BCB Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BCB Bank Bundle
Our initial look at BCB Bank's industry through Porter's Five Forces reveals a dynamic landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving customer expectations. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the financial sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping BCB Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BCB Community Bank, like many financial institutions, needs to tap into capital markets for funding beyond what its customers deposit. This means banks like BCB are subject to the bargaining power of suppliers such as investors and other banks that lend money in the interbank market.
The strength of these capital suppliers is directly tied to factors like current interest rates, how much money is readily available in the market (liquidity), and how confident investors feel about the banking industry's future. For instance, if interest rates rise significantly in 2024, the cost for BCB to borrow will increase, giving these suppliers more leverage.
Looking ahead to 2025, upcoming regulatory shifts and economic outlooks will be crucial in shaping both the cost and the sheer availability of this essential capital. A positive economic forecast might boost investor confidence, potentially lowering borrowing costs for BCB, while stricter regulations could limit access or drive up prices.
Technology providers, especially those offering specialized core banking systems, advanced cybersecurity, and innovative digital platforms, wield significant bargaining power in the current financial climate. BCB Community Bank's dependence on these critical services, particularly in areas like AI integration and robust data protection, allows these tech firms to influence pricing and contract terms.
The global cybersecurity market, for instance, was valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating increasing demand and a stronger position for providers of these essential services. Similarly, the market for digital banking platforms is experiencing rapid expansion, further solidifying the leverage of key technology suppliers.
The availability of skilled labor, especially in crucial banking sectors like lending, compliance, and technology, directly influences BCB Community Bank's operational expenses. A tight labor market, particularly in the competitive New Jersey and New York metropolitan areas where BCB is concentrated, can drive up wage expectations and recruitment costs.
This dynamic significantly enhances the bargaining power of employees, who are essentially the suppliers of essential labor to the bank. For instance, in 2024, the unemployment rate in New Jersey hovered around 3.5%, indicating a relatively tight labor market for many professions, including those BCB relies on.
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies like the Federal Reserve and FDIC, while not direct suppliers of goods, hold considerable power over BCB Bank. Their mandates for compliance, particularly in areas like AI and cybersecurity, impose significant operational costs. For instance, banks are expected to invest heavily in meeting evolving data privacy and security standards. In 2024, the cost of regulatory compliance for the banking sector continued to be a substantial expense, with many institutions allocating billions annually to meet these requirements.
The burden of adapting to new regulations, such as those emerging for artificial intelligence applications in banking, directly impacts BCB Bank's flexibility in resource allocation and strategic planning. This constant need to adapt and invest in compliance effectively acts as a cost imposed by these powerful oversight entities.
- Significant Compliance Costs: Banks face substantial expenses to meet federal and state regulatory requirements.
- Impact on Strategic Flexibility: Evolving regulations, especially in technology and security, can limit a bank's ability to innovate or reallocate resources.
- AI and Cybersecurity Focus: New regulatory scrutiny on AI and cybersecurity necessitates ongoing investment and adaptation.
- Indirect Supplier Power: Regulatory bodies dictate operational standards, influencing costs and business practices akin to supplier demands.
Deposit Funding Sources (Wholesale Deposits)
Beyond individual customer deposits, BCB Bancorp can tap into wholesale funding sources such as brokered deposits or institutional funds. The entities providing these funds wield bargaining power influenced by prevailing market interest rates and BCB's perceived creditworthiness. Intense competition for these wholesale deposits can escalate their cost, directly affecting the bank's net interest margin.
- Wholesale Funding Reliance: BCB Bancorp's use of brokered and institutional deposits means it relies on entities other than its retail customer base for capital.
- Market Rate Influence: The cost of these wholesale deposits is heavily tied to broader market interest rate movements, which are outside the bank's direct control.
- Creditworthiness Factor: The bank's financial health and reputation play a significant role in attracting these funds, as providers assess risk.
- Competitive Landscape: Other financial institutions also seeking wholesale deposits can drive up the price BCB Bancorp must pay, squeezing profitability.
Suppliers of capital, including investors and interbank lenders, hold significant bargaining power over BCB Community Bank. This power is amplified by factors such as rising interest rates, market liquidity, and investor confidence in the banking sector. For instance, the Federal Reserve's benchmark interest rate, which influences borrowing costs across the economy, saw multiple increases throughout 2023 and remained a key consideration for banks in 2024.
Technology providers are also powerful suppliers, especially for specialized core banking systems, cybersecurity, and digital platforms. BCB's reliance on these critical services, particularly for AI integration and data protection, allows tech firms to dictate terms and pricing. The global cybersecurity market alone was valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023, highlighting the essential nature and supplier leverage in this area.
The availability of skilled labor, particularly in areas like lending and compliance, directly impacts BCB's operational costs. A tight labor market, as seen in New Jersey and New York with unemployment rates around 3.5% in 2024, increases wage expectations and recruitment expenses, strengthening employee bargaining power.
Regulatory bodies, while not traditional suppliers, exert considerable influence by imposing compliance costs. Adapting to new rules, especially concerning AI and data privacy, requires significant investment, akin to supplier demands. The banking sector's annual spending on regulatory compliance often runs into billions, demonstrating the financial impact of these oversight entities.
| Supplier Type | Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on BCB | Example Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Providers (Investors, Lenders) | Interest Rates, Market Liquidity, Investor Confidence | Increased borrowing costs, reduced access to funds | Federal Reserve interest rate hikes throughout 2023; continued elevated rates in early 2024 |
| Technology Providers (Core Banking, Cybersecurity) | Dependence on specialized systems, demand for digital solutions | Higher pricing for essential services, specific contract terms | Global cybersecurity market ~$200 billion (2023); strong growth in digital banking platforms |
| Skilled Labor | Labor market tightness, demand for specialized banking skills | Increased wage expectations, higher recruitment costs | New Jersey unemployment rate ~3.5% (2024), indicating a tight labor market |
| Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Federal Reserve, FDIC) | Mandates for compliance, evolving standards (AI, Cybersecurity) | Significant operational costs for compliance, reduced strategic flexibility | Continued substantial annual investment in regulatory compliance across the banking sector |
What is included in the product
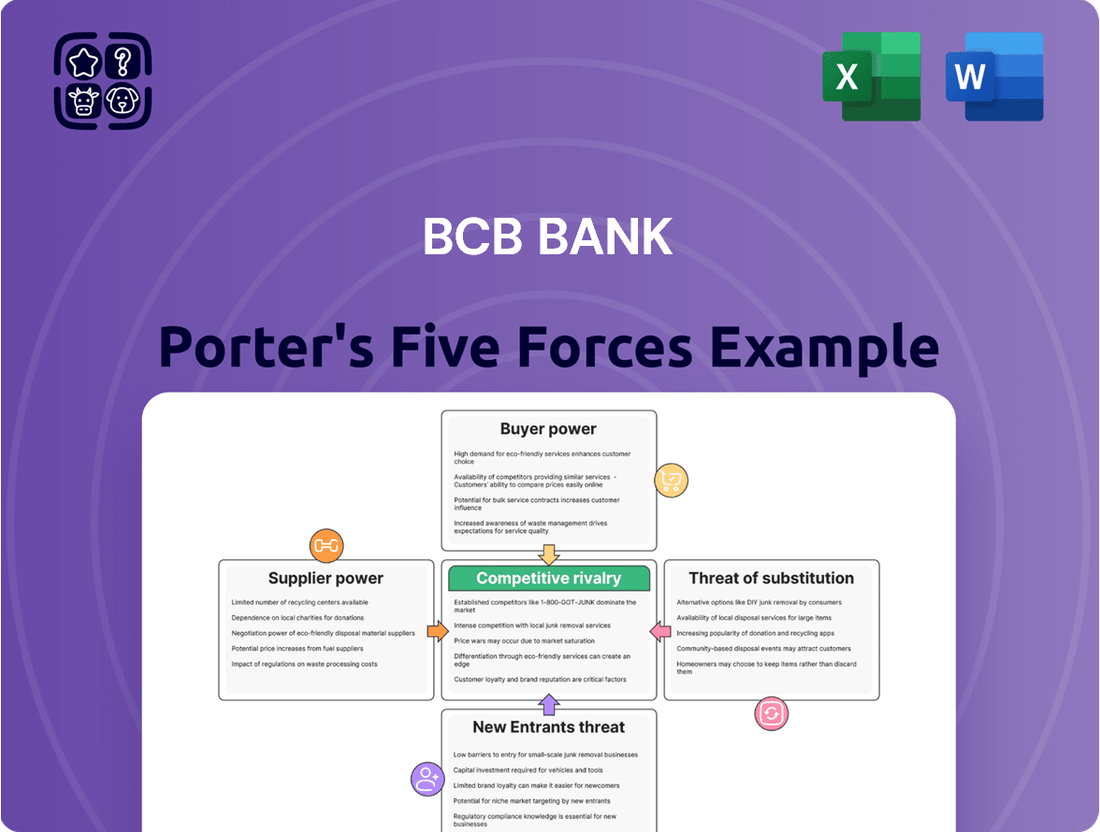
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for BCB Bank dissects the competitive landscape, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector.
BCB Bank's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces, perfect for quick decision-making and identifying key pain points in the banking landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the New Jersey and New York metropolitan areas face a highly competitive banking landscape. They have access to numerous options, from large national institutions to smaller regional banks and credit unions, all vying for their business.
This abundance of choice significantly amplifies customer bargaining power, especially concerning deposit accounts. For instance, as of mid-2024, average savings account rates across major banks hovered around 0.40%, while some online banks and credit unions were offering upwards of 4.50% APY for high-yield savings accounts, demonstrating the tangible impact of rate competition.
Consequently, customers can readily switch to institutions offering superior interest rates or enhanced services. This ability to easily move funds empowers them to demand better terms, putting pressure on banks like BCB Bank to remain competitive in their offerings to retain and attract deposits.
The bargaining power of customers for BCB Community Bank is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative lending sources. For loan products, customers can readily access funding from a diverse range of providers, including online lenders, credit unions, and even private equity firms for commercial financing.
This broad spectrum of alternatives, particularly evident in the mortgage and consumer loan markets, empowers customers to actively compare rates and terms. In 2024, the online lending sector continued its robust growth, with platforms offering streamlined application processes and competitive pricing, directly challenging traditional banks like BCB and diminishing their pricing power.
The proliferation of digital banking and fintech solutions significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. By offering seamless online account management, payment processing, and even loan origination, these platforms reduce customer dependence on traditional banks. For instance, by mid-2024, over 70% of banking transactions in developed economies were conducted digitally, a trend that empowers consumers to switch providers based on fees, interest rates, or service quality with greater ease.
Information Transparency and Access
Customers today enjoy unprecedented access to financial product information. Online comparison tools and financial news outlets provide detailed insights into interest rates, fees, and services offered by various banks. For instance, in 2024, platforms like Bankrate and NerdWallet saw significant user engagement as consumers actively sought the best banking deals.
This increased transparency directly empowers customers. They can easily compare BCB Bank's offerings against competitors, identifying more favorable terms or lower costs. This ability to shop around and leverage competitive pricing strengthens their position when negotiating or choosing a financial provider.
- Informed Decisions: Customers can now readily access data on average savings account yields, mortgage rates, and ATM fees across numerous institutions.
- Price Sensitivity: A 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of retail banking customers would switch providers for a 0.50% higher interest rate on savings.
- Leveraging Competition: The proliferation of fintech apps and comparison websites means BCB Bank faces constant scrutiny and pressure to remain competitive on pricing and service.
Customer Loyalty and Switching Costs
Customer loyalty and switching costs significantly influence the bargaining power of BCB Bank's customers. While moving accounts can involve some administrative effort, the actual financial and time costs associated with switching banks for basic services are often perceived as low. This ease of movement empowers customers to seek better rates or services elsewhere, thereby increasing their leverage.
For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of consumers reported being open to switching banks if offered better incentives. Data from a recent industry survey indicated that over 40% of retail banking customers would consider switching for a higher interest rate on savings accounts or lower fees. This suggests that BCB Bank must remain competitive to retain its customer base.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can often open new accounts and transfer funds with relative ease, minimizing disruption.
- Price Sensitivity: A considerable percentage of customers are motivated to switch by more attractive interest rates and fee structures.
- Digital Convenience: The rise of user-friendly online banking and mobile apps has further reduced the perceived effort involved in switching.
- Information Availability: Customers have easy access to comparative information on bank offerings, facilitating informed decisions to switch.
The bargaining power of BCB Bank's customers is substantial due to the highly competitive banking environment in the New Jersey and New York metropolitan areas. Customers have numerous alternatives, ranging from large national banks to smaller credit unions, all vying for their business, especially for deposit accounts where rate competition is fierce. For example, as of mid-2024, while major banks offered around 0.40% APY on savings, some online institutions were providing over 4.50% APY, highlighting the ease with which customers can secure better terms.
This ease of switching, coupled with readily available information on rates and fees through comparison websites, empowers customers to demand more favorable terms from BCB Bank. The rise of digital banking further reduces switching costs and increases customer leverage, as over 70% of banking transactions were digital in developed economies by mid-2024. Consequently, BCB Bank faces continuous pressure to remain competitive on pricing and service to retain its customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Numerous banks, credit unions, and online lenders offer similar products. |
| Information Accessibility | High | Comparison sites like Bankrate and NerdWallet are widely used. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Over 40% of customers would switch for better rates or lower fees. |
| Digitalization of Services | High | Over 70% of banking transactions are digital, facilitating easy account switching. |
Preview Before You Purchase
BCB Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact BCB Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the banking sector. You'll gain insights into the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes, all presented in a professionally formatted and ready-to-use document.
Rivalry Among Competitors
BCB Community Bank operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, particularly within the New Jersey and New York metropolitan areas. This region is teeming with financial institutions, from major national players to a vast array of regional and community banks, all vying for customer attention and capital. For instance, in 2023, the New York-New Jersey metropolitan area alone boasted hundreds of FDIC-insured institutions, creating a crowded marketplace.
The sheer density of competitors, including well-established entities like Valley National Bank and ConnectOne Bank, means BCB faces constant pressure on deposit rates and loan pricing. This intense rivalry necessitates strategic differentiation and aggressive market penetration tactics for BCB to effectively capture and retain market share.
Competitors are aggressively vying for market share by offering attractive interest rates on both deposits and loans, a strategy that directly impacts BCB Community Bank's profitability. For instance, in early 2024, several regional banks, responding to Federal Reserve rate adjustments, increased their savings account APYs to over 4.5%, putting pressure on established players to match or exceed these offers.
The financial landscape is also shaped by a rapid pace of product innovation, particularly in digital banking. New entrants and established rivals are rolling out user-friendly mobile apps, advanced payment solutions, and personalized financial management tools. This forces BCB Community Bank to invest heavily in technology to keep its digital offerings competitive, ensuring it doesn't lose customers to more agile competitors.
Competitive rivalry can be particularly fierce when players concentrate on specific niches or customer groups. For BCB Community Bank, this means facing intense competition from other community banks that also prioritize personalized service and deep understanding of their local areas.
For instance, many regional banks in BCB's operating areas, such as the Mid-Atlantic, specialize in serving small to medium-sized businesses or specific demographic segments, creating concentrated competitive pressure within those specific markets. In 2024, community banks continued to leverage their local presence to attract deposits and loan customers, often competing directly with larger national institutions on relationship-based banking.
Marketing and Brand Differentiation
Competitive rivalry in the banking sector, particularly in the New Jersey and New York markets where BCB Community Bank operates, is intense. Banks here pour significant resources into marketing and brand development to capture and keep customers.
To thrive, BCB Community Bank needs to carve out a distinct identity. This means excelling in service quality, actively participating in community initiatives, and offering unique products that set it apart from the substantial branding efforts of larger, more established financial institutions.
- Marketing Spend: In 2023, the US banking industry saw marketing expenditures rise, with larger banks often allocating hundreds of millions to advertising and brand campaigns.
- Brand Loyalty: While customer acquisition is key, retention is driven by trust and perceived value, areas where community banks can leverage their local ties.
- Differentiation Strategy: BCB's focus on community engagement and personalized service aims to build a loyal customer base, a crucial differentiator against national brands.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions have been a significant trend in the banking sector. For instance, in 2023, global M&A volume in financial services reached approximately $165 billion, indicating a robust environment for consolidation. This activity often results in larger, more powerful competitors emerging, capable of leveraging greater economies of scale and offering a wider array of services.
This consolidation directly impacts regional banks like BCB. As larger institutions merge, they gain enhanced market presence and operational efficiencies. This can create a more challenging landscape for smaller banks, potentially leading to increased pressure on pricing, customer acquisition, and service innovation.
- Increased Competition: Larger, merged entities can offer more competitive pricing and a broader product suite.
- Economies of Scale: Consolidated banks benefit from lower per-unit costs, giving them a cost advantage.
- Expanded Reach: M&A activity often leads to a wider geographical footprint and customer base for the acquiring bank.
BCB Community Bank faces intense rivalry from a multitude of financial institutions in its operating regions. This includes large national banks with extensive resources and numerous regional and community banks, all competing for customer deposits and loans. For example, as of Q1 2024, the average savings account yield across major US banks hovered around 4.0%, a figure that community banks often need to match or exceed to remain competitive.
The competitive pressure is amplified by aggressive pricing strategies, particularly on interest rates, and a rapid pace of digital innovation. Competitors are enhancing mobile banking platforms and offering new payment solutions, forcing BCB to invest in technology to retain its customer base. Many regional banks, like those in BCB's Mid-Atlantic service area, are also focusing on niche markets, such as small business lending, intensifying competition within those specific segments.
Mergers and acquisitions further consolidate the market, creating larger, more formidable competitors. In 2023, financial services M&A volume was substantial, meaning BCB must contend with entities that benefit from greater economies of scale and broader product offerings, putting pressure on BCB's pricing and service innovation.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Actions | Impact on BCB |
|---|---|---|
| National Banks | Aggressive marketing, broad product suite, digital investment | Pressure on pricing, need for strong digital offerings |
| Regional Banks | Competitive rates, relationship banking, niche specialization | Direct competition for specific customer segments, rate matching required |
| Community Banks | Local focus, personalized service, community engagement | Competition for loyal customer base, differentiation is key |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech companies, such as Square and PayPal, are increasingly offering services that directly compete with traditional banking. These platforms provide seamless digital payment solutions and peer-to-peer lending, often with lower transaction costs than established banks. For instance, in 2024, the global digital payments market was projected to reach over $10 trillion, highlighting the substantial customer base migrating to these fintech alternatives.
Credit unions pose a significant threat as substitutes, offering member-centric services and often more favorable rates on loans and deposits, directly competing for BCB Bank's individual customer base. For instance, in 2023, credit unions saw a substantial increase in membership, with over 1.5 million new members joining, highlighting their growing appeal.
Beyond credit unions, a diverse array of non-bank lenders, such as online mortgage providers and specialized commercial finance firms, present viable alternatives for borrowers. These entities streamline the lending process and cater to niche markets, thereby diminishing customer dependence on traditional banking institutions like BCB Bank for financing needs.
Direct investment platforms and robo-advisors present a significant threat by offering accessible, low-cost alternatives to traditional bank savings and wealth management. These digital solutions empower individuals to manage their investments directly, bypassing banks like BCB for their financial needs.
This shift diverts potential deposits and fee-based revenue away from BCB. For instance, the global robo-advisor market was valued at approximately $1.5 trillion in assets under management (AUM) by the end of 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong competitive force.
Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets present a potential, though currently limited, threat of substitution for traditional banking services. As these technologies mature, they could offer alternative stores of value and mediums of exchange, gradually impacting the demand for conventional currency and banking products.
While the widespread adoption of digital assets as a primary financial tool is still in its early stages, their growth cannot be ignored. For instance, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies, which experienced significant fluctuations throughout 2023 and into early 2024, still represents a substantial pool of value outside traditional financial systems. This evolving landscape means banks must monitor the development of blockchain technology and its potential to disintermediate certain banking functions.
- Evolving Landscape: Cryptocurrencies and digital assets are developing as potential alternatives to traditional financial services.
- Long-Term Potential: Over time, these digital assets could substitute for conventional stores of value and mediums of exchange.
- Current Impact: While the threat is nascent, the growing market capitalization of digital assets, exceeding trillions of dollars at various points in recent years, indicates a nascent but real shift in financial behavior.
- Banking Adaptation: Traditional banks need to observe and potentially adapt to the rise of blockchain technology and its implications for their core services.
In-House Corporate Financing and Treasury Management
Larger corporations can bypass traditional banking for certain needs. For instance, in 2024, the commercial paper market continued to be a significant source of short-term funding for many large businesses, allowing them to raise capital directly from investors rather than relying solely on bank credit lines. This internal capability reduces demand for BCB Bank's lending products.
Sophisticated treasury management systems also empower businesses to manage cash flow, optimize liquidity, and execute payments internally. Companies with robust treasury operations can reduce their reliance on banks for these essential financial functions, thereby diminishing the revenue streams BCB Bank might otherwise generate from cash management fees and services.
- Internal Financing Capacity: Businesses can issue their own commercial paper, a practice that saw significant activity in 2024, providing an alternative to bank loans.
- Sophisticated Treasury Management: Advanced in-house systems allow corporations to manage liquidity and payments, substituting for bank-offered cash management services.
- Reduced Reliance on Bank Services: The growth of these internal financial capabilities directly challenges the traditional role of commercial banks like BCB in serving large corporate clients.
The threat of substitutes for BCB Bank is substantial, with fintechs, credit unions, and non-bank lenders offering increasingly attractive alternatives for consumers and businesses. Direct investment platforms and robo-advisors also siphon off wealth management clients, while cryptocurrencies present a nascent but evolving challenge. Furthermore, large corporations can bypass traditional banking channels for funding and treasury services.
| Substitute Category | Key Offerings | Impact on BCB Bank | 2024/2023 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Companies | Digital payments, P2P lending | Reduced transaction fees, customer migration | Global digital payments market projected over $10 trillion in 2024 |
| Credit Unions | Member-centric services, better rates | Loss of individual deposits and loans | Over 1.5 million new credit union members in 2023 |
| Non-Bank Lenders | Streamlined loans, niche financing | Reduced demand for traditional lending products | N/A (General trend) |
| Direct Investment/Robo-Advisors | Low-cost investment management | Diversion of deposits and wealth management AUM | Global robo-advisor market ~$1.5 trillion AUM by end of 2023 |
| Corporations (Direct Funding) | Commercial paper, internal treasury | Lower demand for corporate lending and cash management | Commercial paper market significant source of short-term funding in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector faces substantial threats from new entrants due to significant regulatory barriers and capital requirements. New banks must navigate a complex web of licensing procedures and adhere to strict capital adequacy ratios, anti-money laundering (AML), and know your customer (KYC) regulations. These requirements, which are anticipated to intensify as regulators focus on financial stability through 2025, demand considerable upfront investment and operational expertise.
Establishing a new bank, like BCB Bank, demands significant upfront capital. This includes the costs associated with setting up physical branches, ATM networks, and crucially, sophisticated technology systems. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to open a new bank branch can range from $2 million to $5 million, depending on location and scale.
Even digital-first or neo-banks face substantial investments in robust IT infrastructure, including secure cloud computing, advanced data analytics platforms, and stringent cybersecurity measures to protect customer data. These essential technological outlays, often running into tens of millions of dollars, act as a considerable barrier, deterring many aspiring new entrants from entering the banking sector.
Existing banks, including BCB Community Bank, possess a significant advantage due to their long-standing brand recognition and the deep customer trust they have cultivated over many years. This established reputation makes it difficult for newcomers to attract and retain customers.
New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and customer service to build a comparable level of credibility and trust. For instance, in 2024, the average customer acquisition cost for financial services remained a substantial barrier, often exceeding $200, highlighting the expense involved in convincing consumers to switch from trusted institutions.
Deposit Gathering and Funding Challenges
New entrants into the banking sector face significant hurdles in gathering deposits, a crucial funding source. In highly competitive areas like New Jersey and New York, where established institutions already command strong customer loyalty, attracting a stable and cost-effective deposit base proves challenging for newcomers. This difficulty can force new banks to rely on more expensive wholesale funding, immediately placing them at a competitive disadvantage compared to incumbents with lower funding costs.
The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by these deposit gathering and funding challenges. For instance, as of Q1 2024, the average interest rate paid on deposits by community banks was around 1.8%, whereas wholesale funding sources could easily exceed 4.5% for shorter-term maturities, illustrating the significant cost differential.
- Deposit Acquisition Difficulty: New banks struggle to build a core deposit base against established competitors with strong brand recognition and existing customer relationships.
- Funding Cost Disadvantage: Reliance on wholesale funding, which is typically more expensive than retail deposits, increases operating costs for new entrants.
- Market Saturation: In mature banking markets, attracting new customers and their deposits requires substantial marketing investment and competitive product offerings.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
New entrants face significant hurdles in acquiring and retaining skilled banking talent, especially those with specialized knowledge in regional markets or specific lending sectors. Established institutions often possess deep talent pools and robust internal structures, making it challenging for newcomers to assemble a competitive team.
For example, in 2024, the U.S. banking industry continued to grapple with a shortage of experienced professionals in areas like cybersecurity and digital banking. A survey by the American Bankers Association indicated that over 60% of banks reported difficulty in finding qualified candidates for technology-related roles, a trend that directly impacts the ability of new entrants to establish a strong operational foundation.
- Talent Gap: New banks struggle to attract experienced professionals who are often committed to established institutions.
- Competitive Compensation: Incumbents can offer more attractive compensation and benefits packages, further hindering new entrants' recruitment efforts.
- Training Investment: The cost and time required to train new employees to meet industry standards represent a substantial barrier for startups.
The threat of new entrants in the banking sector, including for BCB Bank, is currently moderate. While high capital requirements and stringent regulations like KYC and AML present significant barriers, the rise of digital banking and fintech innovations offers potential avenues for new players. However, the need for substantial IT investment and cybersecurity measures remains a considerable hurdle.
Customer trust and brand loyalty are significant deterrents for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, customer acquisition costs in banking remained high, often exceeding $200 per customer, making it difficult for new banks to compete with established institutions that have cultivated long-standing relationships. This makes it challenging for newcomers to attract deposits, a vital funding source.
The difficulty in acquiring a stable deposit base, especially in competitive markets, forces new entrants to rely on more expensive wholesale funding. As of Q1 2024, the cost difference was stark, with community bank deposit rates around 1.8% versus wholesale funding potentially exceeding 4.5%. This funding cost disadvantage directly impacts profitability and competitiveness.
Furthermore, attracting and retaining skilled banking talent, particularly in specialized areas like cybersecurity and digital banking, poses another challenge. In 2024, over 60% of U.S. banks reported difficulties finding qualified tech professionals, a hurdle that disproportionately affects new entrants needing to build robust operational teams from scratch.
| Barrier | Estimated Cost/Challenge (2024 Data) | Impact on New Entrants |
| Regulatory Compliance & Licensing | Millions in legal and administrative fees | High upfront investment, time-consuming |
| Capital Requirements | Minimum capital ratios set by regulators | Substantial upfront capital needed |
| IT Infrastructure & Cybersecurity | Tens of millions for robust systems | Essential for operations and data protection |
| Customer Acquisition Cost | >$200 per customer | Difficulty in attracting customers from incumbents |
| Talent Acquisition (Tech Roles) | High demand, competitive salaries | Challenges in building skilled teams |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our BCB Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including the bank's annual reports, regulatory filings from financial authorities, and industry-specific market research reports to capture competitive dynamics.
