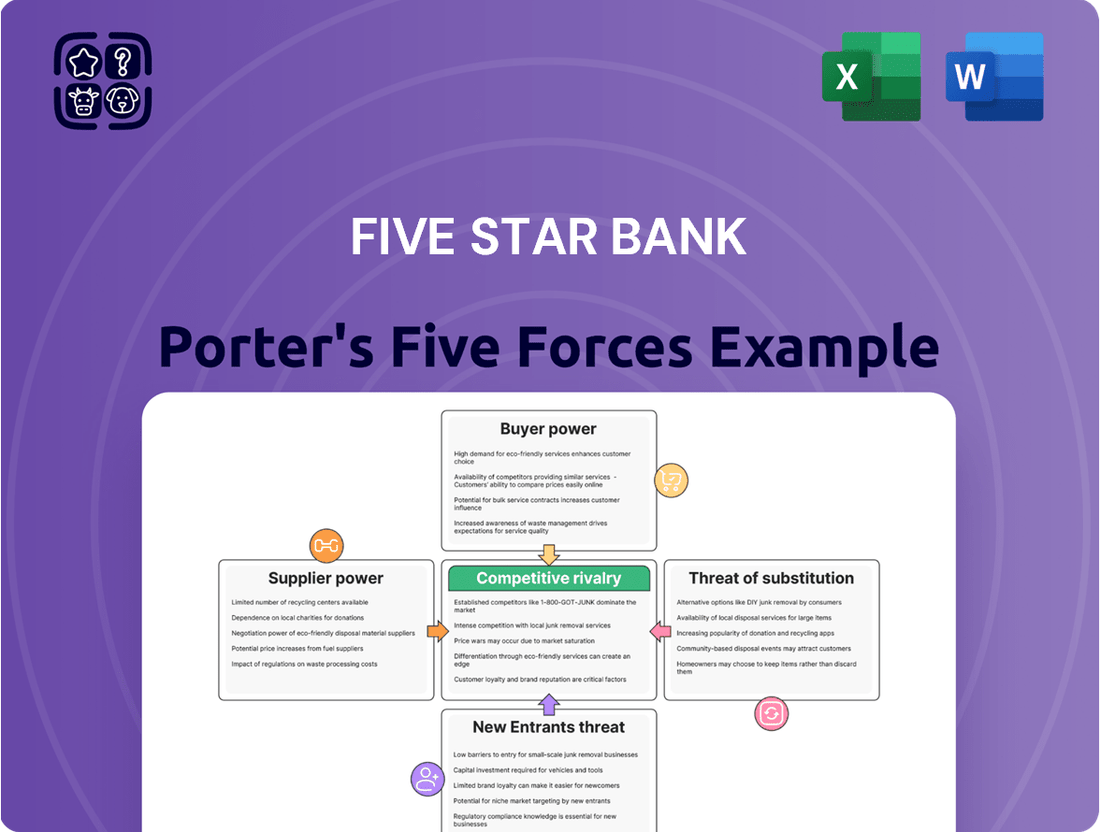
Five Star Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Five Star Bank Bundle
Five Star Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape, where understanding the intensity of competition is paramount. Our analysis reveals how buyer power and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its strategic options.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Five Star Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Five Star Bank, like many financial institutions, depends heavily on technology providers for its core banking systems and digital services. These vendors supply the essential software and infrastructure that power everything from customer accounts to online transactions.
The market for specialized banking technology is quite concentrated. A handful of major players often dominate, meaning they have significant influence. This concentration can translate into greater bargaining power for these technology suppliers.
Switching core banking systems is a costly and complex undertaking. For a bank, the expenses associated with migrating data, integrating new software, and retraining staff can easily run into several million dollars. These high switching costs further solidify the suppliers' strong position.
Suppliers of financial market data, analytics, and intelligence are critical for Five Star Bank's investment and risk management. The quality and uniqueness of data from providers like Bloomberg or Refinitiv can significantly influence the bank's strategic decisions. For instance, in 2024, the global financial data market was valued at over $30 billion, indicating the significant investment banks make in these resources.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is amplified when they offer proprietary data or advanced analytical platforms that are difficult for Five Star Bank to replicate internally. This can lead to higher subscription costs, as seen with specialized AI-driven analytics tools that emerged prominently in 2024, offering predictive insights for trading and risk assessment.
The availability of skilled professionals, especially in high-demand fields like artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and niche financial services, grants significant bargaining power to these talent pools. A scarcity of such expertise, a trend observed throughout 2024, directly translates into upward pressure on compensation and heightened competition for recruitment and retention. This dynamic can notably affect a bank's operational effectiveness and its ability to pursue innovation and expansion.
Regulatory Compliance Services
Suppliers of regulatory compliance services wield considerable influence over Five Star Bank. The bank’s operations in California are subject to extensive regulations, making specialized legal and software providers essential. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines, with the California Department of Financial Protection and Innovation actively enforcing new statutes. For instance, the 2025 amendments to credit reporting laws and bank fee structures necessitate sophisticated compliance solutions, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
The critical nature of regulatory adherence means banks like Five Star cannot easily switch providers without significant disruption and risk. This reliance on specialized expertise, particularly in light of evolving legal landscapes such as the 2025 California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) enhancements impacting financial data, grants these suppliers greater bargaining power. The cost of non-compliance, estimated to cost the financial sector billions annually, further solidifies the suppliers’ position.
- High switching costs for banks: Implementing new compliance systems requires significant investment in time, training, and integration.
- Specialized expertise required: Compliance services demand niche knowledge that is not readily available internally or from generalist providers.
- Risk of penalties: Non-compliance can lead to severe financial penalties and reputational damage, making banks hesitant to compromise on service quality.
- Increasing regulatory complexity: New legislation, such as the projected 2025 updates to data privacy and lending regulations in California, continuously creates demand for updated compliance solutions.
Physical Infrastructure and Security Services
Suppliers of physical infrastructure, like real estate for branches, and essential security services significantly influence Five Star Bank's operational costs and risk management. While the real estate market can be diverse, specialized security providers, particularly those offering cybersecurity solutions, hold considerable sway. The increasing sophistication of cyber threats means that robust cybersecurity is no longer optional, giving these specialized suppliers more bargaining power.
In 2024, financial institutions, including community banks like Five Star Bank, continued to prioritize technology investments to combat evolving cybersecurity threats. Reports indicate a substantial rise in spending on cybersecurity solutions, with the global cybersecurity market projected to reach over $300 billion by 2024. This heightened demand for advanced security services directly translates to increased bargaining power for the suppliers of these critical solutions.
- Real Estate: While often fragmented, securing prime locations for physical branches remains a key cost factor.
- Cybersecurity Services: The growing threat landscape elevates the importance and bargaining power of specialized cybersecurity firms.
- Technology Investment: Community banks are increasing IT budgets, with cybersecurity being a major focus for 2025, reinforcing supplier influence.
Suppliers of specialized technology, data, and regulatory services hold significant bargaining power over Five Star Bank due to high switching costs and the critical nature of their offerings. The concentration in the banking technology market, coupled with the complexity and expense of migrating core systems, empowers these vendors. Furthermore, the increasing demand for proprietary financial data and advanced analytics, as evidenced by the over $30 billion global financial data market in 2024, grants suppliers leverage.
The scarcity of skilled professionals in areas like AI and cybersecurity in 2024 also bolsters supplier power, driving up compensation and competition. Similarly, the essential nature of regulatory compliance services, especially with evolving legislation like the 2025 CCPA enhancements, makes banks hesitant to switch providers, further solidifying supplier influence. Even in physical infrastructure, specialized cybersecurity firms gain power due to the escalating threat landscape and increased IT spending by banks in 2025.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2024-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Banking Technology Providers | High switching costs, market concentration | Millions of dollars in costs for system migration. |
| Financial Data & Analytics Providers | Proprietary data, advanced platforms | Global financial data market valued over $30 billion (2024). |
| Specialized Talent Pools (AI, Cybersecurity) | Scarcity of expertise | Upward pressure on compensation due to high demand. |
| Regulatory Compliance Services | Criticality of adherence, risk of penalties | Billions annually at risk for the financial sector due to non-compliance. |
| Cybersecurity Service Providers | Increasing threat landscape, rising IT investment | Global cybersecurity market projected over $300 billion (2024). |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive landscape for Five Star Bank, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, allowing Five Star Bank to pinpoint and address market threats effectively.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of depositors, both individuals and businesses, plays a significant role in a bank's profitability. Individual retail customers typically wield low bargaining power because their deposits represent a small fraction of a bank's total funding. However, the competitive landscape for deposits has intensified, with banks actively seeking to attract and retain funds. This environment means that customers who are less willing to accept lower interest rates on their savings can exert considerable influence.
In 2024, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions continued to shape deposit costs. While interest rates remained elevated compared to previous years, the competition for deposits meant that banks had to offer more attractive rates to secure funds. This 'war for deposits' effectively increased the leverage of depositors, as banks were incentivized to meet customer demands for higher yields to maintain their liquidity and lending capacity.
Commercial lending clients, particularly larger businesses, wield considerable bargaining power. They can readily shop around, comparing interest rates and loan terms from various financial institutions, including other community banks, larger regional banks, and even specialized non-bank lenders. In 2024, the average interest rate for commercial and industrial loans from U.S. commercial banks hovered around 7.5%, creating a competitive landscape where clients can negotiate favorable terms.
Five Star Bank actively works to offset this client leverage by cultivating deep, personalized relationships. By offering specialized industry knowledge, flexible solutions, and dedicated customer service, the bank aims to become a preferred partner rather than just another transactional lender. This relationship-centric approach helps retain clients even when competitors might offer slightly lower headline rates.
Clients of treasury management services, especially major corporations and institutions, wield significant bargaining power. These sophisticated users demand advanced tools for managing their finances, including cash flow, payments, and investments. Their capacity to switch providers based on service excellence, technological innovation, and competitive pricing grants them considerable leverage.
High-Net-Worth Individuals
High-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) wield considerable bargaining power in the financial services sector, including with institutions like Five Star Bank. Their substantial assets and intricate financial requirements mean they are highly sought after by wealth managers and private banks. This allows them to negotiate favorable terms and access a wider array of specialized services.
Five Star Bank's private banking division directly addresses this segment, recognizing the value HNWIs bring. For instance, in 2024, the global wealth management market saw continued growth, with HNWIs increasingly demanding personalized service and competitive pricing. This competitive landscape amplifies their ability to dictate terms.
- Access to Diverse Providers: HNWIs can choose from a broad spectrum of global and local financial institutions, including boutique wealth management firms and major private banks.
- Significant Asset Value: The sheer volume of assets managed by HNWIs makes their business highly attractive, giving them leverage in negotiations.
- Complex Financial Needs: Their sophisticated investment, tax, and estate planning requirements necessitate specialized services, which they can demand from providers.
- Demand for Value: HNWIs are often price-sensitive and actively seek the best value for their money, driving competition among financial service providers to offer superior products and lower fees.
Digital-First Expectations
Customers today demand a banking experience that’s always on and easily accessible through digital channels. This shift is largely driven by the proliferation of fintech innovators who have set a high bar for user-friendliness and convenience.
Banks failing to keep pace with these digital-first expectations risk alienating customers, who can readily switch to more technologically advanced competitors. In California, for instance, digital banking adoption has surged, with a substantial majority of customer interactions now happening via mobile apps and online platforms.
- 2024 Digital Banking Trends: Studies show over 70% of banking customers in the US now prefer digital channels for most transactions.
- Fintech Impact: The growth of fintech has normalized instant transactions and personalized digital experiences, raising customer standards across the board.
- California Digital Adoption: In 2024, California banks reported that over 65% of customer inquiries and transactions were handled through digital touchpoints, a significant increase from previous years.
The bargaining power of customers for Five Star Bank is influenced by several factors, including access to alternative providers and the increasing demand for digital services. Customers, especially those with significant assets or complex financial needs, can easily compare offerings from numerous institutions. This competitive environment, amplified by the rise of fintech, allows customers to negotiate better terms and demand superior service, directly impacting bank profitability.
In 2024, the banking sector saw heightened competition for deposits and lending, with customers leveraging this to their advantage. For instance, while average commercial loan rates were around 7.5%, businesses could shop around for better deals. Similarly, high-net-worth individuals, seeking personalized wealth management, could negotiate terms due to the broad availability of specialized services.
The expectation for seamless, digital banking experiences further empowers customers. With over 70% of US banking customers preferring digital channels in 2024, banks that lag in technology face a higher risk of customer attrition. This digital imperative means customers can readily switch to competitors offering more convenient and user-friendly platforms.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Five Star Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Five Star Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive evaluation of competitive forces within the banking sector. You'll gain insights into the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, providing a clear understanding of Five Star Bank's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Five Star Bank experiences significant competitive rivalry, particularly from other community and regional banks concentrated in its primary operating areas of Northern and Central California. This intense local competition means many institutions are vying for the same customer base, often focusing on similar demographic and business segments.
The sheer number of these regional players necessitates strong differentiation strategies for Five Star Bank. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, California had over 100 state-chartered banks and numerous national banks operating within its borders, many with a strong regional presence that directly mirrors Five Star Bank's footprint.
This environment compels Five Star Bank to emphasize its relationship banking model and specialized services as key differentiators. Success hinges on building loyalty and offering value beyond standard transactional banking, a challenge amplified by the localized nature of the competition.
Five Star Bank, while rooted in local markets, faces intense rivalry from large national and global banks operating in California. These behemoths, like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, leverage vast resources, comprehensive product suites, and advanced technological infrastructure, presenting a formidable competitive front, especially in attracting deposits and originating loans. For instance, in Q1 2024, Bank of America reported total deposits of $1.9 trillion, dwarfing the scale Five Star Bank can typically access locally.
Fintech companies and digital-first challengers are intensifying competition within the banking sector, impacting institutions like Five Star Bank. These agile disruptors provide specialized digital services, from online lending to mobile payments and robo-advisory platforms. Their innovative, convenient, and often cost-effective offerings are drawing customers away from traditional banks, compelling them to speed up their digital transformation efforts.
California, a prominent FinTech hub, exemplifies this trend, with numerous startups emerging to offer niche financial solutions. For instance, the digital lending market, a key area for fintech disruption, saw significant growth, with online lenders originating an estimated $100 billion in loans in 2023, according to industry reports. This competitive pressure necessitates that community banks like Five Star Bank invest heavily in technology to remain relevant and retain their customer base.
Interest Rate Environment and Deposit Competition
The current interest rate environment directly fuels competitive rivalry among banks. In 2025, with growth potentially moderating and interest rates remaining a key factor, banks are feeling the squeeze on their net interest margins. This pressure intensifies the competition to attract and retain customer deposits.
The ongoing 'war for deposits' presents a substantial hurdle for community banks. Customers in 2025 are showing a distinct reluctance to accept diminished returns on their savings, making it harder for banks to secure stable, low-cost funding. This dynamic forces banks to offer more competitive rates, further impacting profitability.
- Deposit competition intensifies as banks vie for customer funds amid a challenging interest rate landscape.
- Net interest margins are under pressure in a low-growth, lower-rate environment, driving up the cost of funding.
- Community banks face significant challenges in 2025 due to customer resistance to lower deposit yields.
- The demand for higher returns on deposits forces banks to compete more aggressively on pricing.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Costs
The complex and evolving regulatory environment in California significantly intensifies competitive pressures for banks like Five Star Bank. Compliance with new legislation, such as the California Consumer Financial Protection Law (CCFPL) effective January 1, 2025, which aims to regulate non-bank entities and potentially impact bank partnerships, demands substantial investment in technology and personnel.
These compliance costs, including those related to overdraft fee regulations and data privacy mandates like the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), can disproportionately burden smaller community banks. For instance, a 2023 industry survey indicated that compliance expenses for mid-sized banks could range from 1% to 3% of operating expenses, a significant hurdle when competing with larger institutions that possess more robust, in-house compliance infrastructure.
- Increased Operational Burden: Adhering to California's specific regulatory nuances requires dedicated resources, diverting funds from growth initiatives.
- Disproportionate Impact on Smaller Banks: Community banks may struggle to absorb the costs associated with new compliance requirements compared to larger, well-resourced competitors.
- Focus on Consumer Protection: Regulations targeting overdraft fees and data privacy, while beneficial for consumers, add layers of complexity and potential penalties for non-compliance.
Five Star Bank faces intense rivalry from a multitude of community and regional banks within its California operating areas. This crowded market means many banks are competing for the same customers, often targeting similar segments, as evidenced by the over 100 state-chartered banks in California as of Q1 2024.
Furthermore, large national banks like Bank of America, with $1.9 trillion in deposits in Q1 2024, and agile fintech companies offering specialized digital services, present significant competitive challenges. Fintechs, particularly in California, are disrupting traditional banking, with the digital lending market alone estimated at $100 billion in originations in 2023.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by the ongoing 'war for deposits' in 2025, driven by customer demand for higher returns and pressure on net interest margins. This forces banks to compete more aggressively on pricing for customer funds, impacting profitability.
Regulatory changes, such as California's CCFPL effective January 1, 2025, and data privacy mandates, add to the competitive pressure, with compliance costs potentially ranging from 1% to 3% of operating expenses for mid-sized banks, disproportionately affecting smaller institutions.
| Competitor Type | Key Challenge | Example (Q1 2024/2023 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Community/Regional Banks | Market saturation, similar customer focus | Over 100 state-chartered banks in California |
| National Banks | Vast resources, broad product offerings | Bank of America deposits: $1.9 trillion |
| Fintech Companies | Digital innovation, specialized services | Digital lending market: ~$100 billion originations (2023) |
| Interest Rate Environment | Deposit acquisition cost, margin pressure | 'War for deposits' in 2025 |
| Regulatory Compliance | Increased costs, operational burden | CCFPL (Jan 1, 2025), CPRA |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Credit unions present a significant threat of substitution for Five Star Bank. These member-owned institutions offer a comparable suite of financial services, including savings accounts, checking accounts, and various loan products. Their community-centric approach and member-benefit structure can attract customers seeking alternatives to traditional banking.
In 2024, credit unions continued to grow, with the National Credit Union Administration reporting over 5,000 federally insured credit unions serving more than 130 million members. This broad reach and established customer base indicate their capacity to absorb market share from banks like Five Star.
Furthermore, regulatory changes, such as new California laws enacted in 2024 that cap overdraft fees for state-regulated institutions, can reduce the competitive advantage banks might have historically held. This leveling of the playing field makes credit unions a more attractive substitute for consumers sensitive to banking fees.
Online lenders and alternative financing platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional bank loans. These platforms, including fintech companies and peer-to-peer lenders, often boast quicker approval times and more adaptable loan structures, especially appealing to small and medium-sized enterprises that might find traditional banking routes more challenging. For instance, in 2024, the alternative lending market continued its robust growth, with some estimates projecting it to reach hundreds of billions of dollars globally, demonstrating its increasing appeal as a viable alternative to conventional bank financing.
For individuals and institutions holding substantial assets, investment firms, mutual funds, and independent wealth management advisors present a significant threat of substitution to traditional banking products. These alternatives often provide a wider array of investment vehicles, from alternative assets to complex derivatives, and offer specialized financial planning tailored to specific client needs, potentially attracting capital away from banks.
In 2024, the wealth management sector continued to grow, with global assets under management (AUM) in mutual funds alone reaching trillions of dollars, demonstrating the substantial capital flowing into these substitute channels. For instance, the Investment Company Institute reported significant net inflows into equity and bond funds throughout the year, indicating a strong preference for these investment avenues over traditional bank deposits for growth-oriented capital.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending and Crowdfunding
The rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms presents a growing threat of substitutes for Five Star Bank. These digital channels offer alternative avenues for individuals and small businesses to access capital, often bypassing traditional banking processes. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global P2P lending market was valued at over $100 billion, demonstrating a significant shift in borrowing behavior.
These platforms are particularly competitive for smaller loan amounts and project-specific financing, areas where traditional banks may have higher overhead or less flexibility. Crowdfunding platforms, in particular, have seen substantial growth, with global crowdfunding volume reaching an estimated $30 billion in 2023. This indicates a tangible diversion of capital away from conventional financial institutions.
- P2P Lending Market Growth: Global P2P lending market exceeded $100 billion by the end of 2023.
- Crowdfunding Volume: Global crowdfunding volume was estimated at $30 billion in 2023.
- Niche Competition: Platforms are increasingly competitive for smaller loan sizes and project financing.
- Bypassing Traditional Channels: These substitutes offer alternative routes for capital acquisition.
Digital Payment Platforms and Neobanks
Digital payment platforms like PayPal and Venmo, along with neobanks, present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banks like Five Star Bank. These digital alternatives offer streamlined, often fee-free services for transactions and account management, directly competing with core banking functions.
For instance, in 2024, the digital payments market continued its robust growth, with global transaction values projected to reach trillions of dollars. Neobanks are also gaining traction, attracting millions of users with their user-friendly interfaces and lower overhead costs.
- Convenience: Digital platforms offer 24/7 access and instant transactions, appealing to a mobile-first demographic.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many digital payment services and neobanks operate with minimal or no fees, undercutting traditional bank charges.
- User Experience: Neobanks, in particular, are designed with intuitive mobile interfaces, often surpassing the digital experience offered by legacy institutions.
- Market Share: The increasing adoption of these digital services indicates a shift in consumer preference away from traditional banking channels for everyday financial needs.
Credit unions and digital-only banks are increasingly offering competitive alternatives to traditional banking services, attracting customers with lower fees and personalized experiences. In 2024, credit unions saw continued growth, with over 5,000 federally insured institutions serving more than 130 million members, as reported by the NCUA. This broad reach and member-focused model make them potent substitutes for the core offerings of banks like Five Star.
Online lenders and crowdfunding platforms are siphoning off loan demand, particularly for small businesses and individuals seeking faster, more flexible financing. The global P2P lending market surpassed $100 billion by the end of 2023, and crowdfunding volume reached an estimated $30 billion in the same year, illustrating a significant diversion of capital away from traditional banks.
Investment firms and wealth management services are attracting significant capital that might otherwise be held in bank deposits, especially for growth-oriented investors. Global assets under management in mutual funds alone reached trillions of dollars in 2024, with substantial net inflows into equity and bond funds, indicating a strong preference for these investment channels.
Digital payment platforms and neobanks are encroaching on everyday banking transactions, offering convenience and lower costs that appeal to a mobile-first demographic. The digital payments market's transaction values were projected to reach trillions of dollars globally in 2024, with neobanks attracting millions of users through intuitive interfaces and minimal fees.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | 2023/2024 Data Point | Impact on Five Star Bank |
| Credit Unions | Member-owned, community focus, comparable services | Over 5,000 federally insured CUs, 130M+ members (2024) | Attracts customers seeking lower fees and community banking |
| Online Lenders/Crowdfunding | Faster approvals, flexible terms, digital access | P2P Lending: >$100B market (end 2023); Crowdfunding: ~$30B volume (2023) | Diverts loan demand, especially for SMEs and project finance |
| Investment Firms/Wealth Management | Diverse investment vehicles, specialized planning | Global mutual fund AUM in trillions (2024); strong inflows into equity/bond funds | Captures capital seeking growth, reducing traditional deposit base |
| Digital Payments/Neobanks | Streamlined transactions, low/no fees, mobile-first UX | Digital payments market value in trillions (2024 projection) | Competes for everyday transactions and basic account services |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for Five Star Bank is significant, primarily from agile fintech startups. These companies often utilize advanced technology to deliver specialized financial services with greater efficiency and lower costs. For instance, in 2024, venture capital funding for fintech globally reached hundreds of billions, with a substantial portion flowing into startups focused on areas like digital payments, lending, and wealth management.
California, a major fintech hub, continues to attract considerable investment, fostering an environment where new players can rapidly emerge and scale. These startups can quickly carve out market share by targeting niche services or customer segments that traditional banks may overlook or serve less effectively. This competitive pressure forces established institutions like Five Star Bank to innovate and adapt to remain relevant.
A developing concern for traditional banks like Five Star Bank is the rise of public banks and community-owned financial initiatives, particularly in California. These new entrants, spurred by legislation like the California Public Banking Act (AB 857), aim to redirect public funds towards local development and services, potentially drawing business away from established institutions.
Large technology firms and other non-financial entities are increasingly venturing into financial services. These companies, like Apple and Google, are leveraging their extensive customer relationships and advanced technological infrastructure to offer competitive payment solutions, lending, and embedded finance options. For instance, Apple Pay processed over 3.5 billion transactions in 2023, demonstrating significant inroads into traditional banking domains.
Regulatory Hurdles and Capital Requirements
Despite the increasing interest in fintech and alternative lending, the banking sector remains protected by substantial entry barriers. Establishing a new bank in the United States, for instance, typically necessitates a minimum capital infusion of around $50 million. This significant financial commitment, coupled with the stringent compliance demands of regulations like the Community Reinvestment Act, acts as a powerful deterrent to potential new competitors.
These regulatory hurdles and capital requirements create a formidable challenge for newcomers. Potential entrants must not only secure considerable funding but also navigate a complex web of federal and state banking laws. For example, the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956 imposes restrictions on non-bank entities acquiring or controlling banks, further solidifying the position of incumbent institutions.
- Significant Capital Outlay: New US banks often require a minimum of $50 million in capital.
- Extensive Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to rules like the Community Reinvestment Act demands substantial resources and oversight.
- Legal Frameworks: Legislation such as the Bank Holding Company Act limits non-bank entry into traditional banking.
Brand Reputation and Trust
For a new entrant, establishing a strong brand reputation and fostering customer trust in the banking sector is a substantial hurdle. Established institutions like Five Star Bank leverage decades of consistent service and community engagement, which translates into a deep reservoir of trust and perceived reliability. For instance, in 2024, community banks continued to demonstrate strong customer loyalty, often outperforming larger national banks in customer satisfaction surveys, with many reporting high Net Promoter Scores (NPS) reflecting this trust.
New players must therefore allocate significant resources towards marketing campaigns and exceptional customer service initiatives to even begin to chip away at this established goodwill. This investment is crucial to signal stability and competence, counteracting the inherent skepticism new financial institutions often face. The cost of acquiring customers and building brand equity can be considerable, particularly when competing against a backdrop of established, trusted names.
- High Customer Acquisition Costs: New banks often spend significantly more per customer acquired compared to established banks.
- Brand Loyalty of Incumbents: Existing customers of banks like Five Star Bank are less likely to switch due to established relationships and trust.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: New financial entrants face rigorous regulatory oversight, which can impact their ability to quickly build a trusted public image.
- Perceived Stability: Customers often associate longevity with financial stability, a perception new entrants must actively work to build.
The threat of new entrants for Five Star Bank is moderated by significant barriers, though fintech startups and large tech firms pose ongoing challenges. While venture capital funding for fintech reached hundreds of billions in 2024, and companies like Apple processed over 3.5 billion transactions in 2023, the substantial capital requirements (around $50 million for a new US bank) and stringent regulatory compliance, such as the Bank Holding Company Act, deter many potential competitors. Furthermore, established banks benefit from strong brand loyalty and customer trust, which new entrants find costly and time-consuming to replicate.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Minimum $50 million for new US banks. | High; limits the number of well-funded entrants. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Community Reinvestment Act, Bank Holding Company Act. | High; requires significant resources and expertise. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Decades of service, community engagement. | High; difficult and costly for new entrants to build. |
| Technological Infrastructure | Established digital platforms, cybersecurity. | Moderate to High; requires substantial investment for new players. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Five Star Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of verified data, including Five Star Bank's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific research from reputable sources like IBISWorld and S&P Capital IQ. This comprehensive approach ensures an accurate assessment of competitive forces within the banking sector.
