Asana Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Asana Bundle
Asana operates in a competitive SaaS landscape, facing threats from established rivals and emerging solutions. Understanding the intense rivalry among existing competitors and the bargaining power of buyers is crucial for Asana's strategic planning.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the nuanced pressures Asana faces, including the threat of new entrants and the availability of substitutes. Gain actionable insights to navigate Asana's market dynamics and secure a competitive edge.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Asana's reliance on cloud infrastructure, primarily from providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), presents a key area for supplier bargaining power. While AWS is a market leader, the presence of other major cloud platforms such as Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure offers Asana some flexibility and leverage in negotiating terms, preventing extreme supplier concentration.
The uniqueness of Asana's technology stack and the availability of specialized development talent also influence supplier power. If Asana depends on specific third-party software or highly niche expertise that is not readily available elsewhere, those suppliers could command greater influence over pricing and contract conditions.
For Asana, the costs associated with switching major cloud providers, while substantial, are not prohibitive with careful planning and dedicated investment. The complexity and expense of moving extensive data sets and retooling infrastructure are significant hurdles, but they are challenges that can be overcome.
However, the switching costs for Asana's software components and general talent pool are considerably lower. This is primarily because a wide array of tools and skilled professionals are readily accessible in the broader market, making transitions less burdensome in these areas.
The availability of numerous open-source software libraries and a wide array of third-party integrations significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any single supplier for Asana. This broad ecosystem means Asana can readily switch between different providers for components or functionalities without major disruption. For instance, the vast market for cloud infrastructure services, with major players like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, offers Asana considerable choice and negotiation leverage.
Furthermore, Asana’s investment in developing its own proprietary technologies, such as Asana AI and AI Studio, directly counters supplier power. By internalizing core innovation, Asana reduces its reliance on external entities for critical advancements, thereby strengthening its position. This strategic move allows Asana to control its product roadmap and maintain a competitive edge without being beholden to the pricing or terms of specialized external suppliers.
Impact of Supplier Inputs on Asana's Cost Structure
The bargaining power of suppliers can significantly influence Asana's cost structure, particularly concerning cloud hosting and essential talent. For instance, major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure hold considerable sway, as switching costs can be substantial. Efficient management of these infrastructure expenses is critical for Asana's journey towards non-GAAP operating profitability, a target set for fiscal year 2026.
Furthermore, the market for specialized engineering and product development talent is highly competitive, giving skilled individuals and specialized recruitment firms leverage. Asana's ability to attract and retain this crucial human capital directly impacts its innovation capacity and operational efficiency, thereby affecting its overall financial health.
- Cloud Infrastructure Costs: Asana's reliance on cloud services makes it susceptible to price increases from major providers.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention: The high demand for skilled tech professionals grants significant bargaining power to potential hires and recruitment agencies.
- Impact on Profitability: Managing these supplier-driven costs is paramount for Asana to achieve its profitability goals, such as non-GAAP operating profitability by FY2026.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by Asana's suppliers is generally low. Major infrastructure providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), a key cloud service provider for many SaaS companies including potentially Asana, are unlikely to directly enter the work management application space. Doing so would pit them against a significant portion of their existing clientele, a move that would likely alienate their customer base and disrupt their core business model.
While direct competition from infrastructure suppliers is improbable, there's a subtle risk. These providers might enhance their own integrated or proprietary tools. For example, AWS offers various collaboration and productivity services that could become more sophisticated. This could indirectly diminish Asana's unique value proposition or its perceived control over the platform's functionalities, making it harder for Asana to differentiate itself.
For instance, in 2024, cloud infrastructure spending continued to grow robustly, with hyperscalers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform dominating the market. AWS reported revenue of $65.2 billion for 2023, highlighting its substantial market position. This scale and investment in their own service ecosystems mean they have the resources to develop more integrated solutions, even if not directly competing with SaaS applications.
- Low Direct Integration Risk: Major cloud providers are unlikely to build full-fledged work management platforms due to conflicts with their customer base.
- Indirect Competitive Threat: Suppliers may enhance their own bundled tools, potentially reducing the perceived uniqueness of Asana's offering.
- Market Dynamics: The continued growth of cloud infrastructure spending in 2024, with companies like AWS seeing significant revenue increases, provides these suppliers with the capital to develop more advanced proprietary features.
Asana's bargaining power with suppliers is moderate, primarily influenced by the availability of multiple cloud infrastructure providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. While switching costs for cloud services are significant, the competitive landscape offers some leverage. The company's investment in proprietary AI technologies also reduces reliance on external software suppliers.
The market for specialized tech talent presents a greater challenge, as skilled professionals and recruitment agencies hold considerable sway. This dynamic directly impacts Asana's ability to control costs related to innovation and development, which is crucial for achieving its profitability targets, such as non-GAAP operating profitability by FY2026.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Level | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on Asana |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure (e.g., AWS, Azure) | Moderate | Availability of alternatives, switching costs, scale of providers | Influences hosting costs, critical for profitability targets |
| Specialized Talent (Engineers, Product Developers) | High | Demand for skills, competition for talent, recruitment agency influence | Affects innovation capacity, operational efficiency, and talent acquisition costs |
| Third-Party Software/Integrations | Low to Moderate | Availability of open-source alternatives, breadth of integrations, switching costs for components | Offers flexibility in technology stack, reduces reliance on single vendors |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Asana, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Asana's customer base spans a wide range, from small startups to massive corporations, directly impacting how sensitive customers are to pricing. Smaller businesses often have tighter budgets and actively seek out more affordable project management solutions.
Larger enterprises, however, tend to focus more on Asana's robust feature set, its ability to scale with their operations, its security protocols, and its seamless integration capabilities. For these clients, minor price fluctuations are less of a deciding factor than overall value and functionality.
Asana operates on a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) subscription model. This means they must consistently demonstrate and deliver value to their customers to encourage ongoing renewals and prevent churn. The perceived value must outweigh the recurring subscription costs.
The project management software market is brimming with options, meaning customers have a lot of choices when it comes to managing their work. This abundance of alternatives directly impacts Asana's bargaining power.
Competitors such as Monday.com, ClickUp, Trello, Wrike, and Microsoft Planner offer robust solutions. For instance, in 2024, the global project management software market was valued at approximately $6.2 billion, with significant growth projected. This competitive landscape empowers customers, as they can readily switch to a different platform if they find Asana's pricing, features, or customer support lacking.
While adopting a new work management tool like Asana initially requires learning and data transfer, the long-term costs to switch aren't excessively high. Many competing platforms offer comparable core features and integration options, simplifying the transition process for businesses.
However, for larger organizations deeply embedded in Asana's ecosystem, with significant historical data and workflows tailored to the platform, the switching costs can become more substantial. This creates a degree of customer loyalty, or stickiness, for Asana.
Customer Concentration and Size
Asana's customer concentration and size play a significant role in the bargaining power of its customers. The company reported having 726 customers spending $100,000 or more annually as of Q4 FY2025, which represents a 20% increase from the previous year. These larger clients, due to their substantial financial commitments, can exert considerable influence on Asana's pricing and service terms.
While these larger customers hold more sway, Asana's ability to retain them remains strong. The dollar-based net retention rate for Core customers stood at 97% in Q4 FY2025. This indicates that, despite the potential for increased customer bargaining power with growing contract values, Asana is largely successful in maintaining its revenue streams from its key accounts.
- Customer Growth: Asana saw a 20% year-over-year increase in customers spending $100,000+ annually, reaching 726 in Q4 FY2025.
- Bargaining Power Leverage: Larger clients can leverage their significant spending volume to negotiate better terms, posing a potential risk if they decide to switch providers.
- Retention Strength: Asana's dollar-based net retention rate for Core customers was 97% in Q4 FY2025, demonstrating resilience in keeping these valuable clients.
Customer Information Asymmetry
Customer information asymmetry has significantly decreased in the work management software sector. Buyers now have access to a wealth of data through online reviews, comparison platforms, and readily available free trials. This transparency enables them to thoroughly evaluate features, pricing structures, and overall user satisfaction across different vendors.
This heightened awareness directly impacts Asana's bargaining power with its customers. Well-informed clients can more easily identify alternatives that better suit their needs or offer superior value. For instance, reports from 2023 indicated that over 70% of B2B software buyers conduct extensive online research before making a purchase decision.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers can readily compare Asana’s offerings against competitors like Monday.com, ClickUp, and Wrike based on detailed feature sets and pricing tiers.
- Reduced Switching Costs Perception: The availability of cloud-based solutions and standardized data formats lowers the perceived cost and effort involved in migrating to a different platform.
- Price Sensitivity: With clear visibility into market pricing, customers are more likely to push for competitive rates or seek out providers offering more aggressive pricing models.
- Demand for Value: Customers can more accurately assess the return on investment (ROI) of work management tools, demanding demonstrable value and quantifiable benefits from their software investment.
Asana faces moderate bargaining power from its customers due to the competitive landscape and increasing customer awareness. While larger enterprise clients, representing significant revenue streams, can exert more influence on pricing and terms, Asana's strong retention rates suggest it effectively delivers value. The availability of numerous alternatives and transparent market pricing empowers customers to seek competitive options, though substantial integration into Asana can increase switching costs for some.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Asana's Response/Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Small Businesses | High price sensitivity, readily available alternatives | Focus on tiered pricing, free basic version |
| Large Enterprises | Significant spending volume, potential for high switching costs | Emphasis on scalability, security, integration, dedicated support |
| All Customers | Increased market transparency, easy access to competitor data | Continuous feature development, clear value proposition, customer success initiatives |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
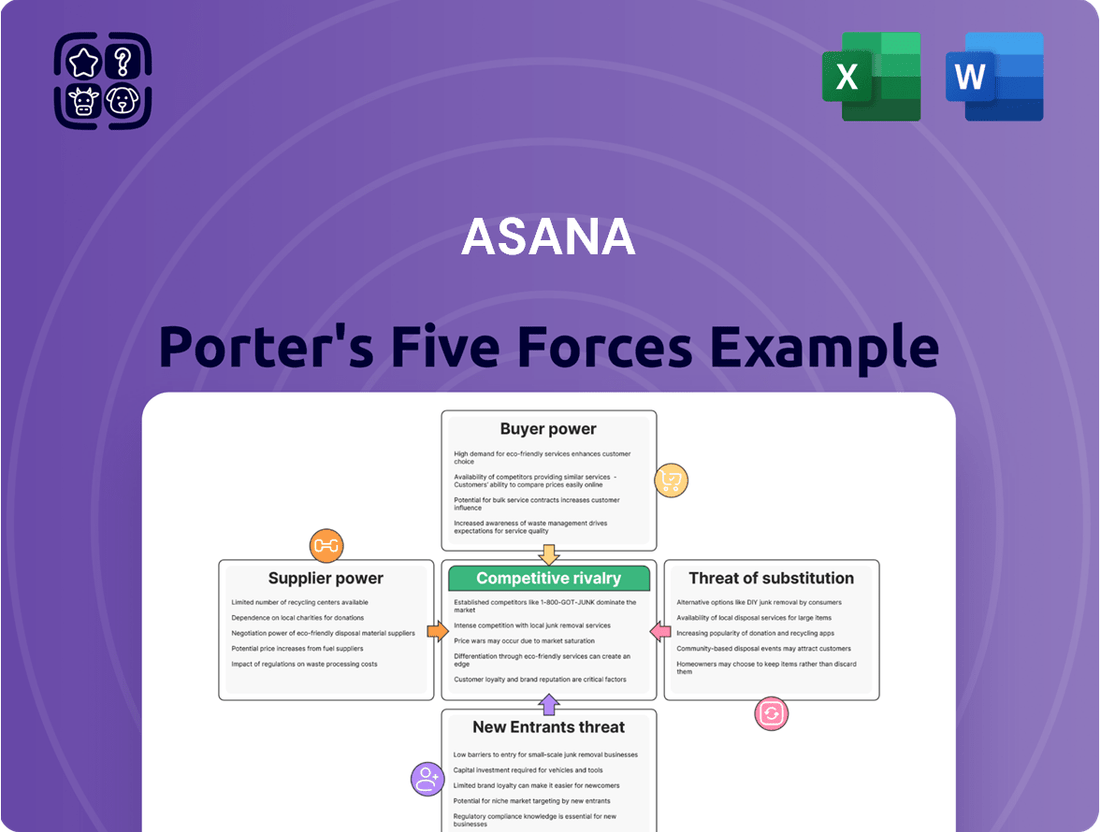
Asana Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Asana Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape for the work management software. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of Asana's industry by examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, offering actionable insights into Asana's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The work management and project management software market is incredibly crowded, with a vast array of companies vying for market share. This fragmentation means Asana constantly faces pressure from numerous players, each offering distinct features and targeting different user needs, from simple task management to complex enterprise-wide solutions.
Key competitors like Monday.com, ClickUp, Trello, Wrike, Microsoft Planner, Jira, and Smartsheet represent just a fraction of the landscape. This diversity means Asana must contend with solutions focused on visual workflows, agile development methodologies, and robust enterprise-level project management, forcing continuous innovation and differentiation.
The task management software market is booming, expected to jump from $4.45 billion in 2024 to $5.14 billion in 2025, showing a strong 15.4% compound annual growth rate. This rapid expansion naturally attracts more players and intensifies the fight for customers.
While the overall market is expanding, the increasing adoption of AI and automation is a major disruptor. Companies must constantly innovate to stay ahead, as these technological shifts can quickly alter the competitive landscape and customer expectations.
Asana strives to stand out with its intuitive design and robust feature set, including integrations that streamline workflows. However, the competitive landscape is crowded, with many rivals offering comparable functionalities, leading to a degree of feature commoditization. For instance, while Asana's AI Studio and AI teammates are key differentiators, competitors are also aggressively adopting AI, making it a challenging space to maintain a unique edge.
While Asana does have mechanisms that create some switching costs for its users, these barriers are not insurmountable. Customers can transition to alternative platforms without facing prohibitively high expenses or significant operational disruptions. This relative ease of switching is evident in the continuous emergence and adoption of competing work management solutions in the market.
Exit Barriers
For established Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies like Asana, exit barriers are often significant. These barriers stem from substantial investments in proprietary technology, ongoing research and development, and the creation of valuable intellectual property. The accumulated costs associated with building a strong brand reputation and acquiring a loyal customer base also make exiting the market a costly proposition.
The practicalities of ceasing operations present further challenges. These include the substantial expenses involved in winding down operations, terminating existing contracts with vendors and service providers, and managing the secure disposal or transfer of vast amounts of customer data. These factors collectively incentivize companies to persevere and continue competing, even when facing intense market rivalry or financial headwinds.
- High Capital Investment: SaaS companies like Asana invest heavily in cloud infrastructure, software development, and specialized talent, making it difficult to recoup these costs upon exit.
- Customer Lock-in: Once customers integrate a SaaS platform into their workflows, switching costs can be high, creating a sticky customer base that is hard to dislodge but also difficult to extract value from if the company fails.
- Brand and Reputation: Years of brand building and establishing trust are assets that are lost upon exit, representing a sunk cost for the company.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic stakes for Asana are substantial, as it navigates a fiercely competitive landscape with the objective of achieving enduring growth and profitability. The company's commitment to innovation, particularly its significant investments in artificial intelligence and the expansion of its partner ecosystem, underscores its ambition to reach a $1 billion revenue milestone.
Asana's performance metrics, such as its net retention rate and ongoing initiatives to enhance operating margins, directly reflect the intense competition for market leadership and the critical need for financial sustainability. In 2023, Asana reported revenue of $669.1 million, a 20% increase year-over-year, highlighting its growth trajectory amidst these competitive pressures.
- Strategic Goal: Asana aims for sustained growth and profitability in a competitive market.
- Key Investments: Significant capital is being allocated to AI development and partner ecosystem expansion.
- Financial Target: The company is striving to achieve $1 billion in revenue.
- Performance Indicators: Net retention rate and operating margin improvements are crucial for market standing and viability.
The competitive rivalry within the work management software sector is intense, with Asana facing a multitude of well-established and emerging players. This crowded market means Asana must continuously differentiate itself through innovation and feature development to capture and retain customers. The rapid growth of the task management software market, projected to increase from $4.45 billion in 2024 to $5.14 billion in 2025 at a 15.4% CAGR, fuels this rivalry by attracting new entrants and encouraging existing ones to enhance their offerings.
Key competitors like Monday.com, ClickUp, and Jira offer robust alternatives, often with specialized features catering to specific industry needs or workflow methodologies. While Asana's AI Studio and integrations are strengths, rivals are also heavily investing in AI and automation, leading to a degree of feature commoditization. This necessitates ongoing investment in research and development to maintain a competitive edge.
Asana reported $669.1 million in revenue for 2023, a 20% year-over-year increase, demonstrating its ability to grow despite fierce competition. However, the market's dynamic nature, driven by technological advancements like AI, requires constant adaptation to prevent market share erosion.
| Competitor | Key Differentiators | Market Position (General) |
| Monday.com | Visual workflow customization, extensive integrations | Strong competitor, broad appeal |
| ClickUp | All-in-one productivity platform, high customizability | Rapidly growing, feature-rich |
| Jira | Agile development focus, robust for software teams | Dominant in software development, enterprise |
| Wrike | Enterprise-grade project management, scalability | Established player, strong in larger organizations |
| Smartsheet | Spreadsheet-like interface, data management | Appeals to data-centric users, hybrid approach |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Asana is considerable, with many tools and approaches capable of handling work management tasks, often more affordably or bundled with existing software. For instance, Microsoft Office 365, with over 380 million commercial seats sold as of late 2023, and Google Workspace, used by over 3 billion users, offer integrated task management features that can suffice for simpler needs.
Furthermore, the availability of free or very low-cost project management solutions, such as Trello or Monday.com's free tiers, directly challenges Asana's market position by providing accessible alternatives for budget-conscious users and smaller organizations.
Customer propensity to substitute for Asana hinges on how easily users can find simpler, more cost-effective alternatives. If teams perceive that a combination of existing tools, like email and spreadsheets, can handle their workflow adequately, they might bypass a dedicated project management platform. This is particularly true if the perceived value of Asana doesn't significantly outweigh the benefits of these simpler methods.
The cost factor is significant; if Asana's pricing is seen as too high relative to the perceived benefits, users will actively seek cheaper or free substitutes. For instance, many small businesses might opt for free tiers of competing tools or rely on integrated features within their existing software suites to manage tasks and projects, thus reducing their need for a specialized solution like Asana.
Furthermore, the increasing sophistication of general collaboration and communication tools presents a growing threat. Platforms that offer integrated task management alongside chat and file sharing can become viable substitutes, especially if they are already part of a company's tech stack. This trend was evident in 2024, with many companies consolidating their software spending, making it harder for standalone productivity tools to justify their cost without a clear, superior value proposition.
Beyond direct software rivals, Asana faces threats from indirect substitutes like traditional project management methods. Think whiteboards, spreadsheets, and heavy reliance on email. While not as streamlined for complex tasks, these simpler, often manual, approaches can still attract organizations hesitant to adopt a dedicated work management platform.
For instance, many smaller businesses or teams with less intricate workflows might find existing tools sufficient. A 2024 survey indicated that 35% of small businesses still primarily use spreadsheets for project tracking, highlighting the persistent appeal of familiar, low-cost alternatives.
Emergence of AI-driven General Productivity Tools
The rapid evolution of AI is a significant threat of substitution for work management platforms like Asana. As AI capabilities expand, general productivity tools and even operating systems are integrating more sophisticated automation for tasks, planning, and collaboration. This could diminish the unique value proposition of specialized platforms.
For instance, by mid-2024, many leading tech companies were showcasing AI features designed to streamline project workflows directly within their existing software ecosystems. This trend suggests a future where core project management functionalities might become embedded in broader digital workspaces, reducing reliance on dedicated tools.
- AI Integration in Existing Software: Microsoft Copilot and Google Workspace's AI features are examples of how AI is being embedded into widely used productivity suites, potentially handling task delegation and scheduling.
- Automation of Core Functions: AI advancements are enabling the automation of tasks like meeting summarization, action item extraction, and even initial project plan generation, directly challenging Asana's core offerings.
- Cost-Effectiveness of Bundled Solutions: As AI capabilities become standard in existing software bundles, businesses may find it more cost-effective to leverage these integrated solutions rather than paying for separate work management subscriptions.
- User Adoption of Familiar Tools: Employees are often more inclined to adopt tools they are already familiar with, making the AI features within their existing operating systems or productivity suites a more likely substitute than learning a new platform.
Complementary Products Becoming Substitutes
Communication platforms like Slack and Microsoft Teams, initially complementary to Asana by facilitating team collaboration, are now evolving. By integrating robust project and task management features, these platforms are increasingly becoming direct substitutes.
This trend means users might opt to manage their workflows within their primary communication tool, bypassing the need for a dedicated project management application like Asana. This convergence directly impacts Asana's market position by expanding the competitive landscape.
- Slack's Project Management Integrations: Slack has been actively enhancing its workflow builder and introducing features that allow for task creation and tracking directly within channels, blurring the lines with dedicated PM tools.
- Microsoft Teams' Evolving Capabilities: Microsoft Teams continues to deepen its integration with the Microsoft 365 suite, offering features like Planner and To Do, allowing for comprehensive task management within the Teams environment.
- User Preference for Consolidation: Surveys in 2024 indicate a growing user desire for consolidated digital workspaces, making integrated solutions more appealing than managing multiple specialized applications.
The threat of substitutes for Asana is significant, driven by integrated solutions and simpler alternatives. For instance, Microsoft Office 365, with over 380 million commercial seats sold by late 2023, and Google Workspace, used by over 3 billion users, offer built-in task management capabilities that can fulfill basic project needs.
Free or low-cost project management tools, such as Trello or Monday.com's free tiers, directly compete by offering accessible options for budget-conscious users and smaller organizations. This accessibility is a key factor, as many businesses, particularly small ones, still rely on spreadsheets for project tracking, with a 2024 survey showing 35% of them using this method.
The increasing sophistication of AI within existing software suites poses a growing substitution threat. By mid-2024, companies were integrating AI to streamline workflows within their platforms, potentially reducing the need for standalone work management tools like Asana. This consolidation trend, noted in 2024 surveys, favors bundled solutions over specialized applications.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Differentiator | Market Penetration Indicator (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Productivity Suites | Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace | Bundled features, existing user base | 380M+ commercial seats (M365), 3B+ users (Google Workspace) |
| Free/Low-Cost PM Tools | Trello, Monday.com (free tiers) | Affordability, ease of use for basic needs | Widely adopted by SMBs and individuals |
| Existing Communication Platforms | Slack, Microsoft Teams | Integrated task management within collaboration | High daily active user counts across both platforms |
| Traditional/Manual Methods | Spreadsheets, email, whiteboards | Familiarity, zero direct software cost | 35% of SMBs use spreadsheets for project tracking (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
While the Software as a Service (SaaS) model generally reduces upfront capital needs for users, creating a sophisticated work management platform like Asana demands considerable investment in research and development. New competitors must secure substantial funding to develop a feature-rich product, incorporate advanced AI functionalities, and meet stringent security and data privacy regulations. For instance, in 2023, Asana reported R&D expenses of $225.6 million, highlighting the ongoing investment required to maintain a competitive edge in the evolving collaboration software market.
Asana's strong brand loyalty, cultivated through relationships with major clients like Amazon and Accenture, significantly deters new entrants. These established customer connections, coupled with the inherent switching costs involved in data migration and user retraining, create a formidable barrier.
New entrants to the project management software market face significant hurdles in accessing established distribution channels. Companies like Asana have cultivated robust sales and marketing networks, encompassing direct sales teams, strategic partnerships, and a highly visible online presence, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market visibility and reach their target customers.
Breaking into these established channels requires substantial investment from new entrants. They must allocate considerable resources towards marketing campaigns and the development of their own effective distribution strategies to acquire a customer base and compete with incumbents who have already built strong relationships and customer loyalty.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
For a work management platform like Asana, which handles sensitive business data, meeting stringent regulatory and compliance standards is paramount. Newcomers must navigate complex requirements such as SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR to build credibility, especially with enterprise clients. For instance, achieving SOC 2 Type II certification can take over a year and cost tens of thousands of dollars, a substantial barrier for startups.
The financial and time investment required to obtain and maintain these certifications presents a significant barrier to entry. This includes ongoing audits and updates to ensure continued compliance, adding to operational costs. In 2024, the average cost for initial SOC 2 Type II compliance was reported to be between $15,000 and $40,000, with annual maintenance costs ranging from $5,000 to $20,000.
- Significant upfront investment: New entrants must allocate substantial capital towards achieving initial certifications.
- Ongoing compliance costs: Maintaining certifications involves continuous auditing and updates, adding to operational expenses.
- Customer trust factor: Enterprise clients often mandate specific compliance standards, making certification a prerequisite for business.
- Time-consuming processes: The certification journey can be lengthy, delaying market entry and revenue generation.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technology
While the basic idea of project management is accessible, companies like Asana have invested heavily in unique technologies. For instance, Asana's Work Graph data model and its AI Studio are key differentiators that are difficult for newcomers to replicate without significant R&D investment. This proprietary technology creates a barrier, as new entrants need to offer truly novel solutions to stand out.
New entrants face the challenge of developing their own intellectual property or finding ways to circumvent existing patents. Asana, for example, holds numerous patents related to its workflow automation and data visualization tools. Without comparable innovation, new competitors may struggle to offer a compelling value proposition that can attract customers away from established platforms, potentially leading to higher customer acquisition costs.
- Asana's Work Graph: A proprietary data model enabling sophisticated task relationships and automation.
- AI Studio: Asana's platform for building AI-powered workflows, offering advanced customization.
- Patent Portfolio: Asana actively protects its innovations through patents, creating legal hurdles for imitators.
- Differentiation Challenge: New entrants must innovate beyond basic project management features to compete effectively.
The threat of new entrants for Asana is moderate, primarily due to the substantial investment required in technology development and brand building. While the SaaS model lowers user entry costs, creating a sophisticated platform like Asana demands significant R&D, as evidenced by Asana's $225.6 million R&D expenses in 2023. New competitors also face hurdles in accessing established distribution channels and building customer trust, especially with enterprise clients who often require stringent compliance certifications.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Asana Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from Asana's own investor relations materials, industry-specific market research reports, and analyses from reputable financial news outlets to capture the competitive landscape.
