F-Secure Oyj Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
F-Secure Oyj Bundle
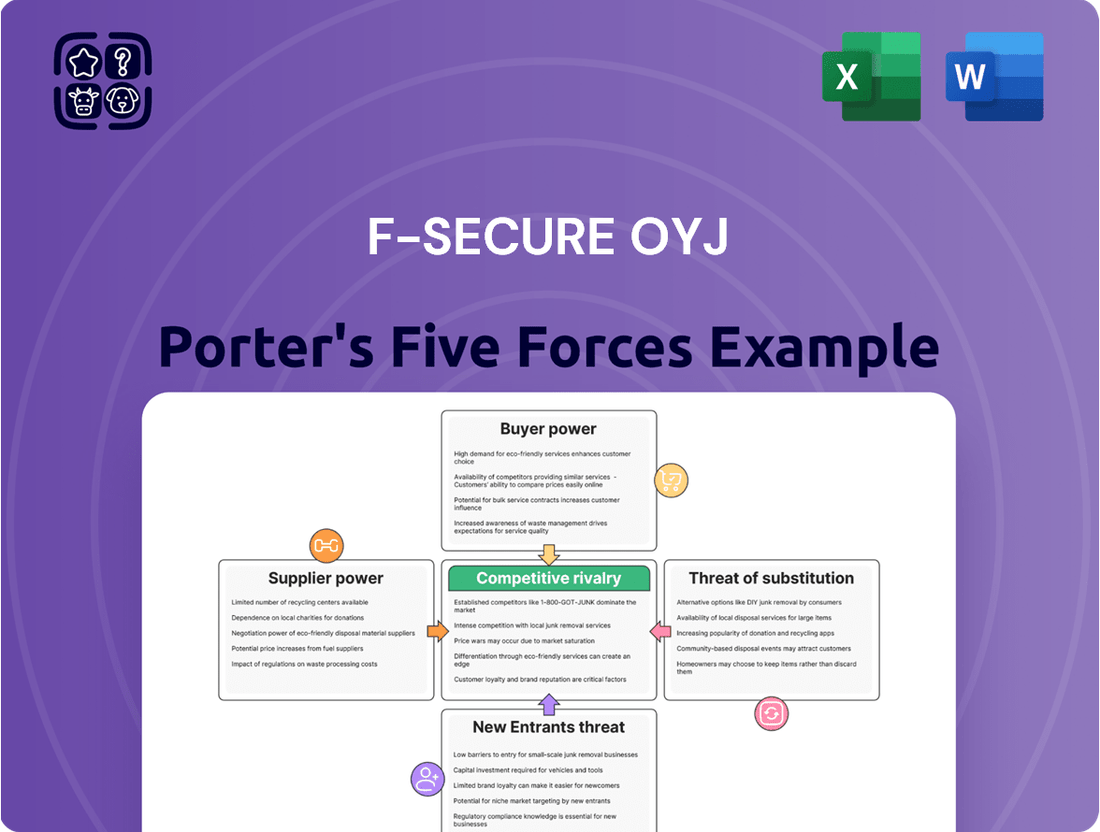
F-Secure Oyj operates in a dynamic cybersecurity landscape, facing intense competition and evolving threats.
The threat of new entrants is moderate, as established brands and high R&D costs present barriers, but the growing demand for digital security fuels innovation.
Buyer power is significant, with customers often having multiple cybersecurity solutions to choose from, driving price sensitivity and demanding robust feature sets.
The threat of substitutes is also considerable, as businesses explore integrated security platforms and managed security services that may reduce reliance on standalone F-Secure products.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping F-Secure Oyj’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The cybersecurity industry heavily relies on a limited number of specialized technology providers for crucial components and advanced solutions. This concentration gives these suppliers significant leverage over pricing and terms for essential inputs. F-Secure, like its peers, depends on these providers for core technologies, such as advanced AI/ML algorithms or secure hardware elements. The high demand for cutting-edge security capabilities, with global cybersecurity spending expected to exceed $215 billion in 2024, further solidifies these suppliers' bargaining power.
The demand for highly skilled cybersecurity professionals significantly outstrips supply in 2024, creating an intensely competitive market for talent.
This scarcity gives cybersecurity experts, especially those proficient in AI-driven threat analysis and EDR, considerable leverage.
Their strong bargaining power directly influences salary and contract negotiations, with average salaries for senior roles often exceeding €80,000 in Europe.
For F-Secure Oyj, this dynamic directly increases operational costs and poses challenges for retaining top-tier talent in a fiercely contested landscape.
F-Secure Oyj relies heavily on timely and accurate threat intelligence data feeds for its cybersecurity solutions, including antivirus and EDR services. The global threat intelligence market, valued at approximately $2.6 billion in 2024, is dominated by a few key providers, giving them significant bargaining power. The quality and exclusivity of this specialized data are paramount, as they directly impact the efficacy of F-Secure's defenses against evolving cyber threats. This dependency means F-Secure must maintain strong relationships with these critical suppliers to ensure competitive product performance.
Cloud Infrastructure Providers
As F-Secure increasingly pivots towards cloud-native security solutions, its operational reliance on major cloud infrastructure providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud intensifies. These dominant providers collectively commanded over 67% of the global cloud infrastructure market share in Q1 2024, granting them substantial bargaining power. The high costs and inherent complexity associated with migrating data and re-architecting applications across different cloud platforms create significant switching barriers for F-Secure. This dependency directly influences F-Secure's service delivery costs and can constrain its operational flexibility, impacting margins and strategic agility.
- AWS held approximately 31% of the global cloud infrastructure market share in Q1 2024.
- Microsoft Azure accounted for about 25% of the market share in Q1 2024.
- Google Cloud's market share was approximately 11% in Q1 2024.
- High switching costs, potentially millions for large-scale migrations, limit F-Secure's alternatives.
Component and Hardware Manufacturers
F-Secure Oyj, particularly for its on-premise solutions and hardware-accompanying services, faces significant bargaining power from component and hardware manufacturers. Supply chain resilience became a critical focus in 2024, with global electronics supply chains still sensitive to geopolitical shifts and raw material costs. Fluctuations in semiconductor prices or availability, for instance, directly impact F-Secure's production costs for physical products such as endpoint security appliances.
This supplier influence is especially relevant for endpoint security solutions that integrate hardware, where delays or cost increases from a few key manufacturers can directly affect F-Secure’s profitability and market competitiveness. In 2024, the average lead times for certain specialized chips, although improving from 2022 peaks, remained a concern for hardware-dependent software providers.
- Global semiconductor market revenue is projected to reach approximately $600 billion in 2024, indicating the scale and potential volatility within the component supply chain.
- F-Secure's reliance on specific, high-quality hardware components for its on-premise offerings creates a dependency that can empower these specialized suppliers.
- Potential for increased operational costs if key component manufacturers raise prices due to inflation or increased demand for their highly specialized parts.
- Risk of product delivery delays or reduced availability if supply chain disruptions, like those seen in early 2020s, re-emerge for critical hardware inputs.
F-Secure Oyj navigates significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on highly specialized technology, critical threat intelligence, and dominant cloud infrastructure providers. The scarcity of top-tier cybersecurity talent and dependencies on key hardware components further elevate supplier leverage. This environment directly impacts F-Secure's operational costs and strategic flexibility in 2024.
| Supplier Category | 2024 Market Data | Impact on F-Secure |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure | Top 3 hold >67% market share | Increased operational costs; high switching barriers |
| Cybersecurity Talent | Senior salaries >€80k (Europe) | Higher wage costs; talent retention challenges |
| Threat Intelligence | Market value ~$2.6B | Dependency for solution efficacy; pricing leverage |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting F-Secure Oyj, detailing industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes.
F-Secure Oyj's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides actionable insights to navigate competitive pressures, acting as a strategic roadmap to alleviate market-related pain points.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large enterprise customers, especially those acquiring extensive cybersecurity solutions, possess substantial bargaining power against F-Secure. Their significant contract volumes, often involving millions in annual spending, enable them to negotiate highly favorable pricing and customized service level agreements. For instance, a major global corporation's 2024 cybersecurity budget could easily exceed tens of millions of euros, giving them leverage. F-Secure must consistently offer competitive terms and demonstrate superior value to attract and retain these crucial clients, as their revenue contribution is vital for the company's sustained growth and market position.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) exhibit moderate bargaining power against cybersecurity providers like F-Secure Oyj. While a single SME holds less individual leverage than a large corporation, the rapidly expanding cybersecurity market, valued at approximately $200 billion globally in 2024, offers them a broad spectrum of vendors and solution choices. F-Secure's strategic focus on the SME sector necessitates offering highly scalable and cost-effective solutions to attract and retain these customers. This competitive landscape means SMEs can readily compare offerings, influencing pricing and service terms.
Individual consumers generally face low switching costs when changing personal cybersecurity providers, as the market is highly saturated. In 2024, the consumer antivirus segment features many competitors, allowing users to easily transition between services like F-Secure, Norton, or Bitdefender. This straightforward process enhances customer bargaining power, compelling companies to prioritize competitive pricing and user-friendly features. Such market dynamics mean F-Secure must continually innovate and offer superior value to retain its customer base.
Price Sensitivity
Due to a high number of available suppliers, buyers in the cybersecurity market often exhibit significant price sensitivity, actively seeking the best value. Both individual consumers and businesses, facing a competitive landscape with numerous providers like NortonLifeLock and McAfee, frequently demand discounts or bundled incentives. F-Secure Oyj must manage its pricing strategy carefully to remain competitive and retain its customer base in 2024.
- The global cybersecurity market size is projected to reach approximately $220 billion in 2024, indicating a crowded field.
- Customers can easily compare prices across various security solutions, including freemium and subscription models.
- Businesses, especially SMEs, are increasingly budget-conscious regarding their cybersecurity expenditures.
- F-Secure’s offerings must balance advanced protection with attractive pricing to counter buyer power effectively.
Access to Information
The internet significantly amplifies customer bargaining power, granting easy access to product reviews, comparisons, and detailed information on various cybersecurity vendors. This transparency empowers buyers to thoroughly compare F-Secure's offerings against competitors, fostering highly informed purchasing decisions. For instance, in 2024, customer review platforms show F-Secure often competes with larger players like Broadcom (Symantec) and Microsoft Defender in enterprise segments, where detailed feature comparisons are critical.
- Customer review platforms like G2 or Capterra provide extensive peer insights, influencing over 70% of B2B tech purchases.
- F-Secure's average customer satisfaction score for its business solutions, as reported in early 2024, generally reflects its competitive standing.
- The ability to compare pricing and features across multiple vendors online drives down profit margins for vendors if their value proposition isn't clear.
- A strong brand reputation, built on consistent positive reviews and effective threat intelligence, is paramount for F-Secure to retain its market share against rivals.
Large enterprises leverage significant contract volumes for favorable terms, impacting F-Secure's pricing. SMEs and individual consumers benefit from a saturated 2024 cybersecurity market, enabling easy comparison and low switching costs. Online transparency further empowers buyers, demanding competitive value from F-Secure.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power | 2024 Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise | High | Multi-million contract leverage |
| SME | Moderate | Diverse vendor choice (Global market approx. $220B) |
| Consumer | Moderate-High | Low switching costs, easy comparisons |
Preview Before You Purchase
F-Secure Oyj Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders, providing a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of F-Secure Oyj. You'll gain detailed insights into the competitive landscape, including the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, the bargaining power of buyers, and the threat of new entrants into the cybersecurity market. Furthermore, the analysis thoroughly examines the bargaining power of suppliers and the threat of substitute products or services that could impact F-Secure's market position. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file, professionally formatted and ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The cybersecurity market is intensely competitive and highly fragmented, with numerous vendors vying for market share. F-Secure Oyj faces significant rivalry from a diverse array of companies, ranging from established giants like Palo Alto Networks, which reported over $1.97 billion in revenue for Q3 2024, to agile, niche specialists. This intense competition, especially within Europe where F-Secure operates, drives constant pressure on pricing models and necessitates continuous innovation in product development. The fragmented landscape also demands robust marketing efforts to differentiate offerings amidst a crowded field.
F-Secure faces intense competitive rivalry from established players and rapidly growing innovators. In endpoint security, primary competitors include Sophos, Trend Micro, and WatchGuard, all offering robust solutions. The broader cybersecurity landscape sees F-Secure vying with market leaders like CrowdStrike, which reported 2024 Q1 revenue growth of 42%, and SentinelOne. Bitdefender also poses a significant challenge with its comprehensive security suite. This intense competition necessitates continuous innovation and differentiation in a market valued at over $200 billion in 2024.
In the competitive cybersecurity landscape, continuous innovation is essential for F-Secure Oyj to differentiate itself. The company actively invests in advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance its threat detection and response capabilities, crucial for staying ahead of evolving cyber threats. For instance, F-Secure’s R&D expenditure for 2024 reflects ongoing commitment to developing new solutions. This strategic focus on integrating cutting-edge technologies is a critical factor in maintaining a strong competitive edge against rivals.
Price and Service-Based Competition
Competition in the cybersecurity sector heavily relies on both price and service quality, pushing companies to offer the most cost-effective solutions with superior customer support. F-Secure Oyj, for instance, strategically leverages its robust partner channel to ensure effective service delivery and market reach. This approach helps manage competitive pressures from both established giants and agile newcomers.
- The global cybersecurity market value is projected to reach approximately $222.6 billion in 2024, emphasizing intense competition.
- F-Secure's partner channel contributes significantly to its service distribution and customer engagement.
- Customer retention often hinges on responsive support and perceived value for money in the highly competitive landscape.
- Pricing models, including subscription services, are continually refined to attract and retain diverse customer segments.
Global and Local Competitors
F-Secure Oyj navigates a complex competitive landscape, facing off against global cybersecurity giants like Microsoft, Palo Alto Networks, and Fortinet, alongside numerous smaller, niche local competitors across its operational markets. This necessitates a highly adaptable strategy to address diverse regional demands and varying competitive pressures. The company's Finnish heritage and established international footprint, with operations spanning over 100 countries, significantly influence its competitive positioning in both consumer and business security segments.
- The global cybersecurity market size is projected to reach approximately $208.7 billion in 2024.
- F-Secure's 2024 Q1 revenue was 29.0 million euros, reflecting ongoing competitive dynamics.
- Key competitors such as Microsoft offer integrated security solutions, leveraging their extensive ecosystem.
- Local players often provide specialized services, challenging F-Secure in specific geographical niches.
F-Secure Oyj faces intense competitive rivalry in a fragmented cybersecurity market, projected at $208.7 billion in 2024. This necessitates continuous innovation, with F-Secure’s 2024 Q1 revenue at 29.0 million euros, highlighting ongoing pressures. Competition from diverse players like Microsoft and CrowdStrike (Q1 2024 revenue growth 42%) drives strategic focus on advanced technologies and robust partner channels.
| Competitor | Focus Area | 2024 Metric | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palo Alto Networks | Network Security | Q3 Revenue: $1.97B | ||
| CrowdStrike | Endpoint Protection | Q1 Revenue Growth: 42% | ||
| Microsoft | Integrated Security | Leverages ecosystem |
SSubstitutes Threaten
A significant substitute threat for F-Secure Oyj comes from large technology companies integrating security features directly into their core platforms. For instance, Microsoft's enhanced security capabilities within Windows 11, continually updated through 2024, reduce the perceived necessity for standalone antivirus solutions. Similarly, major cloud providers like AWS and Azure offer robust native security tools as part of their cloud service bundles, with cloud security spending projected to reach $12.3 billion in 2024. This trend can diminish demand for specialized third-party cybersecurity offerings, impacting companies like F-Secure by shifting customer reliance.
Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) represent a significant substitute threat to F-Secure Oyj, as many organizations, particularly large enterprises, opt to fully outsource their cybersecurity operations. While F-Secure offers its own managed services, the choice to engage a comprehensive MSSP utilizing a different suite of security tools directly competes with purchasing F-Secure's products. This dynamic shifts the decision from buying a specific software solution to acquiring a complete, outsourced security management service. The global MSSP market was projected to reach over $35 billion in 2024, highlighting this substantial alternative for businesses.
The widespread availability of free antivirus software and security tools presents a significant threat, particularly within the consumer market. While these complimentary versions, such as Avast Free Antivirus or AVG AntiVirus Free, often provide limited features compared to F-Secure's comprehensive paid products, they serve as a sufficient 'good enough' solution for many budget-conscious users. This intense competition pressures F-Secure to continually enhance and clearly articulate the superior added value and advanced protection of its premium offerings, like those highlighted in their Q1 2024 financial reports, to justify subscription costs.
In-house Security Teams
Larger corporations with significant resources often opt to build and maintain their own comprehensive in-house cybersecurity teams and infrastructure. This internal capability serves as a direct substitute for purchasing external products and services from vendors like F-Secure. The strategic choice to build versus buy is a critical consideration for these organizations, especially given the rising cost of external solutions.
In 2024, many enterprise-level companies are expanding their internal security operations centers (SOCs) to gain more control over their threat landscape.
- Cost-effectiveness for large scale.
- Customization and control over security posture.
- Data sensitivity and compliance requirements.
- Access to specialized internal talent.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) as a Successor
The evolution from traditional antivirus to Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) represents a significant form of substitution within the cybersecurity market, even as F-Secure offers EDR services. Customers increasingly demand advanced, behavior-based threat detection, rendering traditional signature-based antivirus less sufficient on its own. F-Secure must consistently highlight its robust EDR capabilities to address this shifting market demand, especially as global EDR market growth is projected to continue its strong upward trajectory through 2024.
- The global EDR market size was valued at approximately $2.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $3.2 billion in 2024.
- Customer spending on advanced threat detection solutions, like EDR, is rising, with many organizations prioritizing real-time visibility and automated response.
- F-Secure's emphasis on its Countercept EDR platform is crucial as enterprises seek more comprehensive security postures beyond basic endpoint protection.
F-Secure faces significant substitute threats from large tech companies integrating security into core platforms, like Windows 11, and native cloud security tools, with cloud security spending reaching $12.3 billion in 2024. Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs), a market exceeding $35 billion in 2024, offer comprehensive outsourced security. Free antivirus software and enterprises building robust in-house cybersecurity capabilities also diminish demand. The shift towards advanced EDR solutions, a $3.2 billion market in 2024, further presents a key substitute.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Market Data / Trend | Impact on F-Secure |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated Platform Security | Cloud Security Spending: $12.3 billion | Reduces need for standalone solutions. |
| Managed Security Services (MSSPs) | Global MSSP Market: >$35 billion | Outsourced security competes directly. |
| Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) | EDR Market: >$3.2 billion | Shifts demand from traditional antivirus. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants establishing a large-scale, globally competitive cybersecurity firm is notably low for F-Secure Oyj. This is primarily due to the immense initial investment required for cutting-edge research and development, which can easily run into hundreds of millions of euros annually across the industry to keep pace with evolving threats, as seen in 2024. Building a robust global threat intelligence network, essential for real-time protection against sophisticated cyberattacks, also demands significant capital and time. Furthermore, establishing a trusted brand in cybersecurity, where data breaches can severely damage reputation, presents a substantial barrier. F-Secure's long history and established reputation since 1988 create a significant competitive moat, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to gain market share at scale.
The threat of new entrants is particularly elevated in specialized niche markets within the cybersecurity sector. Startups frequently emerge with highly innovative solutions targeting specific security problems, like the rapidly expanding IoT security segment or specialized consulting services for cloud environments. These smaller, agile companies, often backed by venture capital, can quickly gain market share in their chosen niches. For instance, the global IoT security market is projected to reach approximately $35 billion by 2024, attracting many specialized new players. This agility allows them to potentially disrupt specific segments of the broader cybersecurity market, posing a challenge even to established players like F-Secure Oyj.
New entrants into the cybersecurity market face significant hurdles in accessing established distribution channels. Companies like F-Secure Oyj benefit from an extensive network of service provider partners, which is difficult for newcomers to replicate. Building these crucial relationships demands substantial time and resources, creating a formidable barrier to entry. F-Secure's strong partner channel, contributing significantly to its recurring revenue streams, remains a key competitive advantage in 2024, enabling broad customer reach.
Technological Expertise and Brand Reputation
New entrants face substantial barriers in cybersecurity, needing both advanced technological expertise and a deeply trusted brand. Customers, especially in the demanding B2B sector, are highly risk-averse, hesitant to entrust their critical security infrastructure to unproven vendors. F-Secure’s established history, spanning over three decades, and its consistent recognition, such as being named a Strong Performer in the Forrester Wave: Endpoint Security 2024 report, significantly solidify its formidable reputation.
- F-Secure's 2024 Q1 revenue reached €30.2 million, demonstrating market presence.
- Building trust in cybersecurity can take years, unlike general software markets.
- The cost of R&D for competitive cybersecurity solutions is exceptionally high.
- Regulatory compliance adds complexity for new entrants in data protection.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The cybersecurity industry faces an escalating number of regulations and compliance standards, including GDPR and the NIS2 Directive, which became effective in October 2024. Navigating these complex legal and regulatory frameworks presents a substantial hurdle for new entrants. Established companies like F-Secure Oyj possess the experience and resources to effectively manage these stringent requirements. This regulatory burden acts as a significant barrier to entry, as non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, such as GDPR fines reaching up to 4 percent of global annual turnover. Such compliance costs and risks deter potential competitors.
- Cybersecurity regulations, including NIS2 effective October 2024, create high entry barriers.
- New entrants struggle with complex compliance, lacking established resources.
- F-Secure's experience in regulatory navigation offers a competitive advantage.
- Potential fines, like GDPR's 4% global turnover penalty, deter new market players.
New entrants face substantial barriers in cybersecurity due to immense R&D costs and the challenge of building trusted brands, a process taking years as F-Secure's long history demonstrates. The industry also requires navigating complex regulations, including the NIS2 Directive effective October 2024, which deters new players. Replicating F-Secure's extensive partner channels and established market presence, highlighted by its Q1 2024 revenue of €30.2 million, proves exceptionally difficult for newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Impact on New Entrants | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High R&D costs (hundreds of millions of euros annually) | Global IoT security market to reach $35B by 2024 |
| Brand & Trust | Years needed to build credibility | F-Secure recognized in Forrester Wave: Endpoint Security 2024 |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex legal frameworks, high penalty risks | NIS2 Directive effective October 2024, GDPR fines up to 4% of turnover |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our F-Secure Oyj Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including F-Secure's official annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Gartner and IDC, and relevant cybersecurity trade publications.
We also incorporate information from financial databases, competitor disclosures, and government regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
