widespread recommendation for a competitor's product could directly impact Insulet's market share.
Insurance companies, acting as payers, also exert significant bargaining power. Their coverage decisions and reimbursement rates directly affect the affordability and accessibility of Insulet's products for customers. In 2024, the average out-of-pocket cost for insulin pumps can vary widely based on insurance plans, highlighting the payers' role in customer adoption.
- Provider Influence: Doctors' recommendations are a primary driver of patient choice in insulin delivery systems.
- Payer Power: Insurance coverage and reimbursement policies dictate product affordability and market penetration.
- Cost Sensitivity: High out-of-pocket costs due to payer policies can limit customer adoption of advanced delivery systems.
The bargaining power of Insulet's customers is substantial, driven by increased access to information and a competitive market. Patients are more informed than ever about diabetes management tools, readily comparing Insulet's Omnipod system against alternatives based on features, efficacy, and cost. This knowledge empowers them to demand better value and influences Insulet's product development and pricing strategies.
Healthcare providers and insurance companies also significantly amplify customer bargaining power. Doctors' recommendations heavily sway patient choices, while payer coverage and reimbursement policies directly impact product affordability and market penetration. High out-of-pocket costs, often dictated by these payer policies, can limit customer adoption of advanced delivery systems like Insulet's.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Insulet | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Information Access | Customers easily research and compare diabetes devices online. | Increases customer leverage in demanding specific features and pricing. | Global digital health market valued at over $234 billion in 2023, indicating widespread tech adoption. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Multiple insulin delivery systems (pens, syringes, competitor pumps) exist. | Provides customers with choices, reducing Insulet's pricing power. | Key competitors like Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care continue to innovate and offer integrated CGM systems. |
| Switching Costs | Learning new devices and routines can be time-consuming. | Can retain customers, but significant hurdles may deter switching to Insulet if alternatives are compelling. | User familiarity with tubeless designs like Omnipod can be a factor, but innovation in other systems is reducing switching barriers. |
| Provider Influence | Endorsements from endocrinologists and educators are crucial. | Strong recommendations for Insulet can drive adoption; conversely, competitor endorsements can reduce market share. | Provider recommendations remain a primary driver of patient choice in diabetes management devices. |
| Payer Power | Insurance coverage and reimbursement rates affect affordability. | Limits customer adoption if out-of-pocket costs are too high, pressuring Insulet on pricing and value proposition. | Out-of-pocket costs for insulin pumps vary significantly by insurance plan in 2024. |
Same Document Delivered
Insulet Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Insulet Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the medical device industry. You're looking at the actual document, which means you'll receive this exact, professionally formatted analysis immediately after purchase. This ensures you get a ready-to-use resource without any surprises or placeholder content.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The insulin pump market is quite competitive. Insulet, known for its tubeless Omnipod system, finds itself in a landscape populated by major players like Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care. These companies offer a range of insulin pump technologies, including both traditional tubed pumps and other patch pump designs.
This rivalry extends beyond just pump hardware. The market also includes companies developing continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, many of which are increasingly integrating with insulin pumps to create sophisticated automated insulin delivery systems. For instance, in 2024, the diabetes technology market continues to see significant investment and innovation, with companies vying for market share through product differentiation and technological advancements.
The global insulin pump market is a dynamic space, with projections indicating a substantial rise from USD 5.90 billion in 2024 to USD 9.66 billion by 2030. This robust expansion, while generally a positive sign that can temper intense competition, simultaneously acts as a magnet for new players and spurs existing companies to accelerate their innovation efforts to secure a larger slice of this growing market.
Insulet’s Omnipod stands out with its unique tubeless, wearable design, emphasizing discreetness and user convenience. This distinctiveness is a key factor in its competitive positioning.
However, the competitive landscape is intense. Rivals are actively developing advanced features, seamless integration with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and sophisticated automated insulin delivery (AID) systems. This drives a constant cycle of innovation and feature-based competition within the diabetes management sector.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching between insulin pump systems, or from injections to pumps, presents a notable hurdle for patients. This transition often involves a learning curve and requires adapting to new devices, software, and management routines. While Insulet focuses on simplifying user experience, the inherent complexity of managing diabetes technology means that switching isn't always seamless.
Companies in this space work to make their products 'sticky' by building integrated ecosystems and providing robust customer support. This strategy aims to reduce the likelihood of customers seeking alternatives. For instance, Insulet's Omnipod system, with its tubeless design and user-friendly interface, is designed to foster loyalty.
- Learning Curve: Patients need time to master new pump functionalities and data management.
- Device Integration: Compatibility with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and other health apps can increase switching friction.
- Training and Support: The availability and quality of patient training and ongoing support are critical factors in retention.
- Cost of Switching: Initial costs for new devices and potential loss of established data or support networks can deter switches.
Exit Barriers
The medical device sector, where Insulet operates, is characterized by substantial exit barriers. These are largely driven by the immense fixed costs involved in research and development, sophisticated manufacturing processes, and the rigorous regulatory approval pathways required for new products. For instance, the development of a new insulin pump system can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, making it economically unfeasible for a company to simply walk away from such an investment.
These high upfront and ongoing costs create a strong incentive for companies to continue operating, even when market conditions are challenging or competition is fierce. This persistence, born out of the sunk costs, can prolong periods of intense rivalry as firms fight to recoup their investments rather than exit the market. In 2023, the global medical device market was valued at approximately $520 billion, underscoring the significant capital deployed within the industry.
Consequently, companies like Insulet face a landscape where competitors are less likely to withdraw, potentially leading to sustained price pressures and a constant need for innovation to maintain market share. This dynamic means that even if a competitor experiences financial difficulties, the sheer scale of their investment can keep them in the game, intensifying the competitive rivalry.
- High R&D Investment: Medical device innovation requires significant capital, often exceeding $100 million per major product.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Specialized facilities and stringent quality control add to the fixed cost base.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining approvals from bodies like the FDA involves extensive testing and documentation, representing a substantial investment.
- Sustained Rivalry: Companies are compelled to stay in the market to recover these large, sunk costs, intensifying competition.
Competitive rivalry in the insulin pump market is intense, with Insulet facing strong competition from established players like Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care. These companies offer a variety of insulin pump technologies, including patch pumps and traditional tubed systems, all vying for market share.
The market's projected growth, from USD 5.90 billion in 2024 to USD 9.66 billion by 2030, fuels this rivalry, encouraging continuous innovation and differentiation. Companies are heavily investing in integrated automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, often combining pumps with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs).
High exit barriers, stemming from substantial R&D, complex manufacturing, and rigorous regulatory processes, mean that competitors are unlikely to leave the market easily. This perpetuates a cycle of intense competition and price pressure, as firms strive to recoup their significant investments.
| Competitor | Key Offerings | 2024 Market Presence Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Medtronic | Tubed pumps, integrated CGM systems (e.g., Guardian Connect) | Major player with a broad portfolio of diabetes management devices. |
| Tandem Diabetes Care | Tubed pumps with advanced AID features (e.g., Control-IQ) | Known for its user-friendly interface and innovative AID technology. |
| Insulet | Tubeless patch pump (Omnipod) | Focuses on discreetness and ease of use with its unique tubeless design. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most direct substitute for insulin pumps remains traditional insulin injections via syringes or pens. Despite the convenience and precision offered by pumps, a significant portion of individuals with diabetes continue to manage their condition effectively with multiple daily injections. This preference is often driven by factors such as lower cost, personal comfort with established methods, or a perceived complexity associated with pump technology.
Smart insulin pens represent a growing threat of substitutes for insulin pump companies like Insulet. These pens offer features such as automatic dose tracking and smartphone connectivity, bridging the gap between traditional pens and insulin pumps. For instance, in 2024, the global smart insulin pen market saw significant growth, with analysts projecting a compound annual growth rate exceeding 15% through 2030, indicating increasing adoption.
These devices appeal to a segment of the diabetes management market that finds full insulin pump systems too complex or burdensome but seeks more advanced functionality than conventional insulin pens. This evolving technology provides a less invasive alternative for individuals who desire enhanced data logging and app integration for better diabetes control.
For individuals managing type 2 diabetes, oral medications and other non-insulin therapies represent a significant competitive threat. These alternatives are especially relevant in the earlier stages of the disease, offering less invasive treatment options compared to insulin pumps. For instance, the global market for oral antidiabetics was valued at approximately USD 25 billion in 2023, showcasing a substantial existing alternative.
Continuous advancements in pharmaceutical research are leading to more effective oral and non-insulin injectable therapies. These innovations can potentially reduce the dependency on insulin for a growing number of patients, thereby posing a direct threat to the demand for insulin pump systems. The development of GLP-1 receptor agonists, for example, has shown significant efficacy in glycemic control and weight management, presenting a strong substitute.
Lifestyle Management and Prevention
Intensive lifestyle management, focusing on diet and exercise, can effectively control blood glucose levels for individuals, particularly those with early-stage type 2 diabetes. This approach acts as a significant threat by reducing the pool of potential customers who might otherwise require insulin delivery systems like those offered by Insulet. For example, studies have shown that significant weight loss through lifestyle changes can lead to remission of type 2 diabetes for a portion of patients, thereby negating the need for ongoing insulin therapy.
While not a direct product replacement, successful lifestyle interventions diminish the market size for insulin delivery devices. This means Insulet faces a threat from the growing awareness and accessibility of health and wellness programs. For instance, the global digital health market, which includes lifestyle management apps and platforms, was valued at over $200 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong trend towards non-device-based diabetes management.
- Reduced Demand: Successful lifestyle management can lead to fewer individuals needing insulin delivery devices.
- Market Erosion: The increasing effectiveness and popularity of lifestyle interventions directly shrink Insulet's potential customer base.
- Focus on Prevention: A greater emphasis on preventing or delaying the progression of type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes presents an alternative to device-based treatment.
Emerging Technologies and Future Cures
The long-term threat of substitutes for Insulet's insulin delivery systems is significant, primarily driven by advancements in diabetes management technology. The development of fully automated, closed-loop artificial pancreas systems that drastically reduce or eliminate the need for manual user input represents a direct substitute. While a complete cure for diabetes remains a distant prospect, ongoing innovation in therapeutic approaches and preventative measures could eventually diminish the market for insulin delivery devices altogether.
Consider the potential impact of emerging technologies:
- Advanced Artificial Pancreas Systems: Continued progress in creating systems that automatically monitor glucose and deliver insulin with minimal user intervention could render current patch pump technologies less attractive. For instance, research into implantable glucose sensors and more sophisticated insulin delivery algorithms is ongoing, aiming for greater autonomy.
- Novel Therapeutic Approaches: Breakthroughs in areas like gene therapy, stem cell research, or immunotherapy that offer a functional cure for Type 1 diabetes would fundamentally alter the market landscape, presenting the ultimate substitute. While not an immediate threat, the pace of biomedical research suggests this possibility in the long term.
- Improved Oral Medications or Non-Invasive Delivery: A significant advancement in oral medications that effectively manage blood glucose without injections, or non-invasive delivery methods that bypass the need for subcutaneous devices, would also pose a substantial substitution risk.
Traditional insulin injections via syringes or pens remain a primary substitute, favored for their lower cost and familiarity. Smart insulin pens are also gaining traction, offering enhanced tracking and connectivity, with the global market projected for significant growth. Furthermore, oral medications and lifestyle management are increasingly effective for type 2 diabetes, reducing the need for insulin delivery devices.
The threat of substitutes for Insulet is multifaceted, encompassing both existing and emerging alternatives in diabetes management. Traditional insulin injections continue to be a viable option for many, particularly those prioritizing cost-effectiveness and established routines. Smart insulin pens, meanwhile, offer a technologically advanced alternative that bridges the gap between conventional methods and insulin pumps, appealing to users seeking greater data integration without the full commitment of a pump system. In 2024, the smart insulin pen market showed robust expansion, indicating a growing preference for these hybrid solutions.
Beyond direct insulin delivery alternatives, non-insulin therapies and intensive lifestyle interventions pose a significant threat, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes. The market for oral antidiabetics, valued at approximately USD 25 billion in 2023, highlights the substantial existing alternative. Moreover, advancements in areas like GLP-1 receptor agonists demonstrate the increasing efficacy of non-insulin treatments in glycemic control and weight management. The growing emphasis on lifestyle management, supported by a digital health market exceeding $200 billion in 2023, further erodes the potential customer base for insulin delivery devices by enabling disease remission for some patients.
| Substitute Type | Key Features/Benefits | Market Relevance/Growth (2023/2024 Data) |
| Traditional Injections (Syringes/Pens) | Lower Cost, Familiarity, Simplicity | Still widely used, preferred by cost-conscious or routine-oriented users |
| Smart Insulin Pens | Dose Tracking, Smartphone Connectivity, Data Logging | Growing market, projected CAGR >15% through 2030 |
| Oral Antidiabetics | Non-invasive, effective for Type 2 Diabetes | Market valued at ~USD 25 billion (2023) |
| Lifestyle Management (Diet, Exercise) | Disease Prevention/Remission, Non-pharmacological | Digital Health Market >USD 200 billion (2023), potential for diabetes remission |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in the insulin delivery system market is significantly dampened by formidable regulatory hurdles. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) imposes rigorous premarket approval processes for medical devices. In 2024, the average time to obtain FDA clearance for a new medical device can span several years and involve substantial investment, deterring many potential new players.
Developing, manufacturing, and marketing innovative insulin delivery systems, such as Insulet's Omnipod, demands significant financial resources. This includes substantial investments in cutting-edge research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, and extensive sales and marketing infrastructure. For instance, Insulet reported $440.3 million in R&D expenses for fiscal year 2023, highlighting the ongoing commitment required to stay competitive in this space.
This high barrier to entry, driven by the sheer capital required for product innovation and market penetration, effectively deters many potential new competitors from entering the insulin delivery device market. The need for specialized expertise, regulatory approvals, and establishing a robust supply chain further amplifies these initial investment hurdles.
Insulet benefits from significant established brand loyalty and a robust customer base, boasting over 500,000 active global users for its Omnipod systems as of recent reports. This strong customer attachment makes it difficult and expensive for new entrants to attract and retain users in the diabetes management device market. Building comparable brand recognition and trust, especially in the highly regulated medical device industry, presents a substantial barrier.
Intellectual Property and Patents
Insulet's robust intellectual property, particularly its patents on tubeless insulin pump technology, acts as a significant barrier to entry. These extensive patent portfolios protect Insulet's innovations, making it challenging and costly for new companies to develop comparable products. Without substantial investment in research and development to circumvent existing patents or create truly novel designs, potential entrants face a high hurdle.
The threat of new entrants is therefore somewhat mitigated by the strength and breadth of Insulet's patent protection. Developing a competing product would likely require navigating a complex legal landscape and significant upfront capital to avoid infringement. For example, as of early 2024, Insulet held a substantial number of patents globally covering various aspects of its Omnipod system, from the adhesive patch to the drug delivery mechanism.
- Insulet's patent portfolio is a key deterrent to new entrants in the tubeless insulin pump market.
- Developing alternative technologies without infringing on Insulet's patents requires significant R&D investment.
- The cost and complexity of patent navigation make it difficult for new players to enter.
Access to Distribution Channels and Healthcare Networks
New entrants into the diabetes management device market, particularly those seeking to compete with established players like Insulet, would face significant hurdles in building out their distribution channels and securing access to crucial healthcare networks. These networks are vital for reaching patients, obtaining necessary physician endorsements, and navigating complex reimbursement processes.
Established companies have invested years in cultivating relationships with pharmacies, durable medical equipment (DME) suppliers, and healthcare systems. For instance, Insulet's established distribution partnerships allow for efficient delivery of their Omnipod systems directly to patients' homes. New entrants would need to replicate this extensive infrastructure, a costly and time-consuming endeavor. In 2023, the global diabetes device market was valued at over $60 billion, indicating substantial competition and established market structures.
Furthermore, gaining access to healthcare provider networks and securing favorable reimbursement pathways from insurers is a considerable barrier. Physicians and healthcare systems often prefer to work with proven technologies and reliable suppliers, making it difficult for newcomers to break into these established relationships. Without these established channels, new entrants would struggle to gain market traction and compete effectively with Insulet's existing market penetration.
- Distribution Network Challenges: New entrants must build or acquire extensive distribution networks to reach patients effectively, a process that requires significant capital and time.
- Healthcare Provider Access: Gaining trust and integration with healthcare providers and systems is critical for product adoption and patient referrals.
- Reimbursement Hurdles: Navigating the complex landscape of insurance coverage and reimbursement policies is a major obstacle for new medical device companies.
- Established Relationships: Existing players like Insulet benefit from long-standing relationships with distributors, pharmacies, and healthcare professionals, creating a competitive moat.
The threat of new entrants into the insulin delivery market, particularly for advanced systems like Insulet's Omnipod, remains relatively low. This is due to a confluence of factors including substantial capital requirements for research, development, and manufacturing, coupled with stringent regulatory approval processes. For example, Insulet's significant investment in R&D, totaling $440.3 million in fiscal year 2023, underscores the financial commitment needed to innovate and maintain a competitive edge.
Furthermore, Insulet's strong brand loyalty, with over 500,000 active global users, and its extensive patent portfolio, which protects its unique tubeless insulin pump technology, create significant barriers. Navigating these intellectual property rights and building comparable brand trust is a formidable challenge for any new competitor. The market's complexity and the established infrastructure of players like Insulet also necessitate considerable investment in distribution channels and healthcare provider relationships, further deterring new entrants.
| Barrier Category | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Rigorous FDA approval processes for medical devices, often taking years and substantial investment. | High; deters many potential new players due to time and cost. |
| Capital Requirements | Significant investment in R&D, manufacturing facilities, and marketing infrastructure. | High; requires substantial financial backing to compete. |
| Brand Loyalty & Customer Base | Established trust and user base make it difficult for newcomers to attract and retain customers. | High; requires extensive marketing and product differentiation. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents on key technologies, like Insulet's tubeless pump design, protect innovation. | High; necessitates significant R&D to develop non-infringing alternatives. |
| Distribution & Healthcare Access | Need to build extensive distribution networks and secure relationships with healthcare providers and payers. | High; requires time, capital, and proven reliability. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Insulet Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including publicly available financial reports from Insulet and its competitors, market research reports from leading healthcare analytics firms, and industry-specific trade publications. This blend of financial and market intelligence allows for a robust assessment of competitive intensity and industry structure.
