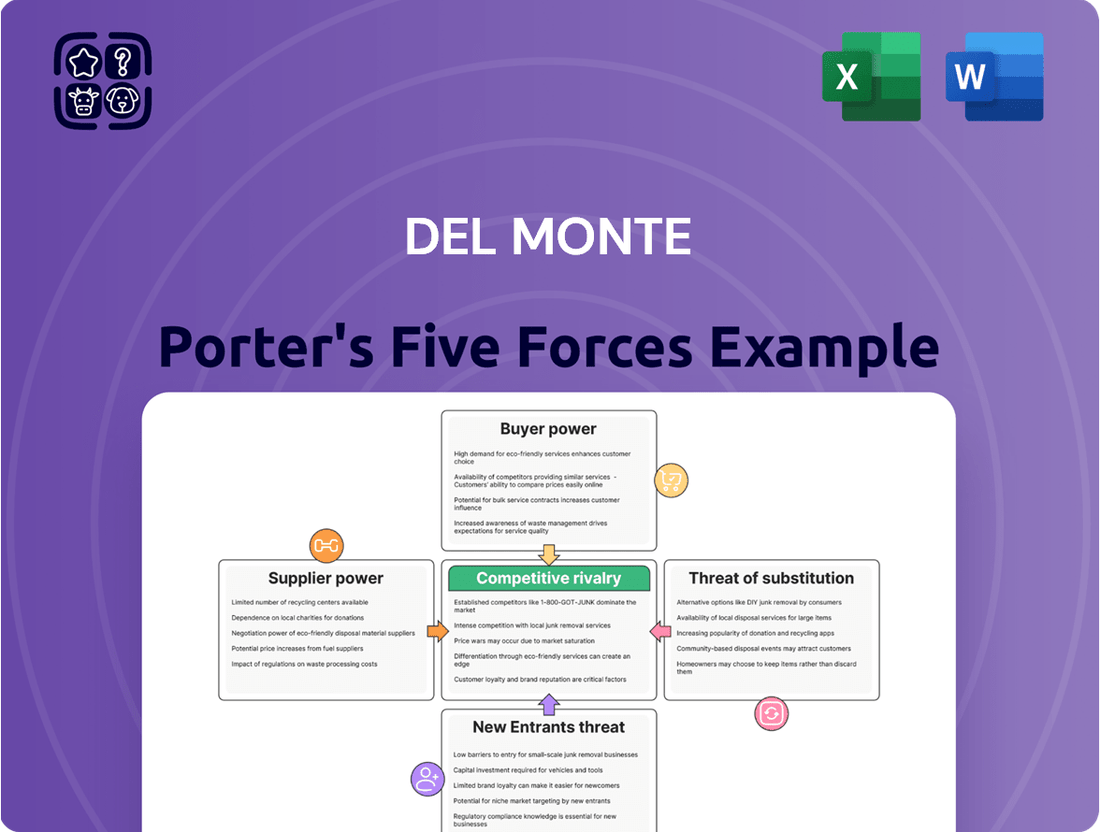
Del Monte Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Del Monte Bundle
Del Monte faces significant industry pressures, from the bargaining power of powerful buyers to the constant threat of substitute products. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder in the food and beverage sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Del Monte’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Del Monte's diverse sourcing strategy, encompassing company-owned farms, affiliated growers, and independent suppliers across the globe, significantly dilutes individual supplier bargaining power. This broad network ensures that no single supplier or region holds undue leverage over the company. For instance, in 2024, Del Monte's integrated supply chain, which includes substantial company-owned agricultural land, allowed for greater control over input costs and availability, a key factor in managing supplier influence.
Del Monte's extensive vertical integration, which includes owning farms and managing its own logistics, significantly diminishes its dependence on outside suppliers for a large portion of its raw materials. This internal control over the production process strengthens Del Monte's bargaining position when dealing with independent growers and contributes to a more reliable supply chain, a key factor in managing supplier power.
Suppliers of fresh produce to Del Monte face significant pressure due to the perishable nature of their goods. They must consistently meet stringent quality standards and adhere to tight delivery schedules to ensure product freshness throughout Del Monte's global supply chain. For example, in 2024, Del Monte's reliance on timely deliveries of fruits like pineapples and tomatoes, which have very short shelf lives, means suppliers who fail to meet these demands risk losing business.
Commodity Nature of Some Inputs
The commodity nature of many of Del Monte's fresh produce inputs significantly weakens supplier bargaining power. When the fruits and vegetables Del Monte sources are widely available from numerous growers, like common varieties of tomatoes or corn, it becomes easier to switch suppliers if prices rise or terms become unfavorable. This abundance of choice for Del Monte means individual suppliers have less leverage to dictate terms.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for fresh produce continued to be characterized by a vast number of small to medium-sized agricultural producers for many staple crops. This fragmentation prevents any single supplier from holding substantial sway over pricing or supply agreements for these commodity items. Del Monte can leverage this competitive landscape to secure favorable pricing and consistent supply chains.
- Commodity Inputs: Many of Del Monte's core ingredients, such as common fruits and vegetables, are treated as commodities with numerous available sources.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: The widespread availability of these commodity inputs limits the bargaining power of any single supplier.
- Alternative Sourcing: Del Monte can readily find alternative suppliers for these common items, further diminishing individual supplier influence.
- Market Dynamics: The fragmented nature of the fresh produce market in 2024, with many small producers, reinforces this dynamic.
Long-Term Relationships with Growers
Del Monte's strategy of cultivating long-term relationships and contracts with its growers, both affiliated and independent, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. These agreements, often crop-specific or region-focused, provide a degree of stability for the growers. However, the terms within these commitments can cap their ability to leverage their position once the contract is in place, steering the dynamic towards a more cooperative partnership.
These established relationships can lock in supply for Del Monte, reducing the need to constantly seek new suppliers and potentially paying higher prices. For instance, in 2024, Del Monte's focus on securing consistent pineapple supply in the Philippines through multi-year agreements with local cooperatives meant those growers had a predictable buyer, but their flexibility to sell elsewhere was curtailed.
- Long-Term Contracts: Del Monte secures supply through multi-year agreements with growers, reducing price volatility and ensuring availability.
- Affiliated Growers: A portion of Del Monte's supply comes from its own managed plantations, directly controlling costs and quality.
- Independent Grower Agreements: Contracts with independent farmers often include specific quality standards and delivery schedules, which Del Monte enforces.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: By committing to long-term partnerships, Del Monte limits the ability of individual growers to demand higher prices or better terms from other buyers.
Del Monte's diversified sourcing, including company-owned farms and a global network of growers, significantly reduces the bargaining power of individual suppliers. This broad base ensures that no single supplier can dictate terms, as seen in 2024 with Del Monte's integrated supply chain providing substantial control over input costs and availability.
The perishable nature of produce like pineapples and tomatoes, critical for Del Monte, forces suppliers to meet strict quality and delivery standards in 2024, limiting their leverage. Failure to comply risks losing business, as suppliers of these fast-moving items must prioritize Del Monte's stringent requirements.
The commodity status of many of Del Monte's inputs, such as common fruits and vegetables, further weakens supplier power. In 2024, the fragmented fresh produce market with numerous small producers meant Del Monte could easily switch suppliers for staple crops, securing favorable pricing and consistent supply.
Del Monte's long-term contracts with growers, including those in the Philippines for pineapple supply in 2024, provide stability for farmers but limit their ability to negotiate better terms or sell elsewhere, fostering a cooperative rather than adversarial relationship.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Del Monte's Strategy | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sourcing Diversification | Lowers power | Global network, company farms | Ensured stable input costs |
| Product Perishability | Lowers power | Strict quality/delivery demands | Critical for fresh produce availability |
| Commodity Inputs | Lowers power | Multiple sourcing options | Fragmented market allowed price leverage |
| Long-Term Contracts | Lowers power | Secures supply, limits supplier flexibility | Provided predictable output for key crops |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the five competitive forces impacting Del Monte, providing a strategic overview of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the influence of substitute products.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of bargaining power, rivalry, and substitutes.
Customers Bargaining Power
Del Monte's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by its major buyers, such as large supermarket chains and food service providers. These entities purchase products in substantial quantities, granting them considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, major grocery retailers often negotiate volume discounts, which can impact Del Monte's profit margins.
The sheer scale of these customers allows them to dictate terms, including pricing, delivery schedules, and promotional support. This pressure is amplified when these buyers have alternative suppliers or can easily switch between brands, forcing Del Monte to remain competitive and responsive to their demands.
Del Monte faces a challenge as consumers often view fresh produce as a commodity, diminishing brand loyalty compared to their processed food lines. This perception makes customers more sensitive to price, increasing their likelihood of switching to competitors or private label brands.
In 2024, the intense competition in the fresh produce aisle, with numerous brands and store-specific offerings, further amplifies this customer power. For example, the average U.S. household spent approximately $1,500 annually on fruits and vegetables in recent years, a figure that can be significantly influenced by price fluctuations and promotional activities from various suppliers.
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the availability of substitutes at the retail level. For a company like Del Monte, consumers at the grocery store have a vast array of choices for fresh produce. They can opt for products from competing national brands, or even choose more budget-friendly options like private label store brands or directly from local farmers at farmers' markets.
This wide selection of alternatives empowers customers. If Del Monte's pricing is perceived as too high, or if the quality doesn't meet expectations, consumers can easily switch to another brand or source. For instance, in 2024, the private label segment in the U.S. grocery market continued to grow, capturing an estimated 20.4% of sales, demonstrating consumer willingness to explore alternatives to national brands for value.
Private Label Competition
The rise of private label brands significantly boosts customer bargaining power against companies like Del Monte. Major retailers, from Walmart to Kroger, are increasingly stocking their own-brand fresh produce and prepared foods. This directly challenges Del Monte's branded offerings, often presenting consumers with a more budget-friendly alternative. For instance, in 2023, private label sales in the U.S. grocery sector saw continued growth, with some categories exceeding 20% market share, putting pressure on national brands to compete on price.
This intensified price competition forces brands to either lower their margins or risk losing market share to these lower-cost store brands. Customers benefit from this dynamic as they gain more choices and the ability to secure comparable products at reduced prices. This dynamic directly impacts Del Monte's ability to command premium pricing and influences their sales volumes.
- Retailer Private Label Growth: Many large retailers are expanding their private label portfolios, offering direct competition to established brands.
- Price Sensitivity: The availability of lower-cost private label options makes consumers more price-sensitive, increasing their bargaining power.
- Market Share Impact: In 2023, private label products captured significant market share in key grocery segments, demonstrating their growing influence.
- Brand Differentiation Challenge: Del Monte faces the challenge of differentiating its products to justify premium pricing against increasingly sophisticated private label offerings.
Fragmented End-Consumer Market
While large retailers wield significant influence, the end-consumer market for food products like those from Del Monte remains highly fragmented. This means that no single consumer, or even small group, can dictate terms to Del Monte.
However, the sheer volume of individual purchasing decisions collectively shapes demand. Consumers, driven by factors such as price sensitivity, perceived quality, and the ease of purchasing, ultimately influence what retailers stock and Del Monte must produce.
- Consumer Price Sensitivity: In 2024, the average household grocery budget saw continued pressure, with a significant portion of consumers actively seeking value. For instance, NielsenIQ data from early 2024 indicated that over 60% of shoppers were making more price-conscious decisions for pantry staples.
- Brand Loyalty vs. Convenience: While Del Monte has established brand recognition, consumers often prioritize convenience and availability. The proliferation of private label brands in major supermarkets further erodes individual consumer power by offering readily available, often lower-priced alternatives.
- Influence on Retailer Demand: Retailers, acting as intermediaries, translate aggregate consumer preferences into demand signals for manufacturers like Del Monte. A widespread consumer shift towards healthier or more sustainable options, for example, would compel retailers to adjust their product offerings, thereby impacting Del Monte's production and marketing strategies.
Del Monte's customers, particularly large retail chains, possess considerable bargaining power due to their substantial purchasing volumes and the availability of numerous alternative suppliers. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, impacting Del Monte's profitability. For instance, in 2024, major grocery retailers often secured volume discounts, a common practice that squeezes margins for suppliers.
The competitive landscape, especially the rise of private label brands, further amplifies customer power. Consumers, faced with a wide array of choices, are increasingly price-sensitive. In 2023, private label products captured a significant share of the U.S. grocery market, with some categories exceeding 20% of sales, demonstrating consumers' willingness to switch for value.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Del Monte | 2024 Data Point |
| Major Retailers (e.g., Supermarket Chains) | High volume purchases, alternative suppliers, private label development | Price pressure, demand for promotional support, margin erosion | Retailers commonly negotiate volume discounts. |
| End Consumers | Price sensitivity, availability of substitutes (including private labels), brand loyalty (lower for commodities) | Influences demand, necessitates competitive pricing, challenges premium branding | Over 60% of shoppers made price-conscious decisions for pantry staples in early 2024. |
Full Version Awaits
Del Monte Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Del Monte Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the canned food industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing valuable insights into Del Monte's strategic landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The fresh produce and prepared foods sector is a battlefield with global giants and nimble regional players. Del Monte contends with diversified food conglomerates, specialized produce distributors, and countless local growers, each vying for market share across different territories.
In 2024, the intensity of this rivalry is palpable. For instance, Dole, a major global competitor, reported net sales of $8.5 billion in 2023, showcasing the scale of operations Del Monte must navigate. Similarly, the presence of strong regional brands in markets like Europe and Asia means Del Monte must constantly adapt its strategies to local tastes and competitive landscapes.
Competitive rivalry in the fresh produce sector, including for companies like Del Monte, is frequently driven by price. This is largely because many of the products are seen as commodities, making it difficult to differentiate beyond price. The perishable nature of these goods further intensifies this, as businesses are often compelled to lower prices to sell inventory before it spoils, directly impacting profit margins for everyone involved.
Del Monte faces significant hurdles in differentiating its fresh produce. While quality, origin, and brand are key, these are often difficult to distinguish significantly from competitors in a crowded market. This forces competition to intensify on operational aspects like supply chain efficiency, ensuring peak freshness, and innovative packaging solutions, rather than solely on product attributes.
The company finds more fertile ground for differentiation within its prepared food and juice segments. Here, innovation in product formulation, convenience, and health benefits allows Del Monte to carve out a more distinct competitive advantage. For instance, the global fruit juice market, valued at approximately $130 billion in 2023, offers substantial room for brands that can innovate with unique flavor profiles or functional ingredients.
Marketing and Distribution Network Strength
Competitive rivalry intensifies through the strength of marketing and distribution networks. Del Monte, for instance, leverages its robust cold chain logistics and expansive market reach, a significant advantage in delivering fresh products efficiently across the globe.
This network strength is crucial for maintaining product quality and availability, directly impacting market share and customer loyalty. Companies with weaker distribution capabilities struggle to compete on freshness and timely delivery, especially in the perishable goods sector.
- Del Monte's Global Reach: Operates in over 100 countries, supported by a sophisticated distribution infrastructure.
- Cold Chain Efficiency: Investments in refrigerated transport and storage are key differentiators.
- Market Penetration: Strong relationships with retailers ensure prominent shelf space and accessibility for consumers.
- Brand Visibility: Extensive marketing campaigns complement the distribution network, reinforcing brand presence.
Innovation in Value-Added Products
The competition among food companies is heating up, especially as they focus on creating more convenient and healthier options. Think about things like pre-cut fruits and vegetables, organic produce, and ready-to-eat meals. These value-added products are becoming a big deal for consumers who are short on time but still want good nutrition.
Companies are really pushing to grab a piece of this growing market. For instance, in 2024, the global market for ready-to-eat meals was projected to reach over $200 billion, showing a strong consumer demand for convenience. This means brands are investing heavily in research and development to create new and exciting products.
- Focus on Convenience: Companies are developing innovative packaging and preparation methods to make meals quicker and easier for consumers.
- Health and Wellness Trend: The demand for organic, non-GMO, and nutrient-rich ingredients is a significant driver for new product development.
- Market Share Battle: Brands are differentiating themselves through unique flavor profiles, sustainable sourcing, and appealing branding to capture consumer loyalty.
- Increased R&D Investment: Significant capital is being allocated to create novel food solutions that cater to evolving dietary preferences and lifestyle needs.
The competitive rivalry for Del Monte is fierce, with both global giants and regional players aggressively vying for market share. This intensity is particularly evident in 2024 as companies like Dole, which reported $8.5 billion in net sales in 2023, demonstrate the scale of competition.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Consumers increasingly turn to processed and frozen fruits and vegetables as viable substitutes for fresh produce. These alternatives, such as canned peaches or frozen berries, boast extended shelf lives and require minimal preparation, appealing to busy lifestyles. For instance, the global frozen fruits and vegetables market was valued at approximately USD 37.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a strong consumer preference for convenience and longevity.
Consumers can easily switch to alternative food categories like grains, dairy, meat, or processed snacks if Del Monte's offerings become too expensive or less appealing. This broad accessibility to other food types poses a significant indirect threat.
For instance, the global packaged food market, which includes many substitutes for fresh produce, was valued at over $900 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow. This vast market size highlights the intense competition Del Monte faces from these alternative food choices.
The growing popularity of home gardening and local sourcing presents a significant threat of substitutes for Del Monte. Consumers are increasingly turning to farmers' markets and direct-from-farm sales for fresh produce, bypassing traditional retail channels. This trend was notably strong in 2024, with many regions reporting increased participation in community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs and a surge in home gardening enthusiasm, partly fueled by a desire for greater food security and connection to food sources.
This shift directly impacts demand for Del Monte's globally distributed products. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 30% of consumers in urban areas had increased their purchases from local farmers' markets compared to the previous year. This growing preference for locally grown, often fresher, alternatives directly competes with Del Monte's canned and packaged goods, potentially eroding market share as consumers seek out more direct and sustainable food options.
Dietary Trends and Preferences
Shifting dietary trends present a significant threat of substitutes for Del Monte. For instance, the burgeoning popularity of plant-based proteins, like those derived from soy, peas, or even fungi, offers consumers alternatives to traditional fruit and vegetable consumption. If Del Monte fails to adapt its product lines to include or highlight these emerging protein sources, it risks losing market share to companies that cater to these evolving preferences. In 2024, the global plant-based food market continued its robust growth, with projections indicating further expansion, underscoring the need for companies like Del Monte to innovate.
Consumers are increasingly seeking out specific superfoods or functional ingredients believed to offer enhanced health benefits. This can lead them to choose specialized products, such as acai bowls, kale smoothies, or goji berry snacks, over Del Monte's more conventional fruit and vegetable offerings. The company must therefore stay attuned to these granular shifts in consumer demand and explore ways to integrate popular superfoods or functional ingredients into its existing or new product portfolios to mitigate this substitution threat.
- Growing Demand for Plant-Based Alternatives: The plant-based food sector saw substantial growth in 2024, with many consumers actively seeking protein sources beyond traditional produce.
- Superfood Trend Impact: Consumption of niche superfoods, often marketed for specific health benefits, can divert consumer spending from broader fruit and vegetable categories.
- Need for Product Innovation: Del Monte's ability to incorporate trending ingredients and cater to evolving health-conscious diets is crucial for countering the threat of substitutes.
- Market Adaptability: Failure to adapt product lines to reflect these dietary shifts could result in a loss of consumer relevance and market share.
Beverage Alternatives
The threat of substitutes for Del Monte's beverage products is significant, encompassing a broad array of alternatives like water, soft drinks, dairy, coffee, and tea. This wide availability means consumers can easily switch if Del Monte's offerings become less appealing or more expensive.
The convenience and often lower price points of many substitute beverages, such as bottled water or generic brand soft drinks, present a constant competitive challenge. For instance, the global bottled water market was valued at approximately $274.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a strong consumer preference for this simple substitute.
- Broad Substitute Landscape: Consumers have numerous choices beyond traditional juices, including water, carbonated soft drinks, milk-based beverages, coffee, and tea.
- Price and Convenience Factors: Many substitutes, like tap water or readily available coffee shops, offer greater convenience and lower costs, directly impacting Del Monte's pricing power.
- Market Trends: The increasing popularity of functional beverages and health-conscious alternatives, such as kombucha and plant-based milks, further diversifies the substitute landscape, challenging traditional juice segments.
The threat of substitutes for Del Monte's products is substantial, as consumers have a wide array of choices. Processed and frozen fruits and vegetables offer convenience and longer shelf lives, with the global frozen fruits and vegetables market valued at approximately USD 37.4 billion in 2023. Furthermore, consumers can easily shift to other food categories like grains, dairy, or meat, especially with the global packaged food market exceeding $900 billion in 2023.
The rise of home gardening and local sourcing presents a direct substitute, with over 30% of urban consumers increasing local market purchases in 2024. Dietary shifts towards plant-based proteins and specialized superfoods also pose a threat, as the plant-based food market continues its robust growth. For beverages, alternatives like bottled water, valued at $274.6 billion in 2023, and functional drinks further diversify the competitive landscape.
| Substitute Category | Market Value (approx. USD) | Key Trend/Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Frozen Fruits & Vegetables | 37.4 billion (2023) | Convenience, extended shelf life |
| Packaged Foods (overall) | >900 billion (2023) | Broad alternative food choices |
| Bottled Water | 274.6 billion (2023) | Convenience, perceived health benefits |
| Home Gardening/Local Sourcing | Growing consumer participation (2024) | Desire for freshness, food security |
| Plant-Based Foods | Continued robust growth (2024) | Dietary shifts, health consciousness |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a global fresh produce and prepared food operation, akin to Del Monte, demands immense capital. Think about the costs involved in acquiring and maintaining vast tracts of farmland, building advanced processing plants, and setting up extensive cold chain logistics and distribution networks. These upfront expenses can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, creating a formidable hurdle for any aspiring competitor.
For instance, in 2024, the global food processing industry saw significant investments, with companies pouring billions into upgrading infrastructure and expanding capacity. New entrants would need to match or exceed these existing capital outlays to even begin competing on scale and efficiency, which is a daunting prospect.
Establishing a global distribution network for perishable goods, like those Del Monte offers, is a significant hurdle for newcomers. This involves substantial investment in logistics, warehousing, and cold chain infrastructure to ensure product quality and timely delivery across varied markets.
New entrants would find it incredibly difficult and expensive to match Del Monte's existing supply chain efficiency and its deeply entrenched relationships with retailers worldwide. These established connections are built over years and provide a competitive advantage that is hard to overcome quickly.
For instance, in 2024, Del Monte Foods Inc. continued to leverage its extensive network, which is critical for maintaining market share in the highly competitive canned and fresh produce sectors. Replicating such a widespread and reliable distribution system would require years of dedicated effort and considerable capital outlay.
Del Monte's established brand recognition and deep-rooted consumer trust, cultivated over many years, present a significant barrier to new entrants. This is especially true in the competitive fresh produce market where quality perception is paramount.
For any new player to gain traction, substantial investments in marketing campaigns and rigorous quality control measures would be essential to even begin replicating Del Monte's hard-won brand equity and customer confidence.
Regulatory and Food Safety Compliance
The fresh produce sector faces significant barriers to entry due to rigorous food safety regulations, complex import/export laws, and diverse agricultural standards globally. New entrants must invest heavily to understand and adhere to these varying requirements, which can be a substantial financial and operational challenge.
For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) mandates preventive controls for food facilities, adding compliance costs. Similarly, the European Union's stringent traceability and labeling rules for produce can be difficult for newcomers to implement effectively.
- Regulatory Hurdles: New companies must navigate a patchwork of national and international regulations, including pesticide residue limits and packaging standards.
- Compliance Costs: Meeting these standards often requires significant investment in quality control systems, testing, and specialized personnel.
- Market Access: Failure to comply can result in product seizures, market bans, and reputational damage, limiting a new entrant's ability to gain traction.
Supply Chain Complexity and Expertise
The intricate global supply chain for perishable goods presents a significant barrier for new entrants. Del Monte, for instance, must navigate sourcing from numerous regions, manage fluctuating seasonal availability, and maintain stringent quality control across its product lines.
This complexity demands specialized expertise and deeply entrenched supplier relationships, which are typically absent in emerging competitors. For example, in 2024, the global fresh produce market, where Del Monte operates, is valued at over $1 trillion, underscoring the scale and logistical challenges involved.
- Global Sourcing: Managing diverse agricultural inputs across continents.
- Seasonality Management: Adapting to varied harvest cycles worldwide.
- Quality Assurance: Implementing rigorous checks for perishable items.
- Logistical Networks: Establishing efficient transportation and cold chain infrastructure.
The threat of new entrants in the fresh produce and prepared foods market, where Del Monte operates, is significantly mitigated by the enormous capital requirements needed to establish operations. Building the necessary infrastructure for farming, processing, and a global cold chain distribution network demands billions of dollars, creating a substantial financial barrier.
In 2024, the ongoing investments in agricultural technology and supply chain modernization by established players further escalate these entry costs. New companies would need to match or surpass these existing capital outlays to achieve comparable scale and efficiency, a daunting prospect for any newcomer.
Furthermore, Del Monte benefits from established brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, built over decades. Replicating these deep-rooted customer relationships and efficient logistics would require years of dedicated effort and substantial financial commitment, making it exceptionally difficult for new players to gain immediate market traction.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Vast investment needed for land, processing, and cold chain logistics. | Billions required to match existing infrastructure. |
| Distribution Networks | Established relationships with retailers and efficient logistics. | Years to replicate global reach and reliability. |
| Brand Recognition | Strong consumer trust and loyalty cultivated over time. | Significant marketing investment needed to build comparable equity. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Del Monte leverages financial reports, industry market research from firms like IBISWorld, and consumer trend data to assess competitive intensity, supplier power, and buyer bargaining. We also incorporate regulatory filings and macroeconomic indicators to understand the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
