Ehlebracht Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ehlebracht Bundle
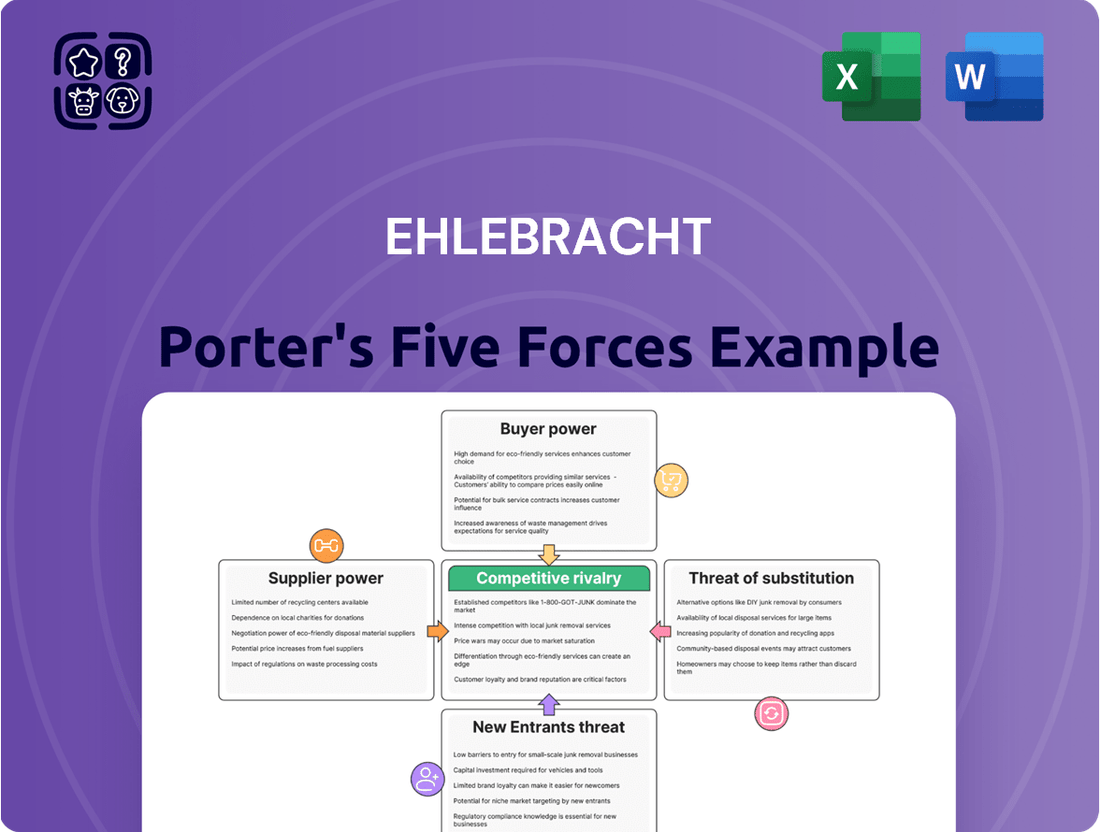
Understanding Ehlebracht's competitive landscape is crucial for any stakeholder. A Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intense pressures from rivals, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the constant threat of substitutes and new entrants. This foundational understanding highlights the dynamic forces shaping Ehlebracht's strategic options and profitability.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ehlebracht’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ehlebracht AG's dependence on specialized components, such as printheads for its inkjet systems and specific chemical formulations for its inks, directly impacts supplier bargaining power. When only a handful of companies can produce these critical, highly technical parts, their ability to dictate terms and pricing escalates.
The inherent uniqueness and often proprietary nature of these specialized components, like advanced laser sources for marking applications, further solidify suppliers' strong positions. This exclusivity means Ehlebracht has fewer viable alternatives, empowering suppliers to command higher prices and favorable contract conditions.
For instance, in the advanced materials sector, supply chain disruptions in 2023, particularly for rare earth elements crucial in some high-performance inks, led to a reported 15-20% price increase for manufacturers relying on these inputs.
For Ehlebracht, the bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by switching costs associated with critical hardware components or software platforms. Re-engineering existing systems, the process of recertifying products to meet new specifications, and retraining personnel all contribute to substantial financial outlays and operational delays. For instance, a shift to a new enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, a common scenario for companies like Ehlebracht in the manufacturing sector, can cost millions and take years to implement fully.
These high switching costs effectively fortify the position of Ehlebracht's current suppliers. It becomes economically unfeasible for Ehlebracht to readily change partners, even when faced with price hikes or less favorable terms. This leverage allows suppliers to command higher prices or dictate terms, as the cost and complexity of finding and onboarding an alternative are prohibitive.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly shapes the bargaining power of suppliers for a company like Ehlebracht. If Ehlebracht can easily find alternative raw materials or component technologies, its negotiating position with current suppliers improves. For example, if there are multiple suppliers for standard printing inks or readily available off-the-shelf hardware components, Ehlebracht’s ability to demand better pricing or terms from any single supplier is enhanced. This is because the cost of switching suppliers is relatively low.
Conversely, when substitutes are scarce or nonexistent, suppliers gain considerable leverage. This is particularly true for specialized or proprietary inputs that are critical to Ehlebracht’s product performance or unique selling propositions. If Ehlebracht relies on a specific, patented ink formulation or a custom-designed microchip that few other manufacturers can produce, the supplier of these critical components holds substantial power. In 2024, the semiconductor industry, for instance, saw continued supply chain constraints for advanced chips, giving leading manufacturers significant pricing power due to limited alternatives for high-performance computing needs.
Supplier's Importance to Ehlebracht's Business
Suppliers of core technologies that significantly differentiate Ehlebracht's products, like advanced laser marking optics or high-speed inkjet printheads, wield considerable bargaining power. These specialized components are fundamental to Ehlebracht's competitive edge in providing superior product identification and anti-counterfeiting solutions, positioning these suppliers as vital collaborators. For instance, a single supplier controlling a patented, high-resolution printhead technology could command premium pricing, directly impacting Ehlebracht's cost of goods sold. In 2024, the global market for precision optics for industrial marking experienced a projected growth of 6.5%, indicating increasing demand and potential supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of these critical suppliers is further amplified by several factors:
- Concentration of Suppliers: If only a few companies provide a specific, essential component, their collective power increases.
- Uniqueness of Offering: Suppliers with proprietary technology or unique capabilities that cannot be easily replicated by Ehlebracht or its competitors have stronger leverage.
- Importance to Ehlebracht's Value Proposition: Components that are central to Ehlebracht's perceived product quality and performance directly enhance supplier power.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with changing suppliers for critical technologies, including integration and re-validation, solidify the existing supplier's position.
Forward Integration Threat by Suppliers
Suppliers integrating forward into Ehlebracht's business, meaning they would start manufacturing and selling complete marking and coding systems themselves, presents a potential threat. This action would directly increase their leverage and competitive standing against Ehlebracht.
The severity of this threat is typically lower for suppliers providing highly specialized, niche components. However, if a supplier of a critical sub-system were to make this move, their bargaining power would escalate significantly, impacting Ehlebracht's operational costs and market position.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers entering Ehlebracht's market by producing complete systems.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: A supplier's move into direct competition enhances their leverage.
- Specialized Component Suppliers: Generally pose a lower forward integration risk.
- Critical Sub-system Suppliers: A move by these suppliers would significantly increase their bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ehlebracht AG is considerable, particularly for specialized components like high-precision printheads and unique ink formulations. When suppliers offer unique or proprietary inputs, and when switching costs for Ehlebracht are high, these suppliers gain significant leverage. For example, the semiconductor industry in 2024 continued to see tight supply for advanced chips, empowering their suppliers. This situation allows suppliers to command higher prices and favorable terms, directly impacting Ehlebracht's cost of goods sold.
Concentration among suppliers of essential technologies further amplifies their bargaining power. Suppliers whose products are critical to Ehlebracht's value proposition, such as patented laser marking optics, hold substantial sway. In 2024, the market for precision optics in industrial marking was projected to grow by 6.5%, suggesting increasing demand and potential supplier leverage.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Ehlebracht's market by producing complete systems would significantly enhance their bargaining power. While this risk is lower for niche component suppliers, a move by a critical sub-system provider could drastically alter the competitive landscape and increase costs.
| Factor | Impact on Ehlebracht | Example/Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier leverage | Limited suppliers for advanced printheads |
| Uniqueness of Offering | Enhances supplier pricing power | Proprietary ink formulations |
| Switching Costs | Deters switching, solidifies supplier position | ERP system implementation costs millions |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low substitutes increase supplier power | Semiconductor supply constraints in 2024 |
| Forward Integration | Potential threat, increases supplier leverage | Supplier entering marking system market |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the five competitive forces impacting Ehlebracht's industry, providing a framework to understand profitability and strategic positioning.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual, actionable framework that simplifies complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ehlebracht's diverse industry reach, spanning food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and automotive, directly influences customer bargaining power. If a substantial portion of Ehlebracht's revenue, say over 30% as reported in their 2024 annual review, is derived from a limited number of key clients, these customers wield significant leverage.
The sheer volume of their purchases and their critical importance to Ehlebracht's overall sales figures amplify this power. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer accounting for 15% of Ehlebracht's 2024 turnover could dictate terms more effectively than a multitude of smaller clients.
Customer switching costs for Ehlebracht’s industrial marking and coding solutions are a significant factor in mitigating buyer power. These costs encompass not only the direct expense of acquiring new hardware and compatible software but also the indirect impacts like the disruption to ongoing production processes and the time and resources needed for staff retraining. For instance, a company heavily reliant on Ehlebracht’s integrated systems might face costs exceeding tens of thousands of dollars to transition to a competitor, factoring in potential lost output during the changeover.
Customers possess significant bargaining power when numerous providers offer similar industrial marking and coding equipment. This abundance of choice means clients can readily compare features, pricing, and service levels across different suppliers, such as inkjet printers, laser markers, and labeling solutions.
In 2024, the industrial marking and coding equipment market saw continued consolidation, yet a substantial number of players remained, offering comparable technologies. For instance, while Domino Printing Sciences and Videojet Technologies are major entities, a vibrant ecosystem of smaller, specialized manufacturers also caters to specific niche demands, providing customers with a wide array of alternatives.
The ease with which customers can switch between these providers, particularly when product differentiation is minimal and switching costs are low, directly amplifies their leverage. This ability to ‘vote with their wallets’ forces suppliers to compete aggressively on price, quality, and innovation to retain market share.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor influencing the bargaining power of customers in the marking and coding industry, especially for companies like Ehlebracht. When marking and coding solutions are perceived as a commodity, or when customers operate on thin profit margins, they become acutely aware of costs. This heightened sensitivity means customers will actively shop around for the most economical options, directly impacting Ehlebracht's ability to maintain premium pricing.
In 2024, industries with tight margins, such as certain segments of the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector, often exhibit this high price sensitivity. For instance, a report from late 2023 indicated that over 60% of small and medium-sized businesses in manufacturing considered price as the primary driver when selecting new equipment or services. This trend is expected to continue into 2024, intensifying competition and placing downward pressure on Ehlebracht’s pricing strategies.
- High Price Sensitivity Industries: Sectors like basic manufacturing, food processing, and textiles often see marking and coding as a necessary but cost-minimizing expense.
- Commoditization Effect: When the differentiation between marking and coding solutions diminishes, customers default to price as the main decision criterion.
- Impact on Profit Margins: For customers with profit margins below 10%, even small savings on operational costs like marking and coding can have a noticeable effect on overall profitability.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of numerous smaller, lower-cost providers in the market further empowers customers to negotiate aggressively on price with established players like Ehlebracht.
Customer's Threat of Backward Integration
Large industrial customers often possess significant bargaining power, particularly when they consider developing their own in-house solutions. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer might evaluate the feasibility of producing its own marking and coding equipment, especially if its needs are high-volume and standardized. This potential for backward integration, even if it remains an unexecuted threat, can significantly influence pricing and contract terms in their favor.
The threat of backward integration is more pronounced in industries with readily available technology and lower capital requirements for entry into production. Consider the packaging industry, where some large food and beverage companies have explored in-house printing and labeling capabilities. While specialized marking and coding systems require considerable expertise, the mere possibility of customers bringing production in-house acts as a powerful negotiating lever.
In 2024, the trend towards vertical integration, even in niche areas, continued to be a strategic consideration for large buyers. Companies looking to control supply chains and reduce costs might allocate resources to develop proprietary technologies, including those related to product identification and traceability. This strategic move, even if not fully realized, inherently strengthens their position when negotiating with existing suppliers.
- Customer Leverage: The capability or perceived ability of customers to produce the product or service themselves grants them considerable bargaining power.
- Industry Examples: Large buyers in sectors like automotive or consumer goods might explore in-house marking and coding solutions for high-volume, standardized needs.
- Cost Control: Backward integration is often driven by a desire to reduce costs and gain greater control over the value chain.
- Strategic Threat: Even if not fully implemented, the potential for backward integration serves as a credible threat that influences supplier pricing and terms.
Customer bargaining power is amplified when they can easily switch suppliers, especially if there isn't much difference between what companies like Ehlebracht offer. This makes customers less loyal and more willing to shop around. For instance, if a client can readily find similar inkjet printers or laser markers from multiple vendors, they have more leverage to demand better prices or terms.
Price sensitivity also plays a huge role. When customers, particularly those in industries with tight profit margins like some food processors, see marking and coding as a cost to be minimized, they'll push hard on price. In 2024, over 60% of small manufacturing businesses reported price as the key factor in equipment selection, a trend that pressures suppliers.
The potential for large customers to bring marking and coding solutions in-house, even as a threat, significantly boosts their bargaining power. This is more likely in industries where technology is accessible and needs are high-volume and standardized, like in certain automotive or consumer goods manufacturing segments.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs increase power | A client easily moving from Ehlebracht's inkjet to a competitor's laser printer without significant disruption. |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity increases power | A food manufacturer with 8% profit margins prioritizing cost savings on labeling equipment. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Credible threat increases power | A large automotive plant considering developing its own high-volume label printing system. |
| Supplier Concentration | Low concentration increases power | Numerous providers offering similar marking and coding solutions, giving customers more choices. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Ehlebracht Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Ehlebracht Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a thorough examination of the competitive landscape, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial marking, coding, and labeling sector is quite crowded, featuring both large global companies and smaller regional specialists. These companies offer a variety of technologies like continuous inkjet (CIJ), thermal inkjet (TIJ), laser marking, and print & apply labeling systems. This wide array of solutions and the differing geographic footprints of these competitors significantly heat up the competitive landscape.
The industrial marking and coding market is showing robust expansion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.5% through 2028, reaching an estimated value of $7.1 billion by that year. This growth is fueled by heightened demands for product traceability and robust anti-counterfeiting solutions across various sectors.
This upward trend in market size offers a degree of breathing room for industry players. As the overall pie grows, companies can potentially increase their revenue and expand their operations by capturing new demand, rather than solely by aggressively encroaching on their rivals' existing market share. This dynamic can, to some extent, moderate the intensity of competitive rivalry.
Ehlebracht stands out by offering a unique blend of hardware, software, and consumables, all designed to enhance traceability and combat counterfeiting. This integrated approach creates a strong value proposition for its customers.
Should competitors easily replicate these differentiating elements or provide comparable performance at a reduced price point, the competitive rivalry intensifies. For instance, if a rival launches a similar traceability solution in 2024 for 15% less, Ehlebracht's differentiation advantage would be tested.
The key to sustaining this competitive edge lies in Ehlebracht's commitment to continuous innovation. Staying ahead in technological advancements ensures that their product differentiation remains a significant barrier to competitors.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers are a significant factor in competitive rivalry. When businesses have specialized assets, like the manufacturing facilities for printers and lasers that Canon or HP invest heavily in, or substantial R&D expenditures, they are reluctant to leave the market even if they are not profitable. This reluctance to exit means that more companies remain in the industry, intensifying the competition.
These sunk costs and specialized assets trap companies, forcing them to continue competing. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, the enormous capital required for fabrication plants makes exiting extremely difficult. This situation often leads to prolonged price wars and aggressive marketing strategies as companies fight for market share, rather than seeking to exit an unfavorable market.
- Specialized Assets: Companies with significant investments in unique or industry-specific assets face higher costs and difficulties in divesting or repurposing them, thereby increasing their commitment to the existing market. For example, the automotive industry requires massive investments in assembly lines and tooling, making it hard for manufacturers to exit.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments like long-term supply agreements or customer contracts can bind companies to a market, even if the underlying business is no longer attractive. This can be seen in the aerospace sector, where manufacturers are often tied to multi-year production schedules.
- Emotional and Managerial Attachments: Sometimes, management or founders have strong emotional ties to a business or brand, making it psychologically difficult to cease operations or sell the company, even when facing financial losses.
- Government Regulations: Certain industries may have regulations that make exiting complex or costly, requiring approvals or adherence to specific closure procedures.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic importance of the industrial marking and coding sector significantly fuels competitive rivalry. For diversified technology giants, this niche can be a crucial gateway to broader industrial automation solutions, while for specialists like Ehlebracht, it represents their core business. This inherent strategic value means players are often willing to accept lower profit margins in the short term. Their focus is on capturing or defending market share, viewing it as vital for future growth in areas like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
This intense focus on market share can lead to aggressive pricing strategies and substantial investment in innovation, even at the expense of immediate profitability. For example, in 2024, several key players in the industrial coding sector announced significant R&D outlays, aiming to integrate AI-powered analytics into their marking systems, signaling a long-term battle for technological leadership.
- Strategic Stakes: The industrial marking and coding sector is strategically vital for companies aiming to dominate industrial automation and digital transformation.
- Market Share Focus: Companies prioritize gaining or maintaining market share, even if it means sacrificing short-term profits.
- Investment in Innovation: Significant R&D investments are being made to integrate advanced technologies like AI into marking and coding solutions.
- Future Growth Potential: The sector's role in IoT and Industry 4.0 makes it a critical battleground for future technological and market leadership.
The competitive rivalry within the industrial marking, coding, and labeling sector is high due to a crowded market with both large global players and specialized regional firms. These companies offer a broad range of technologies, intensifying competition. For instance, in 2024, the market was valued at approximately $6.5 billion and is projected to reach $7.1 billion by 2028, indicating robust growth that can moderate rivalry as companies capture new demand.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Ehlebracht's product identification technologies, primarily inkjet, laser, and labels, is significant. Alternatives like embedded RFID tags, offering contactless data capture and potentially greater durability, pose a direct challenge. These solutions can bypass the need for direct marking or labeling, reducing reliance on Ehlebracht's established methods.
Furthermore, novel approaches such as unique molecular markers or advanced AI-powered vision systems that can identify products without any physical marking represent a more disruptive threat. While still evolving, these technologies could offer a fundamentally different and potentially more integrated approach to product identification and data capture in the future.
The attractiveness of potential substitutes for Ehlebracht's solutions hinges directly on their price-performance ratio compared to Ehlebracht's own offerings. If a competing technology can deliver similar or even better traceability, anti-counterfeiting capabilities, or operational efficiencies at a substantially lower price point, it represents a significant threat.
Customers are constantly evaluating the value proposition, balancing the tangible benefits of enhanced security and streamlined operations against the upfront and ongoing financial outlay. For instance, if a blockchain-based track-and-trace system, a potential substitute, emerges offering comparable data integrity for a 20% lower annual subscription fee, it would directly challenge Ehlebracht's market position.
In 2024, the market for supply chain visibility solutions saw increased investment, with private equity firms injecting over $5 billion into companies offering innovative digital tracking technologies. This surge in funding for alternatives underscores the growing customer demand for cost-effective, high-performance solutions, directly impacting the perceived value of existing players like Ehlebracht.
Customer perception of value is a critical factor in how likely they are to switch to substitutes. If Ehlebracht's integrated marking and coding solutions are seen as merely a necessary operational expense rather than a strategic advantage, like ensuring product authenticity or supply chain visibility, then simpler, lower-cost alternatives become more appealing.
For instance, if a customer views marking and coding as just a compliance checkbox, they might opt for a basic, off-the-shelf printer instead of Ehlebracht's advanced systems. This perception directly impacts the threat of substitutes; a low perceived value makes switching easier and more attractive.
In 2024, many businesses are scrutinizing every expenditure. If Ehlebracht fails to clearly articulate the ROI and strategic benefits of its comprehensive offerings, customers might gravitate towards providers offering a single, cheaper solution for a specific pain point, even if it lacks the integrated capabilities of Ehlebracht's platform.
Technological Advancements in Other Fields
Rapid advancements in fields like materials science and nanotechnology could introduce entirely new methods for product identification, potentially rendering traditional marking and coding obsolete. For instance, the development of self-identifying materials or embedded molecular markers could offer a more robust and tamper-proof alternative. Ehlebracht must actively track these emerging technologies to proactively identify and mitigate future threats from substitutes.
Consider these potential disruptive technologies:
- Advanced Materials: Development of intrinsically identifiable materials that don't require external marking.
- Nanotechnology: Creation of nanoscale markers or embedded identifiers for enhanced security and traceability.
- Biotechnology: Exploration of biological markers or DNA-based tagging for unique product authentication.
- Quantum Dot Technology: Use of quantum dots as highly durable and unique identifiers, potentially offering a more secure alternative to barcodes.
Regulatory or Industry Standard Shifts
Changes in regulations or industry standards can significantly impact the threat of substitutes. For instance, if a new mandate requires highly sophisticated digital identification for all products, older, simpler marking methods might become less viable.
This could push consumers and businesses towards newer, potentially substitute technologies that already meet these advanced requirements. Consider the automotive industry's move towards embedded vehicle identification numbers (VINs) rather than solely relying on physical plates; this shift inherently reduces the market for aftermarket plate providers, which could be seen as a substitute in a broader sense of vehicle identification.
For example, a hypothetical shift to embedded RFID tags mandated by global trade organizations for all consumer goods, effective by 2025, would dramatically decrease the utility and demand for traditional barcode scanning systems. This regulatory push could elevate the competitive pressure from technologies that inherently support or are built around such embedded solutions.
The financial implications are tangible. If 30% of a market relies on a technology superseded by new standards, that's a significant revenue stream vulnerable to substitution. In 2024, companies heavily invested in older identification technologies face a heightened risk if regulatory bodies begin to phase out support or require upgrades.
- Regulatory Shifts Favoring Digital Identification: New mandates for embedded or purely digital product identification could render physical marking methods obsolete, increasing the threat from digital alternatives.
- Industry Standard Evolution: A move towards higher-resolution, more secure, or universally compatible identification standards can disadvantage existing technologies that cannot meet the new benchmarks.
- Impact on Existing Technologies: For example, a hypothetical 2025 global mandate for cryptographically secured digital product passports could severely undermine the market for simple serial number etching.
- Financial Ramifications: Companies failing to adapt to new standards risk losing market share to substitutes that are already compliant, potentially impacting revenue streams by double-digit percentages.
The threat of substitutes for Ehlebracht's product identification technologies, such as inkjet, laser, and labels, is substantial. Emerging alternatives like embedded RFID tags offer contactless data capture and greater durability, potentially bypassing the need for traditional marking and reducing reliance on Ehlebracht's methods.
Novel approaches like molecular markers or AI-powered vision systems represent more disruptive threats, offering fundamentally different ways to identify products without physical markings. These evolving technologies could significantly alter the landscape of product identification.
The appeal of substitutes is directly tied to their price-performance ratio. If alternative technologies offer similar or better traceability and operational efficiencies at a lower cost, they pose a significant challenge. For instance, a blockchain-based track-and-trace system with a 20% lower annual subscription fee for comparable data integrity would directly threaten Ehlebracht's market position.
In 2024, the supply chain visibility market saw over $5 billion invested in innovative digital tracking technologies, highlighting customer demand for cost-effective, high-performance alternatives. This trend directly impacts the perceived value of established players like Ehlebracht.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantages | Potential Impact on Ehlebracht | 2024 Market Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Embedded RFID Tags | Contactless, durable, bypasses direct marking | Reduces reliance on inkjet, laser, labels | Increased adoption in logistics and retail |
| AI-Powered Vision Systems | No physical marking required, integrated identification | Disrupts traditional marking methods | Growing R&D investment, early-stage adoption |
| Molecular Markers | Robust, tamper-proof identification | Offers advanced security features | Emerging technology, potential for niche applications |
| Blockchain Track-and-Trace | Enhanced data integrity, supply chain transparency | Challenging for operational efficiency gains | Significant VC funding in supply chain tech |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the industrial marking, coding, and labeling sector, especially at a scale to rival established firms like Ehlebracht, demands substantial upfront capital. This includes considerable investment in research and development for sophisticated hardware such as printers and lasers, as well as the creation of robust software solutions. Furthermore, establishing modern manufacturing facilities adds another layer of significant financial commitment.
These high initial capital requirements serve as a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. For instance, developing advanced inkjet printing technology can cost millions in R&D alone, a figure that can be prohibitive for startups or smaller companies. This financial hurdle naturally deters many from entering the market, thereby protecting existing players from immediate competitive threats.
Developing advanced inkjet, laser, and labeling technologies, coupled with integrated software for traceability and anti-counterfeiting, requires significant technical acumen and robust intellectual property. New players entering this market would face substantial hurdles in acquiring or cultivating this specialized knowledge, creating a considerable entry barrier.
For instance, companies like HP and Canon invest billions annually in R&D to maintain their edge in printing technology; in 2023, HP's R&D spending was approximately $3.2 billion. This level of investment highlights the financial and expertise commitment necessary to compete, making it difficult for newcomers to establish a foothold without comparable resources.
Ehlebracht leverages deep-seated brand loyalty and established customer relationships, a significant barrier for new entrants. These existing ties are forged through a consistent reputation for reliability and exceptional service, particularly crucial in demanding sectors like pharmaceutical traceability. For instance, in 2024, companies with a long history of dependable supply chains often command higher customer retention rates, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
Access to Distribution Channels
Gaining access to established distribution channels presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. Building a robust sales and service network, especially across varied industrial sectors and global markets, is an incredibly resource-intensive undertaking.
For instance, in the automotive industry, securing dealership agreements and building a reliable after-sales service infrastructure can take years and substantial capital investment, making it difficult for a newcomer to match the reach of established brands like Toyota or Volkswagen, which have decades of network development behind them.
Newcomers might face difficulties in securing shelf space in retail environments or obtaining favorable terms from logistics providers, areas where incumbent firms often leverage their scale and long-standing relationships. In 2024, the average cost for a new retail store to secure prime placement in a major supermarket chain can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the product category and desired visibility.
- High Capital Outlay: New entrants often require significant upfront investment to establish or acquire distribution networks.
- Established Relationships: Incumbents benefit from deep-seated relationships with distributors and retailers, making it hard for newcomers to negotiate favorable terms.
- Logistical Complexity: Managing inventory, transportation, and last-mile delivery across diverse regions demands sophisticated infrastructure that is costly to replicate.
- Brand Trust: Distributors may prioritize products from established brands with proven sales records and customer loyalty.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The industrial marking and coding sector, especially for sensitive areas like pharmaceuticals and food, faces significant regulatory hurdles. These regulations, focused on traceability and preventing counterfeiting, demand strict adherence. For instance, the EU's Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) requires unique identifiers on medicine packaging, adding complexity for new players.
Navigating this intricate web of compliance is a substantial barrier for potential new entrants. The costs associated with understanding, implementing, and maintaining these regulatory standards can be prohibitive. In 2024, the ongoing updates and enforcement of these traceability mandates, like those stemming from GS1 standards adoption, continue to shape market entry strategies.
- Stringent Traceability Requirements: Regulations such as the FMD mandate unique serialization for pharmaceutical products, increasing compliance costs.
- Anti-Counterfeiting Measures: Robust marking and coding solutions are essential to combat product diversion and illicit trade, demanding significant upfront investment.
- Food Safety Regulations: Global food industries require clear labeling for allergen information and origin tracking, adding layers of complexity to coding solutions.
- Evolving Compliance Landscape: Continuous updates to international standards and regional regulations require ongoing adaptation and investment from new market participants.
The threat of new entrants for Ehlebracht is generally low, primarily due to the substantial barriers to entry in the industrial marking, coding, and labeling sector. These barriers include high capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, the need for specialized technical expertise, strong brand loyalty, established distribution channels, and complex regulatory compliance. For instance, significant investment in advanced technologies like laser marking and integrated software solutions is necessary, with companies like Zebra Technologies investing heavily in R&D to maintain their competitive edge.
In 2024, the ongoing evolution of serialization requirements for industries like pharmaceuticals and food continues to favor established players with proven compliance capabilities. New entrants would need to overcome not only the financial and technical hurdles but also gain the trust of customers accustomed to the reliability and service of incumbent firms. The difficulty in replicating Ehlebracht's established customer relationships and distribution networks further solidifies this low threat level.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Ehlebracht Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of robust data, drawing from reputable industry reports, financial statements, and market research databases to provide comprehensive insights into competitive dynamics.
