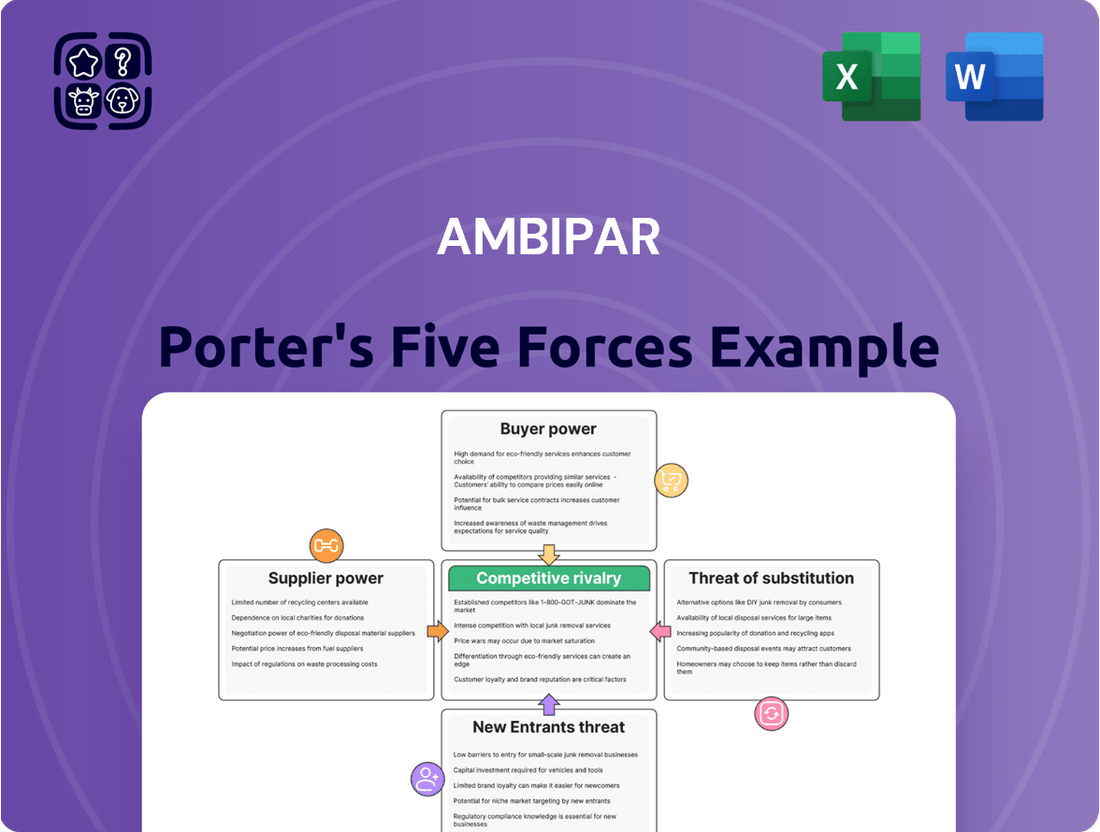
Ambipar Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ambipar Bundle
Ambipar's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ambipar’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for specialized environmental equipment, chemicals, and advanced technology is a key factor influencing Ambipar's operational costs. If only a handful of companies provide essential inputs, these suppliers gain considerable power to set prices and terms, potentially squeezing Ambipar's profit margins.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for specialized spill containment equipment saw a notable consolidation, with the top three manufacturers accounting for over 60% of sales. This concentration means Ambipar must carefully manage relationships and explore long-term contracts to secure favorable pricing for these critical items.
Ambipar's broad international presence and established network of partnerships are crucial in counteracting this supplier concentration. By sourcing from a diverse range of global providers, Ambipar can reduce its reliance on any single supplier and leverage competition to negotiate better terms for its extensive operations.
The costs Ambipar might incur if it switches environmental emergency response suppliers are a key factor in supplier bargaining power. These costs can include retraining staff on new protocols, recalibrating specialized equipment to work with different chemical agents or containment systems, and the administrative burden of renegotiating contracts and service level agreements. For instance, if a new supplier uses vastly different response technologies, the investment in new training and equipment calibration could be significant, potentially running into hundreds of thousands of dollars depending on the scale of operations.
Suppliers who provide unique or highly differentiated inputs, like proprietary waste treatment technologies or specialized hazardous material response equipment, naturally hold more sway in negotiations. This is because alternatives are scarce or non-existent, making it difficult for Ambipar to switch to another provider without significant disruption or cost.
Ambipar's strategic emphasis on innovative solutions and circular economy principles can amplify this. For instance, if their commitment to advanced recycling processes requires specific, patented chemical agents or unique processing machinery, the suppliers of these inputs gain considerable bargaining power. This reliance on specialized, potentially patented, inputs can be a key factor in supplier leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Ambipar's service offerings can significantly shift bargaining power. If a key supplier, for instance, a provider of specialized environmental cleanup equipment or technology, were to start directly offering waste management or emergency response services, they would become a direct competitor. This move would allow them to capture a larger portion of the value chain, potentially reducing Ambipar's market share and profitability.
This threat is often considered low in highly specialized business-to-business service sectors like those Ambipar operates in. Such sectors typically require significant capital investment, unique expertise, and established client relationships, making it difficult for suppliers to replicate the full suite of services offered by established players like Ambipar. For example, a chemical supplier would face substantial hurdles in developing the logistical network, regulatory compliance, and skilled personnel needed for comprehensive industrial waste management.
- Low Threat of Forward Integration: Suppliers in Ambipar's specialized B2B service sectors generally face high barriers to entry for offering similar comprehensive services.
- Capital and Expertise Requirements: Entering waste management or emergency response demands significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and specialized human capital, which most suppliers lack.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Many suppliers concentrate on their core manufacturing or supply chain strengths rather than diversifying into complex service provision.
Importance of Ambipar to Supplier
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key factor in assessing Ambipar's competitive landscape. When suppliers are less reliant on Ambipar's business, their leverage increases. For instance, if Ambipar constitutes a minor fraction of a supplier's total sales, that supplier might be less inclined to negotiate on price or offer preferential terms. This dynamic can impact Ambipar's cost of goods sold and overall profitability.
Ambipar's substantial global presence, however, can mitigate this supplier power. By representing a significant portion of a supplier's revenue, Ambipar can negotiate more favorable terms and pricing. For example, in 2023, Ambipar's consolidated revenue reached R$5.6 billion (approximately $1.1 billion USD), indicating a considerable purchasing volume that can be leveraged with key suppliers.
- Supplier Dependency: The degree to which suppliers depend on Ambipar for their revenue directly influences their bargaining power. Lower dependency translates to higher power for the supplier.
- Ambipar's Revenue Share: If Ambipar represents a small percentage of a supplier's total sales, the supplier has less incentive to accommodate Ambipar's demands for better pricing or terms.
- Ambipar's Scale Advantage: Ambipar's large-scale operations and significant purchasing volume can make it a crucial client for many suppliers, thereby reducing the suppliers' bargaining power.
- Strategic Sourcing: Ambipar's ability to diversify its supplier base and engage in strategic sourcing can further diminish the bargaining power of individual suppliers.
The bargaining power of Ambipar's suppliers is influenced by the concentration of providers for specialized environmental services and equipment. When few suppliers exist for critical inputs, they can dictate higher prices and terms, impacting Ambipar's profitability.
In 2024, the market for advanced hazardous waste treatment technologies saw increased consolidation, with a few key players dominating. This means Ambipar must secure favorable long-term agreements to manage costs for these essential components.
Ambipar's global reach and diversified sourcing strategy help mitigate supplier power. By working with a wide array of international providers, Ambipar reduces dependence on any single entity, leveraging competition to negotiate better pricing for its extensive operations.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Ambipar |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Few suppliers for specialized inputs (e.g., advanced waste treatment tech). | Increases supplier pricing power, potentially raising Ambipar's costs. |
| Switching Costs | Costs associated with changing suppliers (e.g., retraining, equipment recalibration). | Higher switching costs empower suppliers, making it harder for Ambipar to change providers. |
| Supplier Differentiation | Suppliers offering unique or proprietary technologies. | Gives suppliers significant leverage due to lack of alternatives. |
| Ambipar's Revenue Share | The proportion of a supplier's sales that Ambipar represents. | If Ambipar is a small client, suppliers have less incentive to offer favorable terms. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Ambipar, evaluating the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitute products.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic clarity.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ambipar's customer base spans a wide array of sectors, including oil & gas, mining, chemicals, logistics, manufacturing, and governmental bodies. This diversification across multiple industries is a key factor in assessing customer bargaining power.
A concentrated customer base, where a few major clients represent a substantial share of Ambipar's revenue, would inherently grant those clients significant leverage. However, Ambipar's broad client portfolio indicates a more fragmented customer landscape, which generally dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer.
For instance, in 2024, Ambipar reported revenue from a multitude of contracts across these varied sectors, suggesting no single industry or client dominates its income streams. This broad distribution limits the ability of any one customer to dictate terms or demand significant price concessions.
The costs and complexities a client faces when moving from Ambipar to a different environmental service provider significantly influence their bargaining power. For comprehensive waste management and emergency response, these switching costs can be substantial. This is because clients often invest in established operational protocols, specialized employee training, and dedicated infrastructure that are specific to Ambipar's services, making a transition difficult and expensive.
Customer information and transparency significantly influence Ambipar's bargaining power. When clients possess detailed knowledge regarding pricing structures, service quality benchmarks, and the availability of competing environmental management solutions, they are better positioned to negotiate favorable terms. This heightened awareness directly translates into increased leverage for customers seeking optimal value.
The environmental management sector, often characterized by stringent regulations and public disclosure requirements, typically provides customers with access to a wealth of information. This transparency regarding operational costs, compliance standards, and performance metrics empowers clients, amplifying their capacity to compare offerings and demand competitive pricing and superior service from Ambipar.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers' price sensitivity is a key driver of their bargaining power within the environmental services sector. When the cost of services like waste management or emergency response represents a substantial part of a client's overall expenses, or when those clients operate in intensely competitive markets, their inclination to seek lower prices escalates, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
For instance, a large industrial manufacturer, whose operational costs are heavily influenced by waste disposal fees, might exert significant pressure on service providers like Ambipar to offer competitive pricing. This sensitivity is amplified if the manufacturer faces global competition where cost efficiency is paramount.
Ambipar's ability to retain clients and secure new contracts is therefore closely tied to its pricing strategies and its capacity to demonstrate value beyond mere cost. The company must balance competitive pricing with the quality and reliability of its specialized services.
Consider these factors influencing customer price sensitivity:
- Cost Proportion: If environmental services constitute over 5% of a client's operating budget, price sensitivity typically increases.
- Industry Competition: Clients in sectors with profit margins below 10% are generally more price-sensitive.
- Availability of Substitutes: The presence of numerous alternative service providers intensifies price pressure.
- Switching Costs: Lower switching costs for customers empower them to negotiate harder on price.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers can exert significant bargaining power if they have a realistic possibility of undertaking the environmental management or emergency response services themselves, a concept known as backward integration. This means they could bring these capabilities in-house rather than relying on Ambipar.
However, for the highly specialized and complex services Ambipar provides, the substantial capital investment and the need for deep technical expertise make this threat generally low. This inherent barrier significantly limits the bargaining power customers can wield through the threat of backward integration.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing state-of-the-art facilities for environmental services often requires hundreds of millions of dollars in investment, a prohibitive cost for most customers seeking to integrate backward.
- Specialized Expertise Needed: The environmental sector demands highly skilled personnel with specific certifications and ongoing training, which is difficult and costly for customers to replicate internally.
- Regulatory Compliance Burden: Navigating and maintaining compliance with stringent environmental regulations is complex and resource-intensive, posing a significant hurdle for potential backward integration.
Ambipar's diverse client base, spanning industries like oil & gas and mining, generally limits the bargaining power of individual customers. The high switching costs associated with specialized environmental services, due to established protocols and training, further reduce customer leverage. For example, in 2024, Ambipar’s broad contract distribution meant no single client dominated revenue, diluting individual customer influence.
Customers' price sensitivity, particularly for those with environmental services representing a significant operational cost or operating in competitive markets, can increase their bargaining power. However, the specialized nature and high capital investment required for environmental management services make backward integration, where customers provide services themselves, a low threat, thereby capping customer bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Ambipar Context |
| Customer Concentration | Lowers power due to fragmented base | Ambipar's diversified client portfolio in 2024 limits individual customer leverage. |
| Switching Costs | Reduces power due to high transition expenses | Significant investment in training and infrastructure for clients makes switching difficult. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases power when services are a large cost component | Clients in competitive sectors may demand lower prices, influencing Ambipar's strategy. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Lowers power due to high barriers to entry | Substantial capital and expertise needed for self-provisioning limits customer options. |
Full Version Awaits
Ambipar Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, professionally written Ambipar Porter's Five Forces Analysis, exactly as you will receive it after purchase. This in-depth analysis meticulously examines the competitive landscape of Ambipar, providing actionable insights into industry attractiveness and strategic positioning. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The environmental management and emergency response sectors feature a dynamic mix of substantial global corporations and a multitude of smaller, specialized regional firms. This diverse competitive structure means Ambipar, despite its global leadership, faces considerable rivalry from both established giants and agile local players.
Ambipar’s proactive expansion, marked by strategic acquisitions and a push into new international markets, underscores the intense competition it navigates. For instance, in 2023, Ambipar completed several acquisitions, integrating companies in Brazil and Europe to bolster its service offerings and geographic reach, a clear signal of the market's competitive nature.
The environmental solutions market is booming, with projections indicating robust expansion. For instance, the global environmental consulting services market was valued at approximately USD 36.4 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% from 2024 to 2030. This strong growth, fueled by stricter environmental regulations and a rising corporate focus on sustainability, can temper direct competitive rivalry. Companies can expand their operations and revenue streams by tapping into this expanding market rather than solely focusing on capturing existing market share from rivals.
Ambipar stands out by offering integrated solutions that go beyond basic waste management. Their focus on waste valorization and circular economy principles means they transform waste into valuable resources, a key differentiator. This approach, coupled with comprehensive emergency response services, including the use of advanced technology like firefighting robots, sets them apart from competitors.
This high degree of product and service differentiation significantly dampens competitive rivalry. When customers see unique value and a broader solution set, they are less likely to switch based solely on price. For instance, Ambipar's commitment to circular economy principles aligns with growing environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals, creating a strong customer loyalty factor.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can significantly fuel competitive rivalry within an industry. When companies face substantial costs or difficulties in leaving a market, they are often incentivized to remain active even when facing low profitability. This persistence can lead to prolonged price wars and increased competition for market share.
In the environmental services sector, where Ambipar operates, exit barriers are notably high. The industry demands substantial investments in specialized infrastructure, such as treatment plants, transportation fleets, and advanced disposal facilities. These assets are often industry-specific, making them difficult to repurpose or sell at a favorable price if a company decides to exit.
Furthermore, long-term contracts with clients and stringent regulatory obligations contribute to these barriers. Companies are often bound by multi-year agreements for waste management, remediation, and other environmental services. Additionally, adhering to environmental regulations, obtaining permits, and maintaining compliance require ongoing investment and operational commitment, making a swift exit impractical and costly.
- Specialized Assets: Environmental services firms invest heavily in unique equipment and facilities for waste treatment, recycling, and hazardous material handling, which have limited alternative uses.
- Long-Term Contracts: Many companies in this sector operate under multi-year service agreements, creating an obligation to continue operations until contract expiration.
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict environmental laws and licensing requirements necessitate ongoing operational standards and investments, making discontinuation complex and potentially penalized.
- Brand Reputation: A company's commitment to environmental stewardship and reliability is crucial; exiting abruptly could damage its reputation and affect future business ventures.
Strategic Commitments and Acquisitions
Ambipar’s aggressive acquisition strategy, marked by the acquisition of 70 companies globally since 2020, including recent expansions into the Middle East, signals a powerful commitment to market dominance. This rapid growth and geographical reach can intensify competitive rivalry as existing players are compelled to react to maintain their standing.
These strategic moves often trigger a response from competitors, leading to increased price competition, innovation races, or further consolidation within the industry. For instance, Ambipar's 2023 acquisitions, which included companies in waste management and emergency response services, put pressure on rivals to consider similar strategic plays or face losing market share.
- Acquisition Pace: 70+ companies acquired globally since 2020.
- Geographic Expansion: Entry into new markets like the Middle East.
- Competitive Impact: Escalation of rivalry as competitors react to market shifts.
The competitive landscape for Ambipar is characterized by a blend of large global players and numerous specialized regional firms, creating a multi-faceted rivalry. Ambipar's proactive expansion, including over 70 acquisitions globally since 2020, intensifies this competition as rivals are pushed to respond to market shifts and maintain their positions.
The environmental services market's substantial growth, with the global environmental consulting services market valued at approximately USD 36.4 billion in 2023 and projected to grow, offers opportunities for expansion that can temper direct rivalry. However, high exit barriers, stemming from significant investments in specialized infrastructure and long-term contracts, can keep less profitable firms in the market, prolonging competitive pressures.
| Competitive Factor | Description | Impact on Rivalry |
| Industry Structure | Mix of large global corporations and smaller specialized regional firms. | Intense rivalry from both established giants and agile local players. |
| Market Growth | Global environmental consulting services market valued at USD 36.4 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 4.7% (2024-2030). | Strong growth can temper direct rivalry by allowing for market expansion. |
| Exit Barriers | High due to specialized assets, long-term contracts, regulatory compliance, and brand reputation. | Can fuel rivalry by keeping less profitable firms in the market. |
| Ambipar's Strategy | Aggressive acquisition pace (70+ companies since 2020) and geographic expansion into new markets. | Escalates rivalry as competitors react to market shifts and consolidation. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Ambipar's services emerges when customers can fulfill their waste management or emergency response needs through alternative means. For instance, companies might opt for in-house waste handling instead of specialized environmental services, or utilize general logistics providers for emergency transportation rather than dedicated environmental responders. This can limit pricing power and market share.
The threat of substitutes for Ambipar's services is influenced by the relative price and performance of alternative solutions. If simpler waste disposal methods, for example, offer a comparable level of functionality at a substantially lower cost, clients may be tempted to choose these less environmentally advanced options. This is particularly relevant for basic waste management needs where the emphasis is purely on disposal rather than resource recovery or valorization.
In 2024, the global waste management market saw continued growth, with a significant portion still allocated to traditional landfilling and incineration, which are often less costly than advanced recycling and valorization techniques. For instance, while the circular economy is gaining traction, basic landfilling costs can range from $20 to $100 per ton depending on location and regulations, whereas specialized waste valorization services, like those offered by Ambipar, can incur higher upfront or operational costs for clients, creating a price sensitivity for some market segments.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives for environmental services like those Ambipar offers is influenced by several key drivers. Regulatory shifts, such as stricter environmental protection laws, can significantly reduce this propensity. For instance, in 2024, many regions saw increased enforcement of waste management and pollution control regulations, making robust solutions more attractive than cheaper, less compliant alternatives.
Corporate sustainability mandates also play a crucial role. As companies increasingly prioritize Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals, they are less likely to opt for substitutes that might compromise their environmental performance or public image. Many businesses in 2024 reported setting ambitious ESG targets, leading them to seek proven, comprehensive service providers.
Furthermore, the perceived risk associated with environmental incidents is a major factor. The potential costs of fines, cleanup, and reputational damage from an environmental mishap can far outweigh the savings from using substitute services. In 2023, several high-profile industrial accidents served as stark reminders, likely increasing the caution of businesses in 2024 regarding their environmental service providers.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
New technologies that offer simpler, cheaper, or more effective ways to manage waste or respond to emergencies could pose a significant threat to Ambipar. For instance, advancements in on-site waste processing technologies, such as advanced bioreactors or plasma gasification, might reduce the demand for off-site disposal and treatment services. Similarly, sophisticated predictive analytics for incident prevention, leveraging AI and IoT data, could diminish the need for reactive emergency response services.
These technological shifts present a clear substitute threat. Companies might opt for in-house solutions or new service providers leveraging these innovations, bypassing traditional external service providers like Ambipar. For example, the global waste management market is projected to reach approximately $2.0 trillion by 2030, with a significant portion of growth driven by technological advancements in recycling and waste-to-energy solutions.
- On-site Waste Processing: Technologies like anaerobic digestion or advanced composting can convert waste into valuable resources locally, reducing the need for transportation and off-site facilities.
- Predictive Analytics for Incident Prevention: AI-powered systems can analyze data from various sources to forecast potential environmental hazards or industrial accidents, enabling proactive measures and reducing reliance on emergency response teams.
- Digitalization of Waste Management: Smart bins, route optimization software, and digital tracking platforms enhance efficiency and transparency, potentially creating new service models that compete with established players.
- Circular Economy Innovations: Focus on material reuse and remanufacturing can decrease the volume of waste requiring traditional disposal, impacting the demand for certain services.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
A stringent regulatory landscape, particularly concerning waste management and emergency response, significantly curtails the appeal of less regulated, potentially lower-cost substitutes. Companies like Ambipar, by maintaining robust compliance with international standards, including those related to decarbonization and the circular economy, establish a distinct advantage over competitors operating with fewer mandates.
Ambipar's commitment to global compliance, evidenced by its participation in sustainability initiatives, acts as a barrier to substitutes that cannot meet these exacting requirements. For instance, in 2023, the company reported a substantial increase in its ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) performance, reflecting its dedication to operating within strict regulatory frameworks.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Strict environmental and safety regulations make it difficult for new, less compliant entrants to offer competitive alternatives.
- Compliance as a Differentiator: Ambipar's adherence to global standards, including those for emergency preparedness, sets it apart from potentially cheaper but non-compliant substitutes.
- Sustainability Alignment: Active involvement in decarbonization and circular economy projects positions Ambipar favorably against substitutes that do not prioritize these evolving regulatory demands.
- Market Access: Meeting stringent compliance requirements is often a prerequisite for market access, effectively limiting the threat from substitutes that fail to meet these criteria.
The threat of substitutes for Ambipar's services is moderate but growing, driven by technological advancements and shifting customer priorities. While basic waste disposal might have cheaper alternatives, specialized environmental management and emergency response require expertise that limits direct substitution. However, innovative technologies and a focus on circular economy principles could offer new ways for clients to manage their environmental needs, potentially reducing reliance on traditional service providers.
In 2024, the global waste management market continued to see a push towards more sustainable practices, yet traditional methods like landfilling remained prevalent due to cost. For example, while advanced recycling technologies are gaining traction, the cost difference between basic landfilling (often $20-$100 per ton) and specialized valorization services can influence customer choices for less critical waste streams.
The increasing emphasis on ESG goals and stricter environmental regulations in 2024 also play a role. Companies prioritizing sustainability are less likely to opt for cheaper, less compliant substitutes, favoring established providers like Ambipar. This trend is supported by data showing a rise in corporate sustainability reporting and adherence to stricter environmental mandates across various industries.
New technologies, such as on-site waste processing and AI-driven incident prediction, present emerging substitutes. These innovations can offer more localized or preventative solutions, potentially reducing the demand for traditional off-site treatment and reactive emergency response. The global waste management market's projected growth to $2.0 trillion by 2030, fueled by such technological advancements, highlights the evolving landscape.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Ambipar | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Waste Handling | Lower cost for basic needs, less specialized | Reduces demand for basic services | Companies managing non-hazardous waste internally |
| General Logistics Providers | Broader service scope, less environmental focus | Threatens emergency transport services | Using standard freight for non-critical material transport |
| On-site Processing Technologies | Local treatment, resource recovery | Decreases need for off-site disposal | Adoption of advanced bioreactors for organic waste |
| Predictive Analytics/AI | Proactive incident prevention | Reduces demand for reactive response | AI platforms forecasting equipment failure to prevent spills |
Entrants Threaten
Launching a business in environmental management and emergency response, particularly on the scale Ambipar operates, demands immense upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in specialized fleets, advanced containment and cleanup technologies, and strategically located operational facilities. For instance, establishing a comprehensive eco-park capable of handling diverse waste streams and emergency scenarios can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
Ambipar leverages significant economies of scale, operating over 500 bases worldwide and offering a broad spectrum of services like waste valorization, treatment, disposal, and emergency response. This extensive infrastructure allows for cost efficiencies that new competitors would find difficult to match.
New entrants face a substantial barrier in replicating Ambipar's integrated service model and global reach. Achieving comparable cost advantages and a comprehensive service portfolio requires immense capital investment and time, making it challenging to compete effectively from the outset.
Building a worldwide network for environmental emergency response and waste management, complete with robust logistical capabilities and highly skilled professionals, presents a substantial barrier to entry. New companies must invest heavily in infrastructure and talent to compete effectively.
Ambipar's existing strong relationships with a diverse range of industries, coupled with its specialized, experienced teams, create a formidable hurdle for any new entrants attempting to gain a foothold in this sector.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation represent a substantial barrier to entry in the environmental services sector. Companies like Ambipar must navigate a complex web of licenses, permits, and stringent environmental standards. For instance, in Brazil, where Ambipar operates significantly, obtaining environmental licenses can be a lengthy and rigorous process, often requiring detailed environmental impact assessments. This regulatory burden, including compliance with evolving ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) mandates, can be a significant deterrent for new, less experienced players looking to enter the market.
The need for specialized knowledge and capital investment to meet these regulatory requirements further solidifies this barrier. New entrants must not only understand but also actively implement and maintain compliance with a wide array of national and international environmental laws. This includes adhering to standards for waste management, hazardous material handling, and emissions control, all of which demand significant upfront investment and ongoing operational costs. For example, the cost of specialized equipment and training to meet hazardous waste disposal regulations can easily run into millions of dollars, making it difficult for smaller or undercapitalized firms to compete.
- Complex Licensing Requirements: Obtaining necessary environmental permits and operating licenses is a time-consuming and resource-intensive process, acting as a significant hurdle for new entrants.
- Stringent Environmental Standards: Adherence to evolving and rigorous environmental regulations necessitates substantial investment in technology, processes, and personnel, increasing the cost of market entry.
- Capital Investment in Compliance: Meeting compliance standards for waste management, pollution control, and safety often requires significant capital outlay for specialized equipment and infrastructure.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Changes in government policy and environmental legislation can create uncertainty, making long-term planning and investment riskier for potential new competitors.
Brand Identity and Reputation
Ambipar's established brand identity and reputation as a global leader in environmental solutions, especially in emergency response and circular economy, present a significant barrier to new entrants. Building comparable trust and credibility, particularly in critical crisis management services where reputation is paramount, would require substantial time and investment from any new competitor.
- Brand Strength: Ambipar's global recognition as a leader in environmental services, including emergency response and circular economy, is a key differentiator.
- Trust and Credibility: New entrants face a steep climb to establish the same level of trust and credibility, which is crucial in high-stakes services like crisis management.
- Investment and Time: Overcoming Ambipar's reputational advantage necessitates considerable financial investment and a prolonged period to cultivate market standing.
The threat of new entrants in Ambipar's environmental management and emergency response sector is generally low. Significant capital investment is required for specialized equipment, global infrastructure, and regulatory compliance, creating high barriers to entry. For instance, establishing a comprehensive eco-park can cost tens of millions of dollars, a figure many new players cannot readily meet.
Ambipar's established economies of scale, with over 500 bases worldwide, and its integrated service model are difficult for newcomers to replicate. This vast operational footprint and broad service offering, from waste valorization to emergency response, provide cost advantages that new entrants would struggle to match. Building a comparable worldwide network demands immense capital and time.
Government regulations and licensing requirements further deter new entrants. Navigating complex environmental laws, obtaining permits, and adhering to stringent standards like those in Brazil, require substantial expertise and investment. For example, the cost of specialized equipment for hazardous waste disposal can easily run into millions, making compliance a significant hurdle.
Ambipar's strong brand reputation and established client relationships, particularly in critical crisis management, are also formidable barriers. New competitors would need considerable time and investment to build similar trust and credibility in the market.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ambipar leverages data from their annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive dynamics.
We supplement this with information from regulatory filings and news articles to capture the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers.
