Bunka Shutter Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bunka Shutter Bundle
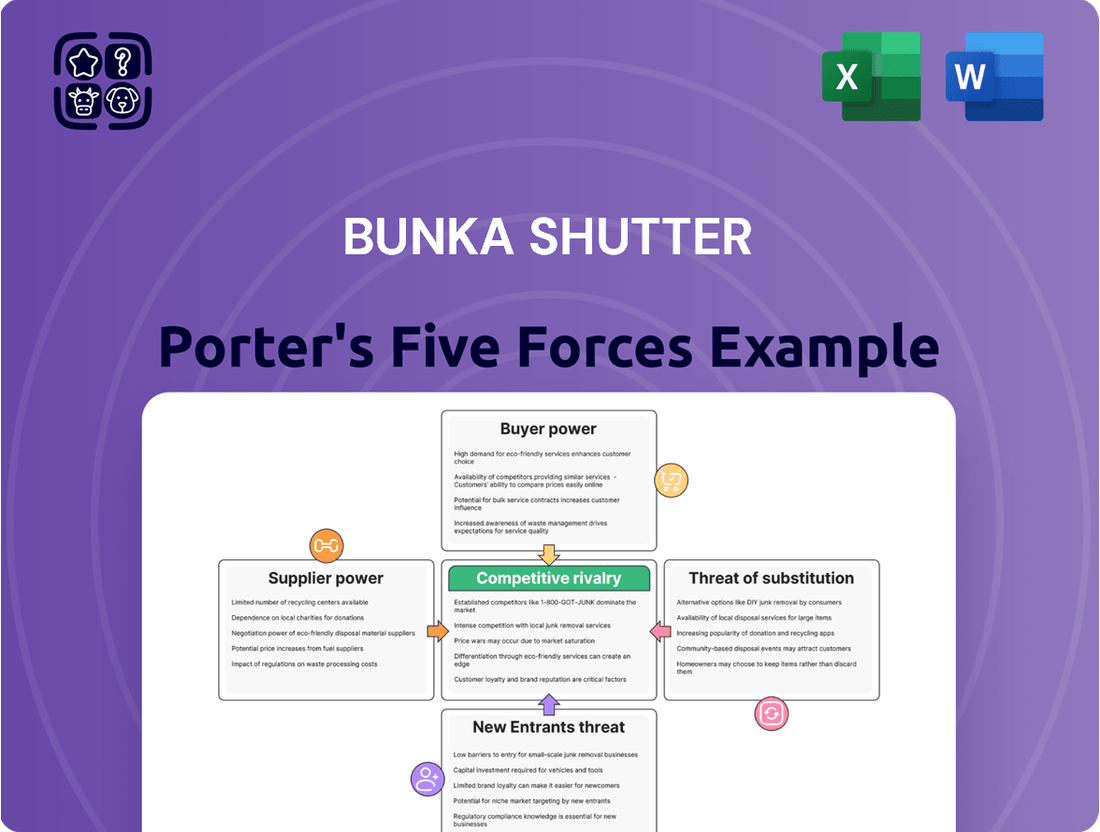
Bunka Shutter operates within a dynamic market, and a Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intricate web of competitive pressures they face. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Bunka Shutter’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The price and consistent supply of essential raw materials like steel, aluminum, and specialized plastics are critical for Bunka Shutter. If these materials become scarce or are dominated by a limited number of powerful suppliers, Bunka Shutter faces the risk of significantly increased costs, which directly impacts its profit margins.
The stability of global commodity markets plays a huge role here. For instance, steel prices saw considerable volatility in 2023, with some benchmarks experiencing fluctuations of over 15% within months, directly affecting manufacturing input costs for companies like Bunka Shutter.
Ongoing supply chain disruptions, a persistent issue in recent years, also contribute to this supplier power. These disruptions can lead to material shortages and price hikes, forcing Bunka Shutter to absorb higher costs or pass them on to consumers, potentially impacting sales volume.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Bunka Shutter is significantly influenced by component specialization. Consider the advanced electronic controls and specialized glass that are increasingly integrated into modern shutter and door systems. If these critical components are proprietary or sourced from a very small pool of manufacturers, those suppliers hold substantial leverage.
This leverage is amplified when switching costs are high. For instance, if Bunka Shutter relies on unique, custom-designed electronic modules, retooling or finding alternative suppliers for these specialized parts can be both time-consuming and expensive. This is particularly relevant given the growing demand in Japan for smart building technologies, which often necessitate highly specific and integrated electronic components.
The availability and cost of skilled labor are crucial factors impacting Bunka Shutter's operational costs and project timelines. In 2024, the construction sector, including specialized areas like shutter manufacturing and installation, continued to face persistent labor shortages. This scarcity directly translates to higher wage demands and increased recruitment expenses for Bunka Shutter, as companies compete for a limited pool of qualified workers. These rising labor costs can significantly affect the company's profitability and its ability to secure competitive pricing for its products and services.
Technology and IP Providers
Bunka Shutter's reliance on external technology and intellectual property (IP) providers significantly influences its bargaining power. If the company heavily depends on specific software, advanced automation systems, or unique patented designs from a limited number of suppliers, these providers can leverage their position to dictate pricing and terms. For instance, in 2024, the increasing demand for smart building integration and IoT capabilities in construction materials means companies like Bunka Shutter may need specialized, proprietary technologies. A dependence on a few key IP holders for these innovations could restrict Bunka Shutter's ability to independently develop new features or negotiate favorable costs, directly impacting its competitive edge and profitability.
- High Dependency on Specialized Software: If Bunka Shutter requires proprietary software for its advanced door systems or manufacturing processes, and only a few firms offer such solutions, those firms gain considerable leverage.
- Licensing of Patented Designs: Dependence on licensed patented designs for unique architectural features or security mechanisms from external entities can lead to royalty payments that increase costs.
- Smart Building Technology Integration: As the market increasingly demands IoT-enabled and smart-connected building components, reliance on specific technology providers for these integrations can consolidate supplier power.
- Limited Innovation Autonomy: When crucial innovative features are tied to external IP, Bunka Shutter’s capacity for independent R&D and cost reduction strategies related to those features is curtailed.
Supplier Concentration and Switching Costs
Bunka Shutter's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by the concentration of its key input providers and the associated switching costs. If Bunka Shutter relies on a limited number of specialized suppliers for critical components, those suppliers gain leverage. For instance, if a particular type of high-strength aluminum or a specialized motor component is only available from one or two manufacturers, these suppliers can dictate terms more effectively.
The costs involved in switching suppliers also play a crucial role. Significant expenses related to re-qualifying new suppliers, retooling manufacturing lines, or redesigning products to accommodate different components can deter Bunka Shutter from seeking alternatives. This inertia strengthens the position of incumbent suppliers, as the effort and investment required to change can be substantial.
To counter this, Bunka Shutter might employ strategies such as diversifying its supplier base for critical inputs, even if it means slightly higher initial costs. Exploring alternative materials or components that are more readily available from a wider range of suppliers can also reduce dependence. For example, in 2024, the global automotive industry saw increased efforts to secure raw materials like lithium and cobalt from multiple sources to mitigate supplier concentration risks.
- Supplier Concentration: A limited number of suppliers for essential components grants them greater pricing and negotiation power.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with changing suppliers, including retooling and requalification, increase supplier leverage.
- Mitigation Strategies: Diversifying sourcing and exploring alternative materials are key tactics to reduce supplier power.
- Industry Example: In 2024, industries faced challenges with critical material sourcing, highlighting the importance of supplier diversification.
The bargaining power of Bunka Shutter's suppliers is substantial, particularly when dealing with specialized components and proprietary technology. A prime example is the increasing demand for smart building integration and IoT capabilities, which often require specific, patented technologies from a limited number of providers. In 2024, this reliance on key IP holders for innovations could significantly restrict Bunka Shutter's ability to negotiate favorable costs for these essential, advanced features.
High switching costs further solidify supplier leverage. If Bunka Shutter has invested heavily in custom-designed electronic modules or specialized manufacturing processes tied to a particular supplier, the expense and time involved in finding and integrating alternatives become prohibitive. This situation is exacerbated by the ongoing global shortage of skilled labor in manufacturing and technology sectors, which drives up costs for specialized inputs and services.
For instance, the scarcity of advanced microcontrollers, crucial for the smart functionalities increasingly sought in modern construction, saw price increases of up to 20% in certain markets during early 2024, directly impacting companies like Bunka Shutter that depend on these components. This concentration of specialized suppliers, coupled with significant barriers to switching, allows them to exert considerable influence over pricing and terms for Bunka Shutter.
What is included in the product
This analysis uncovers the competitive forces impacting Bunka Shutter, detailing the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the shutter industry.
Visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with an intuitive dashboard, instantly highlighting areas of strategic pressure.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers for Bunka Shutter is significantly influenced by their volume and purchase frequency. Large commercial developers or government entities, for instance, represent substantial purchase volumes. Their ability to consolidate orders gives them considerable leverage to negotiate lower prices or more favorable contract terms, directly impacting Bunka Shutter's profitability on these deals.
Conversely, a customer base dominated by individual residential clients, characterized by numerous small, infrequent purchases, dilutes individual customer bargaining power. While the collective volume might be significant, the lack of concentrated purchasing power means fewer opportunities for individual customers to dictate terms, thus strengthening Bunka Shutter's pricing flexibility in this segment.
Bunka Shutter's product strategy significantly influences customer bargaining power. If their shutters are highly standardized, like basic residential models, customers can readily compare prices across different manufacturers. This ease of comparison, particularly for identical products, empowers customers to demand lower prices or better terms, as switching suppliers incurs minimal cost or disruption.
Conversely, for complex projects such as large-scale industrial facilities or unique architectural designs, Bunka Shutter likely offers customized solutions. These bespoke offerings, tailored to specific site requirements or aesthetic preferences, inherently increase switching costs for customers. The investment in unique specifications and potential integration challenges with alternative suppliers means customers have less leverage to dictate terms, as finding a perfect substitute becomes difficult and costly.
In 2024, the construction industry saw a continued demand for both standardized and customized building components. While the overall market for standard shutters remains competitive, the value of specialized, project-specific solutions, particularly in commercial and infrastructure development, allows companies like Bunka Shutter to command higher margins and mitigate customer price pressure due to the inherent switching barriers.
Customer price sensitivity for Bunka Shutter products is a significant factor. With readily available online information and the ease of obtaining multiple quotes from competing shutter manufacturers, customers possess increased bargaining power. This transparency allows them to compare prices effectively, driving down potential margins for any single supplier.
The economic climate, particularly rising construction costs and general inflation observed through 2024, further amplifies customer price sensitivity. As material and labor expenses climb, clients become more discerning about expenditures, actively seeking the best value. This heightened awareness of costs translates directly into stronger negotiation leverage for customers when purchasing shutters.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for customers of Bunka Shutter are a key factor influencing their bargaining power. These costs can manifest in various forms, including the expense of redesigning building elements to accommodate a new supplier's products, the cost of retraining staff on different operating systems, or dealing with compatibility issues if existing infrastructure is not readily adaptable to alternative shutter solutions. For instance, a large commercial building with a complex, integrated security and access control system linked to its shutters might face significant costs in switching to a new provider.
Higher switching costs effectively lock customers into Bunka Shutter's offerings, thereby diminishing their ability to negotiate favorable terms. Conversely, if the process of changing suppliers is relatively straightforward and inexpensive, customers are more empowered to seek out better pricing or service from competitors. This is particularly relevant in markets where shutter systems are more standardized and less integrated into a building's core functions.
- Redesign Expenses: Costs associated with modifying existing structures or layouts to fit a competitor's products.
- Retraining Costs: Investment in training personnel to operate and maintain new shutter systems.
- Compatibility Issues: Expenses incurred to ensure new shutters work seamlessly with existing building infrastructure, such as access control or fire suppression systems.
- Information Costs: Time and effort spent researching and evaluating alternative suppliers and their products.
Backward Integration Potential of Customers
Customers' potential for backward integration, meaning their ability to produce shutters, doors, or partitions themselves, represents a significant aspect of their bargaining power. For very large construction firms or developers, especially those with substantial project volumes, the incentive to bring manufacturing in-house can arise if the cost of sourcing from external suppliers like Bunka Shutter becomes prohibitively high or if supply chain reliability is a major concern. While this is less common for highly specialized or customized products, the latent threat of in-house production or acquisition of a manufacturer can exert considerable pressure on suppliers.
Consider the scale of major developers. For instance, in 2024, major global real estate developers often manage projects worth billions of dollars annually. If a developer's annual spend on shutters and partitions reaches tens or hundreds of millions, the economics of establishing their own manufacturing capabilities, even on a limited scale, become more viable. This capability directly translates to increased bargaining power, as they can credibly threaten to reduce or eliminate their purchases from Bunka Shutter if terms are not favorable.
- In-house production feasibility: Large construction conglomerates might possess the capital and engineering expertise to establish their own manufacturing lines for standard door and partition systems.
- Acquisition potential: A financially strong developer could acquire a smaller, struggling shutter manufacturer to secure supply and integrate operations, thereby neutralizing external supplier power.
- Cost sensitivity: Fluctuations in raw material costs impacting shutter prices can drive large buyers to explore internal production if it promises greater cost stability.
- Strategic control: For critical project components, some developers may seek direct control over manufacturing to ensure quality and timely delivery, especially on large-scale urban development projects.
The bargaining power of customers for Bunka Shutter is influenced by the availability of substitutes and the degree of product differentiation. When customers can easily find similar shutters from numerous competitors, especially for standard models, their power increases, as they can switch suppliers with minimal effort or cost. This is particularly evident in the residential market where product features might be less complex.
Conversely, Bunka Shutter's ability to offer unique designs, advanced features, or integrated solutions for specialized applications, such as high-security or fire-rated shutters, can reduce customer bargaining power. These differentiated products often come with higher switching costs for the customer, making them less likely to seek alternatives purely on price.
In 2024, the market for building materials saw continued innovation, with some manufacturers introducing smart shutters with integrated automation and security features. This trend towards technological differentiation allows companies like Bunka Shutter to command a premium and reduces the customer's ability to substitute with standard, less advanced options.
The bargaining power of customers is also shaped by their perception of Bunka Shutter's brand reputation and the quality of its products. A strong brand associated with reliability and superior performance can reduce customers' sensitivity to price, as they may prioritize quality and trust over cost savings. This psychological factor can significantly dampen customer bargaining power, even if alternatives exist.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Bunka Shutter Context |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High power when substitutes are numerous and similar. | High for standard shutters, lower for specialized or customized solutions. |
| Product Differentiation | Low power when products are unique or have high switching costs. | Bunka Shutter can differentiate through design, features, and integration. |
| Brand Reputation & Quality Perception | Low power when customers value brand trust and quality. | A strong reputation for durability and performance can reduce price sensitivity. |
| Customer Price Sensitivity | High power when customers are highly focused on cost. | Amplified by readily available price comparisons and economic conditions in 2024. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Bunka Shutter Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Bunka Shutter, detailing the competitive landscape, threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. This in-depth analysis is crucial for understanding the strategic positioning and potential challenges within the shutter industry for Bunka Shutter.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Bunka Shutter operates in a market characterized by significant competition, holding the second position in Japan's domestic shutter sector. This implies a concentrated industry structure where a few dominant players, including Bunka Shutter, vie for market share. The presence of other specialized building material manufacturers and larger, diversified conglomerates further intensifies this rivalry, as these entities often possess substantial resources and broader product portfolios.
The growth rate of the building materials market, especially for shutters, doors, and partitions, significantly shapes competitive rivalry within the industry. A robust market expansion generally means more opportunities for all players, potentially tempering intense competition for existing market share.
The Japanese construction materials market, where Bunka Shutter operates, is anticipated to see consistent growth. This expansion is fueled by ongoing urbanization, substantial infrastructure development projects, and a continuous demand for building renovations. For instance, the Japan construction sector's total value was estimated to be around ¥58.3 trillion in 2023, indicating a healthy market environment.
In such a growing landscape, the intensity of competition might be somewhat moderated. While companies still strive to capture market share, the expanding pie allows for more room for maneuver, potentially leading to less aggressive tactics compared to a stagnant or declining market. However, differentiation and innovation remain crucial for sustained success.
Bunka Shutter's competitive edge is significantly shaped by its product differentiation and ongoing innovation. The company distinguishes its offerings through unique features, superior quality, and advanced technology, particularly in smart building integration. This focus on unique value propositions helps to lessen the intensity of direct price wars with rivals.
In the dynamic Japanese market, continuous innovation is paramount. Bunka Shutter actively pursues advancements in smart features, enhanced security functionalities, and improved energy efficiency. These innovations serve as critical differentiators, allowing the company to maintain a strong market position.
For instance, Bunka Shutter's development of advanced automated door systems that integrate seamlessly with smart home and building management platforms sets them apart. This technological leadership, combined with a strong brand reputation built over decades, allows them to command a premium and reduce direct competitive pressures based solely on price.
Exit Barriers
Bunka Shutter faces significant exit barriers due to its substantial investments in specialized manufacturing facilities. These assets, designed for producing specific shutter and door systems, are not easily repurposed or sold, locking capital into the business. For instance, the company's extensive use of automated production lines and dedicated tooling represents a considerable fixed cost that makes exiting the market economically challenging.
These high fixed costs mean that companies like Bunka Shutter may continue operating even during periods of low profitability to avoid realizing substantial losses on their unrecoverable investments. This can prolong competitive pressure within the industry. In 2023, the global construction machinery market, which shares similar capital-intensive characteristics, saw significant investments in advanced manufacturing, indicating a trend of rising exit barriers across related sectors.
- Specialized Assets: Bunka Shutter's manufacturing plants are tailored for shutter production, limiting resale value or alternative use.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant capital expenditure on machinery and infrastructure creates a substantial cost burden for exiting.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term supply agreements or leases can further hinder a swift and cost-effective exit from the market.
Market Concentration and Balance
Bunka Shutter operates in a competitive landscape that features a mix of large, established players and smaller, specialized firms. The building materials sector, in general, has seen a trend towards consolidation and strategic partnerships, suggesting that market concentration can fluctuate. For instance, in the broader Japanese construction materials market, the top five companies by revenue accounted for approximately 45% of the total market share in 2023, indicating a moderate level of concentration.
The presence of both dominant firms and niche specialists creates a dynamic competitive rivalry. While large players may leverage economies of scale and brand recognition, smaller companies often compete on specialized product offerings or customer service. This balance means Bunka Shutter must continually innovate and adapt its strategies to maintain its market position.
- Market Structure: The building materials industry is characterized by a moderate degree of market concentration, with a few major players alongside numerous smaller, specialized companies.
- Competitive Dynamics: Bunka Shutter faces rivalry from both large-scale manufacturers with significant market share and niche providers offering specialized solutions.
- Industry Trends: Strategic alliances and consolidation are observable trends within the broader building materials sector, influencing the competitive intensity.
- Market Share Example: In 2023, the top five companies in the Japanese construction materials market held around 45% of the total market share, illustrating a degree of dominance by larger entities.
Bunka Shutter faces intense rivalry from both large, established competitors and smaller, specialized firms within Japan's building materials sector. The market's moderate concentration, where the top five companies held roughly 45% of the market share in 2023, means Bunka Shutter, as the second-largest player, must constantly innovate to differentiate itself.
The company's strategy of product differentiation through smart features and superior quality, evidenced by its advanced automated door systems, helps mitigate direct price competition. However, the ongoing growth in the Japanese construction market, valued around ¥58.3 trillion in 2023, fuels this competition by attracting more players and opportunities.
Bunka Shutter's significant investments in specialized manufacturing facilities also contribute to sustained rivalry, as high exit barriers discourage companies from leaving the market even during periods of lower profitability.
| Competitive Factor | Bunka Shutter's Position | Market Impact |
| Market Concentration | Second largest in Japan | Moderate rivalry; top 5 hold ~45% (2023) |
| Product Differentiation | Focus on smart features, quality | Reduces price-based competition |
| Market Growth | Benefiting from ~¥58.3 trillion market (2023) | Tempered rivalry, but attracts competition |
| Exit Barriers | High due to specialized assets | Sustains competitive pressure |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Bunka Shutter's products, primarily shutters, is significant and growing. These substitutes are not other shutter manufacturers, but rather alternative solutions that address the same core needs of security, privacy, and environmental control. Think about advanced alarm systems, reinforced glass, or even integrated smart home security technologies that offer a different approach to protecting a property.
The burgeoning Japan smart building market, which was projected to reach over ¥3 trillion by 2024 according to some market analyses, is a key indicator of this trend. As buildings become more technologically integrated, consumers and businesses are increasingly looking for comprehensive security and control systems that might bypass traditional shutters altogether. This growing demand for efficiency, sustainability, and enhanced security features within smart buildings creates a fertile ground for these alternative solutions to gain traction.
The threat of substitutes for Bunka Shutter's traditional doors and partitions is significant, especially with the rise of alternative building enclosure technologies. Innovative wall systems, such as those utilizing advanced insulation or integrated smart functionalities, can perform similar functions to traditional partitions. Furthermore, modular construction units offer a complete building enclosure solution, potentially bypassing the need for separate door and partition components. In Japan, the market for prefabricated housing, a segment heavily reliant on modular construction, saw a steady growth trajectory leading up to 2024, indicating a strong preference for these alternatives.
Advanced glazing technologies, including dynamic glass that can change transparency or tint, present another substitute. These systems can function as both walls and visual barriers, reducing the demand for conventional partitions. The increasing focus on energy efficiency and smart building integration in new construction projects further bolsters the appeal of these integrated solutions. For instance, the Japanese construction market has been increasingly adopting smart building technologies, with an estimated 15% of new commercial buildings incorporating some form of advanced glazing or smart wall systems by 2024.
The threat of substitutes for Bunka Shutter, particularly in the residential market, comes from customers opting for do-it-yourself (DIY) solutions or generic building materials. For simpler shutter and door applications, cost-conscious consumers might turn to mass retailers for unbranded products, bypassing specialized manufacturers. While complex industrial installations are less susceptible, the residential segment sees this as a viable alternative where price is a significant factor. For instance, the global DIY home improvement market was valued at over $120 billion in 2023, indicating a substantial customer base willing to undertake projects themselves.
Changing Architectural and Design Trends
Shifting architectural and design trends pose a significant threat to Bunka Shutter. As building aesthetics evolve, demand for traditional shutter types might decrease if new designs favor minimalist aesthetics or alternative window treatments. For instance, the increasing popularity of smart homes and integrated building management systems could lead to a preference for automated blinds or electrochromic glass over manual shutters.
Furthermore, a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental consciousness in construction could steer developers towards materials and solutions that align with these values. If Bunka Shutter’s product portfolio doesn't adapt to incorporate eco-friendly materials or energy-efficient designs, it risks being sidelined by competitors offering greener alternatives. This is particularly relevant as global green building certifications, like LEED, continue to gain traction, influencing material choices in major construction projects.
The rise of industrially produced materials such as steel, concrete, and advanced glass technologies also presents a substitution threat. These materials can offer different aesthetic qualities and functional benefits, potentially replacing the need for traditional shutters in certain applications. For example, large expanses of reinforced glass or modern facade systems might negate the requirement for external shutters in new commercial buildings.
Bunka Shutter must consider how these evolving preferences impact its market share. The construction industry saw global building material spending reach trillions of dollars in 2024, with significant investment in advanced materials. Adapting product development to align with these trends is crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
- Evolving Aesthetics: Modern architectural styles may reduce the demand for traditional shutter designs.
- Sustainability Focus: Increased preference for eco-friendly building materials and solutions could disadvantage products not aligned with green initiatives.
- Material Innovation: The adoption of advanced materials like steel, concrete, and specialized glass can directly substitute for shutter functions.
- Market Adaptation: Bunka Shutter needs to innovate its product line to meet changing consumer and industry demands driven by these trends.
Technological Obsolescence
Technological obsolescence poses a significant threat to Bunka Shutter. The risk of new technologies emerging that make traditional shutter and door mechanisms outdated is real. Imagine entirely new ways to manage light, privacy, or access that bypass physical barriers altogether, or advanced materials with integrated multi-functional properties, eliminating the need for separate components.
The swift advancement of smart building technologies in Japan underscores this potential disruption. For instance, by 2024, the smart home market in Japan was projected to reach over $10 billion, with a significant portion dedicated to integrated building management systems. These systems could eventually offer solutions that render conventional shutters less essential.
- Emerging Technologies: Innovations in dynamic glass, which can electronically tint or become opaque, present a direct substitute for traditional blinds and shutters.
- Smart Building Integration: As smart home and building automation become more prevalent, integrated solutions for environmental control could reduce reliance on discrete window coverings.
- Material Science Advancements: Development of self-healing or adaptive materials might offer new functionalities that replace the need for robust, mechanical shutter systems.
- Digital Access Controls: For security and access, advancements in biometric or digital key systems could lessen the importance of physical door locks and shutters.
The threat of substitutes for Bunka Shutter's products remains a significant concern, driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. Alternative solutions offering security, privacy, and environmental control are increasingly available, particularly within the burgeoning smart building sector. For instance, advanced alarm systems and integrated smart home technologies are gaining traction. The Japanese smart building market's projected growth beyond ¥3 trillion by 2024 highlights this trend, where comprehensive systems might supersede traditional shutters.
Furthermore, innovative wall systems and modular construction units present viable alternatives to conventional doors and partitions, especially in the growing prefabricated housing market in Japan. Advanced glazing technologies that offer dynamic tinting can also function as both walls and visual barriers, reducing the need for separate partition components. By 2024, it was estimated that around 15% of new commercial buildings in Japan incorporated such advanced glazing or smart wall systems, underscoring the shift towards integrated solutions.
DIY solutions and generic building materials also pose a threat, particularly in the residential market where cost is a primary driver. The global DIY home improvement market's valuation exceeding $120 billion in 2023 demonstrates a significant customer segment willing to opt for less specialized, more affordable alternatives. Bunka Shutter must remain agile in adapting its product offerings to counter these diverse and growing substitution threats.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Market Trend Indicator (Up to 2024) | Impact on Bunka Shutter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Home & Security Systems | Advanced alarm systems, integrated smart home technologies | Japan's smart building market projected over ¥3 trillion by 2024 | Reduced demand for traditional security features provided by shutters |
| Alternative Building Enclosures | Modular construction units, advanced insulated wall systems | Growth in Japan's prefabricated housing market | Bypass need for separate doors and partitions |
| Advanced Glazing | Electrochromic glass, dynamic tinting glass | Estimated 15% of new Japanese commercial buildings using advanced glazing by 2024 | Functions as walls and visual barriers, replacing partitions |
| DIY & Generic Materials | Mass-market unbranded shutters, readily available building materials | Global DIY market over $120 billion in 2023 | Price-sensitive customers opting for cheaper alternatives in residential sector |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the building materials manufacturing sector, particularly for a company like Bunka Shutter, demands substantial upfront capital. This includes investing in state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, advanced machinery, ongoing research and development for product innovation, and building robust distribution networks. These high capital requirements act as a significant barrier, making it difficult for new companies to challenge established players.
For instance, the global construction materials market size was valued at approximately USD 1.2 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow. Setting up operations to compete effectively within this vast market would necessitate millions, if not billions, in initial investment for plant and equipment alone. Bunka Shutter's existing, well-developed infrastructure and established supply chains present a considerable competitive advantage and a formidable hurdle for any potential new entrant aiming to gain market share.
Bunka Shutter benefits from significant brand loyalty and deeply entrenched relationships within the construction industry. These long-standing ties with contractors, architects, and developers are a substantial barrier to entry. New competitors would face the daunting task of investing heavily in marketing and sales to even begin building the trust that Bunka Shutter already commands, a process that is both costly and time-consuming.
Newcomers to the shutter industry face considerable hurdles in accessing established distribution channels. Bunka Shutter, for instance, benefits from a robust nationwide network of dealers and installers, a critical asset that takes years and substantial investment to build. Replicating this reach is a significant barrier, as new entrants must either negotiate with existing distributors who may favor established brands or invest heavily in creating their own sales infrastructure.
Regulatory Hurdles and Standards
New entrants in the shutter industry face substantial regulatory hurdles. Navigating complex building codes, stringent safety standards, and the need for various certifications for building materials can be a significant barrier. For instance, compliance with Japan's rigorous earthquake-resistant and energy-efficient building codes requires substantial investment and expertise, deterring many potential new players.
The time and cost associated with meeting these regulatory requirements are considerable. New companies must dedicate resources to understanding and implementing these often evolving standards, adding a layer of difficulty to market entry. Failure to comply can result in costly delays or outright rejection of products.
- Regulatory Complexity: Building codes and safety standards vary significantly by region and product type, demanding specialized knowledge.
- Certification Costs: Obtaining necessary certifications for materials and manufacturing processes can be expensive, often running into tens of thousands of dollars.
- Compliance Burden: Ongoing compliance with evolving regulations, such as those for fire safety or environmental impact, adds to the operational cost for new entrants.
- Market Access: Non-compliance can directly restrict market access, effectively blocking new companies from selling their products.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Bunka Shutter's proprietary technology and patents act as significant barriers to new entrants. The company holds numerous patents for its innovative shutter designs, automated opening mechanisms, and specialized manufacturing processes, which are crucial for maintaining product quality and operational efficiency.
These intellectual property rights make it difficult and expensive for new companies to replicate Bunka Shutter's advanced offerings. For instance, in 2024, Bunka Shutter continued to invest heavily in R&D, with a reported ¥12.5 billion allocated to developing next-generation smart home integration for its products, further solidifying its technological lead.
- Patented Designs: Bunka Shutter possesses exclusive rights to unique shutter and door configurations that offer enhanced durability, security, and aesthetics.
- Proprietary Manufacturing: The company utilizes specialized, patented manufacturing techniques that ensure high-quality production and cost efficiencies, difficult for newcomers to match.
- Technological Know-How: Decades of accumulated expertise in materials science, automation, and system integration provide Bunka Shutter with a distinct competitive edge.
- R&D Investment: Continued substantial investment in research and development, exemplified by their 2024 R&D budget, consistently creates new technological barriers.
The threat of new entrants in the shutter industry is moderate due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. Bunka Shutter's significant investments in manufacturing, R&D, and distribution, coupled with deep customer relationships, create substantial barriers. For example, the global construction materials market, valued around $1.2 trillion in 2023, demands immense initial investment to compete effectively.
New companies face challenges in replicating Bunka Shutter's extensive distribution networks and overcoming regulatory complexities, including adherence to Japan's stringent building codes. Accessing established channels is difficult, requiring either negotiation with distributors favoring incumbents or building a new sales infrastructure, a process that is both time-consuming and costly.
Bunka Shutter's proprietary technology and patents further deter new entrants, making it expensive to match their product innovation and manufacturing efficiencies. Their 2024 R&D allocation of ¥12.5 billion towards smart home integration underscores their commitment to maintaining a technological lead.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Bunka Shutter's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment needed for plants, machinery, and R&D. | Existing infrastructure and established supply chains. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Difficult to build trust with contractors and developers. | Long-standing ties and strong brand recognition. |
| Distribution Channels | Accessing nationwide networks is challenging and costly. | Robust nationwide dealer and installer network. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating complex building codes and certifications is time-consuming. | Expertise in complying with rigorous standards. |
| Proprietary Technology | Replicating patented designs and manufacturing processes is expensive. | Numerous patents and continuous R&D investment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bunka Shutter is built upon a foundation of publicly available company filings, including annual reports and investor presentations. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial information providers to gauge competitive intensity and market dynamics.
