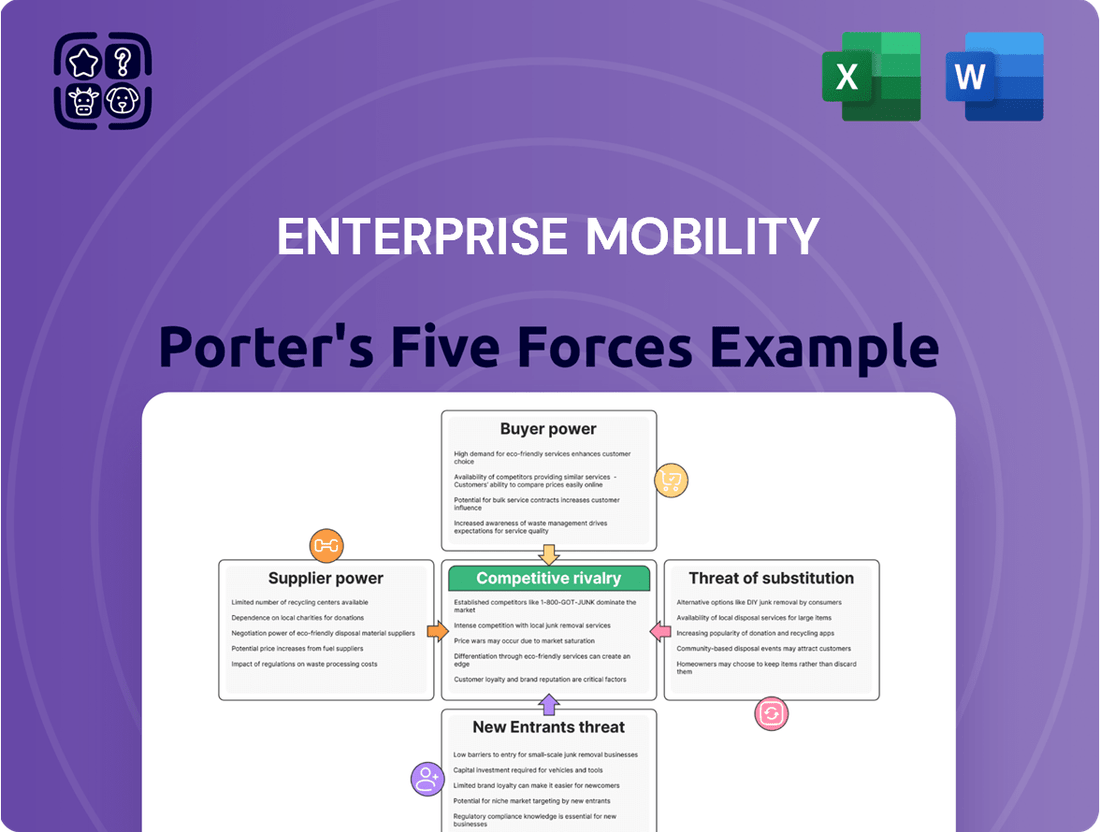
Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Enterprise Mobility Bundle
Understanding Enterprise Mobility through Porter's Five Forces reveals the intricate web of competitive pressures. We've touched on the core dynamics, but the true depth of these forces – from supplier leverage to the allure of substitutes – remains largely unexplored here. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Enterprise Mobility’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Major automotive manufacturers wield considerable bargaining power over enterprise mobility providers. This stems from the substantial capital investment required to build and maintain vehicle fleets, coupled with the necessity for a diverse range of vehicle types to meet varied business needs. In 2024, the global automotive industry continued to face supply chain challenges, impacting production volumes and delivery times, thereby amplifying the leverage of these key suppliers.
Enterprise mobility services are heavily dependent on securing vehicles, whether through purchase or lease agreements, from these manufacturers. Fluctuations in production capacity, the introduction of new models, and manufacturers' pricing strategies directly influence the cost and availability of fleet vehicles. For instance, a shortage of specific vehicle components, like semiconductors, in late 2023 and early 2024 led to extended lead times and increased prices for many models, giving manufacturers greater control over terms.
Technology and software providers for enterprise mobility, particularly those offering specialized fleet management, reservation, and telematics solutions, hold significant bargaining power. Their influence stems from the critical nature of their offerings in ensuring operational efficiency and enhancing customer experience.
When these software and hardware vendors provide unique, highly integrated systems, switching costs for businesses can become prohibitively high. This dependence limits a company's ability to easily change providers, thus strengthening the supplier's negotiating position.
The market for advanced telematics solutions, for instance, saw significant investment in 2024, with companies focusing on AI-driven analytics and predictive maintenance. Providers offering these cutting-edge, difficult-to-replicate features are in a prime position to command higher prices and favorable contract terms.
Fuel and maintenance providers wield notable bargaining power, particularly in areas with fewer service options or when specialized repair skills are essential for fleet operations. The commodity nature of fuel can be somewhat mitigated by large-scale purchasing agreements, but supplier terms and fluctuating market prices still allow for influence.
In 2024, the automotive repair and maintenance sector saw continued demand, with the average cost of a car repair rising by an estimated 5% compared to the previous year, placing pressure on companies to negotiate favorable terms with their service providers. Similarly, fuel costs remained a significant operational expense; for example, the average price of gasoline in the US fluctuated, hovering around $3.50-$3.70 per gallon for much of the year, impacting the leverage available to large fleet buyers.
Real Estate and Infrastructure Lessors
Lessors of prime real estate, such as airport locations, bustling downtown branches, and essential maintenance facilities, wield significant bargaining power in the enterprise mobility sector. Their leverage stems from the strategic necessity of these locations for mobility providers. For instance, a recent analysis showed that airport concession fees, a key component of real estate leasing for airlines and car rental companies, can represent a substantial portion of operating costs, sometimes exceeding 15-20% for prime gate locations.
The demand for specific, high-traffic sites can be intense, particularly in major metropolitan areas. This demand, coupled with the long-term commitment typically required for lease agreements and the substantial capital outlay involved in establishing and customizing a branch or facility, grants lessors considerable negotiation strength. In 2024, commercial real estate lease renewals in prime urban centers often saw rental rate increases of 5-10% year-over-year, reflecting this robust demand and the landlord's advantageous position.
- Strategic Location Value: Airport gates and downtown storefronts are critical for customer access and brand visibility in mobility services.
- High Demand & Limited Supply: Prime locations are scarce, driving up competition and lessor leverage.
- Capital Investment by Lessors: Landlords often invest heavily in infrastructure, which they recoup through lease terms.
- Long-Term Lease Commitments: Mobility firms are locked into leases, reducing their flexibility to switch locations easily.
Insurance and Financing Companies
Financial institutions, such as banks offering loans or leasing companies providing vehicle acquisition arrangements, hold significant bargaining power. In 2024, rising interest rates globally could directly increase Enterprise Mobility's financing costs, impacting profitability. Similarly, insurance companies dictate premiums for fleet coverage, a substantial operational expense.
- Financing Costs: Interest rates on loans and leases directly affect the cost of acquiring and maintaining a fleet.
- Insurance Premiums: The cost of comprehensive insurance coverage for a large vehicle fleet is a major expense.
- Leasing Terms: Favorable or unfavorable leasing agreements can significantly influence operational flexibility and capital outlay.
- Availability of Capital: The willingness and ability of financial institutions to provide capital impact growth and investment capacity.
Suppliers in the enterprise mobility sector, particularly automotive manufacturers and technology providers, exert considerable bargaining power due to high switching costs and the critical nature of their products. This leverage is amplified by factors like supply chain constraints and the specialized, integrated nature of fleet management software.
| Supplier Type | Source of Bargaining Power | 2024 Impact/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturers | Capital investment, diverse fleet needs, supply chain issues | Shortages of components like semiconductors led to extended lead times and price increases for vehicles. |
| Technology & Software Providers | Unique, integrated systems, high switching costs | Investment in AI-driven analytics and predictive maintenance gave providers of these features stronger negotiating positions. |
| Fuel & Maintenance Providers | Limited service options, specialized skills, commodity pricing | Average car repair costs rose approx. 5%, and fuel prices remained a significant operational expense. |
| Real Estate Lessors (Prime Locations) | Strategic necessity, high demand/limited supply, long-term commitments | Rental rate increases of 5-10% in prime urban centers reflected robust demand. |
| Financial Institutions | Financing costs, insurance premiums, leasing terms | Rising interest rates globally increased financing costs for fleet acquisition. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers the competitive forces shaping the Enterprise Mobility landscape, including buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and industry rivalry, to inform strategic decision-making.
Instantly identify and neutralize competitive threats and opportunities within your enterprise mobility strategy, simplifying complex market dynamics for focused action.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual renters, particularly those traveling for leisure, exhibit significant price sensitivity. The proliferation of online travel agencies and comparison websites, such as Kayak and Expedia, allows these customers to effortlessly compare rates across various providers, including Enterprise, Hertz, and Avis. This ease of comparison empowers them to seek out the lowest prices, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
The ability for individual customers to easily switch between rental car companies, or even opt for alternative transportation like ride-sharing services, further intensifies price competition. In 2023, for instance, the average daily rental car rate in the US hovered around $50, a figure that fluctuates significantly based on demand and location, making price a critical decision factor for many consumers.
Large corporate clients, especially those needing extensive fleet management, wield significant bargaining power. Their substantial order volumes allow them to negotiate favorable pricing and specialized service packages. For instance, a major logistics company might secure a 15% discount on fleet management software subscriptions due to its commitment to managing thousands of vehicles.
These clients leverage their long-term contracts and considerable annual spending to demand customized terms and dedicated support. This can translate into tailored reporting features, priority maintenance scheduling, or even custom software integrations, all of which increase the value proposition for the client and the cost of service for the provider.
In 2024, the trend of consolidation among large enterprises means fewer, but larger, clients are seeking fleet management solutions. This increased client concentration amplifies their ability to dictate terms, potentially squeezing margins for fleet management providers who rely on these anchor customers.
Insurance companies referring customers for replacement vehicles after accidents wield significant bargaining power. Their ability to direct a substantial volume of business to specific rental car companies, often through established partnerships and negotiated rates, grants them considerable leverage. This power can influence pricing structures and service expectations, as rental providers vie for these referral streams.
In 2024, major insurance providers continued to leverage their scale. For instance, a significant portion of rental car revenue in the US is directly tied to insurance claims, with some estimates suggesting this channel accounts for over 50% of rental days. This dependency empowers insurers to negotiate favorable terms, impacting the profitability and operational strategies of rental companies.
Diverse Service Offerings for Customers
Enterprise mobility providers are increasingly offering a diverse range of services, from car sharing and truck rentals to comprehensive fleet management solutions. This integrated approach directly counters the bargaining power of customers. By providing a one-stop shop for various mobility needs, companies reduce the incentive for customers to seek out and consolidate services from multiple, smaller providers. For instance, a business needing both short-term vehicle rentals and long-term fleet maintenance can find a single enterprise mobility partner that handles both, simplifying operations and potentially offering volume discounts.
The breadth of services available within a single enterprise mobility ecosystem significantly diminishes a customer's ability to negotiate better terms by playing providers against each other. When a customer can satisfy a wide array of mobility requirements with one company, the perceived switching cost for any individual service increases. This consolidation of needs into a single relationship strengthens the enterprise mobility provider's position. In 2024, the global enterprise mobility market was valued at over $100 billion, with companies actively seeking to expand their service portfolios to capture a larger share of customer spending.
- Integrated Solutions: Offering car sharing, truck rental, and fleet management under one roof limits customer options to switch providers for individual services.
- One-Stop Shop Appeal: Customers looking for convenience and streamlined operations are less likely to fragment their mobility needs across multiple vendors.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: The convenience and efficiency gained from bundled services can outweigh minor price differences, lessening customer leverage.
- Market Growth: The enterprise mobility sector's expansion in 2024 indicates a strong demand for comprehensive service packages.
Customer Loyalty Programs and Brand Recognition
Established loyalty programs and strong brand recognition across Enterprise Rent-A-Car, National, and Alamo significantly curb customer bargaining power. These programs, like Enterprise Plus and Emerald Club, encourage repeat business by offering accumulated benefits such as faster rentals and point accrual. For instance, in 2023, Enterprise Holdings reported over 20 million members in its loyalty programs, a testament to their effectiveness in fostering customer stickiness and reducing price sensitivity.
While price is always a consideration for renters, the perceived value through convenience, reliability, and the tangible benefits of loyalty programs make customers less inclined to switch to competitors. This is particularly true for business travelers who prioritize seamless transactions and rewards. The investment in brand building and customer retention creates a barrier to entry for new players and solidifies the existing customer base, thereby diminishing individual customer leverage.
- Loyalty Program Membership: Over 20 million members across Enterprise, National, and Alamo loyalty programs as of 2023.
- Brand Trust: High brand recognition leads to increased customer confidence and reduced price comparison behavior.
- Convenience Factor: Integrated booking and pick-up processes for loyalty members streamline the rental experience.
- Switching Costs: Customers are hesitant to abandon accumulated rewards and benefits, increasing the cost of switching.
The bargaining power of customers in the enterprise mobility sector is significantly influenced by the availability of information and the ease of switching. With numerous online platforms comparing rates, individual renters can readily identify the most competitive prices. This transparency, coupled with the accessibility of alternative transportation like ride-sharing, empowers consumers and intensifies competition among mobility providers.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Enterprise Mobility Providers |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Leisure Travelers | Price sensitivity, ease of comparison via online travel agencies (OTAs) | Increased price pressure, need for competitive pricing strategies |
| Large Corporate Clients | High volume, long-term contracts, demand for customized services | Ability to negotiate significant discounts and tailored service packages |
| Insurance Companies | Referral volume, established partnerships, negotiated rates | Influence over pricing and service expectations for replacement rentals |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the industry. You're looking at the actual document you'll receive, providing in-depth insights into buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry. Once purchased, you'll gain instant access to this professionally crafted analysis, ready for immediate use in your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The car rental sector is characterized by a high degree of competitive rivalry, largely due to the significant presence of major global players such as Hertz and Avis Budget Group. These established companies vie intensely for market share across all major geographic regions, making the landscape highly competitive.
Competition manifests across several key areas, including aggressive pricing strategies, the development of robust loyalty programs to retain customers, and ensuring consistent fleet availability. Furthermore, enhancing the digital customer experience, from booking to vehicle return, has become a critical battleground for these industry giants.
For instance, in 2024, Hertz reported revenues of $5.9 billion, while Avis Budget Group announced revenues of $12.2 billion. This financial scale underscores their capacity to invest heavily in marketing, technology, and fleet upgrades, further intensifying the pressure on smaller or regional competitors to keep pace.
Competitive rivalry in the enterprise mobility sector intensifies due to substantial overlap in both geographic operating areas and customer segments. This includes airport, local, and corporate rental markets, meaning major players frequently find themselves vying for the same business.
Companies like Enterprise Rent-A-Car, Hertz, and Avis Budget Group often concentrate their efforts on prime locations and lucrative customer demographics. For instance, in 2023, the global car rental market was valued at approximately $100 billion, with significant portions of that revenue derived from these overlapping segments, underscoring the fierce competition for every available rental opportunity.
The enterprise mobility sector is no stranger to intense price wars and frequent promotional blitzes. Companies often engage in aggressive price cuts, especially during periods of high demand like holiday seasons or when the economy shows signs of slowing, all in an effort to capture or hold onto market share.
This continuous downward pressure on pricing directly impacts profitability across the board. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated that average smartphone prices saw a slight dip in certain markets due to heavy discounting by major manufacturers.
These promotional activities, while potentially boosting short-term sales volumes, can significantly erode profit margins for all participants in the long run. It creates a cycle where companies feel compelled to match or exceed competitor offers, making it difficult to maintain healthy earnings.
Differentiation through Technology and Service
Competitive rivalry in enterprise mobility is intense, with companies constantly seeking to stand out. They achieve this through cutting-edge technology like sophisticated mobile applications for booking and management, along with seamless pick-up and drop-off experiences. The integration of connected car features also plays a significant role in differentiating offerings, enhancing convenience and data insights for users.
Superior customer service is another critical battleground, as providers aim to build loyalty through responsive support and personalized experiences. The capacity to innovate quickly and deliver a consistently smoother, more user-friendly journey is paramount. For instance, in 2024, many fleet management solutions saw a surge in adoption of AI-driven predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by an average of 15% for businesses that implemented them.
- Technological Differentiation: Mobile apps, seamless logistics, and connected car features are key.
- Service Excellence: Superior customer support builds loyalty and trust.
- Innovation as a Driver: Companies that innovate faster gain a competitive edge.
- Market Trends: AI in fleet management is reducing operational disruptions.
Diversification into New Mobility Services
Competitive rivalry in the enterprise mobility sector is increasingly defined by diversification into new services, moving beyond traditional car rentals. Companies are actively investing in areas such as car-sharing platforms, flexible subscription models, and specialized fleet management for the burgeoning autonomous vehicle market. This strategic shift intensifies competition as established players and new entrants vie for dominance in these evolving mobility ecosystems. For instance, in 2024, major rental companies have been announcing significant partnerships and acquisitions aimed at bolstering their capabilities in these new service areas, signaling a clear trend towards broader mobility solutions.
The expansion into these new mobility services is a direct response to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements, forcing companies to innovate or risk obsolescence. By offering integrated solutions that encompass ride-sharing, long-term rentals, and even mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms, businesses aim to capture a larger share of the customer journey. This diversification not only creates new revenue streams but also strengthens customer loyalty by providing a more comprehensive and convenient mobility experience. The market is witnessing substantial capital allocation towards research and development in these segments, with projections indicating substantial growth in the subscription and car-sharing markets in the coming years.
- Diversification into car-sharing and subscription models intensifies rivalry.
- Investment in autonomous vehicle fleet management is a key competitive battleground.
- Companies aim to future-proof their business by capturing new revenue streams in emerging mobility services.
- Strategic partnerships and acquisitions are common tactics to gain an edge in these new markets.
Competitive rivalry in enterprise mobility is fierce, driven by major players like Hertz and Avis Budget Group, who aggressively compete on price, loyalty programs, and digital experience. Their substantial revenues, such as Avis Budget Group's $12.2 billion in 2024, allow for significant investments in technology and fleet, pressuring smaller rivals.
This rivalry extends to overlapping customer segments and geographic areas, forcing companies to differentiate through technology, superior customer service, and rapid innovation. For instance, the adoption of AI in fleet management in 2024 reduced downtime by an average of 15% for businesses using it.
The sector is also seeing intensified competition through diversification into car-sharing, subscription models, and autonomous vehicle fleet management, with companies forming strategic partnerships to gain ground in these evolving markets.
| Company | 2024 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Competitive Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Hertz | $5.9 billion | Technology, Fleet Availability, Customer Experience |
| Avis Budget Group | $12.2 billion | Pricing, Loyalty Programs, Digital Integration |
| Enterprise Rent-A-Car | (Not publicly disclosed for 2024 segment) | Customer Service, Diversification, Geographic Reach |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The growing accessibility and efficiency of public transportation systems, such as buses, trains, and subways, present a substantial threat of substitution for car rental services, particularly in urban environments. These networks are becoming increasingly integrated and reliable, offering a viable alternative for many journeys.
For shorter to medium distances, public transit often proves to be a more economical and environmentally conscious choice. Travelers, both for leisure and business, are increasingly opting for these options, especially when navigating congested city centers where parking and traffic can be significant deterrents to private vehicle use.
In 2024, many major metropolitan areas saw continued investment and expansion in their public transit infrastructure. For instance, cities like London and Tokyo already boast extensive and highly utilized public transport networks, making car rental a less attractive proposition for many residents and visitors within those areas.
Ride-sharing services such as Uber and Lyft represent a significant threat of substitutes for traditional car rental companies, especially for short-term urban travel and airport transfers. Their core appeal lies in unparalleled convenience, offering on-demand service that eliminates the burdens of parking and vehicle upkeep for the user. In 2024, Uber reported over 1.8 billion trips globally, demonstrating the immense scale and user preference for this convenient mobility solution.
Personal vehicle ownership remains a significant substitute for car rentals, especially outside of major urban centers. In 2024, the U.S. continued to see high rates of car ownership, with over 280 million registered vehicles. This widespread availability means many individuals opt for their own cars for daily commutes and local errands, viewing rentals as an unnecessary expense for routine travel.
The preference for personal vehicles stems from convenience and a sense of ownership. For most people, their car is readily accessible, familiar, and already paid for, making it the default choice over the process of renting. This reduces the need for rentals for anything other than specialized circumstances, such as extended vacations or when their primary vehicle is in the shop.
Car-Sharing and Subscription Models
Car-sharing services like Zipcar and peer-to-peer platforms such as Turo present a significant threat by offering convenient, on-demand access to vehicles. These alternatives cater to individuals who require transportation occasionally, directly challenging the traditional rental market. For instance, in 2024, the global car-sharing market was valued at over $10 billion, demonstrating its growing appeal.
Emerging car subscription models further amplify this threat. These services provide users with flexibility, allowing them to switch vehicles or adjust terms more readily than traditional ownership or leasing. This flexibility appeals to a broad consumer base, including younger demographics and those prioritizing adaptability over long-term commitment. Many subscription services saw substantial growth in 2024, with some reporting user base expansions exceeding 30% year-over-year.
- Car-Sharing Growth: The global car-sharing market surpassed $10 billion in 2024, indicating strong consumer adoption.
- Subscription Model Appeal: Car subscription services offer flexible terms and vehicle access, attracting users seeking alternatives to ownership.
- Competitive Pressure: These models directly compete with traditional car rentals, particularly for users needing occasional transportation.
- Peer-to-Peer Rentals: Platforms like Turo allow individuals to rent out their own vehicles, expanding the supply of alternative mobility options.
Micromobility Solutions and Active Transport
The proliferation of micromobility, including electric scooters and bikes, alongside a resurgence in walking and cycling, presents a significant threat of substitution for very short-distance travel needs. These alternatives offer a more agile and often cost-effective way to navigate congested urban centers, directly competing with the need for traditional rental vehicles for quick trips. For instance, by mid-2024, many major cities reported significant increases in micromobility usage, with some areas seeing a 20% year-over-year rise in scooter rentals for trips under two miles.
These options can be particularly appealing for travelers seeking to avoid parking challenges and traffic delays inherent in car usage. The convenience of picking up a shared electric scooter or bike for a short journey, often at a lower price point than a car rental, directly erodes the demand for traditional mobility solutions in these specific use cases. The integration of these services into urban transit hubs further enhances their accessibility as viable substitutes.
Consider these factors impacting the threat of substitutes:
- Increased adoption: Many urban areas have seen micromobility services become commonplace, with user numbers growing steadily.
- Cost-effectiveness: For short distances, micromobility is often cheaper than renting a car, especially when factoring in parking.
- Convenience in congestion: Navigating dense city centers can be faster and more pleasant with scooters or bikes than with cars.
- Environmental appeal: Growing environmental consciousness also drives preference for these greener transportation alternatives.
Public transportation systems continue to be a strong substitute, especially in urban areas where integrated networks make them efficient and cost-effective for many journeys. Ride-sharing services offer unparalleled convenience for short trips and airport transfers, with Uber facilitating over 1.8 billion global trips in 2024. Personal vehicle ownership, with over 280 million registered vehicles in the U.S. in 2024, remains a primary alternative due to inherent convenience and familiarity.
Car-sharing and subscription models provide flexible, on-demand access, with the car-sharing market valued at over $10 billion in 2024. Micromobility options like electric scooters and bikes are increasingly viable for very short distances, with some cities seeing a 20% year-over-year rise in their usage by mid-2024.
| Substitute Option | Key Appeal | 2024 Relevance/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Cost-effectiveness, Convenience in Urban Centers | Extensive networks in cities like London and Tokyo reduce car rental need. |
| Ride-Sharing (e.g., Uber) | On-demand Service, Convenience | Over 1.8 billion global trips facilitated by Uber. |
| Personal Vehicle Ownership | Familiarity, Accessibility | Over 280 million registered vehicles in the U.S. |
| Car-Sharing (e.g., Zipcar) | Occasional Access, Flexibility | Global market valued over $10 billion. |
| Micromobility (Scooters/Bikes) | Agility, Cost for Short Distances | Some cities saw a 20% year-over-year rise in usage for trips under 2 miles. |
Entrants Threaten
The significant capital outlay needed to build and maintain a comprehensive vehicle fleet presents a formidable barrier for potential new entrants in the enterprise mobility sector. Acquiring a diverse range of vehicles, from sedans to specialized commercial vans, requires millions in upfront investment. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of a new commercial van can range from $35,000 to $60,000, and a fleet of hundreds or thousands quickly escalates this figure.
This substantial initial investment, coupled with the continuous expenses associated with depreciation, insurance, and regular maintenance, makes it incredibly difficult for startups to achieve economies of scale and compete effectively against established companies like Enterprise Mobility, which benefit from existing infrastructure and purchasing power.
Enterprise Mobility benefits significantly from decades of established brand recognition and deep-seated customer trust across its prominent brands, including Enterprise, National, and Alamo. This extensive brand equity acts as a substantial barrier, making it incredibly challenging for new entrants to gain a foothold.
Newcomers must overcome the uphill battle of building comparable brand recognition and fostering customer loyalty, a process that typically requires significant time and investment. Achieving a reputation for reliability and consistent service quality, which Enterprise Mobility has cultivated over many years, is a critical differentiator that new entrants struggle to replicate quickly.
For instance, Enterprise's consistent investment in marketing and customer service has cemented its position. In 2024, Enterprise Holdings reported revenues of over $30 billion, underscoring the financial strength derived from its established market presence and brand loyalty, a benchmark that aspiring competitors must aim to surpass.
The sheer complexity of operating a global transportation network presents a formidable barrier for new entrants. Enterprise Mobility manages a vast infrastructure, encompassing thousands of physical locations worldwide, intricate vehicle distribution strategies, and extensive maintenance operations. This includes coordinating a workforce of over 90,000 employees globally, a significant undertaking for any newcomer.
Replicating Enterprise's sophisticated operational systems, honed over decades, would require immense capital and considerable time. The challenge lies not just in having vehicles, but in the seamless integration of fleet management, customer service, and back-office support across a dispersed network. In 2023, Enterprise's fleet size exceeded 2 million vehicles, underscoring the scale of this operational challenge.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Costs
New players entering the enterprise mobility sector face significant regulatory challenges. For instance, in 2024, companies offering ride-sharing or delivery services must comply with evolving data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, which dictate how user information is collected, stored, and utilized. These compliance efforts often necessitate substantial investments in secure infrastructure and legal counsel, acting as a considerable barrier to entry.
The transportation industry, a core component of enterprise mobility, is particularly sensitive to regulations. In 2024, vehicle safety standards, emissions controls, and driver background checks are rigorously enforced across many jurisdictions. For a new entrant, meeting these varied requirements, which can differ drastically from city to city or country to country, translates into significant upfront costs for vehicle modifications, certifications, and ongoing monitoring. For example, the cost of obtaining necessary operating permits and insurance in major metropolitan areas can easily run into tens of thousands of dollars per vehicle.
- Licensing and Permits: Obtaining the necessary operating licenses and permits for fleet operations can involve complex application processes and fees that vary significantly by region.
- Insurance Requirements: Adhering to mandated insurance coverage levels for commercial vehicles and ride-sharing services adds substantial operational expenses.
- Safety Standards: Compliance with evolving vehicle safety regulations and driver training protocols requires ongoing investment in technology and human capital.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Meeting stringent data protection laws for user and operational data necessitates robust cybersecurity measures and legal oversight.
Technological Infrastructure and Data Analytics
The threat of new entrants in enterprise mobility, particularly concerning technological infrastructure and data analytics, is significantly mitigated by the substantial investments already made by established players. These incumbents have poured resources into developing advanced systems for everything from booking and managing fleets to optimizing prices and analyzing customer behavior. For instance, major ride-sharing platforms have built complex algorithms that process millions of data points daily to ensure efficient matching of drivers and riders, dynamic pricing, and predictive maintenance for vehicles.
Building a comparable technological backbone from scratch presents a formidable challenge for newcomers. The sheer scale of data involved, coupled with the expertise required to interpret and act upon it effectively, necessitates considerable capital outlay and specialized talent. In 2024, the average cost for developing and maintaining a robust cloud-based data analytics platform for a large-scale mobility service can easily run into tens of millions of dollars annually, not including the initial development phases.
- High Capital Expenditure: New entrants face immense upfront costs for creating sophisticated reservation systems, real-time fleet management tools, and advanced data analytics capabilities.
- Data Expertise Gap: Established firms possess deep expertise in leveraging vast datasets for strategic advantage, a skill set that is difficult and time-consuming for new companies to replicate.
- Economies of Scale in Data Processing: Larger, existing players benefit from economies of scale in data processing and storage, making their operational costs per data point lower than what a new entrant could achieve initially.
- Network Effects in Data: The more data an established platform collects, the better its algorithms become, creating a virtuous cycle that further strengthens its competitive position and deters new market entrants.
The substantial capital required for fleet acquisition and ongoing operational costs, including depreciation and maintenance, creates a significant barrier. For instance, in 2024, the cost of new commercial vehicles can range from $35,000 to $60,000, making fleet expansion a major financial undertaking for new entrants.
Established brand recognition and customer loyalty, cultivated over decades, present another hurdle. Enterprise Mobility's strong reputation for reliability means newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and service quality to build comparable trust. In 2024, Enterprise Holdings reported revenues exceeding $30 billion, highlighting the financial strength derived from its established market presence.
The intricate global operational infrastructure, including thousands of locations and complex fleet management systems, is difficult and costly for new companies to replicate. Managing a workforce of over 90,000 employees globally, as Enterprise Mobility does, adds to this complexity. By 2023, Enterprise's fleet size surpassed 2 million vehicles, demonstrating the scale of its operations.
Regulatory compliance, covering licensing, insurance, safety standards, and data privacy, imposes significant upfront costs and ongoing expenses. For example, obtaining operating permits and insurance in major cities can cost tens of thousands of dollars per vehicle annually.
| Barrier | Description | Example Data (2024/2023) |
| Capital Investment | High upfront costs for vehicle acquisition and fleet expansion. | New commercial van cost: $35,000 - $60,000 |
| Brand Equity | Established trust and recognition deterring new players. | Enterprise Holdings Revenue: >$30 billion (2024) |
| Operational Complexity | Managing global infrastructure, distribution, and workforce. | Enterprise Fleet Size: >2 million vehicles (2023) |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Costs associated with licenses, insurance, and compliance. | Permit/Insurance Cost: $10,000s per vehicle annually |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and technology trend analyses from reputable consultancies.
