D-Link Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
D-Link Bundle
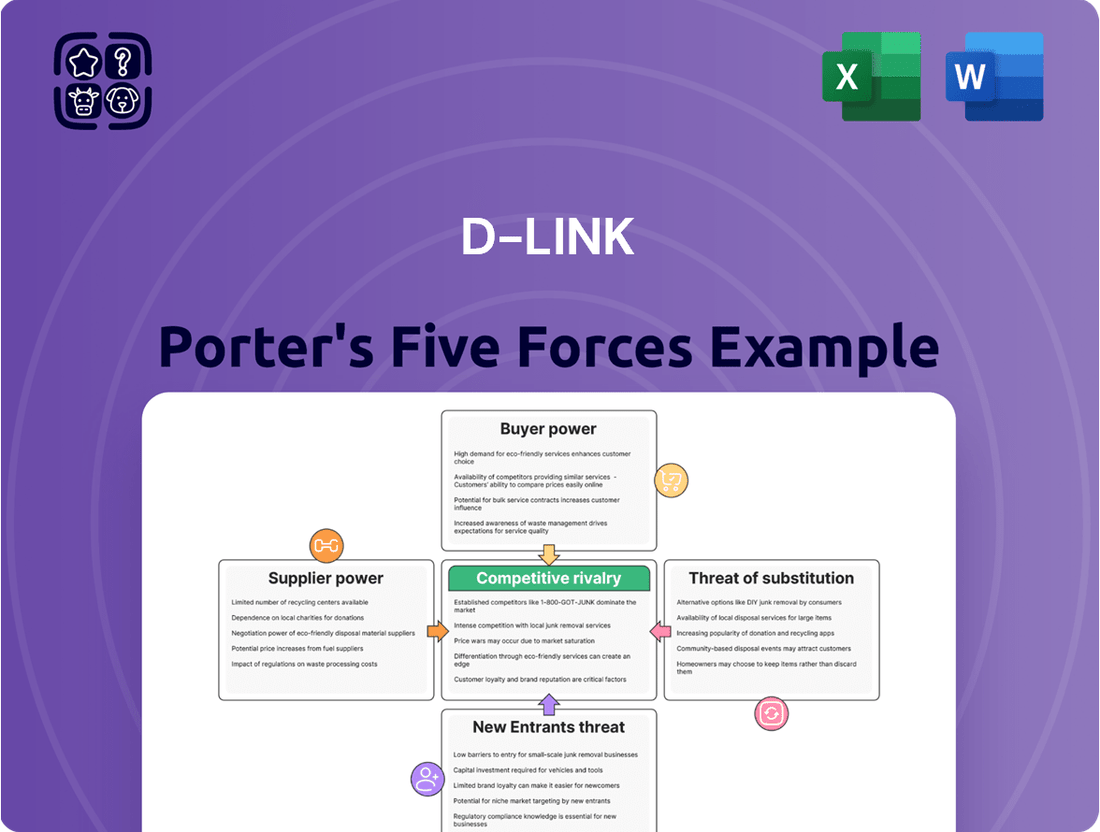
D-Link operates in a competitive landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the threat of new entrants, and the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the networking industry.
The complete Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into each of these factors, providing a comprehensive view of D-Link's strategic position and potential vulnerabilities. Unlock actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
D-Link's dependency on a concentrated group of component manufacturers for essential parts like integrated circuits and chipsets for advanced wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi 7, significantly influences its bargaining power. When these suppliers possess proprietary technology or face production constraints, they gain leverage to set prices and terms, directly affecting D-Link's manufacturing expenses and its capacity for product development.
Suppliers possessing proprietary technology and patents for crucial networking components can wield considerable influence over D-Link. This intellectual property control enables them to dictate pricing, potentially leading to higher costs for D-Link, and to enforce stringent licensing terms.
D-Link's pursuit of innovation and its reliance on advanced networking solutions mean it often depends on these specialized suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the demand for Wi-Fi 7 chipsets, a rapidly evolving area, saw a significant increase, giving early patent holders for this technology a strong bargaining position.
Switching suppliers for D-Link's complex networking components presents significant hurdles. The intricate nature of these integrated systems means that changing a supplier often necessitates substantial product redesigns, rigorous re-certification processes for new parts, and extensive reconfiguration of established supply chains. These considerable switching costs inherently diminish D-Link's operational flexibility and, consequently, bolster the bargaining leverage of its current component providers.
Supplier Concentration and Scale
In the global electronics and networking component market, a few key suppliers operate at a massive scale, serving a wide array of device manufacturers. This concentration of power means these suppliers hold significant leverage in negotiations concerning pricing, delivery timelines, and quality specifications. For D-Link, this can mean their ability to secure favorable terms is directly impacted by the dominant position of these large-scale suppliers.
The bargaining power of these concentrated suppliers is a critical factor for D-Link. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier segment for networking equipment, continued to see consolidation. Major chip manufacturers, controlling essential components, often dictate terms due to high demand and limited production capacity. This dynamic can force companies like D-Link to accept less advantageous pricing or longer lead times, impacting their cost structure and product availability.
- Supplier Concentration: A few dominant players in critical component markets (e.g., semiconductors, advanced chipsets) significantly influence pricing and availability.
- Scale Advantage: Large-scale suppliers benefit from economies of scale, allowing them to offer competitive pricing but also to absorb cost fluctuations, strengthening their negotiating position.
- Impact on D-Link: D-Link's negotiation power is limited when dealing with suppliers who are essential and have few credible alternatives, potentially leading to higher input costs or supply chain disruptions.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while not a prevalent concern for D-Link's component providers, represents a theoretical lever that could shift bargaining power. If a significant supplier were to enter the finished networking product market, it could indeed enhance their leverage over companies like D-Link.
This possibility underscores the importance for D-Link to cultivate robust relationships with its critical component suppliers. Maintaining strong partnerships can mitigate the risk of such a strategic move by suppliers.
However, the sheer breadth and complexity of D-Link's product offerings present a substantial barrier to entry for any component supplier contemplating forward integration. Successfully replicating D-Link's diverse product portfolio would require significant investment and expertise, making it a high hurdle to overcome.
- Theoretical Threat: Component suppliers could theoretically integrate forward into finished networking product manufacturing, increasing their bargaining power.
- Relationship Management: D-Link must maintain strong relationships with key suppliers to counter this potential threat.
- High Barrier to Entry: The complexity and diversity of D-Link's product range make forward integration by suppliers a difficult and costly endeavor.
D-Link faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly for specialized components like advanced chipsets. In 2024, the demand for Wi-Fi 7 technology, a key area for D-Link, saw suppliers with proprietary patents holding considerable leverage, influencing pricing and terms.
The semiconductor industry, a critical supplier segment, experienced ongoing consolidation in 2024, with a few major chip manufacturers dominating. This concentration, coupled with high demand for advanced components, allows these suppliers to dictate terms, potentially increasing D-Link's input costs and impacting product availability.
Switching suppliers for D-Link's complex networking components is costly due to the need for product redesigns and re-certifications, which strengthens the hand of existing providers.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on D-Link | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Market Power | Limited negotiation leverage for D-Link | Few dominant semiconductor manufacturers |
| Proprietary Technology | Higher component costs, strict licensing | Early patent holders for Wi-Fi 7 chipsets |
| High Switching Costs | Reduced flexibility, supplier retention | Complex integration of networking components |
What is included in the product
This D-Link Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive landscape, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the networking hardware industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive overview of industry dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
For its consumer-focused products like basic wireless routers and smart home gadgets, D-Link encounters customers who are very sensitive to price. In 2024, the consumer electronics market continued to see a strong emphasis on value, with many shoppers prioritizing cost-effectiveness when choosing networking equipment.
The market is flooded with many competing brands offering similar products, allowing consumers to readily switch to another company if a better price or a slightly different feature is available. This ease of substitution significantly intensifies price wars and restricts D-Link's ability to dictate prices for these popular items.
The networking and connectivity market, where D-Link operates, is brimming with options. Customers can easily find products with similar features from numerous companies across consumer, small business, and enterprise markets. This sheer volume of choice means customers can readily compare prices and performance, making it easier to switch if they aren't satisfied.
This abundance of similar products significantly boosts customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the global Wi-Fi router market alone was valued at over $10 billion, with numerous vendors competing. This intense competition means D-Link and its rivals must constantly offer competitive pricing and superior value to retain customers, as switching costs are generally low.
D-Link's enterprise and SMB customers, often possessing advanced technical acumen, wield significant bargaining power. These clients frequently participate in rigorous competitive bidding, pushing for tailored solutions and robust negotiations on pricing, service terms, and support packages. This sophistication directly amplifies their influence.
Low Switching Costs for Standard Products
The bargaining power of customers is a significant factor for D-Link, particularly concerning its standard networking products. For many of these items, the cost and effort involved in switching from D-Link to a competitor are minimal. This low barrier to switching directly impacts customer loyalty, enabling them to leverage their position to negotiate better pricing or demand enhanced product features. For instance, a small business needing basic Wi-Fi routers can easily compare prices and specifications from multiple vendors like TP-Link, Netgear, or Asus, putting downward pressure on D-Link's margins for these commodity items.
This dynamic is evident in the competitive landscape of consumer networking hardware. In 2024, the market for entry-level routers and switches remained highly saturated, with numerous brands offering similar functionalities. Customers can readily find comparable products for under $100, making price a primary decision driver. This ease of comparison and substitution empowers buyers, forcing D-Link to remain competitive on price and performance for its more standardized offerings.
- Low Switching Costs: For standard networking equipment, customers face minimal financial or operational hurdles when moving between D-Link and its competitors.
- Customer Leverage: This low switching cost grants customers considerable power to demand better terms, including lower prices and improved product specifications.
- Market Impact: In 2024, the highly competitive market for basic routers and switches, with many options available under $100, amplified this customer bargaining power.
Access to Information and Reviews
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, significantly boosting their bargaining power. Online platforms are awash with product reviews, detailed comparative analyses, and in-depth technical specifications. This wealth of readily available data drastically reduces information asymmetry, allowing consumers to make far more informed purchasing decisions.
This increased transparency directly translates into a stronger negotiating position for customers. Armed with knowledge about pricing, features, and competitor offerings, they can effectively demand greater value for their money. For instance, in 2024, consumer electronics reviews on sites like CNET and TechRadar regularly influence purchasing decisions, with studies indicating over 90% of consumers read reviews before buying.
This trend empowers customers to:
- Research and compare product features and pricing across multiple vendors.
- Access user-generated reviews and expert opinions to gauge product quality and reliability.
- Identify the best deals and promotions through price comparison websites and forums.
- Understand the true market value of products, leading to pressure on sellers to offer competitive pricing.
D-Link faces substantial customer bargaining power, particularly in its consumer segment where price sensitivity is high. The sheer volume of competitors offering similar networking products, such as routers and switches, allows consumers to easily switch providers. This competitive environment, evident in 2024 with a global Wi-Fi router market exceeding $10 billion, forces D-Link to maintain competitive pricing and value to retain its customer base.
Customers also benefit from readily available information, including detailed reviews and price comparisons on platforms like CNET and TechRadar. In 2024, over 90% of consumers consulted reviews before purchasing electronics, empowering them to negotiate better terms. This transparency and ease of information access significantly reduce switching costs for standard products, enabling customers to demand lower prices and improved features.
| Factor | Impact on D-Link | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High for consumer products | Consumer electronics market emphasized value |
| Availability of Alternatives | Numerous competing brands | Saturated market for basic networking hardware |
| Switching Costs | Low for standard equipment | Minimal financial or operational hurdles to change vendors |
| Information Access | High due to online reviews and comparisons | Over 90% of consumers read reviews before buying |
Same Document Delivered
D-Link Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete D-Link Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the networking industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally prepared and formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. You can trust that what you are previewing is the final, ready-to-use deliverable, providing you with actionable insights without any surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The networking market is incredibly crowded, with many strong companies vying for market share. Giants like Cisco, Huawei, HPE, Juniper, and Extreme Networks are major players, but there are also many other regional and specialized companies offering similar products. This means D-Link faces stiff competition across all its product lines, from home routers to complex business network systems.
The networking industry is in a perpetual state of flux, fueled by rapid technological advancements. Innovations like Wi-Fi 7, the expansion of 5G networks, and the integration of AI into networking solutions are constantly reshaping the market. This relentless pace of change creates intense rivalry, pushing companies like D-Link to continuously innovate and update their product lines to stay relevant.
This drive for innovation necessitates significant investment in research and development. Companies must allocate substantial resources to R&D to develop cutting-edge products and features. For instance, the development of Wi-Fi 7 technology alone requires considerable engineering effort and capital outlay. Failing to invest adequately can lead to a rapid decline in market share as competitors introduce superior offerings.
Many of D-Link's core networking products, like routers and switches, are becoming increasingly similar, turning them into commodities. This means companies are battling fiercely on price, which squeezes profit margins for everyone involved.
Competitors often resort to aggressive pricing and special offers to grab a larger slice of the market. For D-Link, this intense price competition is a significant challenge, particularly in segments where they sell a lot of units, directly impacting their bottom line.
Aggressive Market Share Strategies
Competitors in the networking hardware space are relentless in their pursuit of market share. They deploy aggressive tactics like extensive marketing campaigns, building out robust distribution networks, and forging strategic partnerships to gain an edge. This intense competition forces D-Link to not only work hard to keep its current customers but also to actively seek out new avenues for growth.
The competitive environment is characterized by rivals actively vying for market dominance. This often involves significant investment in marketing to build brand awareness and customer loyalty. Furthermore, establishing and maintaining strong relationships with distributors and retailers is crucial for ensuring product availability and visibility. Strategic alliances with other technology companies can also open up new customer segments and product integration opportunities.
D-Link India's financial performance in recent periods, despite ongoing evaluation adjustments, highlights the pressures from these aggressive market share strategies. For instance, reports indicated a notable increase in revenue for D-Link India during fiscal year 2023-24, reflecting its efforts to navigate this competitive terrain effectively. This suggests that while the market is challenging, D-Link is actively implementing strategies to maintain and grow its position.
- Aggressive Marketing: Competitors invest heavily in advertising and promotional activities to capture consumer attention and build brand preference.
- Distribution Network Strength: Companies focus on expanding their reach through widespread availability in retail stores, online channels, and business-to-business sales forces.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with internet service providers, system integrators, and other technology firms help expand market access and product offerings.
- D-Link India's Performance: D-Link India reported a significant revenue growth of approximately 20% for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, demonstrating its resilience amidst fierce competition.
Global and Regional Competition
D-Link navigates a fiercely competitive landscape, with global giants and niche regional players vying for market share across Asia Pacific, Europe, and the Americas. This broad competitive intensity, extending from established multinational corporations to agile local specialists, necessitates constant strategic adaptation. For instance, in 2024, the networking equipment market saw continued aggressive pricing strategies from major competitors like TP-Link and Netgear, impacting D-Link's ability to command premium pricing in certain segments.
The company's strategic planning is further complicated by the varying competitive dynamics inherent in different geographical markets. What works in the mature European market, for example, might not be as effective in the rapidly expanding Southeast Asian markets. D-Link's 2024 financial reports indicated regional performance variations directly linked to the intensity and nature of local competition, underscoring the need for tailored market approaches.
- Global Players: D-Link competes with major international networking brands such as Cisco, HPE Aruba, and Juniper Networks, particularly in enterprise and carrier-grade solutions.
- Regional Specialists: In specific markets, local brands often leverage established distribution networks and a deep understanding of local customer needs, posing a significant challenge.
- Price Sensitivity: Many markets exhibit high price sensitivity, forcing D-Link to balance innovation with cost-effectiveness to remain competitive.
- Product Differentiation: With many competitors offering similar product portfolios, D-Link must continually focus on unique selling propositions and technological advancements to stand out.
The competitive rivalry for D-Link is intense, driven by a crowded market with both global giants and specialized regional players. This forces D-Link to constantly innovate and manage pricing effectively to maintain its market position. For instance, D-Link India saw a notable revenue increase of approximately 20% for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, indicating successful navigation of these competitive pressures.
| Competitor | Market Segment Focus | 2024 Competitive Strategy Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco | Enterprise, Service Provider | Continued investment in advanced security and cloud networking solutions. |
| TP-Link | Consumer, SMB | Aggressive pricing and expansion of Wi-Fi 7 offerings. |
| Netgear | Consumer, SMB | Focus on mesh Wi-Fi systems and high-performance networking. |
| HPE Aruba | Enterprise, Campus Networks | Emphasis on AI-driven network management and edge computing. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The growing popularity of Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) and unified multi-cloud networking presents a major threat. These solutions can lessen the reliance on traditional, on-site networking equipment, offering a compelling alternative for businesses.
Companies are increasingly favoring pay-as-you-go models for network functions to boost flexibility and growth. This shift directly challenges the market for standalone networking hardware.
The NaaS sector is experiencing rapid expansion, with market size estimations pointing to significant growth. For instance, the global NaaS market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach over $30 billion by 2028, demonstrating a clear trend towards substitution.
The rise of Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) presents a significant threat of substitutes for D-Link. These technologies enable the replacement of traditional, hardware-based networking devices with flexible, software-driven solutions. This shift means that organizations can achieve network functionality through virtualized environments, reducing their reliance on physical switches, routers, and other appliances that D-Link specializes in.
For instance, many enterprises are actively adopting NFV to consolidate network functions onto fewer, more powerful servers, often running on commodity hardware. This directly competes with D-Link's portfolio of dedicated physical networking equipment. The ability to deploy and manage network services through software offers a compelling alternative, potentially leading to lower capital expenditures and increased agility for businesses, thereby impacting demand for D-Link's core offerings.
Managed Network Services (MNS) present a significant threat to D-Link. Many businesses, from large enterprises to smaller operations, are increasingly choosing to outsource their entire networking infrastructure and its ongoing management to specialized Managed Service Providers (MSPs). This trend means companies can opt for comprehensive solutions that include hardware, software, and ongoing support, effectively bypassing the need to purchase and manage their own D-Link equipment directly.
This outsourcing model shifts the financial burden, both in terms of initial capital expenditure and day-to-day operational costs, away from the end-user business. For instance, the global managed services market was valued at approximately $274 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong preference for these outsourced solutions. This growth directly competes with D-Link's traditional hardware sales model, as businesses may lease or subscribe to network services rather than invest in physical D-Link products.
Integrated Solutions from Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
Integrated solutions from Internet Service Providers (ISPs) present a significant threat of substitutes for companies like D-Link. ISPs frequently bundle networking hardware, including modems and Wi-Fi routers, directly into their service packages. This bundling strategy makes it less appealing for consumers and small businesses to acquire standalone networking devices, as they receive a ready-to-use solution as part of their monthly bill.
This convenience factor is a powerful substitute because it simplifies the entire process for the end-user. Instead of researching, purchasing, and setting up separate networking equipment, customers benefit from a single point of contact for both internet service and connectivity hardware. This streamlined approach reduces the perceived value of purchasing individual components from third-party manufacturers.
The threat is amplified by the fact that many ISPs offer these bundled solutions at competitive or even subsidized prices. For instance, a significant portion of broadband subscribers in 2024 likely received a modem and router as part of their initial setup, effectively eliminating the need to shop for these items elsewhere. This integrated offering directly competes with D-Link's core product lines, potentially impacting sales volume and market share.
- ISP Bundling: ISPs package modems and routers with internet service plans.
- Convenience: Simplifies setup and support for end-users.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Bundled hardware can appear more affordable than standalone purchases.
- Market Impact: Reduces demand for third-party networking equipment manufacturers.
Emerging Wireless Technologies and Direct Device Connectivity
Advancements in wireless technologies, like improved mesh networking and potential direct device-to-device communication standards, pose a significant threat of substitutes. These innovations could bypass traditional central networking hubs, diminishing the demand for D-Link's core router and switch products.
For instance, the increasing adoption of Wi-Fi 7, which offers higher speeds and lower latency, could enable more seamless direct device connections, reducing reliance on a central router for certain applications. D-Link's 2023 revenue was approximately $900 million, highlighting the importance of its existing product lines to its financial performance.
- Wi-Fi 7 Adoption: Expected to grow, enabling direct device communication.
- Mesh Networking Enhancements: Could reduce the need for a single central hub.
- Direct Device Connectivity: Emerging standards might bypass traditional network infrastructure.
- Impact on D-Link's Revenue: A shift away from central hubs could affect its $900 million revenue stream.
The threat of substitutes for D-Link is significant, driven by evolving technology and changing business models. Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) and unified multi-cloud networking offer flexible, pay-as-you-go alternatives to traditional hardware. The global NaaS market, valued at around $10.5 billion in 2023, is projected to exceed $30 billion by 2028, illustrating this shift.
Software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) allow companies to replace physical devices with software-driven solutions, reducing reliance on hardware like D-Link's. Managed Network Services (MNS) also present a strong substitute, with the global market valued at approximately $274 billion in 2023, as businesses increasingly outsource their network management.
Furthermore, integrated solutions from Internet Service Providers (ISPs) that bundle networking hardware with service plans simplify setup and can be more cost-effective. Advancements in wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi 7, also enable direct device-to-device communication, potentially bypassing traditional central networking hubs and impacting D-Link's $900 million revenue stream from 2023.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Market Trend/Data Point | Impact on D-Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) | Pay-as-you-go, flexible, cloud-based | Global NaaS market: ~$10.5B (2023) to >$30B (2028) | Reduces demand for owned hardware |
| SDN/NFV | Software-driven, virtualized functions | Adoption by enterprises for consolidation | Replaces physical networking devices |
| Managed Network Services (MNS) | Outsourced infrastructure and management | Global MNS market: ~$274B (2023) | Bypasses direct hardware purchase |
| ISP Bundling | Hardware included with internet service | Common practice for broadband subscribers (2024) | Simplifies setup, reduces third-party sales |
| Advanced Wireless | Direct device communication (e.g., Wi-Fi 7) | Increasing adoption for speed and low latency | Diminishes need for central hubs |
Entrants Threaten
Entering D-Link's networking hardware market requires immense capital. Significant investments are needed for R&D, manufacturing, and establishing global supply chains. The market's projected growth to $266.61 billion by 2025 underscores the scale of investment necessary to even consider competing.
D-Link, like many established technology companies, enjoys a significant advantage due to its long-standing brand reputation and deeply ingrained customer loyalty. This makes it challenging for new players to enter the market.
New entrants would need to invest heavily to build brand awareness and trust, a process that took D-Link years and substantial resources. For instance, in 2023, D-Link continued to emphasize its commitment to quality and reliability in its marketing, a strategy that has fostered a loyal customer base over decades.
Existing relationships with distributors and retailers also act as a barrier. D-Link's established network means its products are readily available, whereas newcomers would struggle to secure similar shelf space and partnerships, a hurdle that significantly increases the cost and complexity of market entry.
The networking industry, including companies like D-Link, demands significant upfront investment in research and development to create cutting-edge connectivity solutions. This often involves proprietary intellectual property and patents, making it difficult for newcomers to compete without substantial resources. For instance, the development of Wi-Fi 7 technology, which began seeing commercial products in 2024, requires advanced engineering skills and significant R&D budgets.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certification Processes
The networking equipment industry presents significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory hurdles and complex certification processes. Companies must ensure their products meet a wide array of national and international standards, including safety certifications and interoperability requirements. For instance, in the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) mandates specific testing and compliance for radio frequency emissions, a process that can take months and incur substantial costs. Similarly, the CE marking in Europe signifies conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards, adding another layer of complexity.
Navigating these often costly and time-consuming compliance procedures acts as a substantial deterrent for new entrants. These requirements, while crucial for ensuring product safety and compatibility across diverse networks, inherently increase the friction for market entry. For example, obtaining certifications for Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 6E or upcoming Wi-Fi 7 involves rigorous testing against evolving specifications, which can be a major hurdle for smaller or emerging companies lacking the necessary resources and expertise. This regulatory landscape effectively filters out less prepared competitors, protecting established players.
The financial implications of these regulatory demands are considerable. Companies must allocate significant budgets for testing, legal counsel, and certification fees. A study by Statista indicated that the global market for wireless networking equipment alone was valued at approximately $120 billion in 2023, a sector heavily influenced by regulatory compliance. For a new player, the upfront investment in meeting these standards before even generating revenue can be prohibitive.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Significant investment required for testing and certification, impacting profitability for new entrants.
- Interoperability Standards: Adherence to global standards like IEEE 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) and future iterations necessitates ongoing R&D and validation.
- Market Entry Friction: The lengthy and complex certification process delays product launches and increases time-to-market, favoring established firms.
- Safety and Security Mandates: Compliance with safety standards and cybersecurity regulations adds further layers of complexity and cost.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
Existing large-scale manufacturers like D-Link leverage significant economies of scale in procurement, production, and distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, major networking equipment providers often operate massive manufacturing facilities, enabling them to negotiate bulk discounts on components, thereby reducing their per-unit cost of goods sold. This cost advantage makes it challenging for new entrants, who must absorb higher initial production expenses, to compete effectively on price.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle due to the entrenched cost advantages enjoyed by established players. Without the volume to secure similar pricing on raw materials or spread R&D costs across a vast product base, newcomers are inherently at a cost disadvantage. This disparity in production expenses, often amplified by efficient supply chain management developed over years, creates a significant barrier to entry for potential competitors seeking to gain market share in 2024.
- Economies of Scale: D-Link and similar companies benefit from lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations.
- Procurement Power: Bulk purchasing of components leads to significant cost savings for incumbents.
- Production Efficiency: High-volume manufacturing reduces overhead and labor costs per unit.
- Distribution Advantages: Established logistics networks offer cost-effective delivery, a hurdle for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants into D-Link's networking hardware market is moderately low. Significant capital investment is required for R&D, manufacturing, and global supply chains, with the market's projected growth to $266.61 billion by 2025 highlighting the scale of necessary investment.
Brand loyalty and established distribution networks pose considerable barriers, as new entrants must invest heavily in marketing and securing shelf space. The industry also demands substantial R&D for cutting-edge technologies like Wi-Fi 7, which began seeing commercial products in 2024, requiring advanced engineering skills and significant budgets.
Stringent regulatory hurdles and complex certification processes, such as FCC compliance in the US and CE marking in Europe, add layers of complexity and cost. These requirements, including rigorous testing for Wi-Fi standards, can be prohibitive for smaller companies. For instance, the global wireless networking equipment market was valued at approximately $120 billion in 2023, a sector heavily influenced by compliance costs.
Economies of scale provide established players like D-Link with significant cost advantages in procurement, production, and distribution. Bulk purchasing and efficient manufacturing reduce per-unit costs, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on price in 2024.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2023-2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, manufacturing, supply chains. | Prohibitive for many potential competitors. | Market projected to reach $266.61 billion by 2025. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Established customer trust and retail partnerships. | Difficult to gain market access and customer adoption. | D-Link's continued emphasis on quality in 2023 marketing. |
| Technology & R&D | Need for advanced solutions like Wi-Fi 7. | Requires significant engineering expertise and budget. | Wi-Fi 7 commercial products emerging in 2024. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex certifications (FCC, CE). | Time-consuming and costly, delaying market entry. | Global wireless networking equipment market valued at ~$120 billion in 2023. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume operations. | Cost disadvantage for new entrants. | Bulk purchasing of components by major networking providers in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of publicly available data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and government economic indicators. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive pressures.
