Calavo Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Calavo Bundle
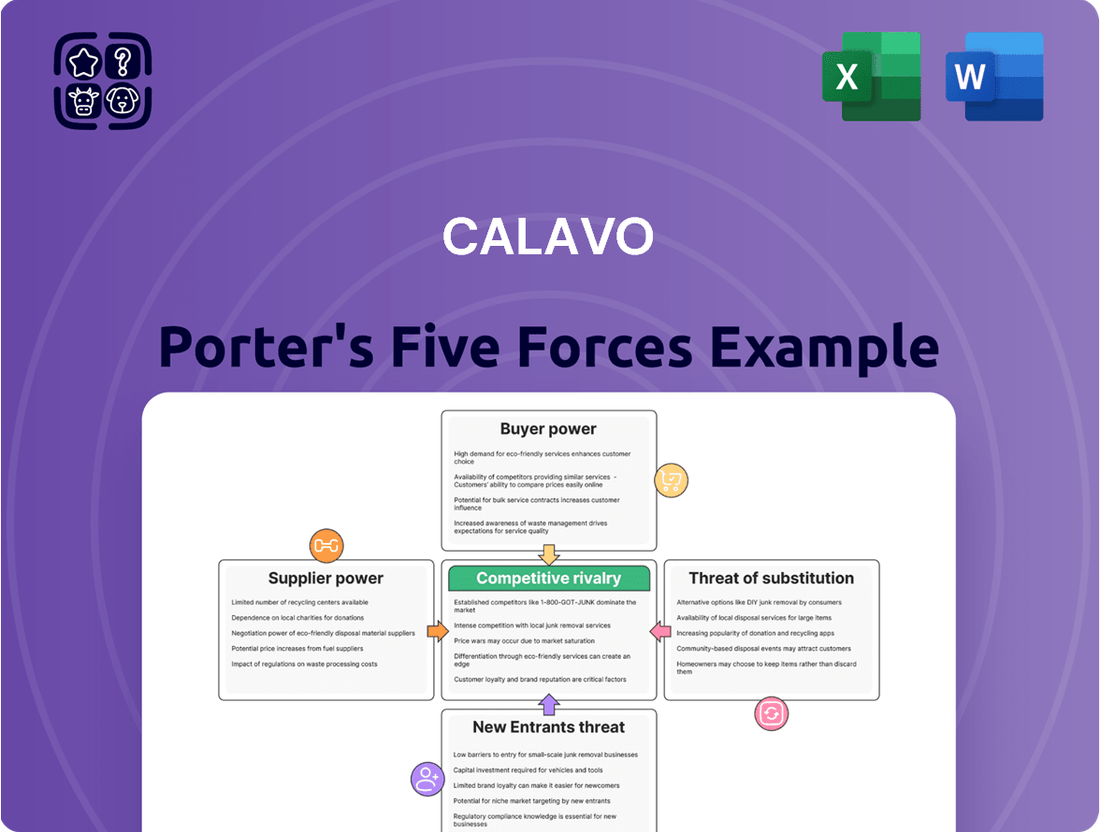
Calavo's industry is shaped by intense competition and the significant bargaining power of its buyers, particularly large retailers. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the avocado and prepared avocado product markets. The threat of new entrants, while present, is somewhat mitigated by established distribution networks and brand recognition.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Calavo’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The global avocado market, while growing, can show supplier concentration for specific varieties or in key growing regions. This means Calavo might depend on a smaller group of large avocado producers for a substantial part of its supply. For instance, Peru, a major avocado exporter, saw its avocado exports reach over 370,000 tonnes in 2023, with a significant portion coming from a few large agricultural companies.
When a few suppliers dominate the market, they gain considerable bargaining power. This leverage allows them to influence pricing and dictate terms, especially considering the inherent seasonality and regional variations in avocado harvests. This concentration can put pressure on Calavo's procurement costs and supply chain stability.
Suppliers offering avocados with unique attributes, such as specific organic certifications or premium quality, can leverage this to command higher prices from Calavo. These specialized growers cater to Calavo's diverse clientele, including retail and foodservice sectors, which have distinct product requirements. Calavo's emphasis on maintaining consistent quality and adhering to precise product specifications further strengthens the bargaining power of these select growers.
Switching primary avocado growers or other fresh produce suppliers for Calavo involves significant hurdles beyond simply finding a new vendor. These include the time and resources needed to establish new quality control protocols, reconfigure complex logistics to accommodate different product specifications or delivery schedules, and the inherent risk of supply disruptions during the transition period. For instance, in 2024, the agricultural sector continued to face challenges with labor availability and transportation costs, making supplier transitions even more complex and costly for buyers like Calavo.
These operational and relationship-based switching costs directly enhance the bargaining power of Calavo's existing suppliers. When it is difficult and expensive for Calavo to change suppliers, current suppliers can demand better terms, higher prices, or more favorable contract conditions, knowing that Calavo faces substantial penalties for seeking alternatives.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Large-scale avocado growers, particularly those with substantial capital and existing infrastructure, hold the capability to integrate forward. This means they could potentially move into packing, ripening, or even direct distribution of avocados, bypassing companies like Calavo.
If these powerful suppliers decide to bypass intermediaries, it directly increases their bargaining power. This strategic shift could significantly alter Calavo's established supply chain dynamics, potentially leading to less favorable terms for Calavo.
- Forward Integration Threat: Major avocado growers can integrate forward into packing, ripening, and distribution.
- Impact on Calavo: Supplier bypass of intermediaries like Calavo strengthens supplier power and disrupts supply chains.
- 2024 Data Context: While specific forward integration by avocado growers in 2024 isn't publicly detailed, the trend of consolidation in agriculture suggests larger entities are increasingly capable of such moves. For instance, the global avocado market, valued at approximately $13.6 billion in 2023, is expected to grow, potentially incentivizing large growers to capture more value downstream.
Volatility of Agricultural Yields and Input Costs
The bargaining power of suppliers for Calavo is heavily impacted by the unpredictable nature of agricultural yields. Factors like adverse weather events, pest infestations, and disease outbreaks can drastically reduce the volume of avocados and other produce available, giving suppliers more leverage to dictate prices. For instance, California avocado growers faced significant challenges in 2023 due to drought conditions, impacting overall supply.
Furthermore, escalating input costs for suppliers directly translate into increased pressure on Calavo. Expenses related to labor, water, and fertilizers have been on an upward trend. In 2024, the average cost of fertilizer per acre for many agricultural operations saw a notable increase compared to previous years, forcing suppliers to seek higher prices to cover their own operational expenses and maintain profit margins.
- Weather Dependency: Agricultural output, particularly for avocados, is highly susceptible to weather patterns, leading to supply fluctuations.
- Pest and Disease Impact: Outbreaks can decimate crops, further constricting supply and strengthening supplier negotiation power.
- Rising Input Costs: Increased expenses for labor, water, and fertilizers compel suppliers to pass these costs on through higher prices.
- Limited Substitutes: For specific, high-quality produce, Calavo may have few alternative suppliers, enhancing existing suppliers' leverage.
The bargaining power of Calavo's suppliers is influenced by market concentration and the ability of major growers to integrate forward. For instance, in 2023, Peru's avocado exports exceeded 370,000 tonnes, with a significant portion originating from a few large entities, highlighting potential supplier leverage. When suppliers can bypass intermediaries like Calavo, their power increases, potentially disrupting existing supply chain dynamics.
| Factor | Impact on Calavo | Supporting Data/Context (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased pricing power and potential for dictated terms. | Peru's avocado exports in 2023: >370,000 tonnes, with supply often from a few large companies. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Risk of suppliers bypassing Calavo, altering supply chain dynamics. | Global avocado market valued at ~$13.6 billion in 2023; consolidation trends suggest capability for larger growers. |
| Switching Costs | Makes it difficult and expensive for Calavo to change suppliers. | 2024 agricultural sector challenges include labor availability and transportation costs, complicating supplier transitions. |
| Product Specialization | Suppliers of unique or premium avocados can command higher prices. | Calavo's need for consistent quality and specific product specifications strengthens specialized growers' leverage. |
What is included in the product
Calavo's Porter's Five Forces analysis meticulously examines the competitive intensity within the avocado and fresh produce industry, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic visualization of Calavo's market position.
Customers Bargaining Power
Calavo's customer base, which includes major retail grocery chains like Kroger and Costco, along with large foodservice distributors, frequently places substantial orders for fresh and processed avocado products. These significant purchase volumes grant these key customers considerable bargaining power. In 2023, Calavo's top ten customers accounted for approximately 60% of its total revenue, highlighting the concentration of its customer base and their influence.
For many standard fresh produce items and even some processed avocado products, Calavo's customers may face relatively low switching costs. This means they can easily find comparable quality and reliable supply from alternative distributors, which significantly boosts their bargaining power.
In 2024, the competitive landscape for fresh produce distribution remained robust, with numerous regional and national players vying for market share. This abundance of choice for buyers directly translates to increased leverage when negotiating terms with suppliers like Calavo.
Calavo's customers, particularly those in the retail and food service sectors, face a market with numerous avocado suppliers. This competition means they can often switch to a different provider if Calavo's pricing or terms become unfavorable. For instance, in 2024, the global avocado market continued to see significant production from countries like Mexico, Peru, and California, providing ample supply options.
Price Sensitivity of End Consumers
The price sensitivity of end consumers significantly impacts Calavo's bargaining power with its customers. Retailers and foodservice providers operate in intensely competitive markets, making them highly attuned to consumer price demands. This means they often pass cost pressures down the supply chain, forcing Calavo to manage its own pricing carefully.
For example, in 2024, the average inflation rate for food away from home remained a concern for consumers, impacting their willingness to absorb higher prices. This environment compels Calavo to maintain competitive pricing, often absorbing cost increases itself rather than fully passing them on to its direct customers.
- High Consumer Price Sensitivity: End consumers in the retail and foodservice sectors are very sensitive to price changes, directly influencing sales volumes and profit margins for Calavo's customers.
- Supply Chain Pressure: Competitive pressures on Calavo's customers translate into demands for competitive pricing from Calavo, limiting its ability to pass on its own cost increases.
- Margin Squeeze: This dynamic can lead to a squeeze on Calavo's margins as it needs to absorb higher input costs to remain competitive in its pricing.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
While avocados are specialized, major customers like large retail chains or foodservice companies have the financial muscle to consider backward integration. This means they could potentially start their own sourcing, packing, or processing operations, bypassing suppliers like Calavo. For instance, in 2023, major U.S. grocery retailers saw significant growth, with some reporting billions in annual revenue, giving them the capital to explore such vertical expansion strategies.
This theoretical ability for large customers to integrate backward acts as a powerful bargaining tool. It pressures Calavo to offer competitive pricing and favorable terms to retain these crucial clients. Even if these customers don't actually integrate, the mere possibility influences negotiations, as Calavo must anticipate and counter this potential threat.
- Customer Integration Potential: Large retail and foodservice clients can theoretically invest in avocado sourcing, packing, and processing.
- Financial Capability: Major players in the grocery sector, with revenues in the billions, possess the resources to fund such integration.
- Negotiating Leverage: The threat of backward integration gives customers significant power to demand better prices and terms from Calavo.
Calavo's customers, especially large grocery chains and foodservice providers, hold significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the availability of alternative suppliers. This leverage is amplified by the price sensitivity of end consumers, forcing Calavo to maintain competitive pricing and absorb cost increases. The potential for customer backward integration further strengthens their negotiating position, compelling Calavo to offer favorable terms to retain key clients.
| Factor | Impact on Calavo | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High dependence on few large buyers | Top 10 customers accounted for ~60% of revenue in 2023 |
| Switching Costs | Low for many standard products | Easily sourced from competitors |
| Price Sensitivity | High due to consumer demand | Inflationary pressures in 2024 impacted consumer spending |
| Supplier Competition | Abundant global avocado supply | Increased options for buyers |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential for large customers to self-supply | Major retailers have billions in revenue to fund expansion |
Full Version Awaits
Calavo Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Calavo Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive pressures within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate access to this valuable strategic tool.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The avocado market has seen significant global expansion, drawing in new capital and encouraging existing companies to scale up. This growth fuels intense competition among participants. For instance, the global avocado market was valued at approximately USD 13.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 21.8 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% during this period, according to various market research reports from early 2024. This rapid expansion naturally intensifies rivalry as more players enter and existing ones seek to capture a larger share.
However, within the broader fresh produce sector, certain segments might be more mature. In these slower-growing areas, competition becomes even more pronounced as companies battle fiercely for existing market share. This dynamic can lead to price pressures and a greater emphasis on differentiation and operational efficiency to stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Calavo operates in a market characterized by numerous competitors, ranging from large, integrated produce companies to smaller, specialized avocado distributors and regional players. This diversity in competitor size and focus intensifies rivalry.
The presence of private-label brands further fragments the market, adding another layer of competition that Calavo must navigate. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. avocado market saw significant growth, with imports playing a crucial role, bringing in various international suppliers and increasing competitive pressures.
While the fresh avocado market is largely characterized by commodity products, Calavo distinguishes itself through a focus on consistent quality and dependable global sourcing. This differentiation is further bolstered by their significant investments in extensive ripening capabilities and value-added services, such as custom packaging and precise grading. These offerings help Calavo move beyond pure price competition, although less differentiated segments of the market remain intensely competitive.
High Fixed Costs and Perishable Goods
The fresh produce sector, including companies like Calavo, is characterized by significant fixed costs. These investments are necessary for specialized infrastructure such as packing facilities, cold storage warehouses, and advanced transportation networks designed to handle perishable items. For instance, maintaining a robust cold chain is critical, and the associated capital expenditures can be substantial.
The perishable nature of fresh produce, with its limited shelf life, compels companies to operate at high volumes to recoup these fixed costs and minimize spoilage. This urgency to sell inventory quickly often translates into intense price competition among players in the market, as they strive to capture market share and ensure product turnover.
- Capital Intensity: The fresh produce industry requires significant upfront investment in specialized infrastructure like packing houses and cold storage.
- Perishability Pressure: The short shelf life of goods necessitates high sales volumes to avoid losses, driving aggressive competition.
- Logistics Complexity: Maintaining the integrity of perishable goods through sophisticated logistics adds to operational costs and competitive pressures.
- Volume-Driven Pricing: The need to move inventory efficiently often leads to price wars as companies compete to sell their products.
Exit Barriers and Specialized Assets
Calavo Growers, like many in the fresh produce sector, faces significant exit barriers. These include specialized assets such as advanced ripening facilities, which represent substantial capital investment. For instance, the need for controlled atmosphere storage and specialized packing lines means exiting the market isn't as simple as selling off generic equipment.
Furthermore, long-term contracts with growers create a sticky situation. These agreements, often spanning multiple harvest seasons, lock companies into ongoing commitments, making a swift departure financially unviable. This contractual obligation can also lead to persistent overcapacity if demand falters, as companies are contractually bound to purchase produce.
Established distribution networks are another major hurdle. Building and maintaining relationships with retailers, wholesalers, and logistics providers takes years and significant investment. Divesting these networks is complex and often yields a poor return, forcing companies to remain operational even during periods of intense price competition. In 2023, Calavo reported its revenue was $1.19 billion, reflecting the scale of operations tied to these networks.
- Specialized Assets: Investment in ripening technology and cold chain infrastructure.
- Long-term Grower Contracts: Commitments that restrict operational flexibility.
- Distribution Networks: Established relationships with buyers and logistics providers.
- Market Presence: The cost and difficulty of exiting a mature, competitive market.
Calavo operates in a highly competitive environment with numerous players, from large corporations to smaller regional distributors, all vying for market share. The global avocado market's rapid expansion, projected to reach USD 21.8 billion by 2030, attracts new entrants and intensifies existing rivalries. This dynamic means companies like Calavo must constantly innovate and focus on efficiency to maintain their position.
The market's commodity nature in many segments leads to price-based competition, especially for less differentiated products. Calavo counters this by emphasizing quality, global sourcing reliability, and value-added services like custom packaging and ripening. Despite these efforts, the pressure to move perishable inventory quickly, driven by significant fixed costs in specialized infrastructure, often results in aggressive pricing strategies across the industry.
Calavo's competitive landscape is further shaped by the presence of private-label brands and the sheer volume of imports, particularly into key markets like the U.S. in 2024. This broad spectrum of competition necessitates a strategic approach that balances operational efficiency with distinct value propositions to stand out.
The intensity of rivalry is amplified by high barriers to exit, including specialized assets and long-term grower contracts, which keep companies invested even during challenging periods. Calavo's 2023 revenue of $1.19 billion underscores the scale of operations tied to these market realities.
| Factor | Impact on Rivalry | Calavo's Response |
| Market Growth | Increased competition due to new entrants | Focus on differentiation and efficiency |
| Commodity Nature | Price-based competition | Emphasis on quality and value-added services |
| Perishability | Pressure for high volumes and quick sales | Optimized logistics and supply chain management |
| Private Labels & Imports | Market fragmentation | Strengthening brand and sourcing capabilities |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Consumers increasingly prioritize healthy eating, and the market offers a wide variety of nutritious alternatives to avocados. For instance, berries, known for their antioxidant properties, and bananas, a good source of potassium, provide comparable nutritional value and can easily be incorporated into daily diets as substitutes. In 2024, the global fruit and vegetable market continued its robust growth, with consumers actively seeking out diverse healthy options, directly impacting the demand for specific products like avocados.
For Calavo's processed avocado products like guacamole and avocado pulp, a significant threat comes from alternative processed food items and spreads. These substitutes, ranging from other dips and salsas to convenience foods made from various vegetables or dairy, can easily capture consumer interest and spending. The sheer variety available in the market means consumers have many choices if Calavo's products become too expensive or less appealing.
The threat of substitutes for Calavo's avocado products is largely determined by how substitutes stack up in terms of price and what consumers believe they are getting. If other healthy snacks or even processed spreads can deliver similar nutritional benefits or taste for less money, consumers might easily switch away from avocados.
For instance, in 2024, the average retail price for Hass avocados fluctuated, but if alternatives like Greek yogurt-based dips or other fruit purees consistently offered a lower cost per serving with comparable health claims, Calavo would face increased pressure. Consumers are always looking for the best bang for their buck, and a significant price advantage for a substitute could erode Calavo's market share.
Shifting Consumer Preferences and Dietary Trends
Shifting consumer preferences and evolving dietary trends pose a significant threat of substitutes for avocados. For instance, the rise of low-fat diets or increased adoption of alternative healthy fat sources like nuts and seeds could directly impact avocado demand. In 2024, the global market for plant-based diets continued to expand, with projections indicating further growth, potentially diverting consumers from traditional options like avocados.
A decline in avocado consumption, perhaps due to changing health perceptions or a surge in popularity of other nutrient-dense foods, would amplify the substitution threat. Consumers are increasingly seeking diverse nutritional profiles, and if avocados are perceived as less beneficial compared to emerging superfoods, their market share could erode.
- Growing popularity of plant-based diets: Increased consumer adoption of vegan and vegetarian lifestyles in 2024 directly impacts demand for animal products but also influences choices within plant-based categories, potentially favoring other healthy fats.
- Emergence of alternative healthy fat sources: The market for nuts, seeds, and their butters (e.g., almond butter, tahini) has seen robust growth, offering consumers diverse options for healthy fats.
- Shifting health perceptions: While avocados are generally viewed positively, any negative health reports or trends focusing on specific macronutrient ratios could lead consumers to seek alternatives perceived as more aligned with their dietary goals.
- Innovation in food products: New product development in the healthy snack and meal replacement sectors could introduce compelling substitutes that offer similar nutritional benefits or convenience to avocados.
Innovation in Food Technology and Ingredients
The threat of substitutes for Calavo Growers, particularly concerning avocados, is evolving due to advancements in food technology. Innovations in food science are leading to the creation of ingredients and products that can replicate the taste, texture, and nutritional benefits of avocados, potentially at a lower cost or with improved shelf stability.
These emerging alternatives could significantly impact Calavo's market share. For instance, plant-based dairy alternatives have seen substantial growth, and similar innovations in savory applications could offer direct substitutes for avocado's culinary uses. The market for plant-based foods, a category where such substitutes would likely emerge, was projected to reach $162 billion globally by 2030, indicating a substantial and growing competitive landscape.
- Technological Advancements: Research into cellular agriculture and precision fermentation could yield avocado-like fats and flavors without traditional cultivation.
- Cost and Shelf-Life Advantages: Successful substitutes would likely offer cost efficiencies or longer shelf lives compared to fresh avocados, which are perishable and subject to price volatility.
- Consumer Acceptance: The adoption rate of these novel food technologies will be crucial; early successes in plant-based meats and dairy suggest a growing consumer openness to alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Calavo's avocado products is significant, driven by consumers' increasing health consciousness and the availability of diverse nutritious alternatives. In 2024, the global fruit and vegetable market continued its expansion, with consumers actively seeking a variety of healthy options, which can divert demand from avocados towards other nutrient-rich foods like berries and bananas.
For Calavo's processed items like guacamole, substitutes include a wide array of other dips, spreads, and convenience foods. These alternatives, often made from different vegetables or dairy, compete directly for consumer spending and attention. If Calavo's offerings become less appealing or more expensive, consumers have readily available choices.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by innovations in food technology, which are creating ingredients that mimic the taste, texture, and nutritional benefits of avocados. These emerging alternatives could offer cost advantages or improved shelf stability, posing a direct challenge to Calavo's market position.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Competitive Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient-Rich Fruits | Berries, Bananas | Nutritional value, versatility in diet |
| Healthy Spreads & Dips | Greek yogurt dips, hummus, nut butters | Price per serving, taste, perceived health benefits |
| Plant-Based Alternatives | Avocado oil-based products, other vegetable purees | Cost, shelf-life, technological innovation, consumer acceptance |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the avocado and fresh produce market, like the one Calavo operates in, demands considerable financial resources. Companies need to invest heavily in land for cultivation if they are vertically integrated, or secure reliable supply chains. Building advanced packing houses, ripening centers, and ensuring a seamless cold chain for distribution are also significant capital outlays.
These high initial costs create a substantial barrier, effectively deterring many potential new competitors from entering the industry. For instance, establishing a modern packing facility alone can cost millions of dollars, not to mention the ongoing expenses for logistics and quality control.
The need for extensive capital for infrastructure and operations means that only well-funded entities can realistically consider entering this sector. This financial hurdle significantly limits the threat of new entrants, providing a degree of protection for established players like Calavo.
Calavo's established distribution channels and relationships represent a significant barrier to new entrants. The company boasts deeply entrenched ties with a wide array of growers, major retailers, foodservice operators, and club stores, built over years of consistent service and reliability.
New competitors would struggle immensely to replicate this extensive network and secure the necessary shelf space or supply agreements with these critical customers. For instance, Calavo's strong partnerships with major grocery chains, which account for a substantial portion of fresh produce sales, are difficult for newcomers to penetrate.
Calavo's established brand loyalty, built on years of consistent quality and food safety, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. New companies would need to invest heavily in marketing and cultivating trust with both suppliers and consumers to even begin to challenge Calavo's market position.
Regulatory Hurdles and Food Safety Standards
The fresh produce and processed food sectors face significant regulatory burdens. New companies must meticulously adhere to complex rules covering food safety, quality assurance, import/export procedures, and environmental impact. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) enforces the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), which imposes strict preventive controls on food producers, adding substantial compliance costs and operational complexity for any new entrant.
Navigating these intricate regulatory landscapes requires obtaining numerous certifications and permits, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive. These hurdles effectively raise the barrier to entry, as new businesses must invest heavily in compliance infrastructure and expertise before they can even begin competing.
- Regulatory Complexity: Stringent food safety, quality, import/export, and environmental regulations create significant compliance challenges.
- Cost of Compliance: New entrants face substantial upfront investments in meeting regulatory standards and obtaining necessary certifications.
- Time to Market: The lengthy process of navigating regulatory approvals can delay market entry for new competitors.
- FSMA Impact: The FDA's Food Safety Modernization Act mandates preventive controls, increasing operational burdens and costs for food producers.
Economies of Scale in Sourcing and Logistics
Economies of scale in sourcing and logistics present a significant barrier for new entrants in the avocado industry, much like for established players such as Calavo. These existing companies leverage their sheer volume to secure preferential pricing for avocados and other produce globally. In 2024, for instance, major distributors often negotiate contracts that lock in lower per-unit costs due to their substantial purchasing power.
Furthermore, the intricate and expansive logistics networks required for fresh produce distribution are incredibly capital-intensive to replicate. Building out the necessary cold chain infrastructure, transportation fleets, and warehousing capabilities to match industry leaders would demand immense upfront investment. This makes it difficult for newcomers to achieve the same cost efficiencies in getting products to market, creating a substantial hurdle.
- Global Sourcing Advantage: Large companies like Calavo can negotiate better prices due to their high-volume purchases of avocados and other produce.
- Logistics Network Efficiency: Established players benefit from optimized, scaled logistics and distribution networks, reducing per-unit delivery costs.
- Capital Investment Barrier: New entrants face significant upfront costs to build comparable sourcing and logistics infrastructure, hindering their ability to compete on price.
The threat of new entrants into the avocado and fresh produce market remains moderate due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for cultivation, packing, and distribution, coupled with established distribution networks and brand loyalty, deter many potential competitors. Stringent regulatory compliance, particularly concerning food safety, further elevates the cost and complexity for newcomers.
Economies of scale in global sourcing and logistics provide established players like Calavo with a distinct cost advantage. New entrants would need substantial investment to replicate these efficient networks and achieve comparable pricing power. For instance, in 2024, major distributors' bulk purchasing power significantly impacts unit costs for produce.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for land, facilities, and cold chain logistics. | Substantial financial hurdle, limiting entry to well-funded firms. |
| Distribution Networks | Established relationships with growers, retailers, and foodservice operators. | Difficult for newcomers to replicate, hindering market access and shelf space. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Years of consistent quality and food safety build consumer trust. | Requires significant marketing investment and time to build comparable credibility. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex rules for food safety (e.g., FSMA), quality, and import/export. | Increases operational costs, time to market, and requires specialized expertise. |
| Economies of Scale | Volume-based cost advantages in sourcing and logistics. | New entrants struggle to match price competitiveness without similar scale. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Calavo Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, Calavo's own annual filings, and publicly available financial statements of key competitors.
