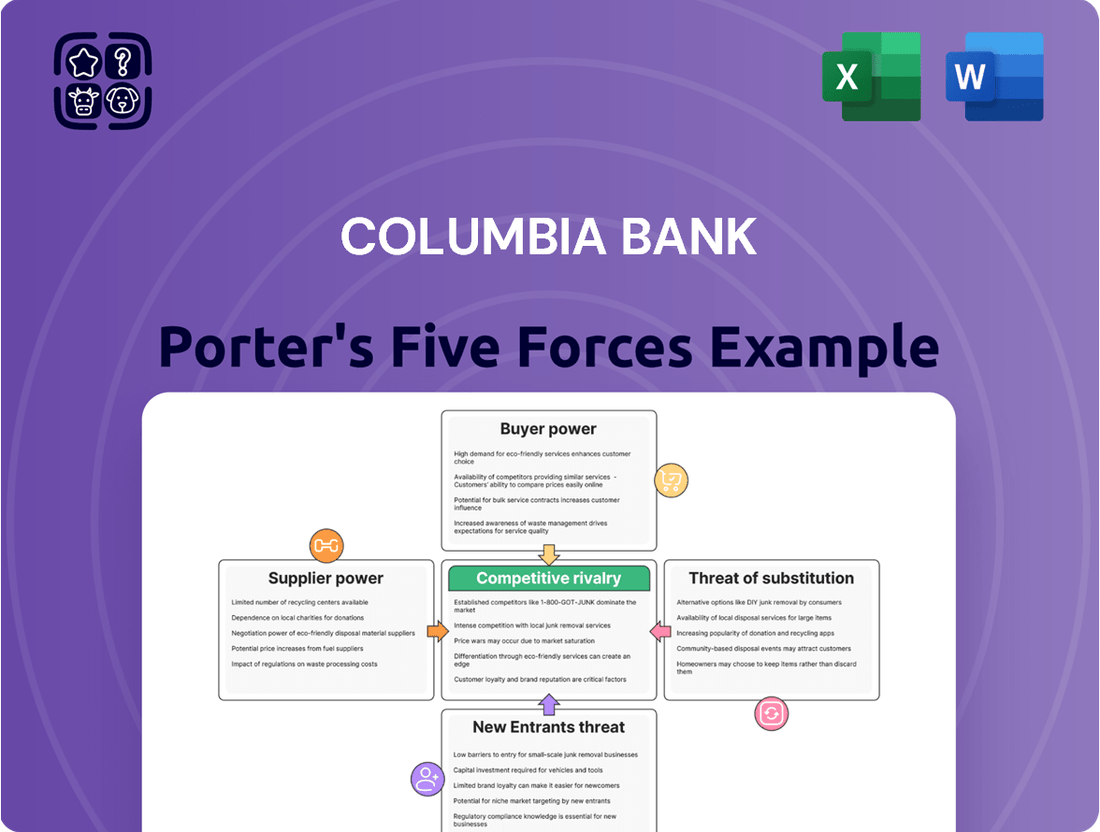
Columbia Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Columbia Bank Bundle
Columbia Bank navigates a landscape shaped by the bargaining power of its customers and the subtle threat of substitute financial products. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Columbia Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, revealing the real forces shaping its industry.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
For Columbia Bank, depositors are the primary suppliers, and the interest rates paid on deposits directly influence profitability. In the first quarter of 2024, Columbia Bank saw its cost of interest-bearing liabilities rise to 3.25%, a figure that later stabilized within that quarter.
By the first quarter of 2025, this cost had decreased to 2.52%. This fluctuation suggests a dynamic bargaining power among depositors, as the bank adjusted its rates to attract and retain funds.
Access to capital markets is a critical factor influencing a bank's operational flexibility and funding costs. Banks, including Columbia Bank, utilize these markets for wholesale borrowings, such as advances from the Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB). In the first quarter of 2025, Columbia Bank's reduction in FHLB advances indicates a strengthening deposit base, which can reduce reliance on potentially more volatile wholesale funding and thus lessen supplier bargaining power.
As financial services rapidly embrace digital transformation, banks like Columbia Bank heavily rely on technology and software providers for essential functions such as core banking systems, robust cybersecurity measures, and user-friendly digital platforms. This reliance grants these suppliers a degree of bargaining power.
The banking sector's commitment to technological advancement is evident in projected spending increases for 2024 and 2025. Reports indicate a significant focus on areas like fraud detection, enhancing digital banking capabilities, and leveraging data analytics, all areas where specialized software and tech solutions are critical. For instance, global spending on financial technology is anticipated to reach $3.1 trillion by 2027, underscoring the growing dependence on these external technology partners.
Labor Market for Skilled Employees
The bargaining power of suppliers, specifically concerning skilled labor, is a significant factor for Columbia Bank. The availability and cost of talent in high-demand fields such as technology, finance, and wealth management directly impact operational expenses and competitive positioning. In 2024, financial institutions are intensely focused on attracting and retaining skilled employees, recognizing that a strong talent pipeline is crucial for innovation and service delivery.
Talent acquisition and retention remain paramount concerns for financial institutions throughout 2024 and into 2025. For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 9% growth for financial managers between 2022 and 2032, indicating continued demand. This tight labor market for specialized skills means that banks like Columbia Bank may face increased wage pressures and competition for top talent.
- High Demand for Tech and Finance Skills: The banking sector's increasing reliance on digital transformation and data analytics drives demand for IT professionals, cybersecurity experts, and financial analysts.
- Wage Inflation: Competition for scarce skilled labor can lead to higher salary expectations and increased recruitment costs for banks.
- Impact on Operational Costs: Rising labor costs directly affect a bank's profitability and its ability to invest in other strategic areas.
- Strategic Importance of Talent Management: Effective talent acquisition, development, and retention strategies are critical for maintaining a competitive edge.
Regulatory and Compliance Services
Banks, including Columbia Bank, rely heavily on regulatory and compliance services, creating a degree of supplier power. The complex and ever-changing landscape of financial regulations necessitates specialized expertise from legal, compliance, and auditing firms. For instance, the introduction of the EU's Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) in January 2025 signifies a growing demand for specialized compliance support, potentially amplifying the bargaining power of firms offering these critical services.
The increasing regulatory burden directly impacts banks' operational costs and their ability to navigate legal frameworks. Firms that can effectively manage these complexities and ensure adherence to directives like DORA are in a strong position. This specialized knowledge is not easily replicated, giving these service providers leverage when negotiating contracts and fees with financial institutions.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Banks face growing demands for compliance, driving demand for expert services.
- Evolving Compliance Landscape: New regulations, like DORA effective January 2025, create opportunities for specialized providers.
- Demand for Specialized Expertise: Legal, compliance, and auditing firms with deep knowledge in financial regulations hold significant bargaining power.
For Columbia Bank, depositors represent a key supplier group, with interest rates paid on deposits directly impacting profitability. In Q1 2024, the cost of interest-bearing liabilities was 3.25%, decreasing to 2.52% by Q1 2025, indicating shifts in depositor bargaining power as the bank adjusted rates to manage its funding. The bank's reduced reliance on Federal Home Loan Bank advances in Q1 2025 also signifies a stronger deposit base, lessening the bargaining power of wholesale funding providers.
| Supplier Type | 2024 Data/Trend | 2025 Data/Trend | Impact on Columbia Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Depositors | Cost of Interest-Bearing Liabilities: 3.25% (Q1 2024) | Cost of Interest-Bearing Liabilities: 2.52% (Q1 2025) | Decreased bargaining power due to stronger deposit base and potentially lower rates. |
| Wholesale Funding (e.g., FHLB) | Moderate reliance | Reduced reliance on FHLB advances (Q1 2025) | Lower bargaining power for wholesale lenders as internal funding strengthens. |
| Technology Providers | Increased spending on digital transformation, fraud detection, data analytics. | Continued investment in tech solutions. Global fintech spending projected to reach $3.1 trillion by 2027. | Significant bargaining power due to critical reliance on specialized software and platforms. |
| Skilled Labor (Tech, Finance) | High demand and competition for talent. 9% projected growth for Financial Managers (2022-2032). | Continued tight labor market for specialized skills. | Increased wage pressures and recruitment costs, impacting operational expenses. |
| Regulatory/Compliance Services | Growing demand for specialized expertise due to complex regulations. | New regulations like DORA (Jan 2025) amplify demand for compliance support. | Strong bargaining power for firms offering specialized legal, compliance, and auditing services. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Columbia Bank's unique position in the financial services industry.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces dashboard, instantly highlighting areas of strategic vulnerability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers, especially those with substantial balances, possess significant power to shift their deposits to banks offering better interest rates. This deposit mobility is particularly pronounced when interest rates are volatile, as seen in recent market conditions.
Columbia Bank has observed a trend where customers are moving funds from non-interest-bearing accounts to those that offer interest, a direct response to the pursuit of higher yields. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, the bank reported a notable increase in interest-bearing deposit balances as rates climbed.
Customers today enjoy an unprecedented abundance of financial product choices, extending far beyond what traditional banks offer. Fintech innovations and alternative financial service providers present a competitive landscape where consumers can easily find specialized solutions for savings, investments, and lending, significantly increasing their bargaining power.
Columbia Bank addresses this by providing a broad spectrum of financial services, from diverse deposit accounts and various lending options to sophisticated wealth management. This comprehensive approach aims to consolidate customer relationships by fulfilling multiple financial needs under one roof, thereby mitigating the risk of customer attrition to competitors.
Customers now expect digital-first banking, driven by fintech innovations. This means they want seamless online experiences, instant information, and personalized services, putting pressure on traditional banks to adapt.
The demand for digital onboarding and portfolio management is high. For instance, in 2024, a significant percentage of banking customers preferred digital channels for most transactions, a trend that continues to grow, forcing institutions like Columbia Bank to enhance their digital offerings to meet these evolving expectations.
Loan Demand and Creditworthiness
The bargaining power of customers, in the context of loan demand and creditworthiness, significantly shapes a bank's lending landscape. When demand for loans is high and borrowers are perceived as creditworthy, banks generally have more leverage. Conversely, weak demand or concerns about borrower credit quality can empower customers, forcing banks to offer more favorable terms.
In 2024, the U.S. banking sector experienced relatively subdued loan growth. However, anticipation is building for a potential rebound in loan demand for 2025, partly fueled by expected interest rate reductions. This shift could alter the power dynamic, with potentially more borrowers entering the market and seeking credit.
- Loan Demand Trends: U.S. banks saw slower loan growth in 2024, but forecasts suggest increased demand in 2025, especially if interest rates decline.
- Borrower Creditworthiness: The perceived ability of borrowers to repay loans directly impacts a bank's risk appetite and its power in setting lending terms.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing, potentially increasing customer bargaining power by creating more competitive lending environments.
Wealth Management Client Demands
Wealth management clients are becoming more assertive, demanding highly personalized investment strategies, clear fee structures, and constant accessibility to their advisors and financial data. This heightened expectation for tailored service and transparency significantly increases their bargaining power.
Clients are increasingly seeking control, often looking for platforms that offer direct involvement in investment decisions and robust digital tools for monitoring and management. The growing interest in alternative investments, such as private equity and hedge funds, further empowers clients as they seek specialized expertise and potentially higher returns, forcing firms to adapt their offerings.
- Personalization: Clients expect strategies designed around their unique risk tolerance, goals, and life stages, moving away from one-size-fits-all approaches.
- Transparency: Demands for clear, upfront information on fees, performance, and investment holdings are paramount.
- Digital Access & Control: Clients want intuitive digital platforms for real-time portfolio tracking and engagement, giving them greater oversight.
- Alternative Investments: A growing segment of clients is actively exploring and demanding access to a wider array of alternative asset classes.
Customers, particularly those with significant balances, hold considerable sway by easily transferring deposits to institutions offering more favorable interest rates, a trend amplified by volatile market conditions. This deposit mobility, coupled with an expanding array of financial products beyond traditional banking, significantly enhances customer bargaining power.
Columbia Bank's response involves offering a comprehensive suite of financial services to retain clients by meeting diverse needs, while also prioritizing digital enhancements to align with customer expectations for seamless online experiences and instant information access.
The bargaining power of customers is also evident in the lending market; while subdued loan growth was observed in 2024, an anticipated rebound in 2025, potentially driven by lower interest rates, could shift leverage towards borrowers.
Wealth management clients are increasingly demanding personalized strategies, transparent fee structures, and constant accessibility, further solidifying their bargaining position.
| Customer Characteristic | Impact on Bargaining Power | Columbia Bank's Strategic Response |
|---|---|---|
| Deposit Mobility & Rate Sensitivity | High, especially with volatile rates. Customers can easily switch for better yields. | Offer competitive interest rates and a diverse range of deposit products. |
| Access to Fintech & Alternative Providers | High, offering specialized solutions beyond traditional banking. | Enhance digital offerings and explore partnerships to broaden service scope. |
| Demand for Digital Experience | High, expecting seamless online interactions and personalized services. | Invest in user-friendly digital platforms for transactions, onboarding, and portfolio management. |
| Loan Demand & Creditworthiness | Moderate to High, depending on market conditions and borrower quality. | Adapt lending terms based on market demand and borrower risk assessment. |
| Wealth Management Expectations | High, demanding personalization, transparency, and digital control. | Provide tailored investment strategies, clear fee disclosures, and robust digital advisory tools. |
Full Version Awaits
Columbia Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It comprehensively details the competitive landscape of Columbia Bank through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Columbia Bank faces intense rivalry from a multitude of traditional banks, including regional, national, and community institutions. These competitors offer a broad range of similar financial products and services, creating a crowded marketplace.
The U.S. banking sector is anticipating further consolidation in 2025. This trend suggests that larger, more diversified financial institutions may gain a competitive edge, potentially impacting smaller players like Columbia Bank.
Fintech firms are intensifying competition for traditional banks like Columbia Bank, introducing innovative, tech-focused services that often come with lower fees and a superior customer journey. For example, digital-only banks are increasingly offering core banking services at significantly reduced operating costs, directly challenging established players.
This aggressive fintech landscape means Columbia Bank faces pressure to adapt its own offerings, as companies like Chime, which boasts over 14 million customers as of early 2024, demonstrate the appeal of streamlined, digital-first banking experiences. The continued growth of these platforms highlights a shift in consumer preference towards convenience and cost-effectiveness, forcing traditional institutions to innovate or risk losing market share.
The prevailing interest rate environment is a critical factor influencing bank profitability and strategic decisions, especially concerning net interest margins. Columbia Bank, like its peers, navigates this landscape, understanding that shifts in rates directly affect earnings.
Looking ahead, regional banks, including Columbia Bank, are projecting a tightening of interest margins in the coming years. However, despite this anticipated pressure, the overarching sentiment regarding the sector's performance remains optimistic.
For instance, in early 2024, the Federal Reserve maintained its benchmark interest rate within a certain range, a decision that influences lending and borrowing costs across the economy and directly impacts how banks like Columbia Bank price their products and manage their balance sheets.
Focus on Niche Markets and Customer Segments
Columbia Bank is strategically targeting niche markets and specific customer segments to carve out a distinct position in the competitive banking landscape. By aiming to be the 'Business Bank of Choice,' the bank is concentrating its efforts on fostering enduring relationships within New Jersey.
This focus on specialized segments allows Columbia Bank to tailor its services and product offerings, thereby enhancing customer loyalty and reducing direct competition with larger, more generalized financial institutions. For instance, by concentrating on businesses in New Jersey, they can develop deep expertise in the local economic drivers and regulatory environment.
- Niche Market Focus: Columbia Bank prioritizes serving businesses within New Jersey.
- Customer Relationship Building: The bank emphasizes long-term partnerships with its clients.
- Differentiation Strategy: Targeting specific segments helps Columbia Bank stand out from broader competitors.
Investments in Technology and Digital Transformation
The banking sector's competitive rivalry is intensifying due to significant investments in technology and digital transformation. Banks are channeling substantial resources into areas like artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics to streamline operations and elevate customer interactions. This technological arms race is critical for maintaining market share and attracting new clients.
By 2025, the banking industry's technology spending is projected to climb, with a particular focus on generative AI and robust cybersecurity measures. For instance, global IT spending in the banking sector was estimated to reach approximately $240 billion in 2023, and this figure is expected to see continued growth, driven by the need for digital innovation and security resilience.
- AI Adoption: Banks are increasingly using AI for fraud detection, personalized marketing, and customer service chatbots.
- Digital Channels: Investment in mobile banking platforms and online services is paramount to meet evolving customer expectations.
- Cybersecurity Focus: With rising digital threats, financial institutions are allocating more budget to protect sensitive data and maintain trust.
- Fintech Competition: Traditional banks face pressure from agile fintech companies that leverage technology to offer specialized, often lower-cost, financial services.
Columbia Bank operates in a highly competitive environment, facing pressure from both traditional financial institutions and agile fintech disruptors. The ongoing consolidation within the U.S. banking sector by 2025 suggests larger players may gain an advantage, while digital-first banks are capturing market share with lower fees and enhanced customer experiences. For example, Chime's rapid growth to over 14 million customers by early 2024 underscores this trend.
The banking industry's escalating investment in technology, including AI and cybersecurity, is a key driver of rivalry. Global IT spending in banking reached roughly $240 billion in 2023, with continued growth anticipated through 2025, particularly in generative AI and digital channel development. This technological arms race necessitates continuous innovation for banks like Columbia to remain competitive and meet evolving customer expectations.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Columbia Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Banks | Broad service offerings, regional/national presence | Direct competition for core banking services |
| Fintech Companies | Tech-focused, lower fees, enhanced customer journey | Erosion of market share, pressure on pricing and digital offerings |
| Digital-Only Banks | Streamlined operations, cost-effective services | Challenge to traditional business models, shift in customer preference |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech companies and digital-only banks present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banks like Columbia Bank. These agile players offer a spectrum of services, from mobile payment solutions and peer-to-peer lending to entirely digital banking experiences, often bypassing established banking infrastructure. It's projected that financial technology will disrupt over 28% of traditional banking services within the next four years, highlighting the growing competitive pressure.
Credit unions and non-bank lenders present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Columbia Bank. Credit unions, with their member-owned structure and community focus, offer a compelling alternative for individuals and small businesses seeking personalized service and potentially lower fees. For instance, as of the end of 2023, there were over 4,700 credit unions in the U.S., holding over $2.2 trillion in assets, demonstrating their substantial market presence and ability to attract customers away from conventional banking services.
Non-bank lenders, ranging from fintech startups to specialized finance companies, further intensify this threat by providing flexible and often faster lending solutions, particularly for consumers and businesses with specific credit profiles or needs not fully met by traditional banks. In 2024, the non-bank mortgage origination market, for example, continues to be a significant channel, with these lenders often capturing market share through streamlined digital processes and competitive rates, directly impacting the loan origination business of banks.
For Columbia Bank's wealth management division, the threat of substitutes is significant. Independent investment advisors, low-cost robo-advisors, and user-friendly online brokerage platforms offer comparable investment and financial planning services, often at a lower price point or with greater convenience.
The wealth management landscape is rapidly evolving, with increased merger and acquisition activity among advisory firms. Furthermore, a notable trend in 2024 is the growing retail investor allocation towards alternative investments, such as private equity and venture capital, which may bypass traditional bank-managed portfolios.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Solutions
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology are emerging as significant potential substitutes for traditional banking functions, especially in areas like payments and decentralized finance. While still in development, these digital assets offer alternative ways to transfer value and access financial services outside of conventional channels.
The growth trajectory of blockchain technology suggests its increasing integration into the global economy. For instance, it's projected that by 2027, approximately 10% of the world's gross domestic product could be represented through tokenized assets on blockchain platforms.
- Payments: Cryptocurrencies offer faster and often cheaper cross-border payment solutions compared to traditional bank wire transfers.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms built on blockchain provide alternatives for lending, borrowing, and trading assets without intermediaries.
- Store of Value: Some cryptocurrencies are viewed as digital gold, offering an alternative store of value, though with higher volatility.
- Tokenization: The tokenization of real-world assets on blockchain could create new investment opportunities and liquidity for previously illiquid assets.
Internal Corporate Finance Departments
Larger corporations often possess robust internal finance departments capable of managing treasury functions, securing credit lines, and executing investment strategies. This internal capacity can diminish their need for certain external banking services, acting as a substitute. For instance, a company with a dedicated treasury team might manage its own cash pooling and foreign exchange hedging, bypassing a bank's specialized offerings.
Columbia Bank's strategy to mitigate this threat involves a strong emphasis on its commercial lending and sophisticated treasury management solutions. By offering integrated services that streamline financial operations and provide expert guidance, Columbia Bank aims to demonstrate superior value compared to what an in-house department can achieve, especially for mid-sized businesses that may not have the scale for extensive internal resources.
The competitive landscape in 2024 highlights this dynamic. While exact figures for the percentage of corporate treasury functions handled internally versus outsourced are varied, surveys consistently show a trend towards greater in-house control for larger enterprises. However, the complexity and regulatory burden of modern finance continue to drive demand for specialized banking expertise, particularly in areas like international payments and risk management.
- Internal Capacity: Large businesses can internalize functions like treasury management, reducing reliance on external banks.
- Columbia Bank's Response: Focus on commercial loans and advanced treasury management services to offer competitive value.
- Market Trend: Larger firms increasingly manage treasury functions in-house, but complexity still favors specialized banking services.
- 2024 Data Insight: While internal capabilities grow, the need for expert banking solutions in areas like risk management remains significant for businesses of all sizes.
The threat of substitutes for Columbia Bank is multifaceted, encompassing digital alternatives, credit unions, and even internal corporate capabilities. Fintechs and digital-only banks offer streamlined services, while credit unions provide a community-focused alternative. Furthermore, sophisticated corporations can increasingly manage financial functions internally, reducing their reliance on traditional banking services.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Banks | Examples | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech & Digital Banks | Agile, lower overhead, user-friendly interfaces | Erosion of market share in payments, lending, and basic banking | Mobile payment apps, P2P lending platforms | Continued rapid growth and innovation in digital offerings |
| Credit Unions | Member-owned, community focus, often lower fees | Attracts retail and small business customers seeking personalized service | Local credit unions offering savings and loan products | Steady growth in assets and membership, competing on service |
| Non-Bank Lenders | Specialized, flexible, faster processing | Captures market share in specific lending segments (e.g., mortgages) | Online mortgage lenders, alternative financing providers | Increasingly sophisticated digital onboarding and underwriting |
| In-house Corporate Finance | Internal expertise, cost control | Reduces demand for treasury management, cash pooling, FX hedging | Large corporations managing their own liquidity and investments | Growing trend for larger enterprises to internalize more functions |
| DeFi & Crypto | Decentralized, potentially lower transaction costs, new asset classes | Disruption of payment systems, lending, and investment avenues | Cryptocurrency payment networks, DeFi lending protocols | Increasing regulatory scrutiny alongside technological advancements |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector presents formidable barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory frameworks and substantial capital requirements. New entrants must navigate complex compliance standards, including Basel III and its evolving iterations, which mandate significant liquidity and capital reserves. For instance, in 2024, many regional banks faced increased scrutiny and capital raising efforts following the stress experienced by some institutions in 2023, underscoring the capital intensity of the industry.
Established banks like Columbia Bank leverage decades of customer relationships and strong brand recognition, creating a significant barrier for new entrants. This deep-rooted trust, often built through community engagement and consistent service, makes it challenging for newcomers to attract a substantial customer base quickly. For instance, in 2024, the average customer tenure in the banking sector remains high, reflecting the stickiness of established relationships.
New entrants, like Columbia Bank, face a significant hurdle in accessing funding and building robust deposit bases. Establishing a stable and diverse source of deposits is crucial for any bank's operational stability, yet this is particularly difficult for newcomers lacking an established branch network or a recognized brand reputation.
In 2024, attracting and retaining deposits remains a paramount strategic objective for financial institutions across the board. Data from the Federal Reserve indicates that while total deposits in the U.S. banking system saw a slight increase in early 2024, competition for these funds intensified, with many banks offering higher interest rates to draw in new customers.
Technological Infrastructure and Investment
The significant capital outlay required for advanced technological infrastructure acts as a formidable barrier to entry for new players in the banking sector. Establishing secure and sophisticated digital platforms, robust cybersecurity measures, and cutting-edge AI capabilities demands substantial investment and specialized knowledge, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively with established institutions like Columbia Bank. For instance, the global banking sector's investment in technology is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars annually, with a significant portion allocated to digital transformation and cybersecurity upgrades.
New entrants face the challenge of matching the technological sophistication and security protocols already in place at established banks. This includes developing and maintaining advanced digital banking interfaces, implementing comprehensive fraud detection systems, and integrating AI for personalized customer experiences and operational efficiency. Banks are actively increasing their technology spending; for example, many large financial institutions reported technology budgets in the billions of dollars for 2024, reflecting the critical need to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
- High Capital Investment: Building and maintaining state-of-the-art technological infrastructure, including cloud computing, data analytics, and AI, requires significant upfront and ongoing financial commitment.
- Cybersecurity Demands: Implementing robust cybersecurity systems to protect sensitive customer data and financial transactions is a complex and costly endeavor, essential for maintaining trust and compliance.
- Talent Acquisition: New entrants need to attract and retain skilled IT professionals, data scientists, and cybersecurity experts, which can be challenging given the competitive market for such talent.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to stringent financial regulations often necessitates advanced technological solutions for data management, reporting, and security, adding to the cost of entry.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
New banks face a significant challenge in attracting and keeping experienced banking professionals, especially in crucial areas like commercial lending and wealth management. This struggle for talent is a widespread concern throughout the financial sector.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. banking industry experienced a notable demand for skilled professionals, with job postings for commercial loan officers seeing a 15% increase compared to the previous year. New entrants must invest heavily in competitive compensation and robust employee development programs to overcome this hurdle.
- Talent Gap: A shortage of experienced bankers in specialized fields makes it difficult for new institutions to build a strong team.
- High Turnover Costs: The cost of recruiting and training new employees can be substantial, impacting profitability.
- Competitive Landscape: Established banks often have well-defined career paths and attractive benefits, making it harder for newcomers to compete for top talent.
The threat of new entrants for Columbia Bank is generally low due to substantial barriers. These include significant capital requirements, a highly regulated environment, and the need for established customer trust and brand loyalty. Newcomers must also overcome the high costs associated with advanced technology and cybersecurity, as well as the challenge of attracting experienced banking talent.
In 2024, the banking sector continued to see consolidation, with smaller institutions often being acquired rather than new ones emerging, further limiting new entrants. The ongoing investment in digital transformation by established banks also raises the technological bar for any potential new competitors.
The intense competition for deposits, as evidenced by rising interest rates offered by many banks in early 2024, demonstrates the difficulty new players face in building a stable funding base without an established reputation and branch network.
Access to specialized talent remains a key differentiator, with established banks leveraging their resources to attract and retain experts in areas like AI and cybersecurity, making it harder for new entrants to compete effectively.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Columbia Bank leverages data from their annual reports, SEC filings, and investor relations materials. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and data from financial information providers to capture competitive dynamics.
